There are no trifles in the arrangement of the roof: from the rafter system to the installation of additional parts. Particular attention is always paid to insulation, hydro- and vapor barriers, because this determines how correct the internal microclimate will be and how long the roof itself will last. But not everyone knows exactly how attic ventilation in a private home should be arranged and how to protect the under-roof space from overheating and dampness. But this is important! With a competent approach, you will solve the problem of not only preserving the insulation and extending its life, but also icing of the coating itself. Let's take a closer look at this aspect.
Well-designed attic roof
In modern construction, they try to provide all structures with maximum thermal insulation and seal them in order to reduce heat loss.
This concerns structures enclosing the attic, perhaps most of all. After all, it is through the roofing system that the greatest amount of heat can escape. If the layers of hydro-, steam- and thermal insulation in the roofing pie are folded without ventilation gaps, the insulation system will practically not work. Moisture that falls out in the form of condensation due to temperature differences, household fumes, and rainwater that has penetrated under the roof will not have the opportunity to escape outside.
Water is an excellent conductor; due to its content in the insulation, heat waves will freely pass outside. In addition, it provokes rotting of the wood from which the rafter frame is made, and often the cladding of the attic.
Draining the roofing pie is perhaps a separate extensive topic. However, its effectiveness significantly affects the microclimate of the attic, especially in the summer heat, when the top layer of the roof warms up to +100C. Therefore, we will briefly talk about how this should be arranged.
With proper organization of the roofing pie, with the installation of ventilation ducts of the required cross-section, the insulated slopes are regularly washed by air currents. As a result, the dried roof does not allow heat waves to pass through, and building structures do not get wet or fail.
The purpose of any roof ventilation devices is to ensure air movement from the overhangs to the ridge. The easiest way to do this is under a roof made of slate or ondulin: under the waves of roofing material, the air freely rises to the ridge; in this case, the overhangs are not tightly hemmed.
The situation with metal tiles and corrugated sheets is almost the same, but it is advisable to provide their eaves with ventilation grilles or cover them with an air-permeable seal. The relief roof must be separated from the waterproofing by a spacer bar - it forms a ventilation gap required to remove fumes and atmospheric water accumulated under the coating.
Other materials, in particular soft tiles or sheet metal, require the artificial creation of 1 or even 2 ventilation layers of 3–5 cm, separating the vapor barrier from the insulation, and the waterproofing film from the coating.
For the inflow and exit of air flows into the roofing system, openings must be made to allow the flow to move freely
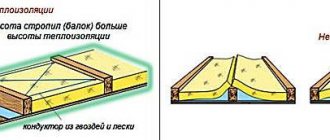
For this purpose, ventilation ducts are arranged by laying sheathing and counter-lattice. Air will rise between the slats. If the thickness of the rafters is not enough to lay all layers of the roofing pie and provide ventilation gaps, the rafter legs are extended with bars.
For inflow into the roof overhangs, perforated inserts are used - soffits or ventilation grilles, at regular intervals along the entire length of the overhang. For exhaust, a special ridge with aeration or point aerators are installed.
The total cross-sectional area of all openings for ventilation of the under-roof space should be 1 m2 for every 300 - 500 m2 of roof slope area.
Both the under-roof space and the gable sheathing can be ventilated through point aerators if the organization of long aerators or slots is impossible
Ventilation of the gables is carried out between the sheathing and the façade cladding material. If the sheathing is installed horizontally, then the sheathing supports are vertical, and they do not interfere with natural ventilation.
If the frame slats need to be fixed horizontally, there are several solutions for gable ventilation:
- Fasten small sections of slats horizontally in a checkerboard pattern. It's economical and efficient, but it can be difficult to get everything level.
- Install long slats, but make holes in them in a checkerboard pattern.
- Construct a vertical counter lathing. Ventilation in this case will be most effective, but the most material will be required.
If the sheathing is diagonal, preference should be given to the vertical arrangement of the slats.
Technical solutions:
1) The exhaust ducts used according to GOST 17079-88 have a large cross-sectional area. Aerodynamic calculations show the possibility of reducing channel cross-sections, since the available gravitational pressure significantly exceeds the pressure loss of the air flow for most floors of a multi-story residential building.
2) The air removed from the premises of the top floors of the building using household fans and discharged into the general volume of the attic will be removed by one industrial fan, which also extracts air from these premises, but supplies it in a compact stream into the exhaust shaft. The jet ejects air, which is removed by natural ventilation from the general volume of the attic, and enters the exhaust shaft (Fig. 2). This system allows using a jet with a small flow rate to eject a large amount of air, which can be adjusted by changing the diameter of the nozzle creating the jet.
Rice. 2. Diagram of a natural ventilation system with an ejector.
a) For the correct operation of such a system, it is necessary to determine the critical sections, m, of the jet x1, x2 according to the formula [3]:
(1)
where is the relative distance from the air distributor to the jet cross-section under consideration, , ;
— cross-sectional area of the shaft, m2.
The distance from the nozzle to the exit of the ejection shaft must be no less than section x1 and no more than x2.
b) The speed coefficient for a compact jet is determined by the formula [3]:
(2)
where is the angle between the jet axis and the line connecting the center of the initial section of the jet with the point at which V = 0.5Vx, .
c) Determine the air flow, m 3 / h, in the jet cross section x1, x2 using the formula [3]:
(3)
where is the cross-sectional area of the air distributor, m2.
d) The flow rate of ejected air, m 3 /h, is determined by the formula [3]:
(4)
On the scale of mass development, optimization of the sections of the exhaust shaft channel and the use of an industrial fan with an ejecting jet allows:
- Increase the usable area of the premises;
- Reduce the amount of materials required for the production of ventilation blocks (concrete and reinforcement);
- Reduce transportation costs for the delivery of reinforced concrete products;
- Reduce labor costs for the manufacture and installation of this structure;
- Prevent disruption of natural ventilation when wind blows into the exhaust shaft;
- Reduce the amount of precipitation entering the “warm attic” through the exhaust shaft, which reduces the air humidity in it;
- Save energy on the operation of ventilation equipment;
- A fan installed in the attic space does not create resistance to natural ventilation (unlike domestic ventilation);
- Use natural ventilation during the warm season, in the absence of air density differences;
- Increase available pressure due to air ejection;
- Prevent “thrust overturning” due to wind pressure;
Technology with an ejecting jet can be used not only in new construction, but also in the reconstruction of existing buildings, with minimal capital costs, which pay off with energy savings in the operation of ventilation equipment (consumption is 3.5 times less than the minimum, Table No. 1).
Comparative table of energy consumption of ventilation equipment
*Household and centrifugal fans with minimal energy consumption
Nuances of arranging ventilation systems for cold and warm attics ↑
To ventilate a room under a roof, it is not at all necessary to create complex engineering systems or install exhaust fans. As a rule, in such cases, ordinary vents are made in the attic, which are able to ensure natural circulation of air flows.
Ventilation system without attic insulation ↑
Natural air circulation through the vents Adjusting air flows in accordance with the need at one time or another is very important, so you should leave free access to the grilles without covering it with rafters. You also need to make dampers on the ventilation ducts, which will allow you to increase, decrease or even block the air flow.
Such an adjustment system is necessary for a hermetically sealed roof, for example, corrugated sheets or metal tiles, where the sheets fit tightly at the joints. If the ceiling is made of materials such as wave slate or ondulin (in the absence of a waterproofing film), vents should not be made - there are enough gaps between the waves for air circulation.
Ventilation on the gable through a dormer window
All gable and mansard roofs have gables, where a grille is installed for ventilation of the attic space, and on one side it is placed with the holes down, and on the other, adjustments are made. In cases where the structures have hip, half-hip or multi-gable gables, as a rule, there are no gables, but, nevertheless, a dormer window can be made there where a grille can be placed.
Pipe device (aerators) for roof ventilation
If there is no entrance from the street into a cold attic, and there are no dormer windows, which is often found in modern architecture of private housing construction, then roof fans - aerators - are installed. Such a device is a pipe in the form of a glass, protected from above from precipitation by a headband. In some cases, a check valve is also added there.
Ventilation system calculation
Ventilation system for a warm attic ↑
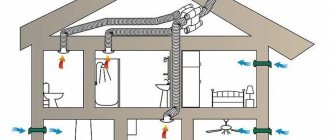
The situation with air circulation in a heated attic, that is, an attic, looks somewhat different. In the room itself, the air exchange process occurs, as in living rooms - through doors, windows, vents and grilles specially provided for this (possibly with forced exhaust). But here it is necessary to separately provide a ventilation gap under the roofing material in view of its insulation from the bottom side.
Air circulation diagram in the attic with heating
If the roofing material on your house is ondulin or slate, then to ensure good circulation it is enough to maintain a distance of 20-30 mm between the roof and the insulation (waterproofing) - the air will pass through the wave joint. But in cases where corrugated sheeting, metal tiles, seam or soft coverings are used, the roof will be sealed, which will contribute to the formation of condensation and, as a result, fungal mold.
In addition, condensation will destroy the metal coating, and moisture can also penetrate inside through a loose connection of the waterproofing. In such cases, gaps for air circulation are left at the eaves hem (below) and under the ridge (above). For metal, additional waterproofing is also used during its installation.
Recommendations
Gable roofs are equipped with attic ventilation through openings in the gables. They are often made of wood, which greatly simplifies the task. Slit vents are made in windy roof overhangs, covering them with wooden beams. If the house has stone gables, then the best ventilation option for them is dormer windows. To prevent birds and flying insects from entering the house, the windows are blocked with modern mosquito nets or bars.
If the roof is covered with wavy porous material (tiles, slate), then installation of additional ventilation systems is not required. The wavy coating allows air to pass freely. Metal tiles are insulated from condensation with film.
To prevent ventilation pipes from freezing, they must be insulated.
Attic space: the need for ventilation
The device is the most important part of the design. Ventilation is involved in the heat exchange processes of the entire residential building.
During the hot season, the roof can heat up over one hundred degrees, and heated hot air enters the house, aggravating the heat in it. In cold weather, other problems may arise. Cooled air forms drops of condensation on insulated floors: this moisture negatively affects wooden elements.
Even basic ventilation can prevent premature deterioration.
Attic ventilation ensures mixing and equalizing the temperatures of the roof structure and the external environment. It prevents the formation of ice during the melting of the snow cover, avalanches and the appearance of large icicles
Arranging a high-quality air exchange system is actually extremely important
Waterproofing
Waterproofing is a layer that covers the insulation on the street side. An insulating membrane is laid on the rafters, it protects against moisture from entering from the outside. The role of waterproofing can be played by roofing material, a diffuse membrane or a condensate film.
In a “cold” roof, waterproofing is also usually done. It is needed to protect the rafters from rainwater leakage.
For some types of waterproofing, it is important to maintain the correct location of the inside and outside. This system is used so that moisture and steam can leave the roofing pie, but cannot pass through from the street.
Ventilation system options for cold attics
The classic option would be to make a ventilation system through dormer windows. This ventilation device is quite simple and can be done independently. How to do it is another question, there are several schemes, but we will use the classic one.
Dormer windows should be mounted on opposite gables, their dimensions should be 600x800 millimeters. A fairly good installation method (due to the simplicity and level of the cross-section, which allows for the necessary air exchange), however, it is not without problems.
The main disadvantage of the technique is the appearance of stagnant air pockets or zones. To avoid this problem, you can make dormer windows of somewhat smaller sizes, combining them with a very effective cornice-ridge ventilation system.
You can also install vent hoods, and this method is very popular in Europe. Vents are openings in a building on which it is necessary to install grilles to protect against the entry of various atmospheric precipitation or debris from the street.
In addition to the use of dormer windows and vent openings, you can use deflectors or ventilation turbines (forced ventilation with a supply and exhaust system). The principle of their operation is similar, but they provide much better traction.
Basic rules for roof installation
Be sure to follow the rules for installing the ventilation system, regardless of what type of system you use. Ignoring the instructions can result in either the system becoming ineffective or unsafe.
Ventilation hood in the attic of a building
Basic rules and regulations:
- for any type of roof, the area of the ventilation ducts should be 400-500 cm²/meter, which will correspond to the required gap height of 40-50 millimeters;
- Please note that dust entering the gap of the ventilation system is hygroscopic, which means it can potentially lead to moistening of the insulation;
- It is imperative to additionally protect the vents if they are mounted on valleys, eaves or on ridges/ridges - protection must be installed from birds, various insects, litter from the street (including foliage);
- in cases where the length of the roof covering is more than 10 meters, it is highly recommended to use auxiliary structures to enhance the operation of the ventilation system;
- constantly monitor the ventilation system - if the air duct is narrowed, this will negatively affect the entire system, which can ultimately lead to condensation;
- do not try to make the gap height very large - this will in no way enhance ventilation, and even on the contrary, will worsen it due to the occurrence of turbulence and air resistance.
Basic elements of under-roof ventilation
The width of the ventilated under-roof space depends on the roofing material you use. The under-roof space is the air gap between the bottom of the roofing material and the waterproofing film or membrane, behind which there is a layer of insulation. For example, if the roof of your house is covered with metal tiles or any other metal-based material, the ventilated gap should be at least 2.5 centimeters.
When using soft (bitumen) tiles or other rolled materials, the thickness of the air gap must be at least 5 centimeters. The specified standards must be observed when ventilating the attic. The main elements of the under-roof ventilation system are aerators and soffits. The former play the role of exhaust openings, and the latter provide an influx of fresh air, and, therefore, prevent the formation of condensation and drip moisture.
There are conventional aerators, mounted in the inclined plane of the roof slope, and ridge aerators, which are installed at the highest point of the roof, that is, on the ridge. The number of aerators depends on the type of roofing material and the manufacturer's recommendations, but there is a general rule. It states that for every 500 sq.m. the ventilated area should be 1 sq.m. ventilation holes. This ratio allows for high-quality ventilation of the room, avoiding noticeable heat leaks.
Ridge aerators are considered the most effective, as they have a large outlet area. Ventilating the attic floor using ridge aerators is quite simple and does not cause difficulties even for beginners. The main thing is to follow the instructions, use high-quality fasteners and ensure good waterproofing at the junction of the roofing material.
As mentioned earlier, soffits are an important part of roof air exchange systems. Soffits are perforated siding panels designed to cover the eaves of the roof along the entire perimeter of the building. In addition to the assigned functional load, they give the roof a complete look
Soffits are not only perforated, but also non-perforated. The required number of perforated soffits is determined taking into account the area of the roof slopes. The use of these elements is possible only if a special gap between the materials was provided when installing the “pie”
In addition to the assigned functional load, they give the roof a finished look. Soffits are not only perforated, but also non-perforated. The required number of perforated soffits is determined taking into account the area of the roof slopes. The use of these elements is only possible if a special gap between the materials was provided when installing the “pie”.
To achieve maximum effect, it is better to use one type of aerator: either ridge or inclined to ensure better air exchange. Correct installation of spotlights and aerators eliminates the formation of condensation and drip moisture. When forced ventilation is used, supply fans are installed in the under-roof space
Particular attention should be paid here to connecting the fan or fans to the power supply. At the same time, it is necessary to ensure fire safety and more or less free access for their maintenance, replacement or repair.
Annotation.
The work analyzes the functioning of the ventilation system in an existing residential building with a “warm attic”, identifies shortcomings in its operation, proposes and calculates new technical solutions to optimize its operation, resource and energy saving.
Ventilation of residential buildings is carried out naturally, without the use of mechanical stimulation of air movement, due to the available gravitational pressure, which exists due to the temperature difference between the external and internal air, as well as under the influence of wind.
The influx of outside air occurs through special valves that are installed in the walls or window frames, and the removal is carried out through air intake devices installed in the premises, and then into the channel system, into the warm attic and the exhaust shaft (Fig. 1) [5].
Cold attic ventilation
Cold attic ventilation needs to be regulated. Therefore, you should not cover the rafters and sheathing. Alternatively, you can make lining with gaps that will ensure unhindered air circulation. If slate or ondulin was laid on the roof, and there are no vapor- and wind-proofing films, there is no need to worry about ventilation - air can circulate freely between the waves of the roof, entering the attic and exiting out. Metal tiles are also capable of allowing air to pass through, but condensation forms on it. Therefore, the use of film is mandatory (read more: “How to eliminate condensation under the roof”).
You can make vents in the attic in a more economical way - install standard ventilation grilles. One grille needs to be turned with the holes down, and the other should be made adjustable. To prevent insects from entering the attic, install a mosquito net.
For a hip roof, ventilation is created using a different technology. The entrance hole is made in the hem, at the bottom, and the exit at the ridge, at the top. If the overhang lining is made of wood, the beams can be placed loosely, maintaining an interval of several millimeters between them. If the lining is plastic, there must be holes - these panels are called soffits.
A lot depends on the type of roof. For slate and euro-slate, a classic ridge is installed, for a flexible roof - a turtle (valve). A ceramic roof requires a special valve. The installation of a cold attic under a metal tile roof allows for ventilation using a regular ridge. It is not only a financially beneficial replacement for a valve. The ridge also allows you to create a ventilation system in a short time.
Sometimes a dormer ventilation window is made in the attic (it can be glazed or grilles installed), but this method of creating ventilation is more complex, and good practical and theoretical preparation is required to implement the plan.
Insulation of ventilation pipes
Insulated Pipes
Ventilation pipes must be insulated in the attic and above roof level. This procedure is carried out to avoid the accumulation of condensation, which will accumulate on the internal walls and flow down. Since the joints of the ventilation pipes are not made airtight, moisture will penetrate the supporting structures, ruin the finish and lead to the gradual destruction of the building. And the ventilation ducts themselves suffer from contact with moisture if they are made of galvanized pipes.
In winter, the opening of the ventilation duct becomes overgrown with frost and in just a month a standard pipe with a diameter of 15 cm will completely close.
The appearance of condensation in ventilation ducts is inevitable: people exhale water vapor, wash dishes, bathe and do laundry. This releases moisture into the air. The humidity of warm air in a residential building can reach 100%. When water comes into contact with the cool surface of ventilation shafts, it settles on it.
To prevent this process, the ventilation pipes in the attic are insulated. This is where the boundary between the warm air of the house and the cold air of the unheated attic passes.
The cheapest insulation option: mineral wool. It does not burn, but when wet it completely loses its qualities. Corrugation with mineral wool insulation is easier to install.
Polystyrene foam in the form of special removable “shells” is very easy to install and inexpensive. But it burns well, emitting toxic smoke, so it is not recommended for residential buildings.
The best materials for insulating ventilation ducts: polyurethane foam, polyethylene foam, polypropylene foam.
Ventilation of a warm attic
Modern heating systems practically do not use natural circulation. Ventilation of the attic above the attic is simply necessary for a comfortable stay in the room. Thus, when converting an attic into an attic, you need to make the roof ventilated. For flexible tiles and sheet metal, a ventilated area is created - a counter batten is sewn onto the rafters. For metal roofs it is better to use windproof films. Counter battens for slate roofing are not necessary, since air must circulate freely from bottom to top.
The entrance is created in the binder, and the exit is created in the ridge. The attic will be ventilated in the same way as other rooms. Air will enter through the windows (VTK valves can be installed), and air will exit through the ventilation holes. When they are absent in the walls, fungal aerators are installed in place of the hood on the roof (read: “Under-roof ventilation and its importance”).
Preparation for work
Before starting work in the attic of a wooden house, you need to check the joints of the floors
It is important to note: there should be no gaps or cracks on the base. Any gap is blocked using lime mortar and tow.
Frame elements are impregnated with antiseptic compounds and fire retardants.
If ventilation ducts have not been created before, the time has come to make them.
If you plan to make insulation using a roll scheme, you need to equip the floor slabs with logs (special bars). To secure them, concrete screws or dowels can be used.
When you plan to turn the attic into an attic, the heating pipes must be insulated. The following types of technical wool are best suited for them:
- glass;
- mineral;
- slag;
- stone;
- basalt.
Please note: the cheapest options should be used in areas with mild winters. If the frosts are severe enough, you will have to buy more expensive and reliable insulation.
It is necessary to clean the surface as much as possible from the slightest traces of dust and other contaminants. All areas of heating systems are overlapped at least twice with protective materials.
Detailed plan as a starting point
They usually try to complete the arrangement of an attic in a country house with minimal financial investment. In this case, the plan still plays the role of an estimate, so it should not be neglected.
- Preliminary plan. Here you must decide what you want to see at the finish line. You can draw on paper or use 3D modeling programs. At this stage, you decide whether an additional window is needed in the attic, how to line the inside of the attic, in general, the desired design of the attic.
First, a sketch of the attic design is drawn
- Preliminary design. Next, take the documents for your dacha and, based on the plan, draw a sketch of the attic with dimensions in several projections. With it, it will be easier for you to calculate the amount of material, and at the same time draw the electrical wiring route, the location of the hatch to the attic, etc.
Now you need to solve several issues that determine the amount of materials, the amount of work and the size of the budget.
A list of questions:
- Is roof insulation necessary?
- is it necessary to reinforce the ceiling;
- Is it necessary to insulate the floor;
- is a hatch needed and what kind of hatch will it be?
- what kind of staircase will there be?
- Costings. The next step is drawing up an estimate. You need to figure out what you have and calculate what and how much you still need to buy.
- Secondary measurement. Next, you need to clean out the attic and measure everything with your own hands with a tape measure, after which you can purchase the material and get to work.
This is interesting: Attic ventilation as the basis of comfort
After cleaning and actual measurement, the amount of material and scope of work may change significantly
Three main misconceptions and eliminating the consequences ↑
The principle of under-roof ventilation
In order for attic ventilation in a private house to be done correctly, in addition to knowledge of the basic requirements, it is necessary to get rid of the misunderstanding of its purpose. There are three main misconceptions that have falsely received the status of rules and are used in the design and construction of houses in the private sector.
The first misconception is about the seasons ↑
It is generally accepted that flowing air circulation in the attic is needed only in the summer (hot) season:
- Hot weather is not the only criterion for the need for attic ventilation. For unheated attics or for ventilation in warm rooms, it is necessary to maintain a minimum difference between the internal and external temperatures;
- When it gets cold outside, the lack of flowing air circulation leads to the formation of condensation. This moisture contributes to the formation of dampness and fungal mold, and in winter - frost;
- This situation is extremely dangerous because microbial spores can enter the living space through the ceiling. It will be extremely difficult to deal with the consequences.
Air flow diagram
Misconception two - it will be cold in the house ↑
Ventilation in the attic helps cool the living space, since warm air is used to heat the floors:
- In fact, the reason for cooling rooms is insufficient thermal insulation of walls, floors and ceilings. The room, to a greater extent, cools not from the loss of warm air, but from the penetration of cold;
- In addition, in the absence of waterproofing on the ceiling, not only heat but also moisture passes through it, which serves as an additional reason for the formation of condensation in the attic.
Misconception number three – size doesn’t matter ↑
The size of the holes for air circulation does not matter:
- this is not so, and if we are talking about a ventilation gap under the roof, then the minimum distance to the insulation should be 20mm. It is set by choosing the cross-section of the slats for the counter-lattice;
- when arranging vents for cold attics, you should adhere to the norm - 1 sq. m of ventilation holes (in total) per 500 sq. m of total room area;
- If you meet these requirements (ventilation gap or vent area), then you can get rid of condensation while avoiding critical losses of warm air.
Way out of the situation with poor ventilation ↑
Frozen condensation on the rafter system and sheathing
If ventilation was made taking into account the above misconceptions, then in the cold season condensation will form, which freezes in winter, as shown in the top photo. In such cases, you have to correct the situation, but there is a way out, and it leads to good results with simple actions.
The simplest roof aerator
You can make additional vents or dormer windows, protecting them with bars so that pigeons do not fly into the attic and nest (they can also nest in the vents, if there is space there). But the most convenient thing, especially if the roof is made of metal (corrugated sheeting, metal tiles or seam roofing), is to install the simplest passive aerator. If desired, of course, you can purchase and install an electric or turbine hood of this type.
Depending on the roofing material, the base of the hood is selected - it can be wavy, like slate or ondulin, or flat, like corresponding roofing materials. As a rule, such devices are equipped with installation instructions from the manufacturer, a set of self-tapping screws, and outdoor sealant for fastening.
Attic ventilation is a necessity
To install such a ventilation system in the attic, you need to cut a hole in the roof, the area of which should not be less than the hole in the hood, but not exceed the dimensions of the mounting base. An angle grinder (grinder) is used for cutting, and the disc is selected in accordance with the roofing material (metal or diamond-coated).
To summarize, we can say that ventilation in the attic is not an arrangement for luxury homes, but an urgent need of every building, on which the comfort in the rooms depends. And the availability of doing the work yourself significantly reduces the cost and allows you to quickly correct the situation with poor air circulation.
A few final tips
- pay attention to the strength of the ventilation, it must withstand any weather fluctuations;
- you can put continuous soffits under eaves with fine screening mesh. To prevent corrosion, the holes should be made of aluminum or plastic;
- to prevent the formation of frost in the attic, install vents inside the room between the rafters and make holes so that they cannot become clogged with debris;
- You can install a fan on the roof for better air extraction. The distance between it and the supply system must be at least 8 m;
- the air supply unit should be placed in the cleanest place in the attic;
- install a recuperator that can cool or heat the air, thereby preventing condensation from forming in a cold attic;
- equip ventilation pipes with grilles or diffusers;
At first glance, there is nothing complicated in arranging ventilation, but in fact it is better to take this issue seriously and consult with specialists. After all, the microclimate in the house and your health, as well as the durability of the building itself, depend on its quality.