The principle of operation of the node
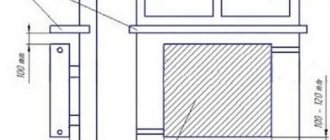
Understanding what an elevator is, it is worth noting the need for this complex to connect heating networks and private consumers with its help. The thermal unit is a module that performs the functions of pumping equipment. To see what an elevator is in a heating system, you need to go down into the basement of almost any apartment building. There, among the shut-off valves and pressure meters, you will be able to find the desired element of the heating system (the diagram is shown in the figure below).
When figuring out what an elevator is, it is worth determining its functionality based on the tasks it performs. These include the redistribution of pressure from inside the heating system, while dispensing coolant at an acceptable temperature. In fact, the volume of water doubles, moving along the lines from the boiler room. This effect is achieved in the presence of water in a separate sealed vessel.
The temperature of the coolant coming from the boiler room is usually in the range of 105-150 0 C. It is not possible to use it with this parameter in domestic conditions for safety reasons.
Regulatory documents regulate the limiting temperature value for the coolant, which should be no more than 95 0 C.
For reference. Currently, the issue of reducing the temperature of hot water from 60 0 C, provided for by SanPin, to 50 0 C, is being actively discussed, citing the need to save on resources. As experts note, the consumer will not notice such a minimal difference, and in order to ensure proper disinfection of water in pipes every day, it is recommended to increase it to 70 0 C. It is too early to judge how rational and thoughtful this initiative is. Changes to SanPin have not yet been made.
Returning to the topic of the heating system elevator, we note that it is he who provides the temperature in the system. Thanks to these actions, it is possible to reduce risks:
- With overheated batteries it is easy to get burned;
- Heating radiators are not always able to withstand long-term exposure to elevated coolant temperatures under pressure;
- The wiring of polymer or metal-plastic pipes does not provide for their use with such hot coolants.
Why is this particular node convenient?
Elevator unit in any apartment building
You can hear the opinion that it would be more convenient not to use a heating elevator with this operating principle, but to directly supply water at a lower temperature. However, this opinion is erroneous, because the diameters of the lines will have to be significantly increased to transfer the colder coolant.
VIDEO: Elevator unit of the central heating main
In fact, a competent design of a thermal heating unit allows you to mix into the supply volume of water part of the return volume, which has already cooled down. Although some sources refer to the elevator unit of the heating system as outdated hydraulic equipment, it has proven its effectiveness in operation. More modern devices used instead of the elevator unit circuit are the following types:
- plate heat exchanger;
- mixer with three-way valve.
Elevator operation
Considering the elevator unit of the heating system, what it is and how it works, it is worth noting that the working design is similar to water pumps. However, operation does not require energy transfer from other systems. It shows its reliability under certain conditions.
From the outside, the base part of the device is similar in appearance to a hydraulic tee mounted on the return branch. However, through a standard tee, the coolant would painlessly penetrate into the return line without passing through the radiators. Such behavior would be meaningless.
Standard elevator layout
The classic diagram of the elevator unit of the heating system contains the following components:
- A prechamber, a supply pipe, at the end of which there is a nozzle of a certain diameter. The coolant enters it from the return.
- A diffuser is mounted in the outlet part. It transfers water to consumers.
Today there are units where the diameter of the nozzle is adjusted by an electric drive. This makes it possible to optimize the coolant temperature automatically.
The choice of a unit with an electric drive is based on the fact that it is possible to change the coolant mixing coefficient within 2-5, which is impossible in elevators where the nozzle diameter is not adjustable. Thus, a system with an adjustable nozzle allows significant savings on heating, which is possible in houses where central meters are installed.
How does a thermal unit circuit work?
In general, the operating principle can be described as follows:
- water moves along the line from the boiler room to the entrance to the nozzle;
- during passage along a small diameter, the speed of the working coolant increases significantly;
- an area with a slight vacuum is formed;
- due to the resulting vacuum, water is sucked from the return;
- turbulent flows in a homogeneous mass are sent to the outlet through the diffuser.
You can see everything in more detail on the working diagram.
For efficient operation of the system, which involves the circuit of the elevator unit of the heating system, it is necessary to ensure that the pressure between the supply and return is greater than the value of the calculated hydraulic resistance.
Disadvantages of the system
In addition to positive qualities, a thermal unit or thermal unit diagram has a certain drawback. They are as follows. The heating system elevator does not have the ability to adjust the output temperature mixture. In such a situation, you will need to measure the heated coolant from the main line or from the return pipeline. It will be possible to lower the temperature only by changing the dimensions of the nozzle, which is structurally impossible to do.
In some cases, elevators with electric drives save the day. Their design includes a mechanical drive. This unit is driven by an electric drive. In this way it is possible to vary the diameter of the nozzle. The basic element of this design is the throttle needle, which has a conical shape. It fits into the hole along the inner diameter of the structure. Moving over a certain distance, it manages to adjust the temperature of the mixture precisely by changing the diameter of the nozzle.
Both a manual drive in the form of a handle and a remote-started electric drive can be mounted on the shaft.
Thanks to such modernized solutions, the boiler room in the basement does not undergo significant, expensive re-equipment. It is enough to mount the regulator to get a modern heating unit.
Malfunctions
In most cases, breakdowns are caused by the following factors:
- equipment clogging;
- a gradual increase in the diameter of the nozzle during operation, as a result of which the temperature of the coolant is more difficult to control;
- clogged mud traps;
- breakdown of fittings;
- failure of regulators, etc.
It is not difficult to determine the breakdown of this device; it immediately affects the temperature of the coolant and its sharp drop. In case of minor deviations from the norm, most likely, we are talking about clogging or a slight increase in the diameter of the nozzle. If the difference is very significant (more than 5 degrees), then you need to carry out diagnostics and call a specialist for repairs.
The diameter of the nozzle increases either due to corrosion in contact with water, or as a result of involuntary drilling. Both ultimately lead to an imbalance in the system and must be corrected immediately.
You need to know that modern modernized systems can be operated with electricity consumption metering units. Without this device in the heating circuit, it is difficult to achieve an economical effect. Installing heat and hot water meters can significantly reduce utility bills.
VIDEO: How the unit works
Areas of application
IHP for heating air in the ventilation system
TP are necessary for proper distribution of heat between consumers. These include:
- Hot water supply. Part of the heat, as hot water is supplied through pipes, is used to heat the bathroom and kitchen.
- Heating systems – maintain a comfortable temperature in residential and public spaces.
- Ventilation system – the air is heated before entering the building.
- Cold water supply does not apply to consumers, but to supply elements. Cold water serves as a regulator.
They install TP for heating, water supply, air conditioning in both old and new buildings.
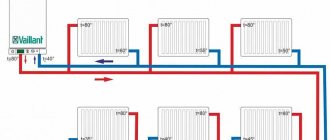
Water heating system for a private house or cottage.
Water heating is the most common in our country, and probably throughout the world. In a private house, water heating is a ring in which heating devices (radiators, convectors, registers, etc.) and a hot water boiler are connected to each other. The boiler is also called a heating apparatus or heat generator. For clarity, look at the following picture:
Here the water circulates in a ring from the boiler to the radiators and back, alternately cooling and heating up. All water CO are divided into two types:
- With natural coolant circulation - in this case, the coolant circulates under the influence of gravity.
- With forced circulation of the coolant - in such a system the coolant is pumped through the system using a circulation pump.
Currently, CO with forced circulation is used almost everywhere, and natural circulation is used only in those places where there is either no electricity at all or serious interruptions in it are possible. Large diameter pipes are used for their installation. If we talk about polypropylene, then the minimum pipe diameter for a gravity heating system will be 50 mm, but it is better if it is 63 mm. I also wrote a short review about such systems. If interested, read it. And further I will talk only about systems with forced circulation.
They come in single-pipe and double-pipe. For example, the picture above shows a two-pipe CO system, in which all heating devices are connected in parallel between the supply and return main pipes. This ensures the same inlet water temperature in each radiator. The disadvantage here is that the pipelines are larger than those of a single-pipe, which does not look much different:
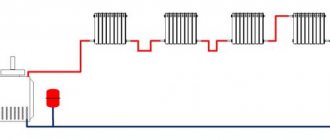
In a single-pipe system, the “hottest” radiator will be the radiator closest to the boiler. The water temperature will be maximum there. The coolant will arrive at the furthest radiator having cooled down considerably. This causes a drop in the heat transfer of each section. Therefore, more of these sections are needed. From here it becomes clear that by saving on pipes, we spend money on radiators. Therefore, for each individual case, it is worth calculating separately which of the two COs will be more profitable for you in terms of cost.
Boilers using various fuels are used as thermal energy generators in water CO:
- Solid fuel - use firewood, coal, pellets
- Gas - use liquefied or natural gas.
- Liquid fuel - use diesel fuel.
- Electric - heat water using heating elements or electrodes.
If you need to learn more about any of the types of boilers, then you need to follow the appropriate link
Water CO for a cottage or private house is often done “by eye,” that is, without any calculations. A “guru” (usually not completely sober) comes to the site and immediately begins to write down in his notebook a long list of components that you will need to buy. In principle, if you have a house with an area of up to 100 square meters, then you can do without calculations and a project. Here the probability of error still remains, but it is less than for large cottages. There, the project is already necessary due to the long length of pipelines, the presence of French windows, winter gardens and other nuances that will need to be taken into account.
Features and Specifications
When installed correctly, the elevator unit of the heating system performs circulation and mixing functions. This device has the following advantages:
Built-in electrical installation
Tax authorities do not have the right to classify fixed assets in the appropriate group. This classification must be carried out by the economic operator itself with the help of the authorized statistical body. A permanently connected electrical installation cannot be considered a separate fixed asset. This increases the building's starting value.
Lighting fixtures, sconces and measuring instruments
If the electrical installation is not integrated into the building structure, it can be considered a stand-alone detector. For individual funds, permanent tax offices receive light inside and outside buildings that are not permanently associated with the building. They can be detached without damaging their structure or the building.
- Lack of connection to the electrical network.
- Efficiency.
- Simplicity of design.
Flaws:
- Inability to regulate outlet temperature.
- Accurate calculation and selection is required.
- A pressure difference must be maintained between the return and supply lines.
Common connection options
If you decide to install a single-pipe system, you will have to choose between two types:
- simple circuit without regulation;
- "Leningradka" with the ability to turn off individual radiators.
In terms of control method, the first option is clearly inferior to the second; its only advantage is its budget cost.
Installation of a simple single-pipe system of horizontal or vertical type is simple and reliable, but temperature control in the network is impossible (+)
Installing the Leningradka will cost a little more, since in addition to the pipes you need to purchase a set of shut-off valves. Using bypasses and valves, you can reduce/increase the amount of coolant supplied to the radiator.
Diagram of the Leningradka device: using shut-off valves, you can temporarily turn off individual unnecessary radiators without changing the functional qualities of the entire system as a whole (+)"Leningradka" is recognized by professional heating engineers as the best option for a single-pipe system for a 2-story residential building.
Complete set and installation of equipment
- circulation pump;
- gas or electric boiler (power depends on the size of the house, characteristics of the coolant, etc.);
- expansion tank;
- pipes 20 mm and 25 mm;
- adapters, gaskets, plugs;
- set of radiators;
- Mayevsky cranes.
Along with steel pipes, polymer or metal-plastic pipes can be used, with the latter being preferred.
In heating circuits with closed expansion tanks, air is bled using automatic bleeders equipped with shut-off valves and floats, or Mayevsky valves supplying each radiator
First, they find a suitable place for the boiler and install it, then assemble the pipeline leading to the radiators. Tees are fixed in places of radiator branches and bypasses. The pump is installed on the return line, next to the inlet to the boiler, and connected to the power supply.
The installation location of an open expansion tank is the highest point of the system; a closed one can be mounted in any convenient place, for example, in a boiler room. Radiators are suspended from the walls using special fasteners and equipped with plugs and taps.
Key components of a heating substation
Components of an ITP device
The thermal complex includes several main elements:
- A heat exchanger is an analogue of a boiler room’s thermal boiler. Here, the heat from the liquid in the main heating network is transferred to the coolant TP. This is an element of a modern complex.
- Pumps – circulation, make-up, mixing, booster.
- Dirt filters – mounted at the inlet and outlet of the pipeline.
- Pressure and temperature regulators.
- Shut-off valves - act in case of leaks, emergency changes in parameters.
- Heat metering unit.
- Distribution comb – distributes coolant to consumers.
Larger TPs include other equipment.
How to install correctly
Metal radiators, except cast iron, are quite lightweight. When fastening them, there are no problems with the load-bearing capacity of walls made of aerated concrete or brick. But in some cases, for example, frame houses or rooms with a large glass area, the equipment can be fixed to the floor.
To select fasteners, the battery load is taken into account. Cast iron can be hung on strong hooks or mounted with floor brackets, lightweight steel and aluminum can be hung on plate brackets or overhead corners. Installation diagram:
- for 8 sections - 2 on top and 1 on bottom;
- for every additional 5-6 sections - 1 more on top and 1 on the bottom.
Steel panel radiator diagram
With this arrangement of the fasteners, the heating device will be firmly and securely fixed to the wall. It is recommended to place the brackets closer to the outer sections.
Wall mount
Installation begins by marking the surface. First mark the points on the wall for attaching the lower brackets and screw them loose.
Then the center distance is set upward, the points are marked and the upper brackets are mounted.
The radiator is hung on the wall and checked for horizontalness. If necessary, make adjustments. After this, the brackets are finally fixed.
Three way valve
If it is necessary to divide the coolant flow between two consumers, a three-way heating valve is used, which can operate in two modes:
- constant mode;
- variable hydraulic mode.
A three-way valve is installed in those places in the heating circuit where it may be necessary to divide or completely shut off the flow of water.
The tap material is steel, cast iron or brass. Inside the faucet there is a shut-off device, which can be ball, cylindrical or conical. The tap resembles a tee and, depending on the connection, a three-way valve on a heating system can work as a mixer. Mixing proportions can be varied within wide limits. The ball valve is mainly used for:
- adjusting the temperature of heated floors;
- adjusting battery temperature;
- distribution of coolant in two directions.
There are two types of three-way valves - shut-off and control valves. In principle, they are almost equivalent, but with three-way shut-off valves it is more difficult to regulate the temperature smoothly.
Heating circuit elements
The structural elements of a closed heating system include:
- boiler;
- pump equipment;
- expansion tank;
- heating appliances.
Both the parts necessary to connect structural elements and auxiliary equipment are used.
Equipment adjustment, heating devices
Boiler equipment ensures heating of the coolant to the required temperature. Solid or gaseous fuel is most often used, with gas being the cheapest and most accessible.
The expansion tank affects the safe operation of the system, since it prevents dangerous pressure in the pipeline. The main part is the membrane, which has the following requirements:
- ability to work at elevated temperatures;
- durability;
- compliance with sanitary and hygienic standards.
To increase the service life of the tank, significant pressure drops should be avoided, especially during startup.
The use of a circulation pump equipped with electronic control reduces energy consumption by 40%. Such equipment provides a reduced noise level and has a long service life. The main indicators when choosing a pump are: power, the period covered by the factory warranty, and the duration of the maintenance-free period. The volume of the circuit affects the choice of its power. In addition, the parameter depends on the characteristics of the structural elements of the system, the type of boiler equipment, and the presence of automation.
The circuit of a closed-type heating system consists of pipes, the material of which can be: steel, metal-plastic, reinforced polypropylene. Parameters influencing the choice of material: the ability to work at high temperatures and the ability to withstand a certain pressure.
Steel pipes are durable, as they are capable of operating at pressures of up to 10 atm and temperatures of more than 100 degrees Celsius. However, steel pipes are prone to corrosion, which reduces their service life.
Reinforced polypropylene pipes are capable of operating at coolant temperatures up to 95 degrees Celsius. A special soldering iron is required for their installation.
You can work with metal-plastic at temperatures up to 90 degrees Celsius. Assembly is simple and does not require complex tools. But the fittings are expensive. Such pipes are not allowed to be used in central heating.
Operating conditions determine the choice of heating devices. In apartment buildings, the water temperature reaches 120 degrees Celsius and the pressure is 10 atm. At the same time, the quality level of the coolant is quite low. Such operating conditions necessitate the installation of cast iron batteries. In a private house, conditions are less stringent, so it is possible to install modern radiators with an improved design.
Technical characteristics of standard products
The line of factory-made elevators consists of 7 standard sizes, each assigned a number. When selecting, 2 main parameters are taken into account - the diameter of the neck (mixing chamber) and the working nozzle. The latter is a removable cone, which can be changed if necessary.
See the table below for the dimensions of the component elements of the product.
The nozzle is replaced in two cases:
- When the flow area of a part increases as a result of natural wear. The reason for the development is the friction of abrasive particles contained in the coolant.
- If it is necessary to change the mixing coefficient, increase or decrease the temperature of the water supplied to the house heating system.
The numbers of standard elevators and main dimensions are given in the table (compare with the designations on the drawing).
Please note: the technical specifications do not indicate the nozzle flow area, since this diameter is calculated separately. To select the number of the finished elevator tee for a specific heating system, it is also necessary to calculate the required size of the mixing and injection chamber
Liquid fuel boilers
The cost of equipment and installation of liquid fuel boilers is approximately the same as that of gas heating appliances. The same applies to the level of efficiency, with lower performance of liquid fuel heaters. However, the amount of dirt generated as a result of their operation is the largest of all boilers. Every visit to the boiler room is fraught with dirty hands and the smell of diesel fuel. Not to mention the annual cleaning of the equipment, which is a very messy procedure. In addition, we have to take into account the high cost of liquid fuel, since prices have risen even for its cheapest option - used oil. Typically, diesel boilers are used as backup heat sources, or when all other coolants are unavailable.
Useful links for beginners
We understand that it is impossible to consider all the nuances of designing and constructing closed systems with your own hands in one publication. A beginner will have to take many steps on the way to working heating; our other articles will help protect you as much as possible from mistakes:
When collecting information about installing a closed heating system, try to get it from reliable sources. Don't listen to Uncle Vasya the plumber, whose work you have never seen. As an example, we suggest that you familiarize yourself with the video material, which clearly indicates where to install the expansion tank and why:
Permission to operate
When a heating unit is admitted for operation, the compliance of the serial number of the metering device, which is indicated in its passport, and the measurement range of the established parameters of the heat meter with the range of measured readings, as well as the presence of seals and the quality of installation, are checked.
Operation of the heating unit is prohibited in the following situations:
- The presence of tie-ins in pipelines that are not provided for in the design documentation.
- The operation of the meter is outside the accuracy standards.
- Presence of mechanical damage to the device and its elements.
- Broken seals on the device.
- Unauthorized interference with the operation of a heating unit.
Device
A standard UTE project requires a certain list of mandatory elements and includes the following mechanisms:
- Shut-off units. The resource supply is cut off.
- Mud trap or filters. They prevent the penetration of suspended matter and protect other devices and the overall system from damage and clogging.
- Thermal converter, which is connected to the meter. The device is most often welded into the inlet pipe.
- Thermal energy metering device (computer). Modern models solve a whole range of problems, from measurement to calculation of various parameters.
- Pressure meter. Installation is required if a multi-apartment building consumes more than 0.5 Gcal/hour of heat.
- A simple pressure gauge and a liquid thermometer are installed separately. These are auxiliary elements for service personnel.
- Flow converter, after which the valve is placed.
The system is installed on the incoming pipeline. On the return section there will be a mud trap and a temperature sensor.
In addition to the units traditional for the distribution system, the centralized heat energy metering unit is equipped with a computing unit, as well as a printer and a telemetry module for data transmission
Advantages
- High efficiency.
- Long-term operation of an individual heating point has shown that modern equipment of this type, unlike other non-automated processes, consumes 30% less thermal energy.
- Operating costs are reduced by approximately 40-60%.
- Selecting the optimal heat consumption mode and precise adjustment will allow you to reduce thermal energy losses by up to 15%.
- Quiet operation.
- Compactness.
- The overall dimensions of modern heating units are directly related to the heat load. When placed compactly, an individual heating point with a load of up to 2 Gcal/hour occupies an area of 25-30 m2.
- Possibility of locating this device in small-sized basement rooms (both in existing and newly constructed buildings).
- The work process is fully automated.
- To service this thermal equipment, highly qualified personnel are not required.
- ITP (individual heating point) provides comfort in the room and guarantees effective energy saving.
- The ability to set a mode based on the time of day, apply weekend and holiday modes, as well as carry out weather compensation.
- Individual production depending on customer requirements.
Purpose
A thermal energy metering unit is being organized for the following purposes:
- Controlling the rational use of coolant and thermal energy.
- Control of thermal and hydraulic modes of heat consumption and heat supply systems.
- Documentation of coolant parameters: pressure, temperature and volume (mass).
- Carrying out mutual financial settlements between the consumer and the organization engaged in the supply of thermal energy.
Types of heat meters depending on the measurement method
Currently, the following types of heat meters are widely used:
- Mechanical operating principle or tachometer. The most common modification of heat metering devices. There are vane or rotor (turbine) ones. Quite easy to use and does not require electrical costs. They work thanks to an impeller or rotor and reciprocating fluid movement;
Important! Mechanical heat meters are demanding of the coolant; the water must be clean. The device is equipped with an additional filter element, since its contamination directly affects the accuracy of the readings.
- Electromagnetic. The operating principle is based on interaction with electric waves of the coolant. Of all the presented categories, these metering devices are the most accurate. The disadvantage of the device is its use in horizontal thermal systems;
- Ultrasonic. Thermal energy is measured by measuring the length of the ultrasound signal passing through the coolant. The meters are installed in pairs, opposite each other. They also differ from each other according to: frequency, time, correlation and Doppler principles of operation. Used in open and closed thermal systems;
- Vortex type. They create a vortex flow in the liquid, due to their location on the path of coolant movement, with subsequent recording of the formation and disappearance of magnetic field vortices. It is used in vertical and horizontal heating systems.
Important! Vortex heat meters require straight pipelines, since the quality of measurements directly depends on the composition of the moving hot liquid, its speed and the presence of air masses in it.