Every summer resident strives to grow as many fruit crops and ornamental plants as possible and at the same time achieve an enviable harvest. The most suitable periods for this are spring and summer. However, if you want, some of them can continue to be grown even in the cold winter. To do this, it is enough to think about heating the greenhouse in winter and implement it correctly.
- 1 Why is it necessary to heat a greenhouse?
- 2 Introductory video review
- 3 Electric heating
- 4 Air heating of greenhouses
- 5 Biological heating
- 6 Sunny
- 7 Water heating for a greenhouse 7.1 Video guide
Why is it necessary to heat a greenhouse?
Numerous crops can be grown throughout the year, regardless of the geographic location of the region. To do this, it is recommended to build a spacious greenhouse that will be heated during the cold season, creating a very favorable microclimate for plants.
Someone may think that it will be enough to build insulated and vapor-tight surfaces (roof, walls). However, at very low temperatures, after some time, warm air will seep out and be replaced by colder air. Thus, without auxiliary means it will be almost impossible to maintain a suitable environment (about 17-20 degrees).
Infrared heaters
Infrared heating is ideal for greenhouses, as it is much more economical and efficient than cable heating, which until recently was considered the most reliable. The infrared heater has created worthy competition to the cable heater, heating not the air, but directly the objects inside the greenhouse.
Thanks to this type of heating, the development and growth of plants accelerates, and the crop ripens faster and pleases with its abundance.
Here are the main advantages of infrared heating:
- the entire area of the greenhouse is heated evenly;
- humidity is at the same level, the air does not dry out;
- thanks to infrared radiation, the occurrence of pathogenic fungi and bacteria in the greenhouse is inhibited;
- heat spreads from bottom to top, slowly heating the room;
- plant growth accelerates;
- dust does not circulate throughout the greenhouse;
- mobility and compactness of heaters. They do not occupy the useful space of the greenhouse, as they are installed on the ceiling covering and are easily mounted and dismantled without outside help;
- silent operation of heaters, which has a beneficial effect on both humans and plants.
Thanks to the mobility of infrared heaters, you can easily create different temperature zones in a greenhouse and grow types of vegetables with different heat needs in this room. This is achieved by raising or lowering the heaters. To grow seedlings, heaters are lowered lower to the ground so that the soil warms up faster, and when the seedlings grow, they are raised higher.
Infrared heaters are not afraid of condensation, so they can be safely used in greenhouses with high humidity.
The principle of operation of heaters is similar to natural heating by the sun - the soil is immediately heated, and then the surrounding air, which creates an atmosphere similar to the natural one. At the same time, the plants feel great, because the air does not dry out, and the heat is soft and not scalding. The temperature relay is mounted together with an infrared emitter; the minimum temperature on it does not fall below +5 degrees, which is very good for greenhouse conditions.
Infrared heaters come in different ranges of action. Older models have a flat radiation surface, while newer ones have a spherical one, which allows heat rays to dissipate in a range of 120 degrees, which improves and balances the heating of the greenhouse, and also saves half the energy. This happens because the soil itself is heated, not the air, and heat from the soil spreads throughout the greenhouse, rising upward
It is important that each heater is controlled by a thermostat, then the difference in temperature in the center and along the edges of the greenhouse will be very insignificant
To correctly calculate the intensity of an infrared heater, you need, for example, to take a greenhouse measuring 6x3 m. For such a greenhouse, two heaters 1.7 m long and with a power of 1000-1350 W will be sufficient, which will evenly heat the entire room. The main heating zone will be approximately 2.5 m in length and 3 m in width. For longer greenhouses of 8-9 m, three heaters will be needed.
Infrared heaters weigh very little, which is also one of their advantages. They are thinner and neater than their predecessors, easy to install, emit a very soft heat, favorable for plants, which gratefully respond to growing conditions with a healthy appearance, rapid growth and rich harvests, delivering to the dinner table an abundance of vitamins necessary for our body!
Electric heating
If we consider options for heating a greenhouse in winter, we can note the predominance of electrical systems. Among the many methods, gardeners usually choose one of the following:
- Electrical cable
- Heating mats
- Convection units
- Heat pumps
- Infrared heaters
One of the simplest and most popular methods is heating greenhouses using a convector. It is an installation with spirals inside, through which the air is heated. Air flows are distributed evenly throughout the greenhouse, but the warmest masses accumulate at the top. It is recommended to use the convection method in conjunction with the biological ones discussed later, since it is not capable of warming up the soil on its own.
Using heating mats or electric cables are very effective and inexpensive methods of heating a greenhouse during the winter. Their main advantage is the possibility of installation in those areas that the summer resident needs (outside the greenhouse, between the rows, etc.). The option when heating elements are located directly in the ground is popular. However, if you make a mistake with the temperature, you can overheat the plant root system.
Despite their efficiency, heat pumps for heating greenhouses are not widely used. The reason for this is the high cost of installing the necessary equipment. If the greenhouse is small and is being built for personal purposes, you should not expect a return on investment.
A very interesting and popular option for heating greenhouses is the installation of infrared heaters. If the system is designed correctly, it will be possible to warm up individual parts of the greenhouse in which the plants grow. With some effort, the entire area can be divided into zones, setting in each of them a temperature suitable for a particular crop being grown.
Of course, heating a greenhouse in winter has one significant advantage - the possibility of using them together with temperature sensors. Having made the correct settings, a constant desired air temperature will be maintained inside the greenhouse. The market offers numerous additional equipment designed to normalize the climate inside.
How can I heat
In early spring, greenhouses can be heated in several ways, the choice of which will primarily depend on the purpose of the room. If you plan to heat a small building in which you grow vegetables for yourself, there is no point in purchasing expensive industrial installations. In this case, various stoves or boilers are suitable.
Stove heating in greenhouses was used 20-25 years ago, but it is still relevant today. For these purposes, gardeners and gardeners use specialized boilers or barbecues designed to maintain optimal temperatures. When using stoves, heat is generated by burning fuel. The advantages of such a system are its simplicity and low cost of maintaining the temperature, while its disadvantages are low productivity and labor-intensive operation.
Heating of large polycarbonate greenhouses can be done using water or electric heating. In the first systems, it is necessary to use boilers, pumps and pipelines through which the hot coolant will move. With water heating, heat is generated by burning gas or using electric current.
Electric heating involves the use of electrical appliances to heat the air in the greenhouse.
Heating using cables. The principle of operation of such a system is simple: the heat cable is installed under the ground (similar to the installation of a heated floor) and connected to power sources. When turned on, it will heat the soil, and from it the heat will spread throughout the room. The system is economical and efficient. Most often it is used in greenhouses for growing plants in early spring or late autumn. This heating method is ineffective for heating a room in the winter.
Year-round greenhouses can be heated using gas systems. For these purposes, summer residents and gardeners often use catalyst burners connected either to the main gas pipeline or to household cylinders. Gas heating is suitable for warming up both large and small-sized greenhouses in the winter. The best heating systems are those that use infrared (IR) heaters. They have many advantages compared to other heating options.
The principle of operation of IR devices is similar to the effect of sunlight on plants. The equipment emits heat, which is absorbed by surrounding objects and subsequently transferred to the air. Depending on the type of installation, the room can be heated from above or below. Some growers organize high-quality heating from all sides. However, this heating method is one of the most expensive.
Often, heaters are placed on the ceiling surface above the beds. The weight of one device is relatively small - its weight does not exceed 5 kg. Most modern greenhouses allow you to place any number of such units. Installation of IR equipment is not complicated, so installation can be done with your own hands without the involvement of hired craftsmen.
Date: September 25, 2022
Air heating of greenhouses
Air heating methods are among the most primitive, but they still have not lost their popularity. The simplest option for its implementation is to lay a pipe through the greenhouse, one end of which will go outside. A fire will have to be lit under it, and heated air will flow through the pipe into the greenhouse.
It will not be possible to maintain the temperature constantly in this way, but you can quickly warm the plants in the event of severe and unexpected frosts.
Heating units with a fan are among the cheapest and most compact. They allow warm air masses to be distributed throughout the greenhouse as evenly as possible. With their help, summer residents not only heat greenhouses, but also have the opportunity to dry the air in them, recreating a favorable microclimate for planting.
Emergency insulation of the structure
Often, summer residents are faced with the need to urgently warm up the greenhouse. This situation can arise, for example, if there is a sharp drop in temperature or mechanical damage to the structure, as a result of which it becomes too cold inside. Emergency methods of warming up are chosen based on budget and capabilities, and are often combined with additional work.
Urgent insulation of a greenhouse
For example, urgent insulation can be carried out along with disinfection; For the last action, various methods are used, including sulfur fumigation. This procedure allows you to remove fungus and harmful microorganisms that grow in the soil and on the walls due to high humidity and high temperature. For this purpose, a sulfur block for a polycarbonate greenhouse is purchased; one piece is enough for 20 cubic meters of space. The insulation process can be combined with burning it; this will not harm the plants.
The emergency warm-up itself is performed as follows:
- The dome of the greenhouse must be covered with rolled material: it can be a film with a foil surface, tarpaulin, roofing felt, dense polyethylene.
- The outside needs to be filled with sand. It is done around the perimeter of the entire foundation; a mixture of leaf and sawdust can be added to it.
- Foam panels are installed inside along the length of the base. To protect them from condensation, it is recommended to wrap the sheets in geotextile or other material with a non-woven backing.
- The entrance will need to be equipped with a homemade vestibule: to do this, it needs to be covered with plastic film. If you don't have one, a tarp will do. In the same way, you need to close the holes used for ventilation.
- Inside the greenhouse, barrels containing humus mixed with shavings are installed. Containers should be filled to ½ full. The gradual decomposition of organic matter will lead to an increase in atmospheric temperature.
- To speed up the process, you can place a portable heater inside that runs on gas fuel. It is enough to turn it on for 1-1.5 hours for the temperature to rise to the desired level.
Emergency heating will help preserve seedlings and protect seeds if frost unexpectedly strikes, for which the structure was not originally designed.
It is recommended to take care of the insulation of a polycarbonate greenhouse during the construction stage. If after construction it turns out that the air inside is cold or the soil may freeze, it is necessary to seal the cracks and install an active and biological heating system. Competent actions will maximize the protection of the building from heat loss.
Insulation of a winter greenhouse - on video:
Biological heating
Most of the considered types of greenhouse heating in winter are not able to simultaneously heat the air and soil. To keep the root system of cultivated crops warm, it is recommended to resort to biological methods.
Biological heating methods are based on the decomposition of organic substances. This process is always accompanied by the release of carbon dioxide. The most widely used method for achieving this goal is horse manure.
The advantage of a biological solution to the problem is that it is accompanied by a process of evaporation, while simultaneously moistening the soil. The number of waterings will be significantly reduced.
Foundation and insulation of the blind area
In order for a heated polycarbonate greenhouse to be done correctly with your own hands, it is also necessary to build a foundation, taking into account all the rules. It can be made of a strip type, blocks or concrete. An insulated blind area should be installed around such a base in order to retain the heat of the soil inside the building. The work is carried out as follows:
- Along the perimeter next to the foundation, the top layer of earth is removed, and then wooden formwork is constructed;
- The bottom of the soil, from which the upper part has been removed, is covered with a layer of sand;
- Insulation is laid on top of the sand. It could be polystyrene;
- Depending on the type of final layer, the following work is performed. If the blind area will be finished with concrete, then first construct a mesh of reinforcement, and then proceed to pouring. But you can also lay out paving stones. To do this, first fill in the required thickness of sand, and then proceed to laying out.
Sunny
Without using special equipment, it is almost impossible to achieve a favorable microclimate inside the greenhouse. However, in areas where the sun shines throughout the year and the temperature does not drop too low, natural solar heating may be an option.
One of the prerequisites is that the roof of the greenhouse must be transparent so that the sun's rays can freely pass inside. The latter will heat up the plants and soil, and in turn they will heat up the surrounding air.
In addition to the above conditions, it is necessary to adhere to other features when organizing solar heating of the greenhouse in winter:
- The greenhouse should be located in the brightest place on the site, which is not covered by shadow most of the daytime
- To prevent the wall covering from cooling quickly and spontaneously, it is necessary to choose a location with a minimum amount of air flow
- It should be borne in mind that the temperature inside will reach its maximum only around the evening.
- The best form of greenhouse is arched
- In order for the soil to warm up better, it is recommended to make the greenhouse as low as possible
Natural solar heating is the simplest, most beneficial and cheapest. A significant disadvantage is considered to be low efficiency, especially in cloudy or cloudy weather.
Other effective heating methods
And now about those methods that are gaining more and more popularity among owners of polycarbonate greenhouses day by day.
Option #1 – IR heaters and cable
The latest trend in greenhouse heating is new infrared heaters and heated floors. They have a number of undeniable advantages:
- Firstly, the very term “greenhouse effect” suggests the same principle as those of these heaters: infrared radiation passes through the vacuum and atmosphere without obstacles and, upon reaching the surface, begins to warm it. And the air already heats the surface itself - that’s why, the higher you are from the ground, the colder it is, although, it would seem, it is closer to the sun in this case.
- This is the most environmentally friendly and harmless way to heat your greenhouse.
- No dry air! And this is very valuable, you will agree. With IR heaters, you can forget about different sensors and humidifiers - this problem will no longer exist.
- IR heating is absolutely safe for plants and humans - no harmful emissions, no combustion products, no emergency situations. And, most importantly, this miracle of technology doesn’t even need a chimney.
- Saving! The earth is heating up quite quickly, despite the fact that the air is not very warm. And there is no heat loss at all, as, for example, with gas or water heating.
Infrared heaters are easy to install, work without failure and are inexpensive. Yes, and it’s fashionable - and they want to see a variety of technical innovations in their own greenhouses made of modern polycarbonate.
This is what it looks like:
Option #2 – batteries on the roof
Solar batteries are a know-how that everyone has known about for decades, but is rarely used in practice. Although abroad such plates on the roof of greenhouses are used much more willingly - yes, it’s worth spending all the money once, but you will forever forget about when to go refill the gas cylinder, how much to pay for electricity and what to do in its absence, where to get firewood and who to put in throw them into the oven on a cold night.
Option #3 – solar heating
The sun, of course, heats the greenhouse better than any other device. But it doesn’t always give the temperature that is needed. And in this case, enterprising gardeners try to extract as much benefit as possible from free heat. And to do this, they position the greenhouse in a special way, look for the warmest and sunniest place for it, make the beds at an angle and cover the internal walls with a reflective coating. This is how a solar vegetarian, a thermos greenhouse and similar structures appeared in due time. And thanks to the unique thermal insulation of polycarbonate, this type of heating really has the right to life.
So, at least for starters, place your greenhouse in a place where the sun is shining early in the morning and the earth begins to warm up early. Load some heat accumulators onto the tracks, and it will also be quite warm at night. The main thing is that there are no drafts in this place - they usually cool the greenhouse very much, or take care of an obstacle to the wind.
The shape of the greenhouse, if possible, choose an arched one - it has the least heat loss. Before installation, do the following: dig a hole 15 cm deep at the site of the greenhouse and cover the ground in it with a heat insulator, then with a layer of plastic film for waterproofing. On top is coarse-grained wet sand and excavated soil. The greenhouse will become noticeably warmer.
Water heating for a greenhouse
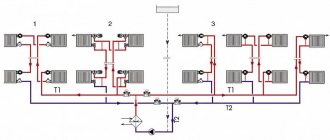
Most often, summer residents set up water heating for the greenhouse in winter, which anyone can do on their own. At its core, it will resemble a classic home heating system, when a heated coolant fluid circulates through pipes and radiates its heat.
To implement this method, it is necessary to select the most suitable location for the heating installation (it can be a boiler, stove, etc.). They can also be located in a separate room, but not far from the greenhouse.
It is necessary to determine the type of coolant circulation:
- Natural circulation is the simplest method, when the heated liquid rises through a pipe to an expansion tank located above the boiler, and from it flows at a slope naturally into the pipe lines
- Artificial circulation - it is similar to natural, but the movement of the coolant is carried out due to the installed circulation pump
It is recommended to give preference to the second method, since it ensures a higher speed of liquid movement through the pipes and does not allow it to stagnate. You should not fill the lines with ordinary water - it will probably freeze soon. The best option would be diluted antifreeze.
Video guide
Let's sum it up
Heating a greenhouse in winter can be organized in any convenient way. Moreover, each summer resident is able to do all the work independently, without the involvement of a specialist and with minimal initial costs.
For those who are going to make a greenhouse for the winter for the next few years, it is recommended to combine 2-3 methods, turning on biological heating. This will allow you to definitely warm up the greenhouse from the ground to the top and protect yourself in case situations arise when one of them is ineffective or for some reason is impossible.
A polycarbonate greenhouse, how to leave it for the winter. Preparing a polycarbonate greenhouse for winter
In greenhouses coated with polycarbonate, known for its thermal insulation properties, the last harvest of vegetables can be harvested even in November-December. Sheets made of cellular polycarbonate retain heat a third better than glass, so the autumn harvest of peppers and tomatoes is not afraid of autumn frosts.
With the onset of the first cold months, it is necessary to prepare the greenhouse itself for wintering. Preparing a greenhouse will not take much time and effort if you know the properties of polycarbonate as a material.
After you have harvested, you should clean the greenhouse of dried dirt, dust, plant debris, garter twine and dig out the top layer of soil (about nine centimeters deep). This will help eliminate pathogens of vegetable crops that may appear in the spring. Sometimes a sulfur bomb is used to treat the greenhouse, which effectively destroys mold fungi and larvae of harmful insects.
If a polycarbonate greenhouse is used only for seasonal harvests, it would be a good idea to throw a layer of manure or snow into it. This will prevent the soil from freezing, which can result in the death of beneficial soil organisms (for example, earthworms). A layer of snow, melting in the greenhouse at the beginning of spring, will perfectly moisten the soil.
Polycarbonate is unpretentious in maintenance; before wintering, its coating can be easily cleaned with a weak detergent solution or soapy water. Do not wash polycarbonate sheets with chlorine, solvents or aldehydes.
Polycarbonate perfectly withstands low temperatures and gusty winds, so there is no need to disassemble the greenhouse for a long winter. But care should be taken to ensure that after heavy snowfalls, snow cover more than ten centimeters thick does not accumulate on the roof of the structure. To remove a layer of snow, simply tap your hand on a polycarbonate sheet from inside the greenhouse. Do not scrape ice and snow from the outside of the greenhouse with sharp objects - this can damage the polycarbonate sheets and lead to a decrease in its light transmittance and reduce protection from ultraviolet rays.
Don’t forget to check the locks and secure all the windows and doors of the greenhouse with latches. Agree, these measures are simple, but they will help prepare a polycarbonate greenhouse for the cold season and the subsequent working season.
Cable heater
This heater consists of a cable in special polypropylene insulation, braided armor made of galvanized steel wire and a special sheath. Cable diameter is 6 mm, bending radius is 35 mm.
The main advantages of a cable heater are:
- relatively easy installation;
- acceleration of plant growth;
- extension of the growing season of vegetable crops;
- increasing the number of plant species grown;
- a bountiful harvest;
- possibility of regulating soil heating.
Typically, with cable heating, the electricity consumption is 75-100 W/sq.m. Special thermostats are designed to regulate the temperature.
The optimal temperature for soil is 15-25 degrees, and for seedlings in peat pots - 30 degrees. When heating the soil with an electric cable, the heating element itself is also located in the soil or under the ground in an asphalt concrete monolith. When heating air, heating elements are suspended in a special way, and then voltage is applied to them. Heating elements can be hidden in pipes, which perfectly protect them from various damage and moisture. True, you will need a lot of such pipes.
The safest cable batteries are made in the form of an asphalt concrete sheet or asphalt expanded clay concrete slab. They have excellent accumulation properties and warm the soil much more evenly. And most importantly, they are absolutely electrically safe.
Types of infrared heaters
Infrared heaters of the following types:
- light;
- long wave.
In IR light heaters, the surface heats up to 600 degrees. This equipment is suitable for very large greenhouses. Long-wave devices heat up much less and are better suited for small greenhouses.
Infrared devices can operate from:
- electricity;
- gas;
- liquid fuel.
Infrared heaters for greenhouses are able to heat a greenhouse with an area of 18 square meters. m. When operating on gas, only two cylinders of liquefied gas are consumed during the winter.
The shape of such heating devices is different. They are produced in the form:
- lamps;
- film (tape) panels.