What you need to know when performing calculations
In some cases, the volume of the heating system can be determined experimentally. In this case, the structure is filled from the water supply system with marks on the meter for water consumption. If this method does not work, then you will need to carry out mathematical calculations. In this case, the summation of the volume indicators of all circuits and devices that are in the system is performed. Some parameters can be determined, and other indicators are calculated using geometric formulas.
For example, technical documents indicate the volume for boilers. An important indicator is the volume of the special tank
When using any tank, it is important to note that it should not be filled to the very top. This is specifically taken into account in the program
The table shows the boiler power indicators
In some cases, it is important to calculate the volume without an expansion mechanism. In this case, in the column where the expansion tank is indicated, you must put a zero
In this case, the calculated indicator will become decisive when choosing a suitable design.
The expansion tank is an important part of the heating system, which must be suitable for its characteristics.
The volume of the heat exchange device is also important. In the case of collapsible batteries, the number of sections and their type are indicated. At the same time, the volume of the most popular radiators is already taken into account in the program. For non-removable convectors, it is necessary to indicate the design value according to the passport. If the building has heated floors, then the calculation is performed depending on the type of pipes and the sum of the lengths of all circuits. The database contains special columns for plastic lines and for unreinforced PEX.
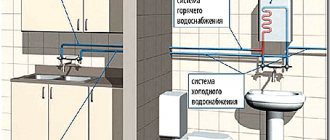
The largest volume of the heating system is occupied by the return and coolant supply circuits. During installation, different types of lines can be used, which differ in diameters and materials of manufacture. Internal diameters may also differ, which affects the volume. This is taken into account in the calculations. In this case, you need to measure individual sections of pipes and indicate this in the appropriate fields. Various types of pipes are introduced: metal-plastic, steel or polypropylene.
Non-freezing coolant option
The system can also install other mechanisms that affect volumes. These include factory-type manifolds, hydraulic separators and boilers. If there are any devices, they are also entered in the corresponding columns of the program.
The final result is displayed in liters.
Save time: selected articles delivered to your inbox every week
Principle of operation
From the physics course we know that fluid is incompressible.
In the heating circuit, water is used as a coolant.
In the temperature range from 20 to 90 degrees, it changes volume, expanding as it heats up.
If we imagine a heating network as a vessel of complex configuration, then heating the contents will cause the walls to rupture due to expansion of the liquid.
To compensate for this phenomenon, an expansion tank is used, which serves as an additional volume for storing excess coolant.
Having expanded, the water enters the tank, and when cooled (approximate prices for a heating cable for water supply) it goes back into the system.
It is simply impossible to remove excess water, since when it cools, air will fill the void and the circuit will cease to function.
Do you know what to do if water flows from the tank into the toilet. Read this useful article for tips and recommendations from master plumbers on troubleshooting.
The scope of application of asbestos-cement pipes measuring 150 mm is written on this page.
Thus, the expansion tank protects the heating system from both excess and shortage of coolant, compensating for all movements of its volume.
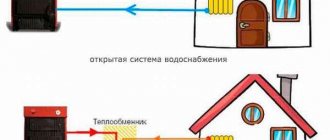
Heating mains: two-pipe, one-pipe
For space heating, two types of mains were designed: single-pipe and double-pipe.
Single-pipe, double-pipe lines
They differ in the way they connect heating devices to the system.
- In single-pipe systems, the connection is serial, the return of the previous radiator is the input for the next one.
- In two-pipe systems, the return flow is immediately diverted into a separate line to the heating boiler.
Single-pipe systems are effective for heating small areas of up to 100 sq.m per floor, while double-pipe systems can cope with larger areas. The difference is in the area on one floor, the amount of materials in the system.
Differences in heating lines:
Due to differences in design, different standards have been developed for the systems.
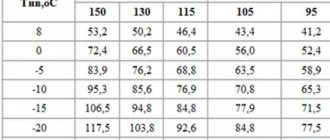
For a two-pipe system, the maximum heating of the coolant is 10 °C more than in a single-pipe system - 105 °C, at the same return temperature - 70 °C.
Selection of circulation pump
The circulation pump helps to identify pressure losses in all sections of the pipeline. To determine the pressure required by the pump to pump coolant through the system, use the formula: P = Rl + Z, where:
- P - decrease in pressure in the line (Pa);
- R - relative resistance to adhesion (Pa/m);
- l is the length of the pipe of one section of the heat pipeline (m);
- Z—pressure reduction in narrow-gauge zones (Pa).
Such calculations are extremely inconvenient and time-consuming, whereas to determine the Rl value of all sections of the pipeline it is enough to use Shevelev’s tables. It must be remembered that pump performance is the total coolant consumption, and not the capacity of the heating system.
Coolant
Heating requires a coolant that transfers heat from the source to the final consumer. The transmission efficiency depends on the viscosity.
In addition to viscosity, the coolant must meet the requirements for the absence of a corrosive component.
An important property is the ability to lubricate the surfaces of highways. The choice of heating system materials, units, mechanisms depends on the coolant
The heat carrier must not be toxic.
Types of coolants
Water as a coolant
The first thing people pay attention to when choosing a heating fluid is water. Has universal properties, is available
Being in its natural state, it has the best heat capacity - 1 kcal. If water gives off heat with virtually no losses when cooling, it is maximum heat transfer.
Has good viscosity. Specific density is about 1000 kg/m².
Eco-friendly. In the event of a heating system emergency, you don’t have to worry about toxic safety—in case of unplanned leaks, the water will not cause harm to your health.
Water in nature contains salts and gases, the presence of which in the heating system is not desirable. Natural water needs to be prepared and purified.
You can't get by with filtering. The easiest way is boiling. Water gets rid of salts in the form of scale. In addition to salt, boiling removes carbon dioxide. It will not be possible to remove all the salts.
If the composition of the water does not allow purification by boiling, resort to chemical methods. You will need slaked lime, soda ash, sodium orthophosphate. When elements are added, soluble salts become insoluble. All that remains is to filter the treated liquid, which can be done in the heating system.
However, it is better to use distilled water. You can make it yourself or purchase it.
Antifreeze as a coolant
Antifreeze has good technical performance; there is no risk of the system freezing when it is idle in winter.
Antifreezes protect the system from corrosion and lubricate well. Additives can be added for specific purposes, such as rust removal.
However, antifreeze has a lower heat capacity and releases heat more slowly than water; the viscosity is high, a circulation pump is needed; penetrating ability is higher, more thorough sealing of heating system components is required; toxicity.
Video: “What to put in the heating system?”
Selection of expansion tank
Compensating devices of all types will be highly effective only if the volume is correctly selected. For this purpose, it is necessary to take into account the property of the liquid, which expands when heated. The coolant in the heating circuits increases by at least 3% of the total volume of the heating system.
Liquid belongs to bodies that are in a transition state (on the verge of solid and gaseous). Accordingly, the expansion tank must have sufficient reserve for thermal expansion. When the system is completely filled with coolant, there is a risk of it being discharged through the safety valves, even within the design volume.
To prevent accidents associated with the expansion of liquid volumes, for private houses with small circuits it is advisable to choose expansion tanks, the volume of which should correspond to a tenth of the total amount of working fluid circulating in the system. This rule applies to heating systems with a capacity of up to 150 liters.
The resulting value is summed with the volume of coolant formed in the expansion tank due to the static load created by the liquid. The resulting result is multiplied by a correction factor established based on the values of the intermediate and final pressure.
Average data
If for some reason the user cannot determine the exact volume of water or antifreeze in heating radiators, then average data that is applicable to heating radiators of certain types can be used. If, say, we take a panel radiator of the 22nd or 11th type, then for every 10 cm of this heating device there will be 0.5-0.25 liters of coolant.
There is another way to determine the internal volume of the radiator section - close the lower necks, and through the upper ones, pour water or antifreeze into the section to the top. But this does not always work, since aluminum alloy radiators have a rather complex internal structure. In such a design, it is not so easy to remove air from all internal cavities, so this method of measuring internal volume for aluminum radiators cannot be considered accurate.