Low heating radiators are found in any group of heating devices. This category includes equipment whose height does not exceed 45 cm. Such small batteries are usually sought for aesthetic reasons: with panoramic glazing or low window sills. Sometimes you need to heat an entire cold wall, in which case this is one of the most effective options. After all, low radiators have low heat transfer, which means their length will be significant, which is what is needed to heat a cold or “wet” wall.
It is clear that you want everything to look stylish, but in heating you cannot focus only on aesthetics: technical data are also very important. That’s why they pay attention to the metal from which they are made. After all, it is its properties that largely determine the characteristics of radiators and their scope of application.
Installing the battery into the system
When choosing one or another type of low radiator, you need to decide on its parameters based on the size of the window and the required heat transfer.
The length of the heat exchanger should be equal to the width of the opening or exceed it by 200-300 mm. Having the skill to use the necessary tools, it is not difficult to connect the radiator to the system with your own hands.
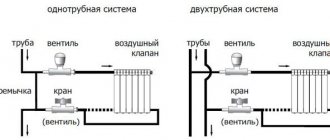
The following instructions will help with this:
- determine the type of system - one- or two-pipe;
- determine the most optimal connection diagram - diagonal, one-sided or bottom;
Unobtrusive interior element
- Next, we install taps on the supply and discharge pipes. allowing to shut off the coolant supply in an emergency;
- We screw the Mayevsky tap (top) and the plug (bottom) into the remaining holes.
- preliminary assembly can be done dry, the final connection is made using linen winding and plumbing paste;
- Batteries made of various metals can be connected to heating systems made of metal, metal-plastic and polypropylene pipes.
Montage in pictures
Aluminum
The lowest aluminum radiators have a height of 245 mm. The Sira campaign has such models. Alux 80 and Alux 100, Rovall 80 and Rovall 100, Swing. They have a good heat output for such miniature products - 89-97 W. Global has a low radiator - model Gl-200/80/D. This model is cast, with a working pressure of 16 bar.
The lowest radiator at Global Gl-200/80/D has a height of 200 mm
There are aluminum radiators with an interaxal distance of 200 mm from the Russian manufacturer, Rifar, Rifar Base 200 and Rifar Forza 200. Moreover, their back wall is solid. You can safely place them with your back to the window and not worry about the appearance from the street.
But these are the smallest radiators. There is a large selection of models, the height of which will not be higher than 45 cm. Every company has such sizes, in almost every line. A center distance of 300 mm, 350 mm or 400 mm also fits into the low category.
Advantages, disadvantages
Any line has low batteries, with an axial distance of 300 or 350 mm
Advantages of aluminum radiators: lightweight, have high heat transfer, small capacity (little water can be placed), and quickly respond to temperature changes.
The most important disadvantage is the chemical reactivity of aluminum and its softness. For normal and long-term operation, a high-quality coolant is required: Ph 7-8, operating pressure - from 5-6 Bar for extrusion models, to 10-12 for cast ones. It is imperative that the coolant contains a small amount of oxygen and suspended matter. Oxygen promotes the oxidation and destruction of aluminum, and suspensions wear down the metal.
But each manufacturer has its own requirements. For example, Chinese aluminum Radena radiators operate at 16 Bar pressure and coolant with Ph 6.5-9. And Sira extrusion models have a working pressure of 16 Bar and a warranty period of 25 years. There are probably other aluminum radiators whose characteristics go far beyond the average: and there are too many manufacturers and models.
When choosing, do not forget about all these technical subtleties: only if the operating conditions coincide with the manufacturers’ recommendations, the heating will work for a long time and without failures.
When installing the system, it is worth remembering that aluminum cannot be combined with copper (or copper-based alloys) directly. This means that when installing copper pipes, it is better to install other radiators. And also do not install bronze or brass fittings. Galvanized fittings and fittings work well with aluminum.
Application area
Scope of application: in individual heating there are practically no restrictions, it is only worth paying attention to the temperature of the coolant, especially if the system has a coal or wood boiler. It is risky to install them in apartments
Unless they are very reliable and proven, and only if the coolant in the system meets the manufacturer’s requirements.
Read about choosing radiators for an apartment and a house in the article “Aluminum batteries: types, selection, connection”
Tall radiators
When the selection of a radiator in size is limited due to lack of space to accommodate a standard device, preference is given to tall and narrow batteries, since these models have a limited width.
Cast iron radiators. Unlike domestic cast iron products of standard dimensions, among foreign products you can find designer devices whose height is unusual for Russian consumers. For example, the Demrad Retro line of cast iron radiators.
Their sizes are as follows:
- the height of the section with a width of 76 millimeters varies from 661 to 954 millimeters;
- depth - 203 millimeters.
Working pressure is 10 atmospheres, they are tested at 13 atmospheres.
The largest sections have a thermal power of up to 270 watts. At the same time, narrow heating radiators can have height dimensions of 2400 millimeters. Working pressure is limited to 6 atmospheres. The high height contributes to the solid heat transfer of the heating radiator. at a temperature delta of 70 degrees, it reaches even more than 433 watts.
Aluminum radiators
. Typically, for tall aluminum radiators, the connections are placed at the bottom to make the pipes invisible.
Bimetallic radiators
. Basically, models of tall and narrow bimetallic radiators are original design designs, and accordingly, all their sizes are non-standard. Basically, these products are rarely sectional - they are, as a rule, monolithic.
An example of such heating devices is the radiator model Sira RS-800 BIMETALL, which has the following parameters:
- section height 880 millimeters;
- depth 95 millimeters;
- length 80 millimeters.
Before calculating the size of a heating radiator, it is necessary to decide on the model of a specific heating device for a room of a certain purpose and area. It should be remembered that heat transfer is affected not by the size, but by the power of the individual sections, which are assembled into one battery. Choice, taking into account the sizes of heating radiators, details in the video:
Problems with large windows - why do they occur?
A French window is, by and large, a glass wall.
Its main advantage - a large glazing area - from the point of view of heating engineering becomes a disadvantage. This is why such windows often “cry”: at the slightest drop in temperature, condensation forms on the inner surface of the glass, which flows down and can form large puddles. If the temperature outside the window has gone into the “deep minus”, then the condensation at the bottom of the window will freeze, forming a layer of ice. In addition, freezing can occur along the perimeter of the structure, so heat loss will be enormous.
And the point is not that you bought low-quality windows - you just can’t argue with physics:
- The thermal conductivity of the window (even if you have chosen an energy-saving double-glazed window) will in any case be higher than that of the walls surrounding it. Thus, the glass becomes the coldest area in the room, and it is on it that moisture from the air will condense.
- Warm air rises and cold air sinks. This is why the lower part of the window, adjacent to the floor, will suffer: it is in this zone that the temperature will be the lowest. So freezing will start from here.
In the case of ordinary windows, the problem is solved by heating with radiators installed under the window sills. They already do a good job, but if you cut a special grill into the window sill board, condensation, if it appears, will only last for a few minutes.
This solution is not suitable for French windows: they do not have a window sill as such, and placing the radiator in front of the glass means significantly worsening the appearance of the entire structure. That is why to solve the problem of condensation and freezing you need to use special heating devices.
How to choose the right low battery
In modern stores you can find a wide variety of models of low batteries, both domestically produced and from well-known brands of manufacturers in other countries. In order not to waste money on purchasing a battery with unused properties, it is recommended to rely on the following:
- It is better to heat rooms with panoramic windows with batteries made of aluminum or two or more different materials.
- In private houses that are not connected to the central heating mains, but use their own boiler, steel or aluminum radiators should be installed.
- The radiator must create an effective thermal curtain when placed in a window opening. To do this, its length must be greater than the width of the window.
Tubular radiators for home heating Bimetallic heating radiators Flat heating radiators Heating radiators for a private home
Features of operation
It is recommended to use steel radiators when organizing private heating.
Radiators made of steel or aluminum are not always suitable for use. Aluminum is not compatible with copper elements, which are often used for plugs or as connectors and taps. The presence of large amounts of oxygen is unacceptable for steel, since under its influence it begins to quickly rust.
Batteries made from these materials can be used in apartments if all operating requirements are met. It is equally important to take into account that it is rational to install radiators made of light and thin alloys when organizing individual heating.
Narrow radiators with a large height must be equipped with an air duct. It is installed opposite the pipeline in the upper manifold. To simplify operation, it is better to choose automatic mechanisms.
Common types of low batteries
Since radiators are designed very simply, the differences between them are based on the geometry of the case, what material it is made of, and what type and size the radiator fins are.
The minimum dimensions of a low radiator are usually 0.2 meters high, 0.5 meters long and 0.1 meters deep. Maximum dimensions can be 0.5 meters high, 6 meters long and 0.23 meters deep.
The design of low batteries is determined primarily by materials, such as:
The batteries are sections obtained by casting. For heat exchange, each section contains a number of ribs determined by the design.
The properties of cast iron determine both the disadvantages and advantages of such a radiator. Cast iron is brittle and like an eggshell, which, due to its convexity, is strong on the outside, but easily destroyed from the inside. Therefore, the water pressure inside such a radiator should be less than 9-11 atmospheres. And since the surface of cast iron after casting turns out to be rough and uneven, debris settles on it inside the radiator over time and creates a layer that weakens the transfer of heat from the water to the cast iron of the radiator. But despite the mentioned disadvantages, a cast iron radiator retains heat well and is not subject to destruction from prolonged contact with water.
The casting method does not allow steel to obtain the ribbed shape required for the radiator. For this reason, low steel batteries are made from individual plates and are often combined with pipes. A low battery based on a pipe framed by plates that serve to increase convection has heat losses due to gaps that occur where the plates are attached to the pipe.
If the radiator is made of steel plates that form cavities for filling them with hot water, the heat transfer is much greater than that of a pipe-based radiator, but the resistance to water hammer is reduced due to the presence of seams connecting the plates, which is one of the disadvantages of such radiators .
Another disadvantage of steel radiators is rust, which appears inside upon contact with air oxygen in a humid environment. In addition to the mentioned disadvantages, steel radiators are very expensive due to labor-intensive manufacturing and the need to use corrosion-resistant steel. In terms of heat transfer properties, they are close to cast iron radiators.
Aluminum batteries can be either cast, extruded, or made from wafers. Their main advantage is their weight, which is significantly less than that of cast iron and steel.
In terms of their ability to withstand water pressure, aluminum radiators are almost one and a half times better than cast iron ones. But the convection properties of aluminum are worse than those of cast iron and steel.
In addition, aluminum is less durable than cast iron and steel, so water hammer can quickly lead to water leaks through cracks that appear in the body. For this reason, the service life of such radiators is shorter than that of cast iron and steel.
This radiator is made of several parts. the material of each of them is selected to best suit the task being performed. In such a battery, water passes through a pipe made of copper alloy or other material. The pipe is capable of withstanding water pressure of several tens of atmospheres and is not subject to destruction from prolonged contact with water. Therefore, its service life will be comparable to a cast iron battery.
To increase the surface area of contact with air, plates made of aluminum or an alloy of non-ferrous metals are placed on the pipe. Such a radiator may have small dimensions, but due to heat loss at the point where the plates are attached to the pipe, its efficiency will be less than that of aluminum batteries.
The complexity of manufacturing and the use of non-ferrous metals makes such a battery more expensive than an aluminum one.
Criterias of choice
Water systems are more difficult to work with; several additional factors may influence the purchasing decision, in addition to the dimensions and material from which the body, fins and pipes are made.
Basic materials used for production
Currently, the main criterion that separates all low radiator models available on the market is the material from which they are made. Along with the traditional ones used in the last century, new types are appearing with better performance properties.
Cast iron radiators
Elements made of cast iron have the longest history of use. They are distinguished by high heat transfer, long cooling and heating, large mass and their low resistance to shock loads.
The increased roughness of the inner surface of the cast sections of a cast iron battery contributes to the accumulation of dirt and rust deposits on its walls, which over time significantly reduces heat transfer.
Note! Despite the fluidity of cast iron, the manufacturer produces heat exchangers with a height of at least 390 mm. This is due to the disadvantages mentioned above
There are batteries made at a sufficient artistic level, which allows you to decorate the interior of rooms.
This is a decoration you can install at home
Steel heat exchangers
Products made from this iron-carbon alloy can be smaller in size than cast iron. They are a plate structure, the basis of which is metal pipelines. This aspect significantly reduces the required amount of coolant in the system and, as a result, increases its efficiency.
In the photo - steel panel batteries
Heat exchangers made from steel have a number of positive and negative aspects. Their weight is significantly lower than cast iron, they are more compact and have greater heat transfer. Disadvantages include susceptibility to corrosion and poor resistance to water hammer.
Steel heating radiators are low in height and have poor repairability. If one of the sections of a cast iron battery is damaged, it is easy to replace or eliminate it.
The steel product will have to be replaced entirely, which will lead to additional costs. The price of such units is one of the most significant in the segment.
Aluminum radiators
Low aluminum heating radiators have a range of advantages over their competitors.
- minimum weight of all similar products;
- good heat dissipation;
- and the plasticity of the metal allows you to obtain products of elegant shapes.
The size of the devices does not affect their characteristics
Note! Aluminum does not have great strength characteristics, which can lead to the formation of leaks due to water hammer in the system that occurs when it is filled or drained. The average service life of such products does not exceed 12-15 years
The cost of radiators made of aluminum is low.
Bimetallic batteries
One of the latest types of heating devices recommended for use in individual heating systems of private houses are the so-called bimetallic batteries. They are made on the basis of steel or copper pipelines equipped with aluminum plates.
Reliable strength of two metals in bimetallic devices
Their advantages include the following:
- sufficient corrosion resistance;
- significant (up to 100 atm.) operating pressure that they can withstand;
- low volume of coolant required for heating.
Such designs also have disadvantages:
- less heat transfer compared to aluminum products;
- the highest cost among all low radiators.
Panel heating systems
If you decide to get a heating system for your home that is completely devoid of visible elements, panel heaters can come to the rescue. These are really low horizontal heating radiators. Their height from the floor does not exceed 20 cm with a thickness of 30 mm.
Such products are located along the walls and covered with decorative overlays (panels). Using this option, you can get a heating system with a height of 100 mm, operating like a standard one with high radiators. The significant disadvantages of this heating option are the high cost and complete unsuitability for repair.
Steel panel
Steel panel radiators are low: they are usually made from 300 mm in height (here it is the height of the radiator, and not the interaxal distance). Any manufacturer has them: Russian Prado and European Purmo and Kermi.
There are also lower ones, but they are rare. So ]Purmo[/anchor] has models Ventil Compact, Purmo Planora and Ramo Compact. Their height starts from 200 mm (center distance 150 mm). We haven't found any others this small.
Steel panel radiators can be very low
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantages of steel radiators include their compact size and the lowest price per kilowatt of power. In addition, steel is a non-capricious metal that does not conflict with other components of the system.
The main disadvantage is the tendency to corrosion, and hence the demand for coolant: Ph 7-8 and lack of oxygen (closed systems). The panel walls have a thickness of 1.25 mm or 1.4 mm. If the coolant is of poor quality, they can be corroded within a few seasons. There is another disadvantage, which is due to the design: the small width of the channels through which the coolant circulates. If there is a large amount of contaminants in the coolant, they quickly become clogged. But flushing such a radiator is a problem. Another disadvantage is the difficulty of cleaning in the presence of plates with convective ribs.
Read more about steel radiators here.
Application area
Normally, panel radiators are installed in individual closed systems (with a closed expansion tank). Coolant circulation must be forced: these heating devices have high hydraulic resistance.
It is not recommended to install them in high-rise apartments; the pressure rarely allows this (working 10 bar). Only in systems that have their own water treatment (independent type of connection) with a mandatory deaeration stage (air removal).
What should the dimensions be?
In order for the heating radiator to give off maximum heat (in this case we are not talking about its thermal power, but about the efficiency of its operation), the dimensions must be as follows:
- The length should be more than 70-75% of the width of the window opening.
- The height should be such that there is 8-12 cm between the floor and the battery, and 6-12 cm between the window sill and it.
If the recommendations are not followed, the operation of the aluminum radiator will be accompanied by heat loss. Therefore, even if he can provide the necessary for a room with an area of 20 square meters. m 200 watts of heat, then due to incorrect dimensions there will be insufficient heat in the room. After all, part of it may be lost under the windowsill or used to heat the floor.
When the length is less than 70% of the width of the window opening, the battery will not be able to create a thermal curtain capable of blocking the movement of cold air entering through the window. The consequence of this situation will be the appearance of cold and warm zones in the room. Also, the windows will be constantly covered with steam. And even the power of the heating radiator, which is greater than the need, cannot become a “magic wand”.
Therefore, if the window is 2 m wide, then the length of the battery should be at least 1.4 m
Of course, in order to select a device with such a length, you will need to take into account sections of different heights and their heat transfer. The calculation may take a long time, but it is worth it
Models without housing
In this case, heating radiators are installed in a specially prepared niche. Its walls are insulated. The most commonly used is polyester foam. Batteries of this type are mainly located in new buildings, where their installation is provided for in the design documentation.
Diagram and principle of operation of a liquid electric radiator
The heating circuit is installed inside the niche at a height of 10 cm from the bottom. This is due to fire safety regulations. Also, the presence of an air gap improves the movement of warm masses and increases the efficiency of the heating device.
The channel with heating elements is closed with a special grille. It must withstand significant loads that are possible during operation.
Also, the grill must be removable so that the channel can be cleaned of accumulated dust. It can move completely away or collapse.
Main dimensions
Dimensions mean:
The center-to-center distance (also called inter-nipple or center-to-center) should not be confused with the height of the heating radiator. The first indicator indicates how many centimeters are between the upper and lower collectors (holes). Height is the distance between the lowest and highest point of the section.
Aluminum heating radiators have the following dimensions:
- The center distance ranges from 150 to 2,000 mm. Very tall radiators are rare. The most popular are radiators with an inter-nipple distance of 500 mm. This is because the current heating network pipe system was created for cast iron batteries, which have the same center-to-center distance. Since many owners did not and do not have the desire to digest pipes, they simply selected/are selecting a suitable radiator and, thereby, increased the popularity of a battery with an interaxial distance of 0.5 cm. This indicator is very important, and therefore manufacturers indicate it in the name of the battery (RAP-500, Rococo 790, Magica 400, etc.).
- The height is in the range of 245-2000 mm. According to this criterion, batteries can be divided into low, medium and high. The features of each type will be discussed below.
- The section depth ranges from 52 to 180 mm. Some models may have greater depth, however, this is rare.
- The section width is 40-80 mm.
Bimetallic devices for panoramic windows
This type of radiator belongs to heat supply equipment, the high cost of which best corresponds to the quality.
Bimetallic radiators differ:
- High working pressure.
- Compatible with other metals. In them, aluminum is used only for the manufacture of the shell, which increases the aesthetics of appearance and heat transfer. As for the internal casing, equipped with outlets for connection to the system, it is made of stainless steel or black steel.
The height of bimetallic radiators for panoramic windows ranges from 24.5 to 45 centimeters.
Features of installing heating radiators for different types of window structures
Correct installation of the heating radiator depends on the type and design of the windows.
For window units of different designs, batteries are used, the dimensions of which correspond to the dimensions of the space underneath them. Based on this, we can distinguish several main options for how to place a convector under a window:
- Standard placement relative to the battery window.
- Installation of convectors near the walls in balcony blocks with a doorway.
- Flat plate convectors for panoramic windows.
- Convector in the floor under the stained glass window.
- Hidden installation of a radiator under the window sill.
- Floor batteries under the panoramic block.
Most of these methods are not clearly regulated in SNiP, so in order to hang a heating radiator correctly, it is necessary to take into account the recommendations of manufacturers and builders.
Standard battery placement
The correct location relative to the battery window is determined by building codes. However, professionals recommend hanging the radiator so that it protrudes beyond the window sill by ¼ of its width. This will create the most effective thermal shield around the window.
In addition, it is recommended to choose a convector for a large window opening with internal fins so that the convection process is maximized.
In balcony blocks
It is recommended to install the convector under the double-glazed window of the balcony block across the entire width of the window sill. It is recommended to place the edge of the battery facing the unit door at a distance of 3-4 cm from it. It is not recommended to install shut-off valves or temperature controllers in this location. For installation, a device is selected whose power is 10-15% greater than the calculated one for this room.
Special convectors for panoramic windows
Heating radiators for panoramic windows are selected based on the size of the space under the window. It often happens that a panoramic window starts at floor level, without a window sill. In this case, it is recommended to install the battery near the window in a floor-standing version. If the floor arrangement of the radiator does not fit into the interior concept, you can install a convector under the floor, covering it with a decorative grille.
Convector in the floor under the stained glass windows
Stained glass windows have recently become increasingly popular not only for decorating staircases and winter gardens, but also work offices and living rooms
And if there is such a window in the room, then it is recommended to install radiators for stained glass windows so that they do not distract attention and fit harmoniously into the interior. The specificity of installing such devices is to ensure the direction of warm air onto the stained glass window as efficiently as possible
Traditional stained glass with a lead or tin rim of glass lets in much more cold than a regular double-glazed window. Therefore, in addition to a conventional radiator, an additional electric heater is often installed in a niche under the window sill.
Hidden installation of radiators under the windowsill
Not many people enjoy the pleasure of having a wide window sill and looking at the falling snow. Typically, such wide window sills are installed in old houses with wide walls. Therefore, in order for the bed to be not only comfortable, but also warm, there must be a massive radiator under the window sill, capable of heating a large area of the window sill. And in order for heat to penetrate into the room, holes are made in the body of the window sill.
Floor batteries
For full-height windows in a room, there is often a lack of an element that visually limits the space. And this is where it’s worth remembering floor radiators. In such devices, instead of wall mounting, ordinary legs are provided, so during installation there is no need to look for a support point for the bracket. The battery is simply installed on the legs, which are fixed to the floor with dowels.
Advantages and disadvantages
The declared advantages of low horizontal radiators are determined by the features of their application already discussed. They appear as follows:
- small sizes, comparable to the dimensions of their baseboard counterparts;
- high heat transfer, which is a distinctive characteristic of most models of floor-standing radiators, with the exception of cast iron samples;
- attractive appearance that does not spoil the interiors of modern premises;
- a wide range of colors, from traditional white to a large palette of different shades.
In addition to gradations of white color, some design solutions use the technique of stylizing wood or stone.
The advantages of heaters include ease of installation due to the method of placement in the window sill. Usually they are installed on legs that are already present on the body of the product, after which the user will only have to connect the pipes to the lower supply. Individual samples are fixed directly on the floor surface or built directly into it. With their help, it is possible to heat large rooms, as well as place them close to the walls, without cluttering up the living space.
The disadvantages of heating batteries of this class include:
- limited methods of laying pipes - the need to be built into a wall or floor;
- the ability to use only one heating method - convection;
- the difficulty of selecting and purchasing a model suitable for specific operating conditions.
The disadvantage of the products is the relatively high cost declared by the manufacturer. It significantly exceeds that of classical battery samples.
Regulatory Requirements
Window sill height
In all Soviet-built houses, without exception, the standard distance from the floor to the window was 70 - 85 centimeters.
As is easy to see, window openings do not start from the floor.
Why? Yes, simply because heating radiators were mounted on the window sill, creating a thermal curtain in front of the window opening.
The function of a radiator is to create a thermal curtain in front of the window.
Why do windows need a thermal curtain? It solves at least two problems:
Eliminates the appearance of cold drafts. Air from the street, penetrating inside through the gaps of the window frames, is mixed with the rising air flow from the hot battery;
A window without a thermal curtain will become a source of cold in winter.
Warms up the glass, eliminating the formation of condensation and frost on them.
The thermal curtain created by the radiator warms up the glass.
There was no GOST for the height of the window from the floor in the USSR, and it still doesn’t exist now. However, indirect mention of this parameter can be found in SNiP 3.01.01-87, which sets out the requirements for load-bearing and enclosing structures.
What should be the height of the window from the floor according to SNiP? The document makes the following recommendations:
- The heating radiator must be separated from the floor by at least 10 centimeters. The gap is necessary so that the proximity of the floor does not limit air convection;
- The gap between the battery and the window sill should be at least 6 - 8 centimeters. The purpose of creating a gap is the same - not to interfere with convection.
Distances from the radiator to the window sill and floor.
To these values you should add the height of the heating device itself.
Dimensions of the MS-140 radiator.
Adding up the size of the gaps and the height of the battery, we get 76.8 cm. This will be the minimum allowable distance from the window to the floor.
Typical height of a window opening above the floor.
Window area
We found out at what height from the floor builders install windows. Now we have to find out whether there are any regulatory restrictions on their maximum area.
An excessively large window area can create problems for the owner.
The answer can be found in SNiP 2.08.01-89, which regulates the construction of residential buildings. According to this document, the ratio of the window to the floor area of the room should be in the range of 1:5.5 - 1:8.
The ratio of window area to floor area for premises for various purposes.
So you decide to go against the rules. You are not interested in what height from the floor the windows are located in apartment buildings of standard designs and what area they have: your windows should be panoramic, from floor to ceiling.
I approve. Three years ago I thought the same way. And now, after this time, I can give a number of compelling arguments in favor of French windows.
Argument one: review
If your windows do not look out onto a garbage dump or the blank wall of a neighbor’s house, why not enjoy the beautiful landscape? For me this argument was the main one. The house is located so that the gables of the attic look out onto the picturesque mountains and the harbor, and I didn’t want to cover them with blank walls at all.
A beautiful landscape is the main argument in favor of a large window area.
Argument two: illumination
As you know, natural light is optimal for the eyes. Our vision was formed under a very specific spectrum of light - solar, and the eyes tolerate deviations from this spectral composition very ... let's say - disapprovingly.
Evolution has adapted our eyes to a very specific spectrum of light.
It is clear that a large window area will provide bright natural light to the room all year round.
This is especially important for children who learn from paper textbooks and write a lot while doing homework.
The larger the windows, the better the room is lit.
Expert advice
There are quite a few popular options for heat supply using floor products.
- In-floor radiators - the main device is located below the floor line, and on the surface there is only a grille, through which cold air masses penetrate into the convectors, and warm ones rise upward. Such installation is quite labor-intensive, and the liner itself is often hidden, which is extremely undesirable in case of emergency situations.
- The use of fan coil units is a system in which the heat exchangers are blown by built-in fans, which optimally redistribute warm air flows. This design ensures uniform distribution of heat over the entire area of the room, and in addition, completely frees the floor from additional communications, since they are all located above and do not “steal” the usable space of the room.
Floor radiators are still considered little-known devices, although there are quite a few situations where they are truly irreplaceable. The devices are connected in the same way as the simplest radiators; they are practical, ergonomic and energy efficient.
See the following video about the advantages of floor heating radiators.