According to the generally accepted formulation, pressure testing of a hot or cold water supply system is the process of testing equipment, pipes and fittings in a certain area of the system by applying increased pressure to it. It can be 2-3 times higher than usual, which makes it possible to ensure that the engineering complex is in good working order. Due to the fact that this type of work is associated with a certain danger of ruptures, it must be carried out with the involvement of experienced specialists who know how to handle specialized tools and who know SNiP (building codes and regulations).
Features and limitations of pneumatic crimping
Pneumatic testing of pipes by air pressure testing poses a certain danger, which is associated with a significant amount of energy accumulated in the compressed gas. A pipe rupture can result in an explosive release of this energy. For this reason, during pneumatic testing, the test pressure is usually taken only 10% higher than the calculated pressure in the pipeline.
For the safety of pneumatic crimping, the following two preconditions are necessary:
- Adequately sized unloading device;
- Intermediate maintenance of test pressure values within 150...180 kPa, with visual inspection of all connections.
Only then is the compression gradually brought to standard values.
Pneumatic pressure testing is performed instead of hydraulic pressure testing in the winter, when there is a danger of water or oil freezing. Its use is limited by the increased operating costs of operating pump-compressor units.
Basic norms and rules for carrying out gas hazardous work
Pneumatic pressure testing of the gas pipeline is carried out in accordance with the regulations, which are provided for in GOST R 54983 2012.
Control pressure testing with air in the connected section of the pipe must be carried out before it is inserted into the existing gas pipeline.
Rules for carrying out gas hazardous work
A control check of the cut-in section of the pipe is usually carried out by generating an excess air pressure of 100 kPa and holding it for 60 minutes. To control the pressure indicator, a pressure gauge with an accuracy class not exceeding 0.6 must be used.
The indicator of the created excess pressure in the pipeline must remain unchanged until the end of the pressure testing procedure and remain until it is connected to the existing distribution communication.
After work on inserting a section of pipe has been carried out and a certificate of commissioning of the facility has been issued, after six months a repeated leak test must be carried out, in accordance with the requirements of the set of rules SP 62.13330.2011.
Hydraulic testing services
If the heating system is installed by a contractor during the construction of a new home, then the responsibility for pressure testing of pipelines lies entirely with the contractor.
In the case when the heating system is already functioning, regardless of whether it is a residential building, a municipal institution, a shopping or office complex, pressure testing is carried out by an organization that services all systems of the building. In housing construction, the law provides for the responsibility of the management company to maintain heating systems in working order, and, consequently, to carry out measures to prepare for the heating season.
For administrative and other complexes, testing of systems is carried out either by the operating organization or by a contractor who has all the necessary permits to carry out a complex of work.
Tools and devices for balancing
To independently adjust the heating radiators and heated floors of a private house, you will need a minimum of equipment:
- electronic contact thermometer;
- screwdriver;
- a thumb or wrench for rotating the balancing valve stem (a hexagon is usually used);
- sheet of paper, pencil.
To measure temperature, it is better to use a contact-type electronic device.
Instead of the indicated thermometer, it is allowed to use a remote (non-contact) pyrometer. Please note: the device measures the temperature of shiny surfaces with a small error. This note applies to radiators with new paintwork.
If you do not have a wiring diagram for a residential building, you should sketch it on paper before starting work. The sketch will help you understand the order in which the batteries are connected to the mains and the distance from the furnace room. Also, flush the mud trap at the entrance to the boiler and heat the system to a temperature of 70-80 ° C, regardless of the street weather.
Call specialists or do it yourself
If for some purpose you require a pressure test certificate for your heating or hot water supply system, you have only one option - order this service from a specialized organization. The cost of heating pressure testing can only be quoted to you individually. It depends on the volume of the system, its structure, the presence of shut-off valves and their condition. In general, the cost is calculated based on the tariff for 1 hour of work, and it ranges from 1000 rubles/hour to 2500 rubles/hour. You will have to call different organizations and inquire with them.
Companies involved in hydraulic system testing have more serious equipment.
If you have upgraded the heating or hot water supply of your own home, and you know for sure that your pipes and equipment are in good condition, there are no salts or deposits in them, you can carry out pressure testing yourself. No one will demand hydraulic test certificates from you. Even if you see that your pipes and radiators are clogged, you can wash everything yourself and then test it again. If you just don’t want to do this, you can call specialists. They will immediately clean the system and pressure test it, and will also issue you a certificate.
Certificate of hydrostatic testing of the system (pressure testing)
Price
- length (internal volume) of the system;
- the age of the system and the condition of its constituent elements (amount of rust and dirt and salt deposits);
- type of equipment used.
Prices from different performers, even within the same city, may differ by 2–3 times. Private teams and craftsmen charge the cheapest for their services.
On average, for flushing and pressure testing the heating system of a building with an area of 400 sq. m (two-story) performers charge from 7 to 15 thousand rubles. As practice has shown, if you know how to bargain, you can agree to complete this amount of work for 4–5 thousand rubles. The work will be completed in 1 – 2 days.
The same work in a building of 5 thousand square meters. m (5 floors) will cost from 30 to 80 thousand rubles.
Some performers indicate prices per unit of volume (150 - 250 rubles / cubic meter) or time (500 - 1000 rubles / hour).
If you want to install the washbasin yourself, be sure to take care of connecting the water seal. Water seal for sewerage: types, purpose and installation features.
You will learn about the types of antiseptics for cesspools in this review.
Which method should I choose?
Many people have a question: which testing option is best for warm water floors? The air method is more convenient, since it is not always possible to put the system into operation in time when cold weather sets in, so there is a danger of freezing the entire pipeline.
With air pressure testing such problems will not arise. This is important for heating floors, since the coolant can be easily drained from the radiators, but this is quite difficult to do from floor circuits.
But with the air method, it is visually difficult to determine a leaky connection or a section of pipe through which air will escape. There will be no such problems with water, and you will immediately determine the right place.
In addition, when choosing a method for testing a heating system, you should take into account the type of pipes from which the water heating is made.
How to pressurize a heating system in apartment buildings
In such buildings, tests are carried out by special service workers using the necessary equipment, after which a pressure test report of the proper form is drawn up.
Before starting hydraulic tests, the following preparatory work is performed:
- first, the condition of the supply unit, risers, main pipes and other elements of the heating system is visually inspected;
- The presence and integrity of thermal insulation on heating mains is checked.
Before pressure testing, be sure to flush the heating system if it has been in use for more than 5 years. To do this, it is necessary to drain the coolant that may be in it and rinse it with a special solution. Only after this they begin hydraulic tests, which are carried out as follows:
- the heating system should be filled with water;
- using a manual or electric pump, create excess pressure in it;
- using a pressure gauge, they determine whether the pressure is maintained or not, and this should last about 15–30 minutes;
- if the pressure does not drop during this time, it means that everything is in order with the sealing, there are no leaks and all elements can withstand pressure well;
- if the pressure suddenly drops, then it is necessary to check all elements (radiators, pipes, additional equipment, connections) for water leaks;
- As soon as the location of the leak is determined, it is sealed or the elements are replaced (pipe section, shut-off valves, connecting fitting, radiators, etc.) and the hydraulic tests are repeated.
In what cases is pressure testing necessary?
- When commissioning water supply and heating systems . Steel pipes are connected by threads and welding, metal-plastic and polyethylene pipes are connected by fittings, polypropylene pipes are connected by low-temperature soldering. Any connection is a potential leak point. To identify all problem areas, a hydraulic pressure is created in the engineering system being tested that exceeds the maximum operating pressure for this system. The logic is simple: if the pipes withstood a pressure of 16 atmospheres for several hours, it means they can withstand a pressure of 8 atmospheres for a long time.
Carrying out the procedure at the preliminary stage
Video: hydraulic testing of water supply and heating
Building codes govern the order in which inspections are carried out.
- First, the water supply is filled with liquid. And leave it in this state for two hours.
- They proceed to create increased pressure for two hours. It happens very slowly. At this stage, it is already possible to identify a number of leaks.
- The pressure is reduced until they reach the calculated values. Then they move on to examining the general condition of the route.
- This pressure is maintained for thirty minutes or more. Without such a step, the deformed shape of the pipes simply cannot be stabilized.
- The next stage is turning off the taps at the entrances. The water is slowly drained using a pressure test pump.
- The route is checked for serious problems, as well as the density and strength of all sections.
SNiP
Data on the procedure for performing pressure testing of pipelines, technological diagrams of this process and safety precautions are contained in the relevant sections of the following SNiPs:
- SNiP 3.05.01-85 (dedicated to internal sanitary systems).
- SNiP 41-01-2003 (outlines the issues of organizing heating, air conditioning and ventilation systems).
- SNiP 3.05.04-85 (applies to external drainage systems).
The method of pressure testing of pipelines of industrial enterprises is specified in industry standards.
Among other things, these documents establish the value of the test pressure. It depends on the material of the pipeline, the thickness of its walls (the minimum value is taken), the difference in height between the uppermost and lower elements of the system and other factors. Most often, the pressure during hydropneumatic tests is developed to the following values:
- in pressure pipelines (water supply): 10 – 15 atm.;
- cast iron sewerage: 1.5 atm.;
- non-pressure polymer pipes: 1.5 – 2 atm.;
- heating systems in apartment buildings (with cast iron radiators): 2 – 5 atm. (according to SNiP - at least 1.5 working pressure);
- input node (in centralized systems): 10 atm.;
When pressure testing a heating system in private homes, a pressure of up to 2 atm is sufficient. (there is no point in pumping higher: the emergency valve is usually set to this level).
SNiP and safety requirements
For safety and operational reasons, it is recommended:
- Do not perform long-term pressure testing on pipes made of PVC.
- Perform testing on a line that is previously disconnected from other sections of the pipeline.
- Monitor leaks only with proven instruments and equipment.
- Do not involve organizations and persons in pressure testing that do not have certificates to perform such procedures.
A short video about how to carry out pressure testing of heating and water supply
Views: 1,105
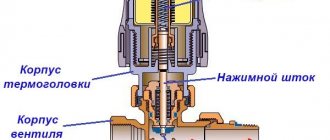
Tools used for crimping
The strength and density of water heating are tested using a pumping device. This device is made in the form of a pump, which is connected to the system pipe using a high-pressure hose and a check valve. When choosing a device, consider the following parameters:
- Performance.
- Pressure.
- Voltage to which electric type models can be connected.
To perform small-scale work, you can use a manual heating system pressure tester, which is equipped with a hydraulic cylinder.
Private cottages are equipped with systems with a working pressure of 2 atmospheres, so the pressure of the water supply network is sufficient for pressure testing. The circuit is filled with water from the tap of the water supply system and the readings of the installed pressure gauges are monitored.
Mechanisms for carrying out
Crimping operators, i.e. Special pumps for carrying out relevant tests differ in design. Based on this feature, they are classified into three types:
- Porshnev.
- Vane-rotor.
- Membrane.
If testing of a pipeline (or other object) of a relatively small volume is required (for example, in private housing construction), then it can be performed using an inexpensive and easy-to-maintain manual pressure tester. This mechanism allows you to pump up to three liters of working fluid into the system in a minute.
To check the systems of a multi-story building, you will need a more powerful mechanism driven by an internal combustion engine or electric. The domestic UGO-30 is equipped with a 16-liter tank and allows you to develop a pressure of up to 30 atm. Manual two-stage pumps UGO-50 and UGO-450 are used when performing more complex tasks.
In domestic conditions, compact devices are used that can be manually controlled.
German-assembled electrically driven crimpers produced by Rothenberger (model ROTEST GW 150/4, for example, designed for testing drinking water and gas supply systems with air) and Ridgid (for example, model 1460-E 19021 are used in systems filled with as a working fluid water, oil or ethylene glycol).
How to correctly draw up a pressure test report for a heating system
To draw up an act according to all the rules, it is important to indicate in it the following:
- Test method used.
- The project according to which the installation and installation of the test object was carried out.
- Date and address of testing events.
- List of persons whose signature must be on the document. In most cases, the property owners and representatives of service organizations are indicated.
- Methods for eliminating identified defects.
- Test results.
- Presence of signs of depressurization of the system or violation of threaded connections and welds. It should also be noted that there is condensation on the surface of pipes and fittings.
Work execution algorithm
Inspection and control pressure testing with air or inert gas are mandatory measures for all gas pipelines.
The procedure for performing work on pneumatic testing of the pipeline.
The section of the gas pipeline subject to testing and inspection is disconnected:
Pneumatic pipeline testing
- the high pressure valve is closed;
- the valve of the low pressure pipeline is tightened;
- appropriate plugs are installed.
To avoid possible rupture of the flange connection, shunt jumpers are installed.
The gas is released through a rubberized hose or a candle, which can be installed on the riser of the condensate collector, to a place where, if possible, it can be safely disposed of at a distance of no closer than 10 meters from the point of release of the gas mixture.
After purging the pipe, devices are installed to fix the pressure gauge and compressor station. If the pipe section is small, a hand pump is used. The gas pipeline is checked for leaks. The required air pressure is ensured using a purge pipe.
Pipe crimping
There are 2 different methods of heating heating: water and air. Using the first option, all thermal systems are most often tested. To do this, liquid under pressure is pumped into a special tap, with which you can quickly detect breakouts and leaks.
The air method is a less effective method for checking pipes, but its main advantage is that during frosts water cannot be used, as it may freeze. To find leaks, soapy water is used to lubricate suspicious areas. The main search method is to determine a breakthrough by ear. The pressure in the system is built up using a compressor through a valve into which water must be supplied.
For multi-story buildings, there are certain testing rules that indicate the minimum pressure for the test. In water heating, panel and convector systems it should be 10 atmospheres, and in a circuit with steel or cast iron pipes - 6 bar.
Equipment and test frequency
Pressure testing of centralized systems is carried out by personnel using standard equipment, so it is hardly worth talking about. But not everyone probably knows about the costs of private heating and water supply. These are special pumps. There are two types - manual and electric (automatic). Manual pressure testing pumps are autonomous, the pressure is pumped up using a lever, and the created pressure is controlled using a pressure gauge built into the device. Such pumps can be used for small systems - pumping is quite difficult.
Manual crimping machine
Electric pumps for pressure testing are more complex and expensive equipment. They usually have the ability to create a certain pressure. It is set by the operator, and it is “caught up” automatically. Such equipment is purchased by companies engaged in professional crimping.
According to SNiP, hydraulic testing of heating systems must be carried out annually, before the start of the heating season. This applies to private houses too, but few people comply with this standard. At best, they check it once every 5-7 years. If you are not going to test your heating annually, then there is no point in buying a pressure tester. The cheapest manual one costs about $150, and a good one costs from $250. In principle, you can rent it (usually from companies that sell components for heating systems or from offices that rent equipment). The amount will be small - you need the device for several hours. So this is a good solution.
Basic pressure testing methods
Today there are many methods for testing overpressure and flushing a heating system. To carry out the work correctly, there is a special document - SNiP, which indicates how to flush pipes in a specific room. This regulatory document defines technological schemes, as well as instructions for observing safety precautions. There are two universal test methods:
- Pressure testing with air or water;
- Chemical washing.
The hydropneumatic method of washing (air or water) has been tested for years. According to SNiP, to flush the pipeline and radiators with water it is necessary:
- Fill the system with water;
- Attach press;
- Check the device indicators.
As a result, under the influence of strong pressure, scale is peeled off, and when drained, it is removed from the system. The air flushing procedure is quite simple. It is carried out mainly in the winter season, in order to avoid freezing of communications. First, the compressor is connected and air is pumped in. Next, pressure indicators are monitored using a pressure gauge. The pressure during air pressure testing must correspond to the maximum limit at which the operation of this system is possible in accordance with SNiP. If the pressure remains at the same level for several hours and does not drop, then the system is sealed and there are no defects or leaks.
Pressure testing of the heating system
When performing air pressure testing, all connections must be lubricated with a soap solution to detect leaks.
Once the work has been checked, all air must be released. It should not remain in pipes and radiators, because air pockets reduce the level of heat transfer.
Next, the pipeline is filled with water or antifreeze, and a test run is carried out.
Chemical washing is carried out by pouring a special reagent into the system, which contains acid and alkali. After two hours of operation of the boiler, the liquid is drained and the pipes are filled with ordinary water. Heating flushing is carried out by utility workers or specially trained personnel from specialized companies.
How it's done
Shut-off valves for pipelines types classification
The general scheme of hydropneumatic tests is as follows:
- The part of the system being tested is isolated by shutting off the shut-off or control valves (the sewer pipes are closed with rubber plugs or wooden plugs wrapped in rags).
- Next, the system is completely filled with water. In the heating system, air is released through air vents installed at the very top.
- A pressure testing pump is connected to the pipeline, which pumps a certain amount of working fluid into the system, creating the pressure required by the test regulations.
- When the required pressure is reached, the pressure tester switches off. In this case, the observer records the readings on the pressure gauge.
- The system remains under pressure for a certain period of time. The exposure time can range from 0.5 hours (for heating systems) to 6 – 8 hours.
- After the appointed time has expired, the observer takes readings from the pressure gauge again. If the pressure differs from the original value, then there is a leak in the system that should be found and repaired. After this, crimping is performed again.
The following connection points are usually used:
- For heating systems: a special valve on one of the radiators, or a drain valve on the elevator unit (in centralized systems).
- For water supply systems: one of the connections to a cold or hot water tap.
- For the sewerage system: any of the revisions, usually installed in increments of 40 - 50 m.
If the heating system has been tested, the Hydropneumatic Test Report is signed by representatives of the heating network and the organization providing heat supply. Next, the inspector checks the coolant for hardness.
When is heating pressure tested?
Tests for “strength and density” in accordance with the Technical Operation Rules (RTE) of thermal power plants from the Russian Ministry of Energy (clause 9.2.12) are carried out in the following cases:
- In cottage-type houses, the system is tested after installation before putting it into operation; diagnostic work is carried out before sealing pipelines into grooves and pouring heated floors. It should be noted that it is possible to re-hydrotest the heating circuits after sealing all pipelines in the walls and screed - this will save expensive finishing materials when leaks are detected.
- Hydrotests are carried out annually at the end of the heating season; their purpose is preliminary preparation for operation of heating networks in the event of their unplanned connection to operation. Before the start of each heating season, a repeated hydraulic check of heating systems is carried out.
- After repairs, before starting up after a long period of inactivity with draining of the coolant, the system needs to be hydrotested for tightness and strength.
It is clear that in all of the above cases, pressure testing is a diagnostic tool that allows you to identify in advance problem areas and equipment that can lead to coolant leakage - which means repairs and lack of heating of the house in cold weather.
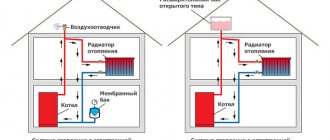
Rice. 3 Example of installation of heating systems with a water-heated floor circuit
Preparation for the procedure
Before testing, it is necessary to inspect the pipes for obvious defects and eliminate them. You will also need to remove the coolant from the heating systems.
Further actions are as follows:
- Flushing the line to eliminate scale, corrosive and organic growths.
- Assessment of the condition of the inner surface of pipes.
- Installation of a non-return valve and pressure gauge, if they are included with pressure equipment.
A non-return valve is required to keep the working fluid in the network.
When preparing for the procedure, it is also important to choose the right pump. Low-power pressure equipment will increase testing time, which can lead to distorted results.
The units are manual and electric. The appropriate one must be selected based on the volumes of the tested highways.
To pressurize the water supply system in a small private house or apartment, a blower pumping through itself a couple of liters per minute will be sufficient. Work on centralized water supply and heating mains involves the use of powerful circulation pumps. For air pressure testing, you can use a car compressor.
Pressure testing of pipelines with air and water
To test the performance of a heating, water supply or sewerage system, you will need a pump (special or one that circulates liquid in the system). It is connected to the heating system either:
- directly to the tap designed to drain the working fluid from the heating system;
- to any of the radiators. To do this, the Mayevsky tap is removed, and in its place an adapter is installed, to which the hose from the compressor is connected.
The water supply test is carried out through the connection pipe of the taps through which cold or hot water is supplied. To connect to the sewerage system, you will need to insert the sediment fitting into one of the revisions, special tees mounted in the outlet pipeline every 40-50 m.
Purchasing a crimping machine for personal use that will be used once a year is hardly advisable. Which pump to use to pump air or water into the system is determined based on the pressure that needs to be created for the test (and it should be 2-3 times higher than the working pressure). To pressurize the heating system of a private household, a car compressor or an electric pump should be sufficient.
The procedure for conducting an inspection in an apartment
Such a responsible process requires careful preparation. It consists of a preliminary inspection of all communications to identify leaks, loose connections, and rusted areas. All problems must be corrected. Next, the pipeline is flushed to remove insoluble contaminants from it: sand, rust, scale, etc. Sometimes a compressor is required for high-quality cleaning.
Direct pressure testing of the water supply network is carried out according to the following algorithm
- The pipeline in the apartment is cut off from the general main by closing the shut-off valves on the hot and cold risers.
- The connection pipe of the tap from which water is supplied is connected to equipment for pressurizing (pressure tester or circulation pump).
- The working environment used for testing is downloaded into the system. This must be done extremely smoothly and slowly, avoiding sudden jumps. All readings are monitored on a pressure gauge.
- Water or air remains in the pipes for a period of time approved by regulations. During this period, it is necessary to try to identify possible leaks.
- Before releasing the working medium, the pressure gauge readings are checked again. If there are no deviations or they are minimal, pressure testing of the water supply system in the apartment is considered complete.
If problems are identified during pressure testing, they must be corrected and then the above procedure must be repeated. The algorithm remains the same regardless of what liquid or gaseous medium is used to test the leaks.
Basic safety provisions when introducing gas into the system
Gas start-up process
The gas start-up process must be performed at low flow rates. The feed speed should be in the range of 15–25 m/s. This is necessary to prevent an explosion of the gas-air mixture from the possible formation of sparks when metal objects rub against the inner surface of gas pipelines. The pressure during the filling process should not exceed 0.1 MPa.
All workers involved in gas-hazardous work are required to wear protective tarpaulin suits, helmets and rubber dielectric shoes, and also carry insulating gas masks, safety glasses and special gloves. In addition, the work team must have a first aid kit equipped with all the necessary medications to provide first aid.
The place where pressure testing of the gas pipeline and other work along the pipeline is carried out must be fenced and equipped, if necessary, with special posts in order to prevent unauthorized people from being in the high-risk zone. During the release of gas into the system, it is prohibited to smoke, conduct hot work and use open flames.