Here you will learn:
- Features of two-pipe heating systems
- Advantages and disadvantages of two-pipe heating systems
- Types of two-pipe heating systems
When developing a heating system for our home, we certainly think about the layout of pipes and connecting radiators. Most often, when creating projects, common schemes with two pipes laid through heated rooms are used. A two-pipe heating system is more difficult to install, but it has many undeniable advantages - this is what we will talk about in our review. We will also look at:
- Structural features of two-pipe heating systems;
- Their main disadvantages are;
- Varieties of two-pipe systems.
At the very end, we will talk about the most effective ways to connect batteries to heating systems.
Characteristic
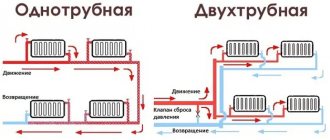
The most common is the two-pipe heating system, despite some advantages of single-pipe structures. No matter how complex such a pipeline with two pipes (separately for supplying water and returning it) may be, most people prefer it.
Such systems are installed in multi-storey and apartment buildings.
Device
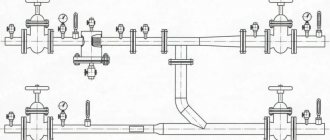
The elements of dual-line heating with lower pipe insertion are as follows:
- boiler and pump;
- auto vent, thermostatic and safety valves, valves;
- batteries and expansion tank;
- filters, control devices, temperature and pressure sensors;
- Bypasses can be used, but are not necessary.
Advantages and disadvantages
The two-pipe connection diagram under consideration reveals many advantages when used. Firstly, the uniformity of heat distribution throughout the entire line and the individual supply of coolant to the radiators.
Therefore, it is possible to regulate heating devices individually: turn them on/off (you just need to close the riser), change the pressure.
Different rooms can be set to different temperatures.
Secondly, such systems do not require turning off or draining the entire coolant if one heating device breaks down. Thirdly, the system can be installed after the construction of the lower floor and not wait until the whole house is ready. In addition, the pipeline has a smaller diameter than in a single pipe system.
There are also some disadvantages:
- more materials are required than for a single-pipe main;
- low pressure in the supply riser creates the need to frequently bleed air by connecting additional valves.
Piping in a multi-storey building
Types of pipe distribution in a multi-storey building
For normal operation of the building's heat supply, you need to know its basic parameters. What pressure in the heating system of a multi-storey building, as well as the temperature regime, will be optimal? According to the standards, these characteristics must have the following values:
- Pressure. For buildings up to 5 floors - 2-4 atm. If there are nine floors - 5-7 atm. The difference lies in the pressure of hot water to transport it to the upper levels of the house;
- Temperature. It can vary from +18°C to +22°C. This applies to residential premises only. On landings and non-residential rooms, a decrease to +15°C is allowed.
Having determined the optimal parameter values, you can begin to select the heating layout in a multi-story building.
It largely depends on the number of floors of the building, its area and the power of the entire system. The degree of thermal insulation of the house is also taken into account.
The pressure difference in the pipes on the 1st and 9th floors can be up to 10% of the standard value. This is a normal situation for a multi-story building.
Single-pipe heating distribution
This is one of the economical options for organizing heat supply in a building with a relatively large area. For the first time, a single-pipe heating system for a multi-story building began to be used on a large scale for “Khrushchev” buildings. The principle of its operation is that there are several distribution risers to which consumers are connected.
The coolant is supplied through one pipe circuit. The absence of a return line greatly simplifies the installation of the system, while reducing the cost. However, the Leningrad heating system for a multi-storey building has a number of disadvantages:
- Uneven heating of the room depending on the distance from the point of hot water intake (boiler or collector unit). Those. There may be options when a consumer connected earlier in the circuit will have hotter batteries than those next in the chain;
- Problems with adjusting the degree of heating of radiators. To do this, you need to make a bypass on each radiator;
- Complex balancing of a single-pipe heating system for a multi-storey building. It is carried out using thermostats and shut-off valves. In this case, system failure is possible even with a slight change in input parameters - temperature or pressure.
Currently, installing a single-pipe heating system in a new multi-story building is extremely rare. This is explained by the difficulty of individual metering of coolant in a separate apartment. Thus, in residential buildings of the Khrushchev project, the number of distribution risers in one apartment can reach up to 5. Those. It is necessary to install an energy consumption meter on each of them.
A correctly drawn up estimate for heating a multi-storey building with a single-pipe system should include not only maintenance costs, but also the modernization of pipelines - the replacement of individual components with more efficient ones.
Comparison with other types
In the lower insert, the supply line is laid from below, next to the return line, so the coolant is directed from the bottom up along the supply risers. Both types of distributions can be designed with one or more circuits, dead-end and associated flow of water in the supply and return pipes.
Natural circulation systems with connections at the bottom are used very rarely, since they require a large number of risers, and the point of inserting pipes in this way is to reduce their number to a minimum. Taking this into account, such structures most often have forced circulation.
Roof and floors - meaning
In the upper supply line, the supply line is above the radiator level. It is mounted in the attic, in the ceiling. The heated water flows to the top, then through the supply risers it evenly spreads over the radiators. Radiators must be located above the return line. To prevent air accumulation, install a compensating tank at the very top point (in the attic). Therefore, it is not suitable for houses with a flat roof without an attic.
The wiring from below has two pipes - supply and discharge - the heating radiators must be higher than them. It is very convenient for removing air pockets using Mayevsky taps. The supply line is located in the basement, in the basement, under the floor. The supply pipe must be higher than the return pipe. An additional slope of the line towards the boiler minimizes air pockets.
Both wirings are most effective in a vertical configuration, when the batteries are mounted on different floors or levels.
Requirements and standards for heating an apartment
A comfortable temperature for the life of each person is determined by a number of factors. Too high, as well as too low a temperature, negatively affects the condition of the human body. Therefore, the temperature at which the body does not turn on its cooling and heating mechanisms is considered normal. These factors include:
- intensity of human activity;
- season;
- daily temperature fluctuations.
People who work in hot shops or athletes who train will not freeze even at low indoor temperatures. While office workers need warmer conditions.
Also, each person’s body adapts to general climatic conditions. Therefore, for a comfortable existence in winter, it is enough to heat the room to +19...+22°C, and in summer - to +22...+25°C.
According to the rules and regulations, in residential premises the minimum temperature threshold should not fall below +18°C. Heating standards for apartments are easier to develop than for work areas, because the activity of people at home is lower than in production. The permissible temperature fluctuations for each room are different:
- kitchen: the optimal temperature is considered to be +19...+21°C, and acceptable - from +18...+26°C;
- toilet: +19…+21°С; +18…+26°С;
- bathroom: +19…+21°С; +18…+24°С;
- corridor: +18…+20°С; +16…+24°С;
- pantry: +16…+18°С; +12…+18°С.
It has been proven that during sleep the body does not need an additional source of heating, therefore, according to GOST, it is allowed to lower the temperature in residential premises by 3°C from 0 to 5 am.
Principle of operation
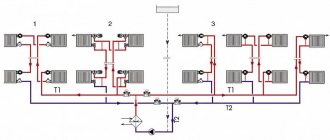
The main characteristic of a two-pipe system is the presence of an individual water supply line to each radiator. In this scheme, each of the batteries is equipped with two separate pipes: water supply and outlet. The coolant flows to the batteries from bottom to top. The cooled water returns through the return risers to the return line, and through it to the boiler.
In a multi-storey building, it is appropriate to install a two-pipe structure with a vertical main line and lower wiring. In this case, the temperature difference between the coolant in the supply pipe and the return pipe creates strong pressure, which increases as the floor rises. Pressure helps water move through the pipeline.
In the lower pipe connection under consideration, the boiler must be in a recess, since the radiators and heating devices must be higher to ensure uniform delivery of water to them.
The air that accumulates is removed by Mayevsky taps or bleeders; they are mounted on all heating devices. Automatic vents are also used, which are fixed on risers or special air outlet lines.
Components of a two-pipe individual heating system
A two-pipe diagram of an apartment’s individual heating network includes the following elements:
- heating boiler;
- thermostatic valves for radiators;
- automatic air vent valve;
- balancing device;
- pipes and fittings;
- radiators;
- valves and taps;
- expansion tank;
- filter;
- temperature manometer;
- circulation pump (if necessary);
- safety valves.
Kinds
A two-pipe heating system can be of the following types:
- horizontal and vertical;
- direct flow - the coolant flows in one direction through both pipes;
- dead-end - hot and cooled water moves in different directions;
- with forced or natural circulation: the first requires a pump, the second requires a slope of the pipes towards the boiler.
The horizontal scheme can be with dead ends, with a passing movement of water, or with a collector. It is suitable for one-story buildings with a significant length, when it is advisable to connect the batteries to a horizontally located main pipe. This system is also convenient for buildings without piers, in panel-frame houses, where risers are conveniently placed on a staircase or corridor.
According to experts, the most effective was the vertical scheme with forced water flow. It requires a pump, which is located on the return line in front of the boiler. An expansion tank is also mounted on it. Due to the pump, the pipes can be smaller than in a design with natural movement: with its help, water is guaranteed to move along the entire line.
All heating devices are connected to a vertical riser. This is the best option for high-rise buildings. Each floor is connected to the riser pipe separately. The advantage is the absence of air pockets.
Supply from city networks
We inherited centralized heat supply to multi-storey residential buildings as a legacy of planned management since the existence of the Soviet Union. Today, this method of providing housing with thermal energy is still the most common.
The main advantage of central heating is that residents of houses do not have to deal with issues related to the operation and repair of equipment and pipelines. The annual launch and necessary overhaul of networks is the responsibility of the city heat supply organization. With centralized and autonomous heating, individual elements can be repaired or altered only in agreement with the heat supply organization.
The design supply temperature in urban networks can be in the range of 90-115˚C, and existing standards for the safe operation of equipment prohibit heating accessible hot surfaces above 60˚C to prevent possible burns.
Therefore, a special elevator unit was installed at the pipe entry into the building. It mixes the hot coolant from the supply with cooled water from the return, returning from the consumer, changing the temperature to an acceptable one. Calculation of elements, maintenance of elements and change of the elevator control nozzle are carried out only by employees of the heat supply organization.
Installation
Conventionally, several stages of work can be distinguished. First, the type of heating is determined. If gas is supplied to the house, then the most ideal option would be to install two boilers: one gas, the second a spare, solid fuel or electric.
Next, you should agree on the installation of the heating system in the project documentation and begin purchasing the necessary materials, devices, and preparing tools.
Stages
Briefly, installation consists of the following points:
- a supply pipe is led upward from the boiler and connected to a compensating tank;
- a pipe from the upper line is removed from the tank, which goes to all radiators;
- a bypass (if provided) and a pump are installed;
- the return line is drawn parallel to the supply line, it is also connected to the radiators and cut into the boiler.
Boiler
For a two-pipe system, the boiler is installed first, for which a mini-boiler room is created. In most cases, this is a basement (ideally a separate room). The main requirement is good ventilation. The boiler must have free access and be located at some distance from the walls.
The floor and walls around it are lined with fire-resistant material, and the chimney is vented to the street. If necessary, a circulation pump, distribution manifold, control and measuring instruments are installed near the boiler.
Radiators
They are installed last. They are located under the windows and fixed with brackets. The recommended height from the floor is 10–12 cm, from the walls – 2-5 cm, from the window sills – 10 cm. The inlet and outlet of the battery is fixed with shut-off and control devices.
It is advisable to install temperature sensors - with their help you can monitor temperature indicators and regulate them.
If the heating boiler is gas, then it is necessary to have the appropriate documentation and the presence of a representative of the gas industry at the first start-up.
Features of hot water supply and calculation of the volume of hot water
Calculation of the amount of hot water in the system depends on technical and operational factors:
- Estimated hot water temperature;
- Number of residents in an apartment building;
- The parameters that plumbing fixtures can withstand and the frequency of their operation in the overall water supply scheme;
- the number of plumbing fixtures that are connected to the hot water supply.
Calculation example:
- A family of four uses a 140 liter bathtub. The bathtub fills in 10 minutes, the bathroom has a shower with a water consumption of 30 liters.
- Within 10 minutes, the water heating device must heat it to the design temperature of 170 liters.
These theoretical calculations work based on average water consumption by residents.
Adviсe
The expansion tank is located at or above the peak point of the main line. If there is an autonomous water supply, then it can be integrated with a supply tank. The slope of the supply and return pipes should be no more than 10 cm per 20 or more linear meters.
If the pipeline is at the front door, it is appropriate to divide it into two elbows. Then the wiring is created from the location of the highest point of the system. The lower line of a two-pipe structure must be symmetrical and parallel to the upper one.
All technological units must be equipped with taps, and it is advisable to insulate the supply pipe. It is also advisable to place the distribution tank in an insulated room. In this case, there should be no right angles, sharp breaks, which will subsequently create resistance and air pockets. Finally, we must not forget about the supports for the pipes - they must be made of steel and cut in every 1.2 meters.