If we are going to save as much as possible in this or that area of life, then we need to have a good idea of where, in what quantities and what our money is spent on. And one of the most sensitive items of family budget expenditure in our time is utility bills. And if there is relative clarity with electricity costs, since for the most part everything is visible and quite clear, then with heating it is somewhat more complicated.
How much heat do we need to heat our home?
It doesn’t matter what scheme or system is used for these purposes, first of all it is necessary to have information about how much heat we need to heat our home? Yes, the question sounds exactly like that, without moving into the “monetary plane” for now. Yes, we will not be able to predict financial costs until we express the required thermal energy in some understandable quantities. For example, in kilowatts.
That's what we'll do today.
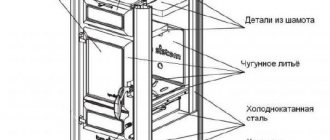
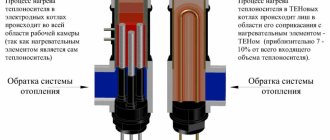
Which boiler to choose for a private house of 100 sq. m?
It is believed that for every 1 square meter of area of a well-insulated room, 1 kW of thermal power of the heat generator is required. This means that for 100 square meters of area you need a boiler with a power of 10 kW.
Interesting materials:
Is it possible to have sweets on a healthy diet? Can acrylic paints be mixed? Is it possible to look at photos of the dead? Is it possible to demolish a load-bearing wall? Is it possible to deregister a car through MFC? Is it possible to remove the tile without damaging it? Is it possible to collect chaga? Can Aramis Stilton be saved? Is it possible to sleep on one side? Is it possible to place an oven under the hob?
Simple area calculations
You can calculate the size of heating batteries for a specific room based on its area. This is the easiest way - to use plumbing standards, which stipulate that a thermal power of 100 W per hour is needed to heat 1 sq.m. We must remember that this method is used for rooms with standard ceiling heights (2.5-2.7 meters), and the result is somewhat inflated. In addition, it does not take into account such features as:
- number of windows and type of double-glazed windows on them;
- the number of external walls in the room;
- the thickness of the building walls and what material they are made of;
- type and thickness of insulation used;
- temperature range in a given climate zone.
The heat that radiators must provide to heat the room: the area should be multiplied by the thermal power (100 W). For example, for a room of 18 sq.m the following power of the heating battery is required:
18 sq.m x 100 W = 1800 W
That is, 1.8 kW of power is needed per hour to heat 18 square meters. This result must be divided by the amount of heat that the heating radiator section produces per hour. If the data in his passport indicates that this is 170 W, then the next stage of the calculation looks like this:
1800 W / 170 W = 10.59
This number must be rounded to the nearest whole number (usually rounded up) - it will be 11. That is, in order for the temperature in the room to be optimal during the heating season, it is necessary to install a heating radiator with 11 sections.
This method is only suitable for calculating the battery size in rooms with central heating, where the coolant temperature is not higher than 70 degrees Celsius.
There is a simpler method that can be used for normal apartment conditions in panel houses. This approximate calculation takes into account that one section is needed to heat 1.8 square meters of area. In other words, the area of the room must be divided by 1.8. For example, with an area of 25 sq.m., 14 parts are needed:
25 sq.m / 1.8 sq.m = 13.89
But this calculation method is unacceptable for a radiator of reduced or increased power (when the average output of one section varies from 120 to 200 W).
Calculation by room volume
In this case, the main indicator is thermal energy equal to 41 W per 1 m³. This is also a standard value. True, in rooms with double-glazed windows, a value equal to 34 W is used.
22x2.6x41/145=16.17 – round up, resulting in 16 sections.
Pay attention to one very subtle nuance. Manufacturers, indicating the heat transfer value in the product data sheet, take it into account according to the maximum parameter
In other words, they believe that the hot water temperature in the system will be at its maximum. In life this is not always true. Therefore, we strongly recommend rounding the final result up.
Manufacturers, when indicating the heat transfer value in the product data sheet, take it into account according to the maximum parameter. In other words, they believe that the hot water temperature in the system will be at its maximum. In life this is not always true. Therefore, we strongly recommend rounding the final result up.
And if the power of the section is determined by the manufacturer in a certain range (a fork is installed between two indicators), then choose a lower indicator for calculations.
Some useful tips
If the answer in a calculation is not a whole number, then it must be rounded up. So, if the answer is 4.6, then it is rounded to 5. This is due to the fact that it is better to exceed the norm a little than to resort to additional lighting devices in the future.
Uniform placement of lighting fixtures around the perimeter has a positive effect on the quality of lighting. In such cases, a larger number of light bulbs are used, but with less power.
As you have already noticed, even a fifth grader can handle the calculations. But the main thing in this matter is to know all the factors influencing lighting. Thus, with the right approach and correct calculations, you can comfortably and pleasantly illuminate your home.
Calculation of heating radiator sections by area
This is the simplest type of calculation of the number of sections of heating radiators, where the volume of heat required to heat the room is determined based on the square meters of the home.
It is not difficult to calculate the area of the rooms, and to determine the required heat, SNiP building standards come to the rescue:
- The average climate zone requires 60-100 W to heat 1 m2 of housing.
- For northern regions, this norm corresponds to 150-200 W.
With these numbers in hand, the required heat is calculated. For example, for middle-class apartments, heating a room with an area of 15 m2 will require 1500 W of heat (15x100). It should be understood that we are talking about average standards, so it is better to focus on the maximum indicators for a particular region. For areas with very mild winters, a coefficient of 60 W can be used.
When making a power reserve, it is advisable not to overdo it, as this will require the use of a large number of heating devices. Consequently, the volume of required coolant will also increase. For residents of apartment buildings with central heating, this issue is not fundamental. Residents of the private sector have to increase the cost of heating the coolant, against the backdrop of increasing inertia of the entire circuit. This implies the need for careful calculation of heating radiators by area.
After determining all the heat needed for heating, it becomes possible to find out the number of sections. The accompanying documentation for any heating device contains information about the heat it produces. To calculate the sections, the total volume of heat required must be divided by the battery power. To see how this happens, you can refer to the example already given above, where, as a result of the calculations, the required volume for heating a room of 15 m2 was determined - 1500 W.
Let’s take the power of one section as 160 W: it turns out that the number of sections will be 1500:160 = 9.375. In which direction to round is the user’s choice. Usually, the presence of indirect sources of heating the room and the degree of its insulation are taken into account. For example, in the kitchen the air is also heated by household appliances during cooking, so you can round down there.
Comfortable room temperature
Comfortable temperature indicators are regulated by the state. In Russia, standards are prescribed for all regions.
Standards for temperature parameters are contained in the document GOST 30.494 - 2011 and include indicators depending on the type of room:
- in the rooms a comfortable temperature is considered to be +20 - +22°C;
- in the kitchen - +19 - +21°C;
- in the bathroom - +24 - +26°C;
- in the toilet - +19 - +21°С;
- in the hallway - +18 - +20°C.
If the temperature does not reach these values, the heating norm for 1 m2 of the house is not met, you can complain and demand a recalculation of the energy consumed.
The standards take into account the purpose of the premises. The bedroom should be ventilated, after which it should be at a normal temperature. In children, the temperature at the upper limit is considered normal, and as the child grows older, it moves to the lower limit. In the bathroom, the increased rate is due to dampness, which makes you feel dank.