It's always nice to put waste materials to good use. And if it concerns fuel and heating, it is also very profitable. A striking example is waste oil heating furnaces. They can use any oil that can burn. Transmission, diesel, machine, confectionery, vegetable... Really any. There are no problems with fuel for such units. What they found, they filled it in. Moreover, a do-it-yourself furnace for mining is also made from waste materials: an old gas or oxygen cylinder, sections of pipes of different diameters or pieces of metal.
What is mining and how to use it
Essentially, it is used motor oil, lubricating the engine and chassis. During the operation of equipment, oil, an initially fairly pure petroleum product, becomes saturated with slag - metal particles (the result of friction and mechanical damage to parts), soot, salts, and resinous compounds. As a result of such saturation, the oil is no longer suitable for lubrication, but it burns well - which allows the product to be used as fuel.
The composition of the waste burns approximately 85%, and during the combustion process it produces about 11 kW/hour of thermal energy per liter. Thus, the product’s fuel qualities are comparable to diesel fuel.
Important: if the oil is heavily clogged with solids, it is advisable to filter it before use.
At the same time, an oil furnace using filtered exhaust will work longer and better; it will have to be cleaned less often to remove carbon deposits.
Tools and materials for creating a furnace
To work you need:
- Grinder along with a welding machine;
- Drill. Drill;
- Locksmith tools included;
- Devices for carrying out measurements.
At the end of the assembly process, you will need to check all seams for leaks. There should not be even a hint of defects.
One of the effective methods is soaping the seams with compressed air supplied to the inside.
Where to use a homemade furnace for mining
Since during the combustion process engine oil, especially used one, does not emit the most pleasant odor, and from a health point of view it is not very useful, it is better not to use stoves of this kind in residential premises. If there is no other way out, high-quality removal of combustion products is mandatory.
Typically, stoves are installed in non-residential premises - utility rooms, garages, sheds, workshops, and so on - where constant heating is not required, but only warming up the air for a relatively short time.
Due to the fact that even the simplest designs of such a “ garage potbelly stove ” make it possible to regulate the intensity of fuel combustion, it is possible to ensure either an economical mode of its use and gradual heating of the premises, or increased consumption with very fast heating of the air volume.
How to remake a brick device?
There are two ways to remake a brick oven :
- by making a burner that is similar in shape to a chopped log or thin log;
- make a door with a shield, which you then insert into the open door or mouth of the oven.
The first option is easier to manufacture, but much more difficult to operate, because lighting such a “log” is not easy. The second option is much more complicated , especially if you make a burner with variable flame power, but it is enough to insert it into the corresponding hole in the stove and seal it with an asbestos cord.
Therefore, we suggest using the second option, because it is not difficult to give the shield the desired shape, just cut the blank with a plasma cutter or any other suitable tool, and then trim it with a grinder.
To prevent the burner from falling out of the hole, you will have to weld the legs to it, which is also not difficult, because such a device cannot be made without welding.
The modification will be especially effective if you use a low-power burner with adjustable fuel supply; even in the most minimal mode, it ensures the correct proportions of fuel and air , due to which the formation of soot is minimal.
In addition, starting in low power mode gently heats the bricks, so the masonry does not collapse and the stove does not suffer damage.
General principles of operation of a furnace for a garage or summer cottage
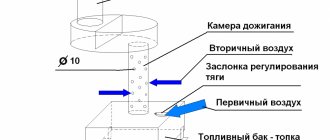
The essence of the process is simple: since the oil itself does not burn so much as it smokes, it must be heated to boiling point and the released vapors must be ignited. Accordingly, you need a container for heating the oil, air supply points and an afterburner chamber. And, of course, the chimney.
The diagram below shows the principle of the simplest stove with a square fuel tank.
So:
- approximately ½…2/3 of the volume is filled with waste into the fuel tank, also known as the firebox. This is no longer possible - either during the boiling process the oil will splash out, or simply not enough flammable vapors are formed;
- after the fuel has settled a little in the tank and gives off a certain amount of evaporation, the contents are set on fire. This is done with the help of a “torch” - a burning splinter, a rag (preferably also oiled), paper. Next, the filling hole is closed and not opened again until the fuel burns out;
- when heated, the oil begins to produce more and more vapors; they rise to the afterburning zone, mixing along the way with secondary air. Since the heated vapors are much higher in temperature than the air surrounding the pipe, oxygen is drawn into the holes very actively, contributing to an increase in the combustion temperature. The draft can be adjusted using dampers, thereby increasing or decreasing the intensity of vapor combustion;
- heating of the surrounding room occurs due to heat exchange between the hot combustion chamber, pipes, afterburning chamber and air. To ensure that the device releases heat longer, a damper is placed between the afterburning chamber and the chimney, reducing the rate of removal of heated and burning vapors.
To ensure uniformity of the process, the afterburning chamber and the firebox are made of approximately the same size (volume).
If the stove is made correctly, the flame has a white-blue color. Accordingly, the combustion temperature is 1000 degrees Celsius and higher. If the flame has golden-orange, reddish tones, the combustion temperature is clearly insufficient - weak draft, low heating of the exhaust, design problems in general. With a blue-white flame, the soot formed during the combustion process partially burns out before reaching the chimney, which significantly reduces the necessary frequency of cleaning the smoke ducts.
Regardless of how correctly the structure is designed and executed, soot and soot will certainly form in it, and non-combustible sediment will accumulate at the bottom of the fuel container. Therefore, it is necessary to make the oven as collapsible as possible - this will make cleaning it much easier.
Features of the chimney device
The length of the chimney in these stoves is assumed to be at least 4 m. This is necessary both to create proper draft and to ensure high-quality removal of combustion waste. It is also important to provide high-quality ventilation in a heated room, since some of the combustion products somehow end up not in the chimney, but inside the room.
The diameter of the chimney is assumed to be at least 100 mm, and the presence of elbows, turns, and complex shapes is extremely undesirable - cleaning the chimney is necessary much more often than with conventional stoves, since the fuel produces a large amount of soot.
The best option for installing a potbelly stove is strictly under the hole in the roof through which the chimney will be led out. In this case, the vertical position of the chimney will ensure stable draft and easy cleaning. The outer part of the pipe must be insulated. If this is not done, condensation mixed with unburnt soot will settle on the inner walls, quickly narrowing the passage for smoke.
Cautions regarding oven installation
There are certain rules that must be followed to avoid fire. Among them the following are noted:
- It is not permissible to install a heating structure in a place where there is a constant draft.
- It is important to protect the oil stove from foreign objects falling on it. The same applies to the presence of flammable elements, as well as working with them near such a device.
- The stove must be installed so that there is at least half a meter of free space around it.
How to make a working furnace: basic principles
Regardless of what type of furnace - supercharged, drip type, with an expansion tank, additional combustion of gases, a water circuit - is chosen for execution, there are general principles for its manufacture.
- High combustion temperatures require large thickness of the walls of the structure. For the upper chamber you need a steel sheet of at least 6 mm, for other parts 4 mm is enough. Instead of sheet steel, you can use barrels, cylinders and other used products of a suitable configuration.
- As mentioned above, the structure must be collapsible. Consequently, permanent connections are unacceptable; bolts, clamps, etc. are required.
- The product is quite compact and light, usually weighing less than 30 kg (without fuel). To prevent the stove from tipping over, it must be secured to the floor.
- As a result of strong heating, the floor may be damaged; it is advisable to make the stove on legs. The height of the legs depends on the floor material - the more flammable it is and the worse it perceives heat, the higher the chamber with burning fuel should be. In this case, the legs should be made of adjustable height and be sure to check the correct position of the stove when installing it with a level - the fuel tank is positioned strictly horizontally.
- The dimensions of the furnace are taken for reasons of ease of installation and sufficient heat transfer (more on this later). Typically, the dimensions fit into a parallelepiped 75x50x35 cm. The height of the chambers (fuel and afterburning) is about 10...15 cm, their width is 30...40 cm. The average volume is 10...30 liters.
- The pipe connecting the chambers is made perforated. The ratio of its diameter to length is 1:4 (approximately), the hole size is 10...16 mm, the total area of the holes is 10% of the total surface area of the pipe.
Below is a drawing of the simplest design of a mining furnace.
The legs are not shown in the drawing; they are manufactured locally. The chimney is also not shown.
This is what the finished structure looks like during operation.
The video shows an example of a working furnace with a retractable compartment for filling fuel.
Pros and cons of using used oil
Recycling furnaces adopt the principle of direct heating of air, and as a result of this use of waste oil, garages, greenhouses, and workshops can be heated.
It is best to use such stoves at car services, because there is no need to look for fuel. It is already at hand in large quantities. Advantages of using used oil:
- There is no burning or soot when oil burns
- ease of operation
- fire safety (used oil itself does not burn, only its vapors burn)
Disadvantages of using used oil:
- used unrefined oil from technical services is not suitable for boilers because it , etc. The use of such unrefined oil will lead to clogging of the filter, injectors, and even may explode in the fuel heating unit. Therefore, used oil needs to be cleaned and filtered, which is impossible to do at home. Prepared, purified waste oil costs approximately 12 rubles per liter (diesel fuel costs from 28.4 rubles per liter).
- any car service center and state-owned motor transport enterprise are required to enter into contracts with companies involved in the disposal of used oil. That is, they pay money to get rid of it, then, accordingly, they will not just give out used oil left and right.
- Used oil should not be kept in the cold. It will freeze outside, so it is necessary to either store the oil in a heated room or bury the barrel to the freezing depth of the ground.
Example of calculating furnace dimensions
As mentioned above, fuel consumption is about 1...2 liters per hour. At the same time, the radiated heat is about 11 kW/hour per liter. Thus, the furnace can produce 11...22 kW per hour. To calculate the required volume of the firebox taking into account the burning time, we accept:
- volume of the room (garage) – 7x4x2.5=70 cubic meters, area 28 sq.m.;
- We believe that for every square meter of a garage-type room, at least 500 W are required (basic 100 W, we enter coefficients for all external walls, non-insulated roof and foundation, large entrance opening, metal structure);
- Accordingly, an area of 28 squares requires 14 kW of energy per hour.
By slightly increasing the minimum power of the stove (increasing the draft), we will obtain the required temperature in the room. But fuel consumption will increase to approximately 1.5...1.6 liters per hour. Therefore, for a burning time of at least 6 hours, the volume of the firebox should be 10 liters. This corresponds to 0.001 cubic meters, that is, the container should have a size, for example, 10x10x10 cm. In reality, the volume of the firebox exceeds the required volume of fuel by 1.5...2 times, that is, the dimensions should be 20x10x10 cm or more, this is suitable for a mini stove. Usually they take it with a substantial reserve, that is, 50x30x15 cm. This allows you not to add fuel every time you ignite.
Important: with large firebox sizes, it becomes necessary to extinguish the fire in the furnace during exhaust before the fuel burns out completely. The extinguishing process is shown in the video.
The length of the pipe is 40 cm, respectively, its diameter is 10 cm. The area of the lateral surface of the cylinder is equal to its height multiplied by the circumference of the base (diameter multiplied by the number π), in our case 40x3.14x10 = 1256 cm2. Accordingly, the area of all holes is one tenth of the total - 125.6 cm2. Considering that the area of one hole with a diameter of 10 mm is equal to πx0.52=3.14x0.25=0.78 sq.cm, such a pipe will require 125.6/0.78=160 holes.
Note! The accepted value is the area of the holes 10% of the total area of the side surface of the pipe - conditionally! The number of holes during manufacturing is taken, among other things, from the strength of the product and is usually noticeably less!
Considering that the unfolded cylinder is a 31x40 cm rectangle, and the holes should be placed in a checkerboard pattern, we will have to make 12 vertical rows of 13 or 14 holes each. Marking vertical rows is simple - divide the upper or lower circumference of the base of the pipe into 12 parts in any geometric way and draw vertical drilling lines.
The distance between the rows will be 3.3 cm. Marking the vertical rows is a little more difficult, since in every second row it is necessary to shift the upper (or lower) marking point by half the distance between the holes. Considering that we need to make holes not on the edge of the pipe, we add 1 to the planned number of holes and calculate the step: for 13 holes it will be 40/(13+1)=2.85 cm, for 14 – 40/(14+1) =2.6 cm.
Important: when drilling, the axis of the drill must be directed towards the axis of the pipe!
Making a drip heater
Most often, craftsmen use old oxygen and propane cylinders with a diameter of 220 and 300 mm, respectively, to assemble droppers. The former are preferable because of their powerful thick walls that can last a long time and not burn out. A pipe made of low-carbon steel (St 3-10) with a wall thickness of 5 mm or more is also suitable.
Advice. The ideal option for a durable housing is a pipe made of heat-resistant stainless steel alloyed with chromium, molybdenum or nickel (for example, 15X1MF or 12X18H12T) with a wall no more than 3 mm. Perhaps you or a neighbor has one in your garage. There is no need to buy it specially - it will be too expensive.
Select rolled metal for other parts according to the drawing of the furnace with top feed of waste into the combustion zone. The blower fan is a “snail” from a VAZ 2108 cabin heater or its Chinese equivalent, the fuel line is a stainless tube with a diameter of 8-10 mm.
The manufacturing technology is as follows:
- Make a fire bowl from a piece of pipe or take a ready-made steel container. It must be removed through the inspection hatch, so do not make the tray too large.
- Cut openings in the body for the chimney pipe and cleanout hatch. In the latter, make a frame and install the door (possibly bolted).
- Make an afterburner. Take your time to drill all the holes indicated on the drawing; do the bottom 2 rows first. You will complete the rest while setting up the oven.
- Weld a cover and an air duct with a flange for mounting the fan to the afterburner. Attach the fuel supply device as shown in the photo.
- Assemble the heating unit and connect it to the chimney.
Advice. For greater stability to the body, it would not hurt to weld a frame from a steel profile or angle according to the example shown in the photo.
The afterburner in the photo is a close-up - side and end views
. To regulate the heating power, you need to provide a fan speed control and a device for dosing the fuel supply (as a rule, an auto-drinker with a jet break is used). According to reviews from craftsmen on a popular forum where heat extraction issues are discussed, fuel consumption in the furnace can be monitored visually. The trend is this: if the oil flows in drops at the break in the stream, then less than 1 liter per hour burns, and when a thin stream flows, more than 1 liter per hour.
Recommendation. Control the fan performance using a cheap Chinese PWM controller (price is about 8 USD).
Different designs of drip bowls
After igniting and warming up the heater, it is necessary to set the optimal operating mode. The procedure is carried out according to the same scheme as with the miracle stove: you need to achieve the most transparent smoke from the chimney by drilling additional holes in the afterburner. The ideal flame color is blue, normal is yellow, and reddish is unsatisfactory. In the latter case, low heat transfer, high consumption and soot formation are observed. For details about the design and assembly of the furnace, see the video:
Instructions for making a furnace for testing with a drawing
Let's take the drawing below as a basis.
Required:
- sheet steel 4 mm and 6 mm (sheet sizes depend on the selected dimensions of the furnace, check according to the drawing), steel pipe with a diameter of 100 mm and a length of 400 mm;
- grinder with a disc for cutting metal;
- welding machine;
- metal drills and drill;
- a sheet bending machine or other device that allows you to bend a sheet into a cylinder;
- studs or bolts with a thread of at least M12, corresponding nuts and washers.
Sequencing:
- Reveal the details. We cut out the elements according to the dimensions shown in the drawing. For rings, strips are used, the width of which is equal to the height of the ring, the length is equal to the circumference with a margin for welding. For example, for a ring with a diameter of 352 mm and a height of 60 mm, a strip of 60x1105 mm will be required. Welding margin is 1…1.5 cm, butt welding is possible.
- Holes of the appropriate size and shape are cut in the finished parts. We take into account the tolerances of the parts - it is better to try on the size of the hole “in situ”. Holes in the pipe are drilled based on the planned combustion intensity and strength conditions: the more holes, the stronger the draft, but the less strong the pipe. Usually holes are drilled in increments of 7…10 cm.
- We first assemble two blocks - the fuel chamber and the afterburner, then fasten them to the pipe. At the same time, to maintain the possibility of disassembly, we do not use welding, we only tightly insert the parts into one another! You can sand or trim the edges a little to make it fit.
- Lastly, the legs are welded and the valves and lids are secured in place - always with bolted connections so that there is access to the containers for cleaning. It is also advisable to weld spacers between the fuel tank and the afterburner chamber. For spacers, you can use reinforcement or any suitable rod.
- The chimney is installed and secured to the structure with bolted or stud connections.
Below is another version of the diagram and drawings of the furnace for do-it-yourself testing. Cylindrical compartments are also used here, but the axes of the cylinders are turned parallel to the ground.
This video shows the assembly of such a stove and the process of its operation.
What is special about a mini oven?
The design of a waste oil heater has a certain specificity:
- The peculiar shape of the lower funnel for the heat-air mass allows the latter to mix well while passing through this section of the furnace.
- The upper funnel plays the role of an afterburning chamber, so it is not separated from the combustion chamber. In order for the gases to linger long enough for final combustion before exiting into the chimney pipe, this structural element is made narrower.
- The individual components of the garage stove are connected with clamps, so the device can be quickly disassembled if necessary. Since the total weight of the structure usually does not exceed 10 kg, when disassembled it can be easily transported in the trunk of a car.
Types of furnaces for mining
It has already been said above that the simplest potbelly stove is not very convenient or effective. Therefore, various modification options have appeared, which we will consider below.
Exhaust stove from an old gas cylinder
Here you will also need 4 mm sheet metal (about 50 sq. cm), but another basic element is more important - a waste gas cylinder with a capacity of 50 liters, better than the old Soviet model, propane. Oxygen is heavier and more massive, making it difficult to work with. In addition, you need:
- steel pipe with a diameter of 100 m, a length of 2000 mm;
- valve with ½ inch thread;
- steel corner with shelf 50 mm, meter or a little more;
- clamps;
- loops;
- a piece of fuel supply hose;
- car brake disc. We select the diameter so that it fits freely into the cylinder;
- another cylinder (freon) to create a fuel tank.
Sequence of work:
- we drain the remaining gas from the cylinder, drill a hole in the bottom and rinse the cylinder with water;
- We cut out two openings in the side wall - a large lower one and a smaller upper one. The fuel chamber will be located in the lower one, and the afterburning chamber in the upper one. By the way, if the dimensions of the lower opening allow, in addition to mining, it will be possible to use firewood as fuel;
- We make the bottom of the afterburning chamber from a steel sheet;
- We make a burner from a pipe - a place where volatile gases mix with air and ignite. Holes are drilled in the burner (according to the principle described above), the inside of the pipe is GRINDED, this is necessary for greater efficiency of the product;
- the finished burner is welded into the bottom of the afterburner chamber;
- We make a waste tray from a brake disc and a piece of steel sheet. We weld the lid in its upper part;
- It is better to use a coupling to connect the burner and the pan cover - this makes servicing the stove easier;
- We provide a fuel supply. To do this, a hole is made in the wall of the cylinder into which a pipe with a threaded edge is welded;
- A valve is placed at the outer end of the pipe and a hose is connected to it. The hose, in turn, is connected to the fuel cylinder;
- the chimney pipe is welded into the upper part of the cylinder, then “taken away” in a smooth upward transition until leaving the room.
In fact, this completes the work with the furnace itself, but it is better to additionally build a heat exchanger - this will increase efficiency.
One of the heat exchanger options - plates welded onto the body - is shown in the photo below.
The finished oven with the doors open (the hinges were needed specifically for them; the pieces of the cylinder cut out in step 2 are attached to the hinges).
Pressurized furnace in operation
This design is also assembled on the basis of a 50-liter cylinder.
The air supply here comes from a fan (for example, from the stove of a VAZ 2108 car), which allows you to increase the draft in the afterburner and at the same time actually make the entire surface of the cylinder a heat exchanger.
The operation process and ignition are shown in the video.
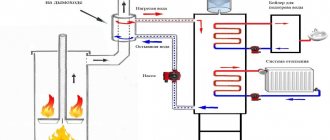
Exhaust furnace with water circuit
Manufacturing a furnace with a water circuit can be almost the same as in the simplest version. The main difference is the organization of heat extraction into the water coolant. In the photo below, this possibility is realized by winding a pipe around the furnace body. In this case, cold water is naturally supplied from below, and heated water comes out from above.
A more “advanced” option is a stove with a “water jacket”. In fact, the body is enclosed in a second, hollow one, inside of which water circulates. The heated liquid is supplied to heating radiators.
True, the phrase “does not smoke” from the manufacturer is a bit of an exaggeration - this is only possible with regular cleaning of the chimney and the use of sufficiently high-quality, filtered fuel.
In the drawing, the device looks something like this.
Drip furnace
This type of stove is safer than those designs into which fuel is poured at once. In addition, in the case of gradual feeding, the burning duration can be freely adjusted.
A mandatory element of the system is a separate fuel tank, the waste from which is supplied in small portions - almost drops - using a special device.
The photo below shows a design where there is a separate tank with an oil line located above the fuel chamber. The base of the furnace is a gas cylinder; a valve is used to regulate the flow rate of the waste. The design of the furnace is discussed in more detail above.
Another type of product is with a retractable fuel compartment and a double afterburner.
It is realized in metal.
Please note: due to supercharging and the absence of fuel losses during filling, the exhaust consumption is reduced by 20...30%.
Advantages and disadvantages
The main and main advantage is that spent fuel and oils are used, which would otherwise be disposed of. If the technology is followed, combustion is so complete that virtually no harmful emissions occur into the atmosphere. Other advantages are no less significant:
- simple design;
- high efficiency;
- low cost of equipment and fuel;
- works on any oils, organic, synthetic, vegetable origin;
- Content of up to 10% of pollutants is allowed.
There are also serious disadvantages. And the main thing is that if the technology is not followed, fuel combustion occurs incompletely. And its vapors enter the room, and this is very dangerous. Therefore, the main and main requirement: furnaces operating on waste oil are installed exclusively in rooms with a ventilation system.
For comparison: this is a waste oil boiler with an inflatable burner. The technology is different, as is the design (more details in the video almost at the end of the article)
There are also disadvantages:
- to ensure good draft, the chimney must be straight and high - at least 5 meters;
- Regular cleaning of the bowl and chimney is required - daily;
- problematic ignition: you must first heat the bowl, then supply fuel;
- water heating options are possible, but their independent design is a difficult task - you cannot significantly lower the temperature in the combustion zone, otherwise the whole process will fall apart (an alternative is to install a water jacket on the chimney, in which case it certainly will not prevent the breakdown of the fuel).
Due to these features, such units are rarely used for heating residential buildings. If they are installed, it is in separate rooms and in a modified form.
Principle of operation
The operation of the furnace is based on the combustion of motor oil vapor in a closed container. The product is not just the cheapest, but a waste product. Most often, used oil and its disposal are a headache for service stations and garage owners. After all, it is strictly forbidden to pour waste into the ground or domestic sewage system. And here “harmful” oil is poured into the stove and serves to benefit humans.
The design of the most common modification, made of metal, consists of cylindrical tanks, lower and upper, a short transition compartment and a chimney. It’s hard to imagine anything simpler. First, the fuel is heated in the first tank: the oil boils, begins to evaporate, and the gaseous product passes into the next compartment (short pipe). Here, oil vapors mix with oxygen, ignite intensely and completely burn in the last, upper reservoir. And from there the exhaust gases are released into the atmosphere through the chimney.
If desired, the heater is equipped with a tray for adding oil. Little is required from the owner: fill the tank with waste, set it on fire and monitor the normal operation of the firebox.
Where can I get drawings, diagrams and ideas?
Before starting to develop a stove project, we recommend that you familiarize yourself with forums where users discuss the manufacture and operation of such heating devices.
There you will find answers to many questions and various technical solutions that will help you make your stove more efficient and safe.
Here are links to such forums:
- www.forumhouse.ru.
- termoportal.ru.
- mastergrad.com.
- forum.auto.ru.
- forum.homedistiller.ru.
- www.chipmaker.ru.
- forums.drom.ru.
- www.bylkov.ru.
- forum.stovemaster.ru.
- chiptuner.ru.
- forum.homedistiller.ru.
- forum.ulmoto.ru.
Types of homemade models
You can independently make from metal only different types of potbelly stoves, which differ in efficiency, but work on the same principle - while the fuel burns, the device releases thermal energy.
Therefore, the differences concern only:
- method of fuel combustion (burner);
- the material from which the heating device is made;
- a method of transferring heat from a flame to the air in a room.
The choice of burner is determined by the availability of materials and your skills, so evaporators are better suited for primitive potbelly stoves.
After all, their production does not require serious effort, but for air heaters, various nozzle options are better suited.
The heater is much more difficult to manufacture, but its efficiency is 1.5–2 times higher due to more intense air movement through special channels. Therefore, further we will talk about various options for manufacturing such furnaces using different types of burners and heat exchanger designs.