The heating system in private houses differs significantly from city apartments due to its complexity; it may contain several circuits of heated floors and heat exchange radiators with a large number of connections. After installation, a performance test procedure is mandatory; for this test, a technique called pressure testing of the heating system is used.
To carry out crimping work, special automatic or manual equipment is used; if it is available, the test will not cause any particular difficulties even for an unprepared homeowner. The only thing you should know when pumping water or air into the system is the pressure limits and time intervals for checking a specific heating network, which are specified in the regulations.
Fig.1 Hydraulic test process in the basement of a building
What is pressure testing of a heating system?
It is not difficult to understand why pressure testing of the heating system is necessary, using simple logical reasoning - after installing the circuit by specialists, it must be checked for functionality before the final payment for the work performed.
Pressure testing is the testing of a heating system by injection of water or air into it for a certain time under pressure exceeding the working pressure by 1.5 - 2 times. In private homes, the circuits of heat exchange radiators and heated floors, collectors and shut-off valves, joints between appliances and pipes, electric circulation pumps, heating boilers and boilers are checked.
This method determines the ability of equipment materials and heating pipes to withstand high pressure, as well as the tightness of all butt joints - a positive test result means the heating system is ready for long-term operation in trouble-free mode.
Rice. 2 How to install a flushing compressor for cleaning pipes
Washing methods
There are a huge variety of methods by which you can flush the heating system of a residential building. More often they are performed by craftsmen using special equipment. For independent work, two methods are most widespread:
- Chemical washing
- Hydropneumatic flushing
When is heating pressure tested?
Tests for “strength and density” in accordance with the Technical Operation Rules (RTE) of thermal power plants from the Russian Ministry of Energy (clause 9.2.12) are carried out in the following cases:
- Primary. In cottage-type houses, the system is tested after installation before putting it into operation; diagnostic work is carried out before sealing pipelines into grooves and pouring heated floors. It should be noted that it is possible to re-hydrotest the heating circuits after sealing all pipelines in the walls and screed - this will save expensive finishing materials when leaks are detected.
- Periodic. Hydrotests are carried out annually at the end of the heating season; their purpose is preliminary preparation for operation of heating networks in the event of their unplanned connection to operation. Before the start of each heating season, a repeated hydraulic check of heating systems is carried out.
- Extraordinary. After repairs, before starting up after a long period of inactivity with draining of the coolant, the system needs to be hydrotested for tightness and strength.
It is clear that in all of the above cases, pressure testing is a diagnostic tool that allows you to identify in advance problem areas and equipment that can lead to coolant leakage - which means repairs and lack of heating of the house in cold weather.
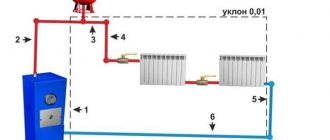
Rice. 3 Example of installation of heating systems with a water-heated floor circuit
Norms and rules for testing
Pressure testing of the heating system is carried out at positive ambient temperatures; testing when the thermometer readings are below zero is allowed only in emergency situations; inside buildings the temperature should not drop below +5 C. The system successfully passes hydraulic tests if:
- No fogging of welding seams, no leaks in heat exchange radiators, boilers, pipes, fittings and other heating equipment were detected.
- The pressure drop in the heating circuit did not exceed 0.2 bar in 5 minutes.
- In panel heating, the pressure drop according to the control pressure gauge in a 15-minute time interval did not exceed 0.1 bar.
- In hot water supply systems (DHW) with metal pipes, the permissible pressure drop did not exceed 0.5 bar. in a 10 minute interval.
- For plastic pipes, the permissible pressure drop was no more than 0.6 bar in the first 30 minutes from the start of hydrotesting; during a subsequent 2-hour test, the pressure drop did not exceed 0.2 bar.
- During air tests of steam and panel heating, the pressure drop did not exceed 0.1 bar. in the first 5 minutes.
Rice. 4 Pressure testing in a private country house
How to pressurize a heating system
There are two main methods of pressure testing of systems:
- Pressure testing with water. The main method for testing heat-transfer circuits, water is pumped into the lower part of the pipeline through the shut-off valve of the drain pipe using an automatic or manual pressure test pump. The advantage of the method is the ease of detecting leaks using water prints.
- Air pressure testing. Not a very effective method due to the difficulty of detecting leaks, it can be used to check the heating circuit in the cold season, when the use of water is difficult due to the possibility of freezing. To pump air, a compressor is used, which is connected to the pipeline through a special adapter. To detect the location of a leak, auditory methods are used; to accurately localize the air-permeable connection, a soap solution is used, similar to checking gas pipes.
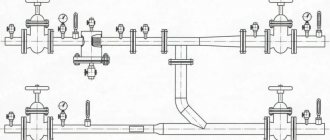
Rice. 5 Pressure testing of pipes with a special flushing compressor
Test pressure
The rules for pressure testing of heating systems are regulated by the PTE for heating installations from the Ministry of Energy (clause 9.2.13) in force since October 1, 2003, according to them the test pressure in an apartment building should not be less than:
- 1 mPa (10 bar, atm.) in home hot water supply and heating systems with water heaters;
- 10 bar (atm.) for panel and convector heating circuits;
- 6 bar (atm.) in a circuit with radiators made of cast iron or stamped steel;
- pressure equal to the working pressure with the addition of 5 bar (atm.) but not more than 10 bar for hot water supply;
- pressure, which must exceed the operating pressure (set by the manufacturer and indicated in the technical parameters of the devices) by 1.5 - 2 times for heating air heaters and heating ventilation.
For panel heating in conjunction with heat exchange devices, the test pressure cannot exceed the tolerances for these devices.
Signs of air locks
The first sign of air in the system is poor heating of the batteries. The battery warms up unevenly, not enough, and if any sounds appear in it, then the answer is clear - the air in the heating radiators is preventing the circuit from working properly. If the radiators have a bottom connection, and its upper part is cold, then air has accumulated in such a radiator and bleeding the air from the heating radiator will restore normal operation.
Removing air from heating circuits
There is a lot written on the Internet about what needs to be done and how to remove air from a heating battery. For open heating systems with an expansion tank, this problem is not relevant. In such systems, the air exits independently through a tank located at the highest point of the circuit. Problems with some radiators may arise, especially if the slope is chosen incorrectly. Such air bubbles are removed using Mayevsky taps or automatic air vents.
For closed systems with forced circulation, the problem of how to get rid of air in the heating system is also completely solvable. Air is removed from the batteries manually by opening the Mayevsky tap. If you hear a hissing sound when you open it, then the actions are correct and there is air in the system. The air must be released until water appears at the outlet of the Mayevsky tap.
The most dangerous air locks are at bends and turns of pipelines.
Such accumulations of air can completely stop the circulation of water in the system. If the installation of problematic areas of the circuit, for some reason, cannot be changed, then a heating system air bleed valve is installed in such problematic areas to bleed it.
Features of aluminum radiators
An unpleasant phenomenon is sometimes observed in aluminum radiators. The radiator material reacts with water. As a result, gases are constantly formed and must be constantly removed from the radiator, and how to remove air from a heating battery is described above. To avoid the problem described above, it is enough to buy and install aluminum radiators with an internal anti-corrosion coating. The correct solution would be to replace the aluminum radiator with a bimetallic one.
Types of testing and crimping of the system
The above standards of the Ministry of Energy on the frequency and testing regimes of heating systems are mandatory for government organizations and public utilities; in private homes, their compliance is by no means mandatory. Pressure testing is always carried out after delivery of the system to the customer before its operation; further inspection is usually carried out no more than once every 5 years.
To carry out testing work, no special skills or knowledge are required, so any owner can do it independently. To do this, there is no point in buying a manual or electric crimping unit (the lowest price for manual devices is about 100 USD), you can rent an electronic device and carry out the tests yourself within a couple of hours.
If there is no desire to carry out the tests yourself and financial resources allow, an official certificate of the work performed is required; a specialized company will help you do the crimping; the services of its specialists will cost an hourly rate of 1000 to 2500 rubles per hour.
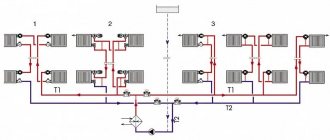
Rice. 8 Testing the system in an apartment building
Pressure testing in an apartment building
Pressure testing of the heating system of an apartment building is carried out to find faults and leaks in fittings and pipes at the end of seasonal heating (from mid-April to May).
If there are complaints from residents about the low heating temperature in their apartments, the radiators are first calculated with their further replacement or installation of additional sections if necessary. All risers are also checked for blockages and pressure flushing of the problematic riser and radiators of the heat exchangers of individual apartments or the entire circuit is carried out.
The following preparatory work is also carried out:
- The shut-off valves in elevators, on central line pipes and risers are inspected. On cast iron valves, the seals in the form of sealing cords are replaced, new paronite gaskets are installed between the flange connections, and stuck bolts are replaced. Other pressure gauges are installed in the elevator units and the old ones are sent for testing; the oil level is monitored in thermometers.
- Pipes and fittings are visually inspected for defective areas, corrosion damage, fistulas, and if problem areas are detected, they are repaired.
- The condition of the thermal insulation of the basement main and risers going to the floors is checked.
Next, pressure testing procedures begin, the system is tested taking into account the technical parameters of the radiator heaters located in the apartments. In accordance with standards that take into account the operating parameters of heat exchange radiators, for cast iron models the permissible maximum pressure is 6 bar. If heating pipes are located in the walls, the maximum coolant pressure should not rise above 10 bar. Thus, with cast iron and steel radiators the test pressure is 6 bar, with panel heating - 10 bar.
Rice. 9 Pressure testing station
Hydrotests are carried out in two stages, first the system as a whole is checked, and then the thermal unit is checked at higher pressure; the system is usually checked in the following sequence:
- Fill the heat-transfer circuit with special network water (has low hardness to avoid scale formation), pumping it with an electric pressure tester under the required pressure (6 or 10 atm.). To do this, the supply and drain hoses of an electric pressure tester are lowered into a container of water, and a pressure hose is connected to the inlet pipe of the network, after which the pressure tester is turned on to a preset pressure and the entire circuit is waited for filling.
- A 30-minute time interval is measured, during which the pressure should not decrease beyond the permissible standards (given above in the PTE); if the pressure gauge does not show a decrease in readings, the pressure test is considered complete.
- A drop in pressure indicates that leaks are appearing in various places; after they are detected, water is drained and the leak is eliminated, then the system circuit is again filled with water and pressure testing is carried out again.
- In the same way, the inlet unit is checked with a pressure of 10 atmospheres; upon completion of the work, an inspector from the control service is called to draw up a report on the readiness of the heating network of an apartment building for the heating season.
Hydropneumatic tests
To remove severe blockages in apartment buildings, hydroflushing is used; before this, highways, elevators, and risers are checked. The entire heating circuit is inspected to find breaks, leaks and correct them. Thermal insulation is checked on risers, highways, in particular in the basement.
The order of actions performed during hydropneumatic tests:
- First, the pipeline is filled with heating fluid, in particular water.
- Pressing equipment for pressing pipes is connected.
- Pressure gauge readings are constantly checked.
If within 30 minutes after connecting the hydraulic pneumatic pump during pressure testing, the pressure gauge readings do not change, this means that the pipeline is sealed and has no breakthroughs. Such a system is considered pressurized. If, according to the pressure gauge, the pressure in it decreases, then a search for sources of leakage begins. This process is repeated until all problems are resolved.
Pumps for flushing pipes are either electric or manual.
It is advisable to check the heating fluid for hardness after completing all pressure testing work. To identify various impurities of oxides and salts. Regulatory hardness limits are about 95 units. If everything is in order, then the pipeline is put into operation.