Comfortable living conditions are ensured by a powerful system of various engineering communications. When planning heating in a private house, it is necessary to correctly calculate not only the parameters of the boiler, but also the elements for transporting the coolant. In this review we will look in detail at how to choose the diameter of a heating pipe.
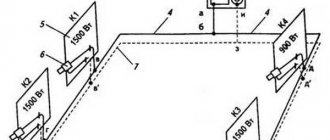
- Convection
- Two-pipe
- For two-pipe version
Effect of characteristics on efficiency
A well-designed pipeline design has a positive effect on the performance of the heating system. The throughput of the structure depends on the cross-section of the components. The parameter shows the volume of hot liquid that will pass at a constant speed per unit of time.
Utility network performance is often influenced by factors. The efficiency of the circuit depends on 4 circumstances:
- Throughput and heat dissipation. The characteristic depends on the amount of water in the system.
- Pressure. The parameter in the heating network is associated with temperature and speed.
- Heat loss. At the joints and on the bends there will be a decrease in performance.
- Noise. The faster the fluid moves, the louder the sound.
In a heating system, with a constant flow of coolant and a decrease in diameter, the rate of water movement increases. On lines with a small cross-section, the fluid velocity will increase. Due to the low pressure in large structures, the flow rate is reduced.
Heat pipe diameterSource mastergrad.com
If the diameter of the pipes for heating a private house is too large, then the power of the pump built into the boiler will not be enough to move it. In a large system there will be a lot of coolant, so the equipment will not be able to cope with the movement of such a volume of liquid. Heating excess water will require spending more energy and time, which reduces the efficiency of the network and increases losses. As moisture passes through all rooms, it cools quickly.
The overall section is prohibited from being used in systems with natural circulation. When the speed is reduced, there is a risk of stopping and boiling the liquid in the heating boiler. With a small diameter, moisture can rupture the utility network.
What does the size of parts affect? Source ekaterinburg.kassot.com
When the speed decreases to 0.25 m/sec, air pockets often appear in the pipes. If the flow speed is more than 1.5 m/sec, then noise appears in the heating system. If the background noise standards are constantly exceeded, the inhabitants of the cottage will find it uncomfortable to live.
Installation of heating devicesSource realstroyservis24.ru
Types of pipes
The selection of the diameter of the heating pipe depends on the material from which the elements are made. The parameters affect not only the cross-sectional dimensions, but also the installation method, the cost of the project and possible heat loss. For heating systems, 4 popular types are used.
Steel
Metal pipes when creating utility networks are an inexpensive and practical option, which have high thermal conductivity and a maximum pressure of up to 30 atmospheres. With proper use, the structures will last 20-30 years. The raw material has no temperature restrictions, so it is often used in a steam system at 100-130 C.
Due to cost and resistance to expansion, property owners often choose carbon steel. Corrosion is the main disadvantage of metal models. During oxidative processes, roughness appears on the surface of the walls, on which deposits accumulate. As plaque grows, the passage for water decreases and the thermal conductivity of the product decreases. When the walls become thinner due to rust, breakouts form. The problem can be minimized by using high-quality coolant in the system and regular flushing of pipes.
Carbon modelsSource x-teplo.ru
Galvanized steel is a little less capricious. The coating protects the metal from corrosion, thereby increasing the service life of the utility network. The models can withstand loads during water hammer and function perfectly in high temperature conditions.
Stainless steel pipes are superior in durability to galvanized and carbon types. A properly installed structure is inert to aggressive coolant, therefore it is not afraid of corrosion and will last more than 30 years. Elements made by seamless welding are suitable for the heating circuit.
Stainless steel optionsSource ovknn.ru
The disadvantage of all steel pipes is the weight and complexity of installation. Structures do not bend without special equipment, so at bends it is necessary to use additional parts that reduce the efficiency of the utility network. Now there are options in the form of corrugation, but they are also unstable to the aggressive environment of coolants.
Copper
The maximum operating temperature is 200-250 C, pressure is more than 30 atmospheres. If installed correctly, the heating system will last 90-100 years. The metal has high resistance to corrosion and freezing. According to production technology, copper pipes are divided into 2 types:
- Unannealed. Very strong material will not crack under pressure up to 40 atmospheres.
- Annealed. After heat treatment (annealing), the products become elastic and flexible, while their strength decreases.
Compared to steel, copper has a high density, so the pipes have thin walls and are light in weight. Due to good thermal conductivity, the circuit heats up quickly and evenly. Thanks to the flat surface, the circulating fluid has minimal resistance. There are no growths on the internal partitions, which eliminates the appearance of blockages and a decrease in efficiency.
Heating solution made of metalSource otoplenie-doma.in.ua
Copper pipes are not compatible with other metals. Upon contact with steel, aluminum or cast iron, chemical processes begin in the liquid and gas is formed. The utility network must provide bleed valves for accumulations. Additional parts should be made of copper or brass, radiators should be made of stainless steel.
In a heating system with copper pipes, a well-purified coolant is used. Solid debris can damage soft metal. Additionally, a mechanical cleaning filter is included in the network. The material has high electrical conductivity, so the circuit must be grounded.
Metal structures for a cottageSource kenoll.ru
Polymer
The maximum temperature of the coolant varies between 90-95 C. The structure will withstand 130 C for a short time, but with prolonged contact the polymer pipes are deformed. If the operating rules are followed, they will last up to 30 years. When connected to heating, the circuit is resistant to pressure surges.
Due to the plasticity of the material, pipes are easy to lay without cutting and without additional connections. For welding, a special apparatus is used that heats the parts. The soldering points in the finished structure are not visible to the naked eye.
Plastic models for a private homeSource teplomir.in.ua
Plastic is not demanding on the quality of the liquid in the heating system. The raw material does not enter into a chemical reaction, therefore it does not rust or be destroyed by corrosion. Ideally smooth walls do not reduce the speed of the coolant and are not covered with plaque.
Reinforced polymer pipes are used for heating, which can be identified by markings on the surface (PPR-FR-PPR, PPR-GR-PPR). The reinforcing material is fiberglass or aluminum.
Heating solutionSource oboiman.ru
Metal-plastic
The pipes consist of 5 layers of modified plastic and thin foil, so they are very durable. The products are resistant to high temperatures (up to 110 C), freezing and thawing, and retain their original shape. Due to the smoothness of the inner walls, deposits do not form on the surface.
In terms of linear expansion, metal-plastic pipes are 2.5 times higher than their steel counterparts. With prolonged exposure to direct ultraviolet and electromagnetic rays, the product quickly loses strength and wears out. Parts must be installed correctly and connections must be tightened tightly. When the bending angle is exceeded, they crack.
What diameters are there?
In the technical parameters of heating pipes, different types of sections are used. When taking into account the mounting structures and the occupied area, take the outer diameter with the walls. Internal characteristics indicate the size of the gaps, therefore they are suitable when calculating network throughput. The conditional version is an averaging to the larger side of the space inside.
In stores, pipes are marked by their outer cross-section, often in inches (25.4 mm). Internal parameters vary depending on the wall thickness, material and purpose of the part. The external characteristics of steel seam models are 3-4% thicker than those of polymer and seamless structures. Copper types are the thinnest, 1-2 mm smaller than others.
Analysis of popular typesSource alchevsk.ua
The size of the heating pipes affects the tasks that the element must perform. Popular diameter parameters range from 16 to 40 mm:
- 16. Used to connect one or two batteries.
- 20. Suitable for installing 1 radiator or a group of up to 5 pieces. The total maximum power is 7 kW.
- 25. Models are used for installing heating structures with dead-end wiring diagrams.
- 32. Used for arranging the utility network of an entire floor or cottage, with a total capacity of up to 19 kW.
- 40. Suitable for 20 batteries, up to 30 kW.
The choice of cross-section of heating pipes determines the throughput capabilities of the system, hydraulic and heat losses. The bulk coolant heats up quickly, and the small size provides better resistance and low noise. Elements of small diameter are cheaper than large ones. Models that are too compact create increased load on the reinforcement, which leads to gusts.
Price for 1m2 of work
It is difficult to independently take into account all the nuances and correctly install the heating network around the house. It is much better to entrust this work to specialists who will offer the best option and a set of additional equipment. Based on experience, designers and installers are able to correctly place emphasis depending on the customer’s wishes: to provide heating with maximum efficiency and ease of use, or to strive to save money on work and installation.
The cost of the work includes separate installation of the boiler, connection of additional equipment, pipe routing and installation of radiators. Each item has its own price list, according to which the cost of all work on equipping the heating system in the house is calculated.
| Type of work | units | Cost, rub. |
| Installation of a heating boiler with a power of up to 50 kW | PC. | 12000-20000 |
| Installation of a boiler with a power of over 50 kW | PC. | 25000-50000 |
| Security group installation | PC. | from 1500 |
| Expansion tank | PC. | from 2000 |
| Circulation pump | PC. | from 2000 |
| Installation and connection of the comb (collector) | PC. | from 1500 |
| Pipe routing D16-25 | linear meters | 60-85 |
| Pipe routing D32-40 | linear meters | 75-90 |
| Pipe routing D55-63 | linear meters | 90-120 |
| Pipe routing D75-110 | linear meters | 100-150 |
| Installation and connection of the radiator | PC. | 2000-5000 |
| Installing a thermostat | PC. | 500 |
| Pressure testing according to the requirements of the boiler equipment manufacturer | from 4500 | |
| Commissioning works | from 3500 |
Routing pipes from the boiler to the radiators can average 300-500 rubles per linear meter, taking into account laying, connection, passage and wall grooves. Prices are indicative for Moscow and the region.
Types of coolant movement
The speed of movement of the hot water flow in the pipes is one of the important parameters that allows you to calculate the diameter of the parts. The recommended movement ranges from 0.26 to 1.4 m/sec. Already at 1.5, heat transfer decreases and noise in the utility network increases. There are 2 types that you need to understand.
Pipe size optionsSource prootoplenie.com
Convection
The natural circulation option is suitable for solid fuel boilers. The operating principle is based on physical laws. The density of a cold liquid is less than that of a hot one. Cool moisture flowing down the pipe displaces warm moisture upward. The speed of movement in such networks is 0.2 m/sec.
A small flow of movement during convection circulation causes the formation of air jams and a decrease in the volume of transferred heat. The expansion tank and Mayevsky taps will help solve the problems.
System with convection movementSource aniko-gas.ru
The diameter of the heating parts with convection circulation must match the boiler outlet pipe. The largest starting section is maintained until the first fork. When laying, the size of the pipes is gradually reduced. In the last node, the characteristics of the elements vary between 16-19 mm.
Forced
Circulation in the circuit is carried out using a pump and a manifold, which are included in the design of the boiler (gas, electric). The user can independently control the speed of the coolant. In engineering networks, parameters are maintained within the range of 0.7-1.2 m/sec.
In options with forced circulation, it is advisable to use pipes of small diameter. In a circuit with a small volume, it is faster and easier to heat water, which increases the efficiency of the design. Installing and masking thin parts is much easier than thick counterparts.
Forced circulation in the systemSource eco-kotly.ru
The cross-section of networks with forced circulation often depends on the heating connection diagram. The size for radial connection from equipment to pipes is 19 mm, for single-pipe and double-pipe - 25 mm. The parameter is not final and is calculated based on the characteristics of the boiler and cottage.
Recommendations for choosing and connecting radiators
An ordinary homeowner, going to a heating equipment store and seeing a wide selection of different radiators there, can conclude that choosing batteries for his home is not so easy. But this is the first impression; in fact, there are not so many varieties of them:
- aluminum;
- bimetallic;
- steel panel and tubular;
- cast iron
Sectional batteries made of aluminum alloy have the best heat transfer rates; bimetallic heaters are not far behind them. The difference between the two is that the former are made entirely of alloy, while the latter have a tubular steel frame inside. This was done for the purpose of using the devices in centralized heat supply systems of high-rise buildings, where the pressure can be quite high. Therefore, installing bimetallic radiators in a private cottage makes no sense at all.
It should be noted that heating installation in a private home will be cheaper if you purchase steel panel radiators. Yes, their heat transfer rates are lower than those of aluminum ones, but in practice you are unlikely to feel the difference. As for reliability and durability, the devices will successfully serve you for at least 20 years, or even more. In turn, tubular batteries are much more expensive, in this respect they are closer to designer ones.
Steel and aluminum heating devices have one useful quality in common: they lend themselves well to automatic control using thermostatic valves. The same cannot be said about massive cast iron batteries, on which it is pointless to install such valves. This is due to the ability of cast iron to heat up for a long time and then retain heat for some time. Also because of this, the rate of heating of the premises is reduced.
If we touch on the issue of appearance aesthetics, then the cast-iron retro radiators currently offered are much more beautiful than any other batteries. But they also cost incredible amounts of money, and inexpensive Soviet-style accordions MS-140 are only suitable for a one-story country house. From the above, the conclusion suggests itself:
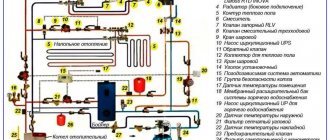
Heating systems
To correctly calculate the diameter of the pipes, you need to take into account the wiring diagram. Resistance affects the parameters of heating equipment and the characteristics of parts (section, material). The cottage uses 2 types of heating systems.
Two-pipe
The heating option with a vertical riser for the placement of pipes can be either upper or lower. Two elements are connected to each radiator: for supplying hot moisture and removing cold moisture. Horizontal wiring is:
- dead end;
- parallel;
- radial (collector).
The maximum temperature for polymers is 95 C, for steel – 130 C. A long utility network with a large amount of coolant works only with forced circulation. Understanding which circuit you are using, it is easy to calculate the total length, speed delays at the joints (bends) and obtain the required resistance.
Advantage of the scheme in a cottage Source 1-teplodom.ru
Proper selection of the diameter of the heating pipe will ensure uniform heating of the batteries. Professionals often prefer polymer parts with a cross section of 25 and 20 mm. Large elements are used as a circuit, smaller ones are used as outlets to radiators. In a compact private house, the main network is assembled from 20 mm, the pipes are made from 16 mm.
Knowing the number of square meters of housing, it is easy to determine the power of the heating equipment and the diameter of the pipes. In a boiler with high productivity, elements with a large cross-section are used. To heat 1 m2 with ceilings of 2.5 m, you need 100 W of equipment intensity. Possible heat losses relevant for a particular region are added to the parameters.
Option with top linerSource eco-kotly.ru
The fluid speed in the pipes should vary from 0.25 to 1.3 m/sec. If the boiler has a built-in pump, then take the average flow value (0.6 m/sec). When choosing a cross-section, the cooling time of the water is taken into account, which on average is 20 C. For heating equipment with a pressure of 10 atmospheres, parts with a cross-section of 25 mm are suitable, for powerful structures of 20-25 - 32 mm.
Single-pipe
In small cottages they use the Leningradka scheme. The system consists of 1 pipe to which all radiators are connected in series. The heating circuit operates in cyclic mode. The equipment supplies hot coolant from the boiler to the batteries, and returns the cooled coolant to the apparatus for heating. The maximum temperature for metal elements is 105, for plastic - 95 C.
A one-pipe system necessarily includes devices called a safety group. Additional devices allow you to quickly reduce the increased pressure in the network, preventing pipe rupture. During installation, components are placed as far as possible from one another. The safety valve is installed just above the boiler. Temperature regulators and Mayevsky taps are installed evenly throughout the entire circuit.
Why is the scheme better Source kupisantehniki.ru
With natural rotation, water moves by gravity through the system, with forced rotation - with the help of pumps. To ensure a balanced design, the cross-section of parts in a single-pipe network often differs in different areas. If the house is one-story and compact, then components with the same diameter are taken. In tiny rooms, even with convection circulation, the size of the elements should not exceed 32 mm.
Single pipe designSource 1-teplodom.ru
What should the surface temperature of the heated floor be?
Actually, I already wrote about this in a separate article, but it would be worth repeating. The maximum maximum floor surface temperatures for rooms for various purposes are listed below
- for living quarters and work rooms in which people mainly stand: 21...27 degrees;
- for living rooms and offices: 29 degrees;
- for lobbies, hallways and corridors: 30 degrees;
- for baths, swimming pools: 33 degrees
- for rooms where active activity takes place: 17 degrees
- in rooms with limited occupancy (industrial premises), a maximum floor temperature of 37 degrees is allowed.
In the edge zones up to 35 degrees.
Boiler power
In a country house, rooms are heated using gas or electric equipment, less often - solid fuel models. Based on the size of the heated space, the power is calculated. For high-quality home heating you need 0.1 kW of thermal energy per square. Parameters may change due to climatic conditions or gentle regime up to 1.3.
The power of the boiler is affected by the material from which the walls are made and the presence of thermal insulation. Increased thermal conductivity, combined with the thinness of the partitions, increases the heat loss of a country house. Even the most efficient model will not cope with heating the building.
What to look forSource eco-kotly.ru
The quality of heating is affected by the presence of a second circuit in the boiler. When hot water is turned on for domestic needs, the performance in the utility system decreases. Designs with this option should have higher parameters than their single-circuit counterparts.
The boiler power depends on the type of fuel. Gas equipment is considered the most practical. The most expensive are electric, the most inconvenient are solid fuel. Pumps are used to optimize coolant circulation and solve the problem of air locks.
How to use tables
If you don’t know what diameter of pipes is needed for heating a private house, you can use the tips. Manufacturers have developed special tables to help calculate the required parameter. The size depends on the heat volume, hot water speed and degree.
For two-pipe version
For clarity, let’s consider calculating the cross-section of pipes for heating a cottage consisting of two floors. Polypropylene models are used for the circuit, and the boiler operating mode is 80/60 with a temperature difference of 20 C. The heat loss of the building is 38 kW. It takes 20 kW to heat the lower rooms, and 18 kW for the upper rooms. In the tooltip, the data is indicated in W.
In the table, the most acceptable speed of hot water movement is marked in pink. The first step is to determine the location from the boiler to the first turn (branch). All liquid passes through the line, so the volume remains initial (38 kW). In the hint you need to find a line along which they reach the zone with a suitable shade and go up. Of the two diameters of 50 and 40 mm, take the smaller one.
After separation, the flows go to the first (20 kW) and second (18 kW) floors. In the table, use the pink marker to search for the required parameters. As a result, a section of 32 mm is obtained, with the help of which both branches are separated.
The circuit is divided into two parts with the same load. On the lower tier there is a double wing, 10 kW each (20 kW). In the upper rooms the branching is already 9 kW (18 kW). The hint searches for a suitable value for both solutions. The resulting diameter is 25 mm. On the first floor, the cross-section is reduced to 20 mm after 2 batteries, on the second floor - after 3.
When calculating heating data, the information at the boiler outlet is important. For reverse flow, the characteristics of the pipes do not change. Each manufacturer has its own tables, and the one discussed in the description is an example for understanding the algorithm of actions.
For single pipe system
The principle of working with hints is similar to that described in the previous subsection, but only the data structure changes. In the table, the acceptable speed of the hot liquid is colored blue, and the power parameters are placed in the header. As a sample, a single-pipe circuit with forced circulation is used for a one-story house with 6 batteries.
To calculate the size of pipes for heating systems, the internal cross-section of the parts is calculated. When entering the network, energy is supplied from the boiler with a power of 15 kW. In the hint, in the area with optimal movement, data close to 15,000 units are sought. As a result, two values are obtained (20 and 25 mm), from which the smaller is selected.
Upon entering the first battery, the load is reduced to 12 kW. In the blue area of the table, the required parameters are found and a diameter of 20 mm is obtained. By the third radiator, the power decreases to 10.4 kW. In the light blue field, a section of 20 mm is determined.
How to correctly calculate the diameterSource tut-proremont.ru
By the fourth battery, the thermal load decreases by 2 kW. In the table with data of 8.5 kW, the recommended pipe size is 15 mm. The parameter is repeated in the fifth design; for the sixth you can take 12 mm.
For metal circuit
When working with steel and copper, you will have to take into account the heat loss that occurs through the walls of the pipes. If the utility network is compact, then a small loss is practically not felt. The longer the contour, the more noticeable the cold. An incorrectly selected diameter will cause low temperatures in the batteries.
Heat loss for a steel pipe with a cross-section of 40 mm and walls of 1.4 mm is calculated using the formula:
Q=k*3.14 (tв-tп).
The “K” value is the linear heat transfer coefficient, which for a metal part is 0.27 W. The parameters in brackets are the water temperature (80 C) and room air temperature (22 C). If we plug in the circuit data, we get 49 W/s. For every meter of system, up to 50 W of energy is lost. In an extended network, losses can become critical, so the shortcoming is neutralized by the correct section.
Tables calculating the diameter can be found on the manufacturer’s website. When marking pipes, external or internal parameters are indicated. Professionals recommend averaging the data, adding 5% error.
For natural circulation
Designs with convection movement of hot water work due to the difference in pressure and temperature at the inlet and outlet of the boiler. The liquid circulates due to gravity, which is enhanced by the pressure of the coolant. For the natural type, pipes with a suitable diameter are needed. The more moisture spins in the system, the stronger the speed. If the cross-section is exceeded, the equipment spends more energy and time on heating, which reduces efficiency.
The convection type of water movement is suitable for compact country houses with a short heating circuit. The design must maintain speed within 0.4-0.6 m/sec. To obtain the cross section, the parameters must be calculated using the formula.
Explanation for searching for a sectionSource tut-proremont.ru
Subtleties with definition
It is impossible to make a scrupulous calculation of the pipe cross-section. You must choose one of several versions. Reason: Different methods are suitable to achieve the same effect. That is, the task arises of supplying the radiators with the required volume. In this case, the elements should heat up evenly.
If work is carried out with a technology that has forced circulation, pipes, a coolant and a pump are used. There are two versions of actions to calculate the diameter of a heating pipe:
- Arrange pipes with a smaller diameter. Then the supply of coolant occurs at a significant speed.
- Create a technology with larger cross-section pipes, but with slower movement.
The first version is more popular. Causes:
- Reasonable prices for pipes of smaller diameters.
- Convenient work with such pipes.
- When laid open, these pipes stand out less.
- When embedded in floors or walls, pipes require small-sized grooves.
- With a modest diameter, less heat is concentrated, resulting in reduced inertia and fuel savings.