Insulating the ceiling with slag, if done correctly, can not only ensure comfortable operation of the room during cold periods of the year, but also provides significant savings on heating.
Speaking about the thermal insulation of a room, it should be understood that all elements of the building are insulated, and ceilings are no exception. For these purposes, a variety of materials are used, but the most budget-friendly, but no less effective option is to insulate the ceiling using slag.
Main types of insulation
Today there are two optimal options: mineral wool (or glass wool) and polystyrene foam.
Each of these materials has its own positive and negative qualities. Mineral wool is produced either in rolls or sheets. The material has the following positive aspects:
- the thermal conductivity indicator has a value of 0.041 W/(m°C), this characteristic may vary depending on the density of the material itself, but such a change will be insignificant;
- good sound insulation, here the density is of significant importance;
- fire resistance: if a fire occurs, then in the absence of open fire the material will quickly extinguish;
- ease of fixation: the structure of mineral wool allows you to easily cope with uneven surfaces, and it is also easy to eliminate voids.
But this material also has disadvantages:
- poor moisture insulation: if such cotton wool gets wet, the thermal insulation will deteriorate by 2 times;
- the installation technology itself has more complex features;
- rolls tend to roll, this factor is influenced by the dishonesty of contractors or improper insulation of cinder block walls on their own.
Polystyrene foam (extruded polystyrene foam), unlike the first option, is more dense in structure, which makes it more durable. The level of moisture absorption is approximately 10 times lower than that of mineral wool. But all qualities are significantly reflected in the price of the material.
Polystyrene foam can be presented in the form of slabs, less often in rolls. The positive aspects of this material include the following:
- good resistance to moisture: even if water gets on the surface, the walls will not lose their thermal insulation properties;
- applicable on flat areas and covers them well;
- depending on the use of certain brands, it may have good fire resistance, therefore, like mineral wool, if there is no open fire near the source, this material will quickly extinguish.
Among the negative aspects, the following characteristics should be highlighted:
- low level of sound insulation;
- some types of foam plastic absolutely do not tolerate fire, therefore, when insulating the walls of a house, you should carefully select the brand, otherwise during a fire it can emit acrid smoke and support the fire itself;
- This material of the usual type has a rather fragile structure, this, in turn, leads to certain installation problems.
There is an opinion that rodents like this material. But it is not so. Rodents do not eat polystyrene foam, but they make their home in it, since it is warm enough.
Ceiling insulation options
When insulating the ceiling with sawdust, you should be careful not to miss the cracks that are always present on the surfaces. To eliminate them, polyurethane foam is used.
There are several options for arranging thermal insulation of the ceiling using sawdust, both using pure wood raw materials and by adding additional additives to it, such as clay, lime, etc.
The most popular methods are:
- use of sawdust in its pure form;
- the use of additives - cement and lime;
- the use of additional components - clay and lime.
What's the easiest way to insulate a cinder block house? Insulation of a cinder block house
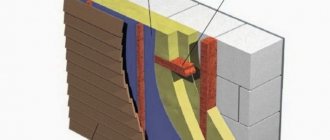
Houses built from cinder blocks, unlike their wooden and brick counterparts, need additional insulation from the outside. The thermal conductivity of a cinder block varies between 0.35-0.6 W/(m 0C), which means that to ensure normal temperature in the house in our harsh climate, it would be necessary to erect a building from cinder block slabs with a thickness of about 1.5- 2 meters, which is extremely unprofitable. That is why buildings made of cinder block slabs of standard thickness are additionally insulated from the outside.
Should you choose external or internal insulation? Professional builders recommend insulating a cinder block house from the outside, since after laying the thermal insulation layer inside the room, the dew point, located between the coolant and the wall, shifts. As a result, moisture will accumulate on the walls, facilitating the spread of moldy fungi.
Another disadvantage of internal insulation is that the thermal insulation material “steals” centimeters of room area. That is why it is rational to insulate a cinder block house from the outside.
Specifications
The parameters of different types of backfill are collected in a table for comparison. The data is averaged, but sufficient for correct calculations of mass and insulation effect.
| Type of slag | Specific gravity, kg/m3 | Thermal conductivity, W/(m*S) |
| Domain | 360 – 1000 depending on faction | 0,12 – 0,18 |
| Boiler house, coal | 750 | 0,24 – 0,32 |
| Fuel | 1000 | 0,25 |
| Metallurgical | From 1000 | 0,35 -0,4 |
The thermal conductivity of solid sand-lime brick is 0.81 W/(m*C). Thus, a layer of coal slag 20 cm thick in terms of insulation properties is approximately equal to a masonry of 2 bricks (51 cm). Considering the difference in price, the developer significantly reduces the cost of materials.
Technology of insulation of building structures
Thermal engineering calculations and instrumental measurements show that 5 - 10% of heat leaves a home through the floor and ground, 20 -30% through the walls and the same amount through the attic floors and roof. For these building structures, you can use slag insulation.
The sequence of work to improve the thermal insulation characteristics of the floor, ceiling, and walls differs.
Floor insulation
The slag layer is filled with a concrete screed.
Depending on the design of the home, floor insulation with slag in private houses is carried out in different ways. If in the spring and after heavy rains water appears in the subfloor or basement, waterproofing must be done.
Brief instructions for insulating an earthen floor:
- The surface is cleared of debris, leveled, and compacted if necessary.
- Waterproofing is done by covering the floor with clay dissolved in water and thoroughly mixed until it forms a dough. Another option: spread a layer of waterproofing roll material and glue the joints with mastic.
- Carefully pour a layer of insulation of the required size - the thicker the better. For most regions, adding 15–20 cm is sufficient.
- Pour 5 cm of sand and tamp it down.
- Pour a cement-sand screed (CSS) 5 - 10 cm.
If the height of the ceilings in the basement does not allow you to arrange such a “pie,” you can fill the floor with concrete using slag as a filler. Before pouring, arrange a sand cushion, which is spilled with water and compacted.
The sequence of work is simple:
- Remove debris, dirt and dust.
- Cracks and technological holes are sealed with cement mortar.
- The plate is treated with an antiseptic to prevent the occurrence of mold and mildew.
- Cover the surface with a layer of vapor barrier film (membrane), which will prevent the penetration of vapors from the basement, but will allow moisture to evaporate into the underground room. Homes with dry basements do not need a vapor barrier.
- A DSP is made on top of the heat insulator layer.
- After drying, finishing is carried out with finishing materials (laminate, chipboard, linoleum).
Ceiling insulation
Insulating the ceiling with slag from the attic
Technologically, the work of insulating the floor and ceiling is no different.
Before insulating the ceiling with slag, you need to carry out calculations so as not to put unnecessary load on the structures. To do this, you need to find out the load-bearing capacity of the floor slabs and compare it with the mass of the backfill.
Slag as a ceiling insulation has the same pros and cons as when used in other building structures.
The height of a non-residential attic allows you to pour a layer of any required thickness (taking into account the characteristics of the slabs). The insulation will retain its properties throughout the entire life of the house.
In order for slag for ceiling insulation to retain its properties, it should not be exposed to precipitation. The dormer window should not be closed tightly - this will help the moisture to evaporate in a timely manner.
- Floor slabs are covered with a layer of waterproofing.
- Add the required amount of backfill.
- A concrete screed with a thickness of 10–15 cm is installed, maintaining a slope to drain water during precipitation.
- Waterproofing is carried out using rolled materials.
To ensure that the coating lasts a long time, follow the instructions of the building material manufacturers.
Insulation of hollow walls
Insulating walls with slag does not require special preparations. As the wall is built, any slag is poured between the outer and inner layers of brick. It is better to choose a porous material of the middle fraction. Such characteristics will make the house warmer; there will be no voids between the pieces of backfill.
What is catalytic oven cleaning?
Understanding what catalytic cleaning means is actually not difficult. This process is possible only in those slabs that have a special rough enamel treated with a reagent (such enamel can be applied only to the back wall or to all side surfaces, depending on the model). This enamel has numerous pores that trap grease and dirt. In these pores, dirt begins to decompose under the influence of high temperatures.
To use such an oven self-cleaning system, the housewife just needs to put some dish in it to cook, using a temperature of 140 degrees or higher. At 200 degrees the cleaning process reaches its maximum. To rid the oven of grease, all you have to do is finish cooking and wipe off any remaining dirt from the enamel with an ordinary microfiber cloth.
Advantages and disadvantages
Metallurgical slag is not used in a humid environment due to its tendency to corrosion.
Despite the difference in technical characteristics, all types of slag as insulation materials have similar positive qualities.
The material is different:
- ease of use;
- low cost;
- optimal air exchange;
- resistance to rotting, fungus formation, and mold growth;
- possibility of use in any premises;
- mechanical strength and chemical neutrality;
- inaccessibility to damage by rodents and insects;
- good thermal conductivity compared to monolithic concrete or brick;
- unlimited use time subject to installation technology;
- fire safety.
The structure of the material imposes restrictions on application. High specific gravity is taken into account when designing load-bearing structures.
Slags are less effective compared to modern specialized products for thermal insulation - polystyrene foam, penoizol, mineral boards, etc.
The metallurgical type is susceptible to rust in high humidity conditions.
Industrial types of insulation are hidden with a screed or poured into the voids of brickwork to prevent harmful substances from entering the air of residential premises.
Calculate the weight
To determine the mass of a heat insulator, it is necessary to multiply its volume by its density. The volume is found by multiplying the layer thickness by the area determined by the product of the length and width of the thermal insulation.
We take the density of the main insulation materials from the table:
| Material | Density, kg/m 3 |
| Fibrous materials | 100 — 120 |
| Expanded polystyrene | 25 — 35 |
| Polyurethane foam | 54 — 55 |
| Expanded clay | 200-400 |
| Ecowool | 42-75 |
| Natural materials | |
| Felt (various types) | 100-150 |
| Foliage (dry) | 50 |
| Tow | 180 |
| Moss | 135 |
| Needles | 43 |
| Straw mats | 85 |
| cotton wool | 80 |
| Thin shavings (packing) | 140-300 |
| Campfire (various types) | 150-350 |
| Sphagnum (peat) | 150 |
| Wood sawdust | 190-250 |
| Straw (stuffed, cut) | 120 |
Natural materials By adding the load of thermal insulation material to the existing calculations for the load of the foundation from walls, floors, and roofs, we determine the possibility of using one or another insulation material.
How to properly insulate a ceiling under a cold roof using long-tested and well-proven insulation materials? These are heat insulators given by nature itself, the beneficial properties of which were revealed by our ancestors. These also include materials produced industrially from environmentally friendly ingredients.
Wood processing industry waste
Previously, construction was a waste-free industry. The shavings and sawdust remaining during wood processing served to protect the house from the winter cold. They were poured between the main walls and the sheathing and used to insulate the ceiling. Similar technologies are still used today.
Main advantages:
- environmental cleanliness;
- availability;
- low cost.
The disadvantage remains the high fire danger. In order to reduce this indicator, they are mixed with clay, cement, and adding fire retardant solutions. It is most advisable to use it for insulating wooden floors. Insulation from inside the room is impossible.
Immediately before starting work, the load-bearing structures of the ceiling are treated with septic tanks. A vapor barrier is installed from inside the room to prevent moisture from penetrating into the insulation volume, which can lead to:
- decreased thermal insulation properties;
- increase in insulator weight;
- gradual destruction of joist boards.
Communication passages are insulated with non-combustible materials. Electrical supply networks are enclosed in boxes or corrugated pipes.
If you use sawdust and shavings in their pure form, prevent the possibility of falling inside the room. To prevent the possibility of rodents entering, lay carbide with slaked lime as the bottom layer. After laying a layer of the required thickness, sprinkle it on top with waste slag to increase fire safety.
Using a mixture of 10 parts sawdust, 1-2 parts clay, and 1-2 parts water and fire retardants allows you to obtain non-flammable or slightly flammable insulation. For high-quality adhesion of clay and cement to sawdust, the mixture must be thoroughly wet.
Types of material
The following types of insulation are obtained from waste from metallurgical production and the energy industry:
- domain;
- metallurgical;
- fuel and coal.
Different types are used to insulate structural elements of a house.
Domain
The material is obtained by smelting cast iron. The composition includes the remains of rock, fluxes and fuel ash. The pieces are very porous, the material is free-flowing.
In private construction, the fine (heavier) fraction is used to fill cavities in walls or to screed concrete floors. The large fraction is light in weight and is suitable for backfilling attic floors.
This type of raw material is used for the production of slag heat-insulating materials.
The most suitable for insulation is slag pumice, which has good heat and sound insulating properties. It also goes into filler for cinder blocks.
Metallurgical
Metallurgical slag can create excessive load on the foundation.
This type most often includes waste from nickel and copper smelters and steel mills.
The material consists of sintered pieces of various fractions. They contain a lot of metal oxides, which is why the mass of the composition is large.
Fuel
The raw materials for production are the remains of fuel oil and coal burned in boiler houses. The fraction and properties depend on the type of combustion (chamber or layer).
Residues of fuel are hygroscopic, so before filling they must be dried for at least 2 months without exposure to precipitation.
It is used for filling cavities in brick walls or under concrete screed on floors and ceilings.
Types of slag
It is permissible to use slags of the following types as insulation for the ceiling:
- fuel;
- coal;
- metallurgical;
- domain.
Each of these types of slag has its own characteristics that require more detailed consideration.
Fuel
Fuel type slag is a bulk material based on loose silicate masses. Such slag is formed as a result of the combustion of coal in fractional or dust form using a layer or chamber method. Fractional slag has a heterogeneous structure; while dust slag has a finely porous and homogeneous structure.
Per unit volume of fuel slag can contain up to 40% ash, which indicates the relatively low strength of the material. In addition, it may contain unburned fuel residues, the presence of which significantly deteriorates the thermal insulation properties of the slag.
The fuel type of slag has pronounced porosity, which means it accumulates moisture well. Therefore, when insulating the ceiling with fuel-type slag, it is necessary to take care of organizing high-quality waterproofing.
The main advantages of fuel type slag include:
- sound insulation at a high level;
- Due to the flowability of the material, it is easy to form a level base when laying floor coverings.
Coal
Coal slag is formed when coal is burned. In this case, high-temperature reactions occur with the participation of inorganic components that are part of the coal.
Coal slag has high strength because one unit of its volume contains only a maximum of 4% ash. The volumetric content of unburned fuel in such slag does not exceed 20% and directly depends on the chemical composition of the coal and the method of its combustion.
Coal slag has the following features:
- crystalline phase in volume maximum 80%;
- granules contain oxides of the following types: calcium, silicon, aluminum;
- According to their chemical composition, they are divided into acidic, basic and superacidic.
Metallurgical
Obtaining metallurgical slags from the remelting of copper or nickel compounds. They are not subject to decay and rust, and have a high tensile strength - a maximum of 300 MPa. Slags of this type are mainly used in the production of fibers for mineral wool.
They have increased resistance to chemicals, high noise insulation properties, low porosity and moisture absorption.
Domain
This type of slag is a by-product of smelting pig iron from ores containing iron in a blast furnace. When the ore is melted, the slag floats to the surface of the cast iron, which greatly facilitates the process of separating the slag from the main mass. The properties of blast furnace slag fully depend on the following:
- fuel used;
- cooling rate;
- ore composition;
- technological process.
How to insulate cinder block walls from the inside
The steam room in the bathhouse is insulated from the inside.
Internal insulation of a cinder block house is not recommended, unless, for example, you can use special paint with ceramic hollow spheres or penofol as additional thermal insulation. They are ineffective as independent materials. Thermal insulation of cinder block walls from the inside is practiced in steam saunas, when it is additionally necessary to protect the walls from moisture. In this case, the main thing is to prevent moisture from the steam room from getting into the insulation layer. Naturally, you can only use mineral wool. Work method:
- a wooden frame is erected on the inside of the walls in the steam room;
- Mineral wool, preferably basalt, is placed between the guides;
- foil insulation is spread over the sheathing - it is very effective for saunas, as it blocks infrared radiation and does not allow steam to pass through;
- a second tier of sheathing is installed on top of the foam foam;
- A wooden lining is attached to the second tier.
Mineral wool needs to be laid in two layers and ensure that the joints do not coincide. The minimum insulation layer is 10 cm. The main thing is not to forget to glue the foam foam joints with special (not stationery) tape. Also, the ventilation gap between the penofol and the wooden paneling should not be neglected. Without it, reflective insulation simply will not work, and besides, the condensation on the foam foam must evaporate. Penofol foil often has small holes that are invisible to the eye. Therefore, to be on the safe side, you need to lay a vapor barrier membrane under the penofol.
What to consider?
It is important to select a material with an appropriate particle size. Fine sawdust from cutting wood has the best thermal insulation properties, but it is heavier, scatters during operation, and is difficult to work with.
Large chips have lower thermal protection characteristics. Therefore, it is better to use carpentry waste. This material does not have to be dried additionally, since already dried wood is used for joinery.
For thermal insulation of the house, you should choose pine sawdust, as it contains resin, which pests do not like.
Pine sawdust will save your home from pests.
Sawdust must be prepared accordingly. The material is treated with an antiseptic composition, dried well and always mixed with fluff lime to protect the insulation system from pests. The required amount of lime is at least 10% of the total mass of wood material.
The mixture is thoroughly mixed until smooth. To ensure uniform mixing, the materials are poured onto a special board made of wood or metal. Then the mass is turned over with shovels until the components are completely mixed.
The layer should vary between 20–30 cm. The secret is good compaction. This is the insulation of the roof with sawdust.
What are the types of insulation materials?
There is a fairly large number of materials. They are distinguished from each other by some important criteria. These include:
- Thermal conductivity. Material with a lower index has better thermal insulation.
- Moisture resistance. The more insulation materials tend to absorb moisture, the better the waterproofing needs to be done.
- Flammability. It is advisable to choose a material that is not flammable.
- Durability. Some isolate tends to wear out quickly and become unusable under certain conditions. This should be taken into account when choosing it.
- Environmentally friendly.
When answering the question, what is the best way to insulate the ceiling, you can consider the following options:
- mineral, basalt, glass or environmental wool;
- polystyrene foam or extruded polystyrene foam;
- expanded clay;
- PPU or penoizol;
- shavings or sawdust;
- tree leaves (usually oak) and straw.
Sometimes in bathhouses the ceiling is insulated with earth or sand. However, this happens quite rarely. Leaves and straw are not used as often. This is an environmentally friendly material that is not durable or moisture resistant. Therefore, to install it, you need to know and strictly follow the technology.
Another important criterion applies to ceiling insulation - low weight. Thermal insulation should not weigh down the ceiling structure. In this regard, earth and sand are rarely used and more often for non-residential premises.
Let's look at each material in more detail.
Criteria for choosing slag wool
When choosing slag wool, you should first of all pay attention to material from well-known manufacturers that has good reviews. Under no circumstances buy insulation from little-known brands at dubious points of sale, where they cannot provide you with the entire list of documents, certificates and licenses for the product. In addition, consider these recommendations:
- The highest quality mineral fiber insulation is offered by German manufacturers. Only they have the most picky certification bodies that will not release low-quality or potentially dangerous products onto the market.
- Check with the seller in which direction the fibers of the insulation are located. When placed vertically, the slag wool will store heat well and absorb sound. If it is chaotic, it will be more durable and withstand dynamic loads.
- Check the GOST of the product on the packaging if the slag is domestically produced. Its presence guarantees the quality of the product.
- Choose the material that best suits your needs. The density of slag wool can be different, and the scope of its use depends on this. The density of 75 kilograms per cubic meter is suitable for insulating roofs and attics. Material with a density of 125 kg/m3 is used on floors, ceilings, and interior walls.
General recommendations
Floors can be insulated both at the construction stage and in a residential building.
But before you start working, you need to clearly formulate your goal. This will allow you to determine the required level of thermal insulation and select suitable materials. For example, if the attic has already been insulated, all you need to do is put a new layer of insulation on top of the old one. If the attic is planned to be used as an attic, then the thermal insulation should consist of three layers: vapor barrier (laid with the rough side down, the smooth side facing the thermal insulation), a thermal insulation layer and waterproofing
It is extremely important to do this, because under the ceiling there is a residential part of the house, and the warm air rising to the ceilings contains so much steam that it can easily ruin any thermal insulation
Before starting insulation work, you need to check the condition of the roof, as well as the beams if we are talking about wooden floors. They must be protected from moisture using a special composition.
It would be a mistake not to leave gaps in the thermal insulation layer. They will be needed to ensure the necessary ventilation of the room and prevent the formation of condensation or accumulation of moisture under the roof.
In addition, all work must be carried out in dry weather, and even better - in the warm season.
Environmental friendliness of slag
The slag used for insulation has a porous structure, due to which this material retains heat well. This material is a production waste. For this reason, it is necessary to think about the harmfulness of slag insulation at the design stage of a building.
The location of the backfill, as well as the technology of insulation with slag, prevents direct contact of the material with a person. The penetration of gaseous emissions and slag dust into the room is excluded, which negates any likelihood of causing any harm to human health.
ATTENTION! When purchasing slag for insulation of any room, require a safety certificate, which will guarantee that the radioactive background emitted by the material does not exceed the norm.
Wall insulation with polystyrene foam
Laying foam plastic is carried out in almost the same way as installing mineral wool.
The first stage is surface preparation. Elimination of defects and application of primer. Next, after preparing the adhesive solution, we proceed to installing the insulation sheets.
Important: there should be no gaps or cracks between the plates!
After laying the insulation boards on top of them, you need to fix the reinforcing mesh. Next, this entire cake is carefully primed and puttied, after which you can proceed to the final stage - applying a decorative coating.
When a house is insulated from the inside, the interior space of the room is significantly reduced. However, this fact is not critical for abandoning insulation completely and suffering from low temperatures outside during cold seasons or throwing money down the chimney to heat the house.
Before answering the question of how to properly insulate a cinder block house from the inside, you need to understand the materials that construction stores offer. Today the market offers insulation based on foam plastic and mineral wool. Installation of both one and the other does not require any specific skills from the performer.
We insulate a cinder block house with polystyrene foam
The difficulty of installing this material lies in the preliminary alignment of the walls on which they will be glued. In the case of a brick wall, plastering and puttying will be required. Wallpaper must be removed from the walls and paint residues must be removed.
Every owner of an apartment or house undoubtedly has a dominant desire to preserve the final result for as long as possible. That is why the use of a waterproofing underlay, even inside the house, should be indispensable. For what? In order to thus prevent the accumulation of condensate that destroys the foam.
To work you will need:
- five-centimeter foam;
- comb or notched spatula;
- glue (usually Ceresit).
Installation work is extremely simple. Insulation plates purchased from a building materials store are attached to the prepared wall using diluted glue. Then they are tapped thoroughly to remove any possible air bubbles from under them. In this matter, an important point is to apply the adhesive mixture directly to the wall and in no case to the foam sheets themselves. They should always be dry.
Next, for optimal insulation of the house, all cracks and loose fits of the material should be treated with polyurethane foam. This must be done in order to isolate the glued layer from changes in humidity in the room.
In the process of fastening foam boards, you can also use special fastening dowels. However, an adhesive solution will be sufficient. The final step will be the front finishing of the walls and their possible painting.
Quite a fast and practical way. Its most important advantage is the elimination of the stage of preliminary leveling of walls. The thing is that mineral wool slabs are installed in a specially created metal structure. Then, step by step, the entire frame is covered with plasterboard slabs, which will give your wall a perfectly flat surface.
So, a special structure is assembled from metal or wooden profiles - lathing. Plasterboard slabs are installed on it. Next, the joints are puttied and the wall is either painted or wallpaper is applied to it.
Should you use sawdust?
The choice is entirely yours. There are buildings for which sawdust is quite suitable as insulation. But when insulating a residential building, it may be better not to save money, but to buy high-quality modern insulation.
Gypsum plaster of walls has been known since ancient times. All kinds of Vetonites and Rothbands had not yet been invented. This building material was mainly used by Armenians, as a result of which it received the name “Armenian plaster”. It should be noted that many could afford to call an electrician or plumber, but only very rich people could afford plastering by a master using this technology.
To this day, despite the huge variety of various plaster mixtures, “Armenian plaster” remains quite in demand.
Armenian plaster technology: preparing the mixture
First you need to mix gypsum with sawdust in a ratio of 3:1. The ingredients should be mixed dry directly on the floor. There is a second option: add sawdust to the already mixed plaster. The finished mixture should resemble sour cream in thickness.
Sawdust is the only filler that improves the sound and heat insulation of Armenian plaster. In addition, they significantly simplify the application of the finished solution to the wall surface. It is unacceptable to use shavings from a thicknesser or jointer instead - only from a circular saw (and then sifted through a sieve with five-millimeter holes).
Armenian plaster: application to the wall
Once the mixture is ready, builders only have five minutes to apply it completely. This does not mean that you need to cook very little at a time. As a rule, in the specified period of time you can use up one small bucket of plaster with some practice.
First, the solution is sprayed onto the wall. As soon as it begins to “set”, you can apply the base layer using a ladle or simply with your bare hands.
You need to work quickly, but carefully. Everything that falls to the ground can no longer be used for its intended purpose. As for the thickness of the applied layer, there are no strict restrictions: you can put as much as the base can support.
When the plane is drawn out, it is necessary to gloss it (wall putty). To do this, pure gypsum should be mixed with some kind of retarder (milk, CMC, etc.), apply the resulting solution with a trowel or spatula and smooth with strong pressure. You will get a smooth and shiny surface.
The main advantages of Armenian plaster:
1. Availability. 2. Environmentally friendly (the base consists of milk, gypsum, sawdust and water). 3. Speed of application (up to twenty square meters per day).
Unfortunately, learning the technique of Armenian plaster on your own (from books) is almost impossible. This requires extensive experience in working together with a highly qualified craftsman. It remains to add that the price for plastering work “using Armenian technology” ranges from 400 to 500 rubles per m2.
If you need a master in Rostov-on-Don to perform this or any other work, as well as advice from our managers, you can contact us by phone +7-903-401-02-93, +7-903-401-04- 26 or call a specialist to your home
Insulation with polystyrene foam
Most often, thermal insulation is made with a sheet of foam plastic or penoplex. These are the most common polystyrene foam insulation materials. In terms of thermal conductivity, it is on par with mineral wool. However, unlike it, it does not have high moisture resistance and is not dangerous for humans. Therefore, insulation of the ceiling with penoplex or polystyrene foam is often done from the side of the living part of the room. Using any of the materials will allow you to achieve a balance in the ratio of price and quality.
Like any other insulation, this one needs hydro- and vapor barrier to prevent condensation from forming. After all, moisture destroys the ceiling. As such insulation it is permissible to use:
- isospan;
- penofol;
- special films and membranes;
- penetrating mixtures and other things.
Despite the fact that sometimes the ceiling is insulated with penofol, it is sometimes used for waterproofing. Thermal insulation is carried out with penofol from the inside of the room. Since it has one foil side, it will reflect heat into the rooms.
Since polystyrene foam is cheaper than penoplex, it is often used for insulating an apartment building, in a cellar for insulating walls, in apartments on the floors and walls outside, on the attic floor of private houses. This material is perfect if you are thinking about how to insulate the ceiling in your country house. Residents of apartment buildings extremely rarely lay thermal insulation on the ceilings. Since the apartments are located one above the other, heat loss occurs only through the external walls. Foam is placed on concrete floors to prevent the cold from passing through from below. This is mainly done by the owners of the lower floors, where the ground transmits the cold in winter. In this regard, the ceiling in the apartment on the top floor is insulated, since it is not possible or advisable to lay the material on the walls of the attic from the inside with your own hands.
The cellar can be insulated with foam plastic from the inside. This is especially true when the cellar is on the ground floor. However, you should be careful because there is a high probability that condensation will appear. The use of hydro- and vapor barrier will correct this deficiency. A kind of cake is made: inside it there are slabs of polystyrene foam, and along the edges of the sheet there are layers of insulation.
Avoiding air purging
Slag, expanded clay, straw are large-porous materials. Air moves freely through them. Convection currents may arise inside them, which will negate all insulation. To prevent this, the insulation must be covered with a vapor diffusion layer - a special membrane, but more often just thick paper, preferably perforated (rolled with a needle roller) and sprinkled with a thin layer of sand for preservation.
Simple schemes for insulating floors and attics using expanded clay or slag or straw can be implemented with your own hands at home, if only you had the material...
Installation
The technology for laying mineral wool as thermal insulation for floors, walls and roofs is extremely simple. It is necessary to equip the frame and lay insulation inside it, not forgetting about the water vapor barrier. In more detail it looks like this:
- On the insulated surface, a frame is made of wooden blocks. The distance between them is made a couple of centimeters less than the width of the roll or slab of mineral wool. So that she lies between them as tightly as possible. On inclined surfaces, for reliability, it can be additionally reinforced with “fungi dowels” or glue. The bars can be replaced with drywall profiles.
- A vapor barrier is laid as the first layer. Then the mineral wool itself, and on top there is another waterproofing layer. When installing outside, an option is allowed when the first hydraulic barrier is skipped. And mineral wool is glued to the walls with a polymer-cement composition. The option depends on the selected material and type of finishing.
- The outer vapor barrier layer is strengthened on the frame. And on top of it is another lathing for pressing down the mineral wool and subsequent decorative finishing. Or plastering is done.
Results
Moreover, such thermal insulation will last for many years. The main thing is to thoughtfully approach the choice of mineral wool for wall insulation and correctly perform a vapor barrier in order to minimize the effect of moisture on the material.
The density of mineral wool insulation largely determines its intended purpose and is one of its main performance characteristics. Its value is influenced by the thickness and number of fibers in the structure (the percentage of foreign impurities is usually not taken into account), as a result, the higher it is, the more expensive the building material is. The insulation is produced in the form of soft mats and hard slabs with a density from 11 to 400 kg/m3; the choice of a specific brand depends on the degree of load of the structures and the construction budget.
For any insulation, the rule is true: the lighter it is, the better, but this cannot definitely be said about mineral wool. Its low thermal conductivity is indeed due to the presence of air between the threads, but when a certain minimum is reached, it ceases to retain heat. In practice, the density of mineral and basalt wool affects its weight and cost, and is also directly or indirectly related to other characteristics: thermal conductivity, noise absorption, load-bearing capacity and ease of installation.
1. Thermal insulation.
This insulation uses the properties of weightless air with a thermal conductivity coefficient of no higher than 0.026 W/m·K. Thanks to the combination of fibers with different directions, manufacturers managed to achieve a similar value of 0.036 for light and soft boards, 0.032 for semi-rigid boards and 0.04-0.046 for dense and cylindrical products (which is more than good for non-flammable insulation). But when a certain mass is reached, the fibers stop retaining air and thermal conductivity deteriorates. The worst protection is observed for loose insulation with a density of up to 30 kg/m3 with a disordered fiber direction - 0.05 W/m K.
2. Noise absorption.
Materials with low air permeability are good acoustic insulators. Therefore, dense and rigid slabs absorb sound in any case (even if this is not their main purpose). But they weigh a lot and are not always suitable for internal soundproofing of rooms; for this purpose it is better to buy specialized brands: glass wool with long and thin threads or basalt with randomly twisted fibers. Rockwool, Izover and other brands have such series; their insulation density is in the range of 45-60 kg/m3.
3. Load-bearing capacity.
Regardless of the design, overly lightweight materials are not used when installing in areas subject to high loads. This is due to the risk of deformation or creasing, low compressive and bending strength. In such cases, high-density insulation materials (at least 150 kg/m3) are clearly required. If there are supporting structures (frame, joists, reliable sheathing), the use of lightweight grades is allowed and encouraged; insulating abilities come to the fore.
4. Laying nuances.
There is a clear connection between density and ease of handling of the material. Lightweight soft insulation can be placed without problems in the inter-lag space of roofing systems (non-used surfaces) when laid from above, but installing them from the ceiling is a more than complicated process. The vertical placement of rolled grades is a little easier, but due to the risk of fibers sliding down, it is better to purchase compacted wall insulation. The most convenient option is considered to be semi-rigid slabs with slightly springy edges (up to 60 kg/m3) or high-density mineral wool.
We insulate the floors and attic of the house with expanded clay, slag, and straw
Despite the boom in polystyrene and the dominance of mineral wool, naturally occurring and cheaper insulation materials such as expanded clay, slag and straw are still popular...
Why is it good to insulate with expanded clay or slag?
Expanded clay or slag - products formed from minerals at high temperatures, have practically no shelf life limitation.
Unlike other popular insulation materials - mineral polystyrene and cellulose wool, for which this period is very, very different from similar indicators of heavy building materials. Hence the need to overhaul insulated (two-layer) structures - to change such insulation.
Also, expanded clay or slag are actually in no way afraid of biological influences, they do not feed rodents, and are not favored by crawling... If you do not moisten the insulation layer, then after many, many years it can be removed in its original form, after the walls have crumbled...
Is it possible to insulate with coal slag - ash?
Many boiler houses run on coal and produce mountains of ash. Solid sintered, hollow and porous alloys of various minerals that were in coal, in bulk form in a layer of more than 10 cm, have a relatively small thermal conductivity coefficient.
Coal slag is always unique and has no analogues; it depends both on the qualities of the coal (which are also unique) and on the combustion parameters. Small debris and dust only add mass and increase thermal conductivity. Ash needs to be sifted out from small components, take larger than 5 mm….
This is a very significant problem, since conditionally free slag is quite difficult to recycle. And tens of tons of it will be needed to insulate it. Compared to expanded clay, it usually has a higher thermal conductivity coefficient (more than - 0.12 - 0.15 W/m2C like expanded clay) and a higher specific gravity (more than 400 - 500 kg/m3). But it can be cheap.
Why insulate with straw?
Expanded clay or slag can be obtained quite cheaply in different places. And in some places, straw or shavings may have a bargain price. These natural and short-lived materials can be given the desired properties if they are treated with cement-lime mortar. Minerals that settle into organic matter provide it with benefits - an increased service life and reduce the caking of the layer, and also frighten both small and large living organisms.
How much insulation is needed
With such a high thermal conductivity coefficient - a large 0.1 W/m2C, it is recommended to use a layer no thinner than 30 cm, but better than 40 - 50 cm.
- Expanded clay or slag is poured from a truck under the floor - under wooden joists.
- Expanded clay can be poured onto soil compacted with crushed stone (floors on the ground) and a screed can be made on top.
It is still problematic to use them on the attic floor - the optimal layer for economic feasibility is 40 cm, but dozens of tones need to be raised to the floor level. The question also arises - will the floors withstand it?, and also - is this an extra load on the foundation?
But on the other hand, wood chips or straw, although not so durable, but separated from the housing by a vapor barrier, will not look bad there if you organize a platform for movement on top...
Avoid getting wet
These are porous, vapor-permeable insulation materials; all steam passing through them will condense inside their layer at the dew point. To remove it, you need to ventilate on one side and prevent steam from entering on the other. Therefore, the insulation is separated from the steam source by a vapor barrier.
In floors on joists, the insulation is separated from the ground by a continuous double roofing material flooring - a conventional vapor barrier under the house. First, roofing material is rolled onto the compacted soil, gluing the joints and wrapping it onto the base. Now the humidity of the insulation will always be the same as in the house.