Hello! Internal heating systems mean a group of devices that supply heat. They include equipment: radiators, control devices, metering and regulation devices, shut-off and control valves, filters, etc.
These systems are divided:
— by type of coolant (air, water or steam);
- according to the wiring method (top or bottom);
- according to the method of connecting heating devices (one-pipe or two-pipe system).
With top wiring, coolant is supplied from the network from top to bottom. When, on the contrary, from bottom to top, then this is a bottom wiring.
Methods for connecting heating devices
Nowadays, the most common are single-pipe water systems with bottom vertical wiring. In this case, the radiator is connected using hoses, because they are easy to install and well guarantee uniform heating. Such a heating system requires clear calculations of the number of sections of radiators, taking into account the level of water cooling and, in addition, carefully adjusted heating devices, since water in single-pipe systems passes through them all sequentially.
The most successful heating concept, in my opinion, is the two-pipe heating system. The principle of its operation provides for the synchronous supply of hot and draining of cold water through different pipes. In addition, this concept makes it easier to calculate individual consumption.
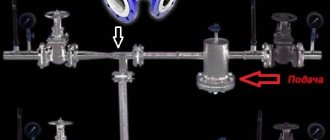
Elevator unit of the heating system
The elevator circuit of the internal heating system was widespread at one time in apartment buildings due to its ability to maintain stability even with changes in pressure and temperature. The elevator does not need constant monitoring since the pressure control is carried out by the selected nozzle diameter. Modern residents of the apartment complex inherited the elevator scheme from Soviet times.
The norm for intra-house heating is a water temperature of 95 degrees, but water at a temperature of 130 to 150 degrees Celsius is supplied through the main pipelines of the heating network. Such a difference is justified by existing temperature schedules for coolant release from a heat source, but is not suitable for entering the internal pipeline.
The mechanical elevator in this scheme is designed to normalize the temperature and pressure of water before it enters the internal heating network. But besides the undoubted advantages, a mechanical heating elevator also has a number of significant disadvantages. And I wrote about this in this article.
Dependent circuit with two-way valve and pumps in the return line
The regulation of heating and hot water systems, as well as the efficiency of thermal energy use, largely depends on its characteristics. Operating efficiency is directly affected by fluctuations in the hydraulic regime in heating networks. In addition, modern projects provide for the provision of remote access to the management of heating points. Today, devices with an electric drive for adjusting the nozzle are popular, making it possible to automatically change the coolant flow rate in the heating system of apartment buildings. When installing an automated heating substation, you can use facade regulation, when the adjustment of one side of the MKD does not depend on the other. The heating system is recharged using appropriate pumping equipment from the return pipeline of the heating networks. The heating system is also a closed loop through which the coolant moves with the help of circulation pumps from the heating point to consumers and back. The coolant is then directed into the return pipeline and returned through the main network for reuse at the heat generating enterprise. The mechanism is designed so that the throttle needle can be moved in the longitudinal direction. It changes the lumen of the nozzle and as a result the coolant flow changes. Substation with weather-compensated regulation
Types of heating elevators
They have a whole range of models, each selected based on the proper implementation of a specific load. These devices differ in their standard range by dimensional steps and throttle nozzles, which are calculated and adjusted for each specific option. I wrote about this in this article.
Heating system design
A thermal unit is a way to connect a home heating system to the main networks. The structure of the heating unit in a typical Soviet-era apartment building includes: a mud trap, shut-off valves, control devices, the elevator itself, etc.
The elevator unit is placed in a separate ITP room (individual heating point). There must certainly be shut-off valves in order to, if necessary, disconnect the intra-house system from the main heat supply. In order to avoid blockages and blockages in the system itself and in the devices of the internal house pipeline, it is necessary to isolate the dirt coming along with hot water from the main heating network; for this purpose, a mud trap is installed. The diameter of the mud trap is usually from 159 to 200 millimeters; all incoming dirt (solid particles, scale) collects and settles in it. The mud trap, in turn, needs timely and regular cleaning.
Control devices mean thermometers and pressure gauges that measure temperature and pressure in the elevator unit.
Three way valve
If it is necessary to divide the coolant flow between two consumers, a three-way heating valve is used, which can operate in two modes:
A three-way valve is installed in those places in the heating circuit where it may be necessary to divide or completely shut off the flow of water. The tap material is steel, cast iron or brass. Inside the faucet there is a shut-off device, which can be ball, cylindrical or conical. The tap resembles a tee and, depending on the connection to the heating system, can work as a mixer. Mixing proportions can be varied within wide limits.
The ball valve is mainly used for:
- adjusting the temperature of heated floors;
- adjusting battery temperature;
- distribution of coolant in two directions.
There are two types of three-way valves - shut-off and control valves. In principle, they are almost equivalent, but with three-way shut-off valves it is more difficult to regulate the temperature smoothly.
With centralized heating, hot water passes through a heating point before entering the heating radiators of apartment buildings. There it is brought to the required temperature using special equipment. For this purpose, in the vast majority of home heating units built during the Soviet era, an element such as a heating elevator was installed. This article is intended to tell you what it is and what tasks it performs.
Operating principle of the elevator unit
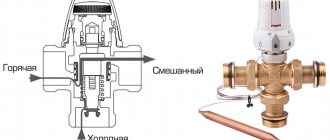
The mixing elevator serves as a device for cooling superheated water obtained from the heating network to a standard temperature before feeding it into the intra-house heating system. The principle of its reduction is to mix water at elevated temperatures from the supply pipeline and cooled water from the return pipeline.
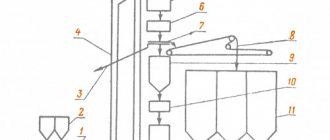
The elevator consists of several main parts. This is a suction manifold (input from the supply), a nozzle (throttle), a mixing chamber (the middle part of the elevator, where two flows are mixed and the pressure is equalized), a receiving chamber (mixture from the return), and a diffuser (exit from the elevator directly into the network with established pressure ).
The nozzle is a narrowing device located in the steel body of the elevator device. From it, hot water at high speed and with reduced pressure enters the mixing chamber, where water from the heating network and the return pipeline are mixed by suction. In other words, hot water from the main heating network enters the elevator, in which it passes through a constriction nozzle at high speed and at reduced pressure, mixes with water from the return pipeline, and then, at a lower temperature, moves into the internal pipeline. You can see what the nozzle of a mechanical elevator directly looks like in the photo below.
In modern modifications of the elevator, the technology for controlling changes in the nozzle cross-section occurs automatically using electronics. In such a system, the mixing ratio of hot and chilled water varies, which reduces the cost of the heating system. These are so-called weather-dependent or adjustable elevators, and I wrote about this in this article.This structure of the elevator has an actuator to ensure its stable operation, consisting of a direction device and a throttle needle, which is driven by a toothed roller. The action of the throttle needle regulates the coolant flow.
Calculation
The operation of the elevator unit depends on the correctly selected dimensions and pressure difference between the discharge and return pipelines. To calculate the parameters of the elevator unit, heating engineers and programmers have created quite a lot of programs. They look like a regular screen form with a customized formula for calculations. After filling out all the rows of the table, the program calculates the parameters of the hot water supply scheme, the dimensions of the elevator and displays the results in the form of a diagram with plotted dimensions and in the form of a table with calculations. The option for displaying results is usually presented in the form of a table.
The calculation of the heating network and the choice of elevator is described in some detail in the Building Codes and Rules:
- SNiP 23-01-99 “Building climatology”, 2000;
- SNiP II-3-79 “Construction Heat Engineering”, 1998;
- SNiP 2.04.05-91 “Heating, ventilation and air conditioning”, 1987;
- Bogoslovsky V.N. “Internal sanitary installations”, 1990.
The mixing thermostat is an alternative to the standard elevator unit. It works in exactly the same way as an elevator - it mixes the hot water coming from the thermal power plant and the cooled water that returns from the radiators. Three channels are connected to the thermostat: one for hot water, the second for return, and the third for supplying the prepared mixture to the heating radiators. If the temperature of the water from the main pipeline is within acceptable limits, the cold flow is completely blocked. As soon as the temperature begins to rise, the valve gradually begins to open, a portion of cool water is added to the hot water, lowering the temperature of the mixture. The hotter the water, the larger the volume of cool water is added. A three-way mixing thermostat valve is necessary to control the proportion of cold and hot water in order to obtain the coolant at the optimal temperature. Advantages: small dimensions, no moving parts, easy temperature adjustment.
Malfunctions of the elevator units of the heating system
Problems can occur for various reasons. This could be a breakdown of the valves or a failure of the control valve settings. If the nozzle itself is clogged, it must be removed and cleaned. If the blockage occurs in the mud trap, even before the elevator, then removal occurs by discharging the accumulated dirt using a discharge valve (dump valve) located in its lower part. If the blockage cannot be removed with this cleaning method, the mud collector must be disassembled and thoroughly cleaned.
When the diameter of the nozzle in a mechanical elevator changes directly as a result of deformation, the internal heating system becomes unbalanced. Such a problem requires immediate replacement of the nozzle itself with a new one.
Checking the condition of the elevator unit of the heating system
Such an examination has a clear sequence:
— checking the integrity of pipes;
— reconciliation of readings from control devices (pressure gauges and thermometers);
— checking pressure losses (internal resistance of the heating system);
— calculation of the mixing coefficient.
After the examination is completed, the equipment is sealed with fixed settings to avoid unauthorized interventions.
The undeniable advantage of the elevator system is its ease of operation. Since she does not need round-the-clock monitoring, it is quite sufficient to carry out routine examinations. Although, I would like to add that I myself am not a supporter of the elevator heating system scheme, and especially the scheme with a mechanical elevator. It is not modern, and was inherited from past times. Then, 30 - 50 years ago, the installation of such heating schemes was completely justified and justified. But a lot of water has passed under the bridge since then.
Premises requirements
In the vast majority of cases, mixing units are installed in the basement of the building. To perform its functions, it is necessary to take into account the characteristics of the room - seasonal changes in temperature and humidity.
There are a number of requirements for these indicators, the fulfillment of which is mandatory. This especially applies to elevator units of the central heating system with installed automatic servos:
- The room temperature should not fall below 0°C;
- To prevent the appearance of condensation on the surface of the pipes, an exhaust ventilation system is installed;
- A separate switchboard must be installed for electrical appliances. It is recommended to provide an autonomous power supply in case of an emergency power outage.
However, in fact, it is rare to see adherence to these rules. As a result, even for the most effective drawing of an elevator unit, its practical implementation may differ significantly. That is why alternative schemes for mixing coolant flows have appeared.
Some new apartment buildings connected to central heating do not have a heating circuit with an elevator unit. To install it, you need to contact the management company.
Installation of the elevator unit of the heating system
The place for its installation, in order to avoid problems, must meet certain parameters. You need a full-fledged room in which there will be a positive temperature, in elevator units with an automatic (weather-dependent) system; in order to avoid power outages, it is better to provide an autonomous power source.
Not so long ago I wrote and published the book “Design of ITP (heating points) of buildings.” In it, using specific examples, I examined various ITP schemes, namely an ITP scheme without an elevator, a heating unit diagram with an elevator, and finally, a heating unit diagram with a circulation pump and an adjustable valve. The book is based on my practical experience, I tried to write it as clearly and accessible as possible.
Here is the content of the book:
1. Introduction
2. ITP device, diagram without elevator
3. ITP device, elevator circuit
4. ITP device, circuit with a circulation pump and an adjustable valve.
5. Conclusion
You can view the book using the link below:
Installation of ITP (heating points) of buildings.
The heating system is one of the most important life support systems at home. Every home uses a certain heating system, but not every user knows what an elevator heating unit is and how it works, its purpose and the opportunities that are provided with its use.
Flaws
- The outlet temperature is not always adjustable. For example, at a low temperature of the coolant in the heating main, after mixing with cooled water (return), water will initially flow into the internal circuit pipes, the temperature of which is not sufficient to heat the room. This problem is currently being solved by installing adjustable units. Adjustment can be carried out manually (by rotating the valve) or automatically (adjustment occurs due to the movement of the rod installed inside the nozzle, the movement occurs due to the connection of a servo drive connected to sensors);
- For stable operation of a system with an elevator unit, precise selection of design is necessary;
- Some users consider one of the disadvantages to be the material investments required to purchase additional equipment and install elevator heating units. But with proper installation of high-quality equipment, even a system with automatic control of nozzle capacity pays for itself within 3-5 years (due to savings on heating fees).
Operating principle
The best example that will show the operating principle of a heating elevator would be a multi-storey building. It is in the basement of a multi-story building that you can find an elevator among all the elements.
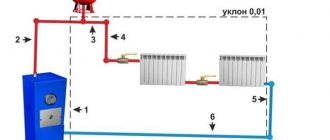
First of all, let's look at the drawing of the elevator heating unit in this case. There are two pipelines: supply (it is through it that hot water goes to the house) and return (cooled water returns to the boiler room).
From the thermal chamber, water enters the basement of the house; there is always a shut-off valve at the entrance. Usually these are valves, but sometimes in those systems that are more thought out, steel ball valves are installed.
As the standards show, there are several thermal regimes in boiler rooms:
- 150/70 degrees;
- 130/70 degrees;
- 95(90)/70 degrees.
When the water heats up to a temperature no higher than 95 degrees, the heat will be distributed throughout the heating system using a collector. But at temperatures above normal - above 95 degrees, everything becomes much more complicated. Water at this temperature cannot be supplied, so it must be reduced. This is precisely the function of the elevator heating unit. We also note that cooling water in this way is the simplest and cheapest way.
Example of implementation of scheme 1 ACU
Schematic diagram of an automated control unit with a sufficient available pressure drop at the inlet
(P1 - P2 > 6 m water column) for temperatures up to AUU t = 95-70 °C
The modern world has long been unable to cope without innovative technologies. There is not a single technology or system that does not use revolutionary solutions. The heating system was no exception. This is due to the fact that this is a fairly significant technology, which is designed to ensure a comfortable existence.
For obvious reasons, special attention is paid when designing a house. Since ancient times, houses were built from the stove, that is, first the stove was built, and then it was covered with walls and a ceiling. This was done for a reason, for this we need to say “thank you” to our climate
This was done for a reason; for this we need to say “thank you” to our climate.
Starting from the middle zone of our spacious country and ending with distant Sakhalin, rather uncomfortable temperatures reign for most of the year. The thermometer ranges from +30 to -50 degrees.
Due to the rather complex temperature resonance, the heating system is as important as the electrical supply. Previously, a competent stove maker who knew how to make a proper stove was valued at the level of a blacksmith. After all, you need to correctly calculate the size of the firebox, the diameter of the chimney, and besides, the stove had to be multifunctional:
- food was prepared in it;
- it heated the room;
- warmed up the water;
- served as a small sleeping place.
That is why the construction of the furnace was complex and time-consuming. It had to have sufficient draft to ensure that all combustion products did not enter the room. But with all this, she had to be economical.
Today, fundamentally little has changed. The main functions and requirements for the heating system remain the same:
- saving;
- maximum efficiency;
- multifunctionality;
- simplicity of design;
- quality and durability;
- minimal operating costs;
- safety.
Fire was the first source of heat for humans. And even now its relevance has not lost its significance. The most primitive way of heating was to make a fire, which provided protection from predators, low temperatures, and served as a source of light.
Further, over time, humanity began to tame the gift of Hermes. Ovens appeared, they were usually built from clay and stones. Later, with the advancement of technology, ceramic bricks began to be used. And it was then that the first ones appeared.
Steel furnaces appeared much later; they determined the formation of the Steel Age. The fuel for the stoves was coal, wood, and peat. With the gasification of cities, furnaces became available. And all this time, man sought to improve the heating system.
Purpose and characteristics
The heating elevator cools the superheated water to the design temperature, after which the prepared water enters the heating devices located in residential premises. Cooling of water occurs at the moment when hot water from the supply pipeline is mixed with cooled water from the return pipeline in the elevator.
The heating elevator diagram clearly shows that this unit helps to increase the efficiency of the entire heating system of the building. It is assigned two functions at once - a mixer and a circulation pump. Such a unit is inexpensive and does not require electricity. But the elevator also has several disadvantages:
- The pressure difference between the direct and reverse supply pipelines should be 0.8-2 Bar.
- The output temperature cannot be adjusted.
- There must be an accurate calculation for each elevator component.
Malfunctions of heating elevators
The diagram of the elevator heating unit may have faults that are caused by a breakdown of the elevator itself (clogging, an increase in the diameter of the nozzle), clogging of mud traps, breakdown of fittings, or violations of the regulator settings.
The breakdown of an element such as a heating elevator device can be noticed by the way temperature differences appear before and after the elevator. If the difference is large, then the elevator is faulty; if the difference is insignificant, then it may be clogged or the nozzle diameter may be increased. In any case, diagnosis of the breakdown and its elimination should only be carried out by a specialist!
If the elevator nozzle becomes clogged, it is removed and cleaned. If the design diameter of the nozzle increases due to corrosion or arbitrary drilling, then the circuit of the elevator heating unit and the heating system as a whole will become unbalanced.
Devices installed on the lower floors will overheat, and those on the upper floors will not receive enough heat. Such a malfunction, which the operation of the heating elevator undergoes, is eliminated by replacing it with a new nozzle with the calculated diameter.
Clogging of the sump in a device such as an elevator in a heating system can be determined by the increase in the pressure difference, monitored by pressure gauges before and after the sump. Such clogging is removed by discharging dirt through the drain valves of the sludge tank, which are located in its lower part. If the blockage is not removed this way, then the mud trap is disassembled and cleaned from the inside.
In this article we are going to find out what an elevator is in a heating system and how it works. In addition to the functions, we will study the operating modes of the elevator unit and methods for its adjustment. So, let's go.
Adviсe
The selection of the necessary parameters for a heating system in an apartment building or private house (cottage) depends on the project and the money allocated to resolve this issue. Most often, the determining factors in this case are financial capabilities and local conditions.
The gravity heating system is the simplest and cheapest. The heat source for such a system is a water boiler using wood, coal or natural gas. There is no pump in this system - convective circulation of water is provided by an expansion tank and pipe inclination.
The density of cold water is slightly greater than the density of hot water; the difference in density leads to the appearance of a slight excess pressure, which, together with the force of gravity, leads to the flow of coolant through the pipes of the system. The system is manually adjusted using valves and gate valves.
Semi-automatic system based on thermal heads and thermostats. System parameters are set manually, and subsequently they are maintained automatically. A system using microcontrollers and self-learning programs can operate completely autonomously for a long time. To analyze events in the system, a monitoring log is maintained. If you want to save as much as possible on the installation of a heating system by doing all the work yourself, but do not know how to use electric welding, you need to choose polypropylene pipes for the heating and hot water supply system. Installation of polypropylene pipes can be done using an ordinary wrench. These pipes are significantly cheaper than others. Installation errors can be quickly and cheaply corrected by re-installation. Welding polypropylene pipes on a machine can be easily mastered by a person who has never done this before.
Polypropylene pipes can be easily laid in hard-to-reach places. Their significant drawback is that to install a heating system you need a welding machine, which you will have to buy or rent. It is best to use polypropylene pipes with fiberglass reinforcement; they are much stronger and more durable.
By choosing metal-plastic pipes for the installation of a water heating system, you will be 100% confident in the reliability of the pipelines and the durability of the pipes laid in the cement screed of the “warm floor”.
Independent troubleshooting of the elevator unit:
- Clogged with garbage. Signs - after lightly tapping the body of the mud trap, cloudiness of the water or the appearance of a stagnant odor is observed. The mud trap needs to be washed.
- Corroded or clogged nozzle. Signs: a loud noise is heard, and the pressure in the system changes sharply during operation. The nozzle requires replacement.
- Clogged sump tank in the return line. Signs: pressure in the return line is increasing. The mud trap needs to be washed.
- Nozzle corrosion. Signs: different water temperatures on the floors. The nozzle needs to be replaced.
What it is
Functions
In simple words, elevator heating units are unusual buffers between building and heating main engineering systems.
They combine a couple of functions:
- They convert the pressure difference between the lines of the highway (3-4 atmospheres) into the 0.2 required for the operation of the heating circuit.
- Help to start or hot water supply systems and stop heating.
- Allows you to switch between different operating modes of the DHW system.
Let us clarify: the temperature of the water in the taps should not be more than 90-95 degrees. In summer, when the water temperature in the highway supply does not exceed 50-55 C, the hot water supply is supplied from this thread. During the peak of cold weather, the hot water supply has to be switched to the return pipeline.
Elements
A simple diagram of an elevator heating unit includes:
- Several input valves on the supply and return lines. The supply is invariably located above the return.
- Several house valves that cut off the elevator unit from the heating system.
- Mud collectors on the supply and, less often, on the return.
- Discharge valves in the heating circuit, allowing you to completely dry it or reset the system, expelling a significant part of the air from it upon startup. It is considered good practice to dispose of waste into the sewer.
- Control valves that allow you to measure the pressure and temperature of the supply, return and mixture.
- Finally, in fact, a water-jet elevator is a flanged tee for pipes with a nozzle in.
How does an elevator heating system work? The principle of its operation is based on Bernoulli's law, which states that static pressure in a flow is inversely proportional to its speed.
Features of the operation of central heating stations, installation of heating points
The heating system is fed by the return pipeline of the heating network. Heat sources and thermal energy transport systems The heat source for TPs are heat generating enterprises, boiler houses, and combined heat and power plants.
Water from the external water supply network is supplied to the DHW heater.
Compensation for the decrease in pressure level is carried out through a group of pumps. Viewed: The DHW circuit can be designated as single-stage, independent and parallel.
Correction mode is automatic. Often, heat from the domestic hot water system is used by consumers for partial heating of premises, for example bathrooms in multi-apartment residential buildings. The flow of hot mains water to the 2nd stage heater is controlled by the temperature controller (thermal relay valve) depending on the water temperature behind the 2nd stage heater.
The schematic diagram of an individual heating point is approved.
Certificate for flushing and pressure testing of heating networks, heating systems and hot water supply systems.
All this equipment must operate exclusively in automatic mode, so it is critically important to correctly set up the entire set of equipment for work in a particular home
Central heating stations should be located on the boundaries of microdistricts between the main, distribution networks and quarterly ones. One of them is the heating system. If there is a central heating point in each individual building, it is necessary to install an ITP, which performs only those functions that are not provided for in the central heating point and are necessary for the heat consumption system of a given building.
This device can be represented as a container. But the cost of such a device is much higher, although its use is more economical. Heat consumption is controlled and taken into account. After the elevator, the return line will also be counted.
After the elevator unit, the mixed coolant is supplied to the heating system of the building. The installation company must be a member of the SRO. Further, as the most common, we consider a TP with a closed hot water supply system and an independent connection circuit for the heating system. Creating a schematic diagram of an individual heating point in AutoCAD P&ID
Territories of responsibility
What is an elevator heating unit - we have at least figured it out.
And who is responsible for it?
- The section of the highway into houses up to the flanges of the inlet valves is the territory of responsibility of the heat transporting organization (heating networks).
- Everything after the entrance valves, and the valves themselves, are the responsibility of the housing organization.
But: selection of a heating elevator by number (standard size), calculation of retaining washers and nozzle diameter are carried out by heating networks. Housing workers only provide dismantling and installation.
Control
The controlling organization is, again, heating networks.
What exactly do they control?
- A couple of times during the winter, control measurements of pressures and temperatures of the supply, return and mixture are carried out . In case of deviations from the temperature curve, the calculation of the heating elevator is carried out again with boring or reducing the diameter of the nozzle. Obviously, this should not be done during the peak of cold weather: at -40 outside, the access heating system can become covered in ice within an hour after the circulation stops.
- In preparation for the heating season, the condition of the shut-off valves is checked . The check is extremely simple: all valves in the assembly are closed, after which any control valve opens. If water comes from it, it is necessary to look for a malfunction; In addition, in any position of the valves, they should not have leaks through the seals.
- Finally, at the end of the heating season, the elevators in the heating system, along with the system itself, are tested for temperature . When the DHW supply is turned off, the coolant heats up to high values.
The main thing
The elevator in the heating system is the main element in the redistribution of superheated water going into the heating system.
The enormous pressure and temperature of the coolant decrease as it passes through the elevator unit.
A reduced/increased nozzle diameter changes the elevator parameters.
Monitoring the serviceability of the elevator is carried out by monitoring the input and output parameters of the system.
To distribute the coolant evenly among different consumers using a heating elevator, you can use a collector or comb.
The negative aspects of using an elevator are the complexity of installation and adjusting the temperature of the coolant, the positive aspects are durability and economy.
Control
We present the order of execution of some operations related to the operation of the elevator.
Start heating
If the system is full, you just need to open the house valves and circulation will begin.
There are a couple more complicated instructions for starting the reset system.
- The discharge on the return pipeline opens and the discharge on the supply closes.
- Slowly (to avoid water hammer) the upper house valve opens.
- Once clean, air-free water has been released into the discharge, it closes, after which the lower house valve opens.
Useful: if modern ball valves are installed on the risers, the direction of operation of the discharge circuit does not matter. But in screw valves, a rapid countercurrent can tear off the valves, after which the mechanic will have to spend a long and painful search for the circumstances of the stoppage of circulation in the risers.
Work without nozzle
When the return temperature is catastrophically low during the peak of cold weather, it is practiced to operate the elevator without a nozzle. The system receives coolant from the highway, not the mixture. The suction is suppressed with a metal pancake.
Differential adjustment
If the return flow is too high and it is not possible to replace the nozzle in a timely manner, adjusting the differential with a valve is practiced.
How to do it yourself?
- The supply pressure is measured, after which the pressure gauge is placed on the return line.
- The inlet valve on the return line closes completely and slowly opens, with pressure controlled by a pressure gauge. If the valve is installed, its cheeks may not completely move down the stem and will slide down later. The price of the wrong procedure is guaranteed defrosted access heating.
At a time, aim to remove no more than 0.2 atmospheres of difference. Repeated measurement of the return temperature is carried out every other day, at a time when all values have stabilized.