Wood is a rather complex material in its chemical composition.
calorific value of firewood
Why are we interested in chemical composition? But combustion (including the burning of wood in a stove) is a chemical reaction of wood materials with oxygen from the surrounding air. The calorific value of firewood depends on the chemical composition of a particular type of wood.
The main chemical binders in wood are lignin and cellulose. They form cells - peculiar containers, inside of which there is moisture and air. Wood also contains resin, proteins, tannins and other chemical ingredients.
To burn brightly and for a long time!
A bright flame and a minimum of smoke can only come from dry firewood.
If you follow the tips for using aspen firewood given in this article, all year round you will be able to enjoy a natural, bright fire that will warm and decorate the space around you. For owners of natural fireplaces or stoves, choosing firewood is a long and responsible process, because the comfort and convenience of all household members depends on it.
The right choice will help you enjoy smoke without soot and the unpleasant “burnt” smell that often happens when using synthetic or chemical fuel for fireplaces. Natural firewood will help not only keep you warm, but also maintain your health, because it’s not for nothing that our ancestors loved to heat the bathhouse “black” so that the smoke would be rich so that it could be inhaled, which is very useful.
Folk tales
Superstitions and beliefs circulate among the people. For example, it is believed that it is better to prepare firewood for a bath during the waning moon. Moreover, the thinner the sickle, the stronger the logs are endowed with healing powers. Once upon a time, the Slavs believed that people who left the world turned into maples in their lives. The appearance of its leaves is akin to open palms, and its branches represent hands raised to the heavens. For this reason, they never fired maple stoves.
In the old days, residents of the Tambov province heated their stoves exclusively with apple trees to keep the house warm throughout the winter, including especially frosty days. Whether to believe all this or not is everyone’s business, but what happened was what happened. What do you, dear readers, think: what kind of firewood is better for a stove, bathhouse or fireplace?
We build a furnace with high efficiency
Let's look at examples of building furnaces from scratch, in which the approach to increasing efficiency was brilliantly implemented.
Kuznetsov brick bell furnace
The efficiency of this furnace is increased by complete and hot combustion of fuel, secondary combustion of pyrolysis gases, free movement of gases, and a large heat exchange area. The large mass of bricks perfectly accumulates and retains heat. The bell-type design is popularly called “greedy” - the temperature of the exhaust gases is lower than that of conventional channel furnaces.
Softwood firewood: pine, spruce, larch
By the characteristic crackling of the logs, which literally caresses the ear, and the bright scattering sparks, you can determine the combustion of pine logs. They give off a lot of heat, but burn out quite quickly. But many shortcomings are quickly forgotten thanks to the unique resinous aroma that comes from burning pine or spruce firewood.
It is worth noting that pine logs produce more heat than spruce logs. Largely due to the high content of resinous substances, due to which the above-mentioned aroma is released. Pine and spruce, it produces an equally invigorating effect. In addition, it can have a tonic effect on the organs of the upper respiratory tract.
Of course, no one will specifically grow fruit trees for the sole purpose of using them for firewood. However, there is still an apple, pear, plum or cherry tree on the site. Over time, you can collect a lot of branches and twigs, which you can put into the firebox. Some people make fires right away, but it would be much more correct to carefully cut them and put them in a woodpile.
It costs nothing to saw and chop firewood; the apple tree is the leader in terms of heat release, and there is practically no smoke. But this choice is more of an aesthetic nature.
Deciduous wood is more often used to fire a bathhouse than coniferous firewood. Ash, alder, birch, and fruit trees are suitable for these purposes.
- Alder, numbering more than a dozen species, was used in Rus' to heat baths for the nobility. Such firewood is easy to dry without even creating special conditions for it. The main thing is that the logs were prepared from wood that grew on not very wet soil. Alder firewood does not lose its natural aroma for a long time. The advantages of alder firewood are rapid combustion, a large amount of heat, and no smoke due to the low resin content. The aroma of alder has a beneficial effect on health, helping to overcome colds, depression and fatigue. Like aspen, alder firewood is used to clean soot from chimneys. Alder firewood is considered an excellent option for cooking barbecue. You can read more about this in the article “Features of choosing firewood for barbecue.”
- Linden firewood is slow to ignite but produces an effective, lasting heat. The steam from the linden tree is considered healing, especially if you add honey to the oven and smear it on the patient’s body. This firewood is considered the best for a bathhouse, but has one drawback - it can be stored for no more than two years.
- High-quality oak firewood, selected from middle-aged trees, is considered a prestigious type of fuel. The steam from oak logs is tart, smells like forest and helps against some chronic diseases; it is recommended for maintaining the health of children. Oak wood is ideal for burning fireplaces.
- Birch firewood has antibacterial properties. The steam in a bathhouse, heated with birch firewood no older than two years, is light, aromatic, good for the respiratory system, and helps fight colds.
Birch wood is hard, and in terms of heat transfer it is second only to oak, significantly surpassing aspen and pine. To get rid of soot clogging the pipe, aspen logs are added to the stove after burning with birch firewood.
- Willow is an affordable, rapidly renewable wood. It burns hot, burns out quickly, does not smoke, and requires significant supplies.
- Wood from fruit trees - cherries, pears, apple trees, plums - is a fairly common option for heating a bathhouse. Such firewood is fragrant, burns hot and smokeless, especially apple wood. Essential oils are used to enhance and change the aroma. If you can use old fruit trees with rotten cores to heat a house, then this option is not suitable for a bathhouse.
After choosing the type of wood and cutting the logs, you need to take care of their proper drying and subsequent storage. To do this, set up a woodpile in the open air or in a shed near the bathhouse. Firewood is laid upside down and not directly on the ground, but on a stand made of beams and poles. You can read more about the methods and features of drying lumber and firewood in the article “How to dry wood correctly.”
Oak - fortress of spirit
Which firewood takes the longest to burn? Undoubtedly oak! They are distinguished by their great strength and density. It’s not for nothing that experts jokingly classify this breed as an elite variety, and only then it is valued as a type of fuel. Due to these properties, oak logs maintain heat at the required level, give strong heat, and the negative impact of various external factors does not in any way affect them.
The smell emanating from the firewood is so pleasant, tart and soft that you can feel the breath of the forest expanses. Like birch, oak can have a beneficial effect on the human body, especially on the psyche. Also promotes relaxation and improves immunity.
The tree is considered to have a long life, and it is not very easy to find wood suitable for kindling. Not just any logs are suitable for this. Firewood from young plants will not produce much heat, but when burning old ones, a decent amount of ash is formed, the air becomes excessively heavy - not every bathhouse guest will be able to withstand it.
Home heating with wood from middle-aged trees is excellent - they provide as much heat as necessary, and even more. But they are quite difficult to find, so oak is used quite rarely as a fuel, and it also grows more slowly.
For reference: once upon a time, good and strong ships were built from oak. Nowadays it is believed that truly tasty and juicy pizza can only be prepared using oak wood. They are also more suitable for lighting a fireplace, the only problem is that such wood is difficult to split.
Softwoods
The softer the wood, the more ash remains after it burns out. This imposes certain obligations on the stoker. First, you need to clean the firebox more often. Secondly, periodically turn the firewood over with a poker to clear the ash from the firebrands, freeing up oxygen for even burning. But this does not mean that all soft breeds are bad and should not be used. For example:
- spruce - easily chipped, great for melting, but can spark when burning;
- pine - has the same properties as spruce, and burns well even when freshly sawn and damp;
- alder - hard to prick, but easy to saw across the grain, burns very well.
Another important property of alder is that when burning it practically does not form soot. Larch, despite its softness, is considered one of the best types of fuel for stoves and fireplaces, and in terms of heat transfer it is equal to oak and apple tree
Aspen wood is often specifically sought for for a fireplace. It crackles pleasantly and will quickly heat up even a large room. Coniferous trees are also often used for baths, since the phytoncides they release during combustion significantly increase the benefits of this procedure and are an excellent prevention of colds and respiratory diseases.
Additional factors for improving heating in the house
You can improve the heating of your home not only by improving the firebox and heat removal. By reducing the heat loss of a building, more significant results can be achieved. Installing high-quality windows, insulating floors and walls, installing an air recirculation and recovery system is sometimes cheaper than redoing the heating system.
When improving heating, you should use only proven methods for improving fuel combustion. In this case, it is better to calculate the savings and funds spent on refurbishment.
Calorific value of wood table for all species
The calorific value of wood depends on the species, age of the tree, growing conditions, place in the trunk, etc. There are higher, or absolute, calorific value, which expresses the amount of heat released during complete combustion of 1 kg of wood, the working calorific value of wood, taking into account humidity and ash content of wood and specific calorific value, which is the ratio of working calorific value to the volumetric weight of wood. Specific calorific value gives a practical characteristic of the heating value of wood.
The gross calorific value of wood is defined as the sum of the calorific values of individual chemical elements obtained during their free combustion. For wood, it can be approximately determined using the formula of D. I. Mendeleev:
Q = 81C+ 300H -26O,
where C, H and O are the percentage content of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen in wood.
An accurate determination of the gross calorific value of wood is carried out in the laboratory by calorimetry. furniture repair at home
Table 3 - Working and specific calorific value of various wood species (according to Arnold)
| Wood species | Air-dried wood (20% moisture content) | Comparative calorific value of wood of various species in relation to the calorific value of hornbeam wood | ||
| working calorific value, cal | volume weight | specific calorific value, Kcal | ||
| Birch | 2240 | 0,622 | 1389 | 0,89 |
| Beech | 2133 | 0,591 | 1258 | 0,80 |
| Elm | 2341 | 0,547 | 1282 | 0,84 |
| Hornbeam | 2148 | 0,769 | 1654 | 1,00 |
| Oak | 2229 | 0,693 | 1538 | 0,99 |
| Spruce | 2274 | 0,472 | 1068 | 0,66 |
| Willow | 2316 | 0,487 | 1128 | 0,71 |
| Horse chestnut | 2309 | 0,575 | 1317 | 0,80 |
| Maple | 2277 | 0,659 | 1503 | 0,91 |
| Linden | 2382 | 0,439 | 1046 | 0,57 |
| Larch | 2307 | 0,474 | 1084 | 0,66 |
| Alder | 2244 | 0,500 | 1122 | 0,67 |
| Aspen | 2329 | 0,430 | 1002 | 0,65 |
| Fir | 2364 | 0,555 | 1312 | 0,70 |
| Pine | 2330 | 0,550 | 1282 | 0,67 |
| Poplar | 2268 | 0,366 | 839 | 0,50 |
| Ash | 2191 | 0,644 | 1403 | 0,92 |
| Average: | 2276 | 0,551 | 1248 | 0,76 |
The calorific value of wood is largely dependent on humidity. As the moisture content of wood increases, its calorific value decreases.
144b8fd5cbdb7f64ab4ed296fa027f9a.jpe
The working calorific value in Kcal can be determined using the empirical formula of Prof. Nadezhdina:
QPc =4370—50 W for air-dried wood
And
QPB = 3870—45 W for driftwood,
where W is the relative humidity of wood in percent, or can be determined from the diagram (Fig. 10).
Rice. 10. Nomogram for determining the calorific value of wood of different moisture content.
Rice. 10. Nomogram for determining the calorific value of wood of different moisture content.
Wood with a moisture content of 70% practically does not burn.
The heat output, or the temperature developed by wood during combustion (combustion temperature), is theoretically equal to 1547°. Practically, taking into account losses (cooling of the flame by excess air, heat loss, etc.), the heat output ranges from 700 to 1200° and on average is taken to be 1000–1025°.
The steam-producing capacity of wood, i.e. the amount of water per kg converted into steam during the combustion of 1 kg of wood, is small and on average equal to 3.8 kg (see Table 4).
Specific heat of combustion of liquid fuels (alcohol, gasoline, kerosene, oil)
A table is given of the specific heat of combustion of liquid fuel and some other organic liquids. It should be noted that fuels such as gasoline, aviation kerosene, diesel fuel and oil have a high heat release during combustion.
The specific heat of combustion of alcohol and acetone is significantly lower than traditional motor fuels.
In addition, liquid rocket fuel and ethylene glycol have a relatively low calorific value - with complete combustion of 1 kg of these hydrocarbons, an amount of heat will be released equal to 9.2 and 13.3 MJ, respectively. Specific heat of combustion of liquid fuels (alcohol, gasoline, kerosene, oil)
| Fuel | Specific heat of combustion, MJ/kg |
| Acetone | 31,4 |
| Gasoline A-72 (GOST 2084-67) | 44,2 |
| Aviation gasoline B-70 (GOST 1012-72) | 44,1 |
| Gasoline AI-93 (GOST 2084-67) | 43,6 |
| Benzene | 40,6 |
| Winter diesel fuel (GOST 305-73) | 43,6 |
| Summer diesel fuel (GOST 305-73) | 43,4 |
| Liquid rocket fuel (kerosene + liquid oxygen) | 9,2 |
| Aviation kerosene | 42,9 |
| Kerosene for lighting (GOST 4753-68) | 43,7 |
| Xylene | 43,2 |
| High sulfur fuel oil | 39 |
| Low sulfur fuel oil | 40,5 |
| Low-sulfur fuel oil | 41,7 |
| Sulphurous fuel oil | 39,6 |
| Methyl alcohol (methanol) | 21,1 |
| n-Butyl alcohol | 36,8 |
| Oil | 43,5…46 |
| Methane oil | 21,5 |
| Toluene | 40,9 |
| White spirit (GOST 313452) | 44 |
| Ethylene glycol | 13,3 |
| Ethyl alcohol (ethanol) | 30,6 |
Subtleties and nuances
- The worst thing is if you have damp aspen firewood. This type of wood produces a small amount of heat, so aspen firewood will be very difficult to light. The logs will slowly smolder when exposed to temperature, releasing very little heat.
- A good option for quickly kindling raw logs is birch or spruce. Despite the fact that these tree species emit a lot of soot and soot when burned, they are optimal for quick kindling. The fire catches on the chips and birch bark in literally a matter of seconds.
- An original way to quickly dry wood was invented by our ancestors. Salt should be poured in large quantities onto wet firewood. The salt will draw out some of the moisture, and the firewood will become usable.
- If we light a fire in nature and we have flammable liquids in our arsenal, for example, diesel fuel, gasoline, kerosene, then it is quite possible to pour these compounds on the wood chips. If we want to use flammable liquids in the stove, we can moisten a rag with them and place it between the logs. The characteristic odor from such liquids will disappear fairly quickly after lighting a fire.
- Some experts recommend putting an empty bottle of vegetable oil in the firebox. With its help you can quickly get the required amount of fire.
Please note that firewood is always purchased raw. It is best to do this in winter, stocking up for the next season, when equipment easily enters the forest. In this case, you will have the firewood for a whole year before using it. They must be stored in a woodpile, protected from precipitation and blown by the wind.
As you can see, there are no particular difficulties with kindling raw firewood; the main thing is to approach this issue thoughtfully and carry out the preparatory work efficiently. With a little patience, you will have a nice, intense fire that provides warmth.
Splitting and preparing firewood
Woodpile of firewood
Firewood basket
Transportation of firewood
Most firewood is in the form of a log. The technology for making logs is simple: tree trunks and thick branches are sawed into lengths of 40-60 cm () and then split with an ax in the longitudinal direction into smaller pieces with an end area of up to 100 cm². For splitting, it is more convenient to use a special splitting axe, the blade of which has the shape of a wedge with an angle of approximately 30°. A cleaver can split even the thickest logs with less impact force. When chopping with an axe, especially thick chocks, there is a high probability of the blade getting stuck in the resulting crack in the chock. Then, in order to chop or free the ax, they turn the ax over with the stuck block up and hit the other block with the butt.
The correct stance when chopping wood is to have your feet wider than your shoulders. This will prevent injury in case of a miss, unsuccessful blow or breakage of the ax. Also, for convenience, it is best to place the block at the height of a person’s belt; most often, a very thick and thick piece of round wood is used as a stand.
The “hottest” firewood is considered to be from birch, and the “coldest” is from aspen.
A firewood basket is used to carry firewood.
Calorific value of firewood: comparison table of different species
Wood is a rather complex material in its chemical composition.
calorific value of firewood
Why are we interested in chemical composition? But combustion (including the burning of wood in a stove) is a chemical reaction of wood materials with oxygen from the surrounding air. The calorific value of firewood depends on the chemical composition of a particular type of wood.
The main chemical binders in wood are lignin and cellulose. They form cells - peculiar containers, inside of which there is moisture and air. Wood also contains resin, proteins, tannins and other chemical ingredients.
What is wood moisture content and what does it affect?
A physical quantity that describes the relative amount of water contained in wood is called moisture content. Wood moisture content is measured as a percentage.
When measuring, two types of humidity can be taken into account:
- Absolute humidity is the amount of moisture that is currently contained in wood relative to completely dried wood. Such measurements are usually carried out for construction purposes.
- Relative humidity is the amount of moisture that the wood currently contains in relation to its own weight. Such calculations are made for wood used as fuel.
So, if it is written that wood has a relative humidity of 60%, then its absolute humidity will be expressed as 150%.
To calculate the calorific value of firewood at a known humidity, you can use the following formula:
Analyzing this formula, it can be established that firewood harvested from coniferous trees with a relative humidity of 12 percent will release 3940 kilocalories when burning 1 kilogram, and firewood harvested from deciduous trees with comparable humidity will release 3852 kilocalories.
To understand what a relative humidity of 12 percent is, let us explain that firewood acquires such humidity when it is dried outside for a long time.
Fuel combustion
In the case of adiabatic combustion of a combustible mixture, it is possible to determine the heat generated, as well as the composition of the products. With a known composition of fuel components, at a constant volume and pressure, it is possible to calculate the thermal effect of a chemical reaction. Thanks to thermodynamic calculation, it is possible to obtain only some information about the process: the temperature of the products, the equilibrium composition.
For a complete description of combustion, including the rate of the process, critical conditions, it is necessary to consider the relationship between the transfer of matter and energy.
When the oxidizer and fuel are pre-mixed, the process is carried out throughout the entire space; it is called volumetric combustion. In unmixed systems, diffusion combustion occurs when the fuel is separated from the oxidizer.
What types of trees should you not light in a fireplace?
It is not for nothing that there are a large number of different trees on Earth. All this is for you, friends! For your hot fires! Each type of wood has its own unique properties.
For example, beech and oak are considered “elite firewood”. The flame burns brightly and evenly. During combustion, the crackling sound is smooth and pleasant to the ear. The heat output of beech firewood is the best among other types of wood. Oak firewood has similar parameters. Their only drawback is that the cost of the logs is relatively high and there are difficulties in splitting them. But oak wood burns for a long time and practically does not emit smoke.
Apple, pear and other fruit species. Their advantage is a pleasant smell. They are used to heat living rooms, the fruity aroma of which becomes stable over time.
Linden and Poplar. Poplar is used exclusively for decorative purposes. Firewood produces little heat and burns quickly. To heat the room, you will have to add firewood every 1.5 hours. Linden logs are the same. The flame is dim, the wood produces virtually no heat or smoke.
Alder and Aspen. The firewood from these trees has a unique property. When burning, they do not emit smoke or soot. In addition to this, their fire burns away the soot inside the chimney. It is recommended, at least once every few weeks, to heat the stove with alder or aspen firewood, so as not to
prevent contamination of the internal cavity of the chimney with soot.
Firewood from coniferous trees: spruce, pine. They contain a lot of resin, which emit a lot of soot. During combustion, in addition to tar, the flue gases also contain a lot of soot, which leads to overgrowing of the internal cavity of the chimney pipe. Spontaneous combustion of soot inside the chimney is often observed, which can render the pipe unusable. So, if you still want to see your home intact when you come home, do not heat it with coniferous wood.
Material selection
Even the best qualities of wood can be negated if it is selected incorrectly for a particular type of activity. For example, it makes virtually no difference what was used for the night fire during gatherings with a group of friends. Lighting a fireplace or stove in a bathhouse is a completely different matter.
We suggest you read the material about where to store firewood Plus to everything about our article today.
For any situation, materials of various thicknesses, types and characteristics are selected
For the fireplace
Home heating can be a challenge if you load your stove with unsuitable wood. This is even more dangerous when using a fireplace, since a shining log can even lead to a fire.
The unobtrusive burning of wood and the heat emanating from the fireplace are the piquancy of the guest room
For long burning and the release of a decent amount of heat, it is necessary to give preference to oak, acacia, and also birch and walnut. To clean the chimney, you can sometimes burn aspen and alder. The density of these rocks is small, but they tend to burn soot.
To equip a high temperature in the steam room of a bathhouse, the greatest heat output from wood is needed. Moreover, you can improve your relaxation conditions if you use rocks that fill the room with a good smell, without emitting harmful substances and resins.
Read also about a potbelly stove for a bathhouse with your own hands Plus everything about our article today.
The quality and type of firewood for a bath play an important role
To heat the steam room, oak and birch logs are, of course, an excellent choice. They are solid, give good heat in a limited volume and also emphasize pleasant evaporation. Linden and alder can also provide an additional healing effect. You can only use perfectly dried materials, but not older than one and a half to two years.
For barbecue
When cooking on a grill or barbecue, the main point is not the burning of wood itself, but the formation of coals. This is actually why it is not advisable to use thin, loose branches. They can be taken exclusively for lighting a fire, and then large hard logs can be added to the combustion chamber. In order for the smoke to have a special smell, it is best to use fruit wood for the barbecue. You can combine them with oak and acacia.
For a barbecue, it is not the fire that is important, but the coals and the smell of smoke.
When using different types of wood, carefully look at the size of the chocks. For example, oak will take longer to burn and smolder than an apple tree, so it makes sense to take much thicker fruit logs.
Firewood
These are sawn or chopped pieces of wood, which, when burned in furnaces, boilers and other devices, generate thermal energy.
For ease of loading into the firebox, wood material is cut into individual elements up to 30 cm long. To increase the efficiency of their use, the firewood must be as dry as possible and the combustion process must be relatively slow. In many respects, wood from hardwoods such as oak and birch, hazel and ash, and hawthorn are suitable for heating premises. Due to the high resin content, increased burning rate and low calorific value, coniferous trees are significantly inferior in this regard.
It should be understood that the value of the calorific value is affected by the density of wood.
| Firewood (natural drying) | Calorific value kWh/kg | Calorific value mega J/kg |
| Hornbeam | 4,2 | 15 |
| Beech | 4,2 | 15 |
| Ash | 4,2 | 15 |
| Oak | 4,2 | 15 |
| Birch | 4,2 | 15 |
| From larch | 4,3 | 15,5 |
| Pine | 4,3 | 15,5 |
| Spruce | 4,3 | 15,5 |
How to increase efficiency
When designing or modifying a wood heating system at home, you should remember the basic rule - all elements must be proportionate, optimal and form a harmonious system. A huge firebox with little heat removal will reduce the level of efficiency, and vice versa, excessive heat removal will lead to operational problems.
The concept of “efficiency” means how much energy released during combustion is transferred in the form of heat to the heated room. This characteristic is influenced by a number of factors:
- Serviceability and cleanliness of the stove.
- Type of fuel burned.
- Fuel burning mode.
- Heat transfer method.
- Heat supply efficiency.
- Availability of additional fuel attachments.
Stove serviceability
A significant decrease in the efficiency of the furnace occurs when it is used incorrectly. There are different ways to burn wood, and if you burn it incorrectly, heat energy will be lost.
The soot deposited on the walls of the heat exchanger is an excellent heat insulator. To increase the efficiency of the furnace, you need to periodically, once every 2 months, clean all important parts from soot.
Attention! Soot in the furnace ducts and chimney can catch fire; do not allow deposits to accumulate in the heating system. Soot combustion is a common cause of fires!
The right fuel for your furnace
It is known that different types of wood produce different amounts of heat. You can increase the efficiency of your stove by using the right fuel. Hard types of wood - oak, acacia, ash - have a greater calorific value. In addition to density, an important characteristic is the moisture content of the firewood. Firewood with a moisture content of 15% is considered optimal, but such indicators can be achieved either by using a drying chamber, or by natural drying under a canopy for years in ventilated stacks.
Optimal combustion modes
The fuel combustion mode is also important. There are different ways to burn fuel efficiently:
- In the mode of pyrolysis decomposition and afterburning of gases.
- In optimal fast combustion mode with sufficient oxygen access.
- Layered combustion of fuel from top to bottom.
Pyrolysis mode
When burning fuel in pyrolysis mode, the efficiency of the furnace increases due to the long combustion time. The firebox is divided into two chambers - a smoldering combustion chamber, where in a slow mode the firewood decomposes into pyrolysis combustible gases, and a gas afterburning chamber. Technically it looks like this:
- Firewood is placed in the firebox; initially, combustion occurs in a hot mode with the supply of a large amount of air. This stage is necessary to create a fire cushion on the wood, as well as to warm up the chimney and the secondary afterburning chamber.
- The firebox door closes. The air supply is set to a minimum - so that there is enough for smoldering. Firewood decomposes into smoky pyrolysis gases, which pass through a hot afterburning chamber.
- The second chamber has secondary air ducts. They are aimed at a catalyst - a massive red-hot ceramic or metal object. In some furnaces, the wall of the secondary chamber acts as a catalyst.
- Relatively cold pyrolysis gases, passing through the catalyst, are heated, mixed with air and burned.
This ensures complete combustion of the wood. The efficiency of pyrolysis combustion plants can reach 85 - 90%.
WOOD SPECIES FOR BOILER FIRES
The main characteristics of firewood for heaters are their calorific qualities and combustion duration. For heating, it is good when wood burns slowly but for a long time. Firewood from deciduous trees best suits these purposes. In general, all conifers are characterized by reduced calorific value, increased smoke production and resin content. It is easiest to split rocks of medium hardness.
Specifics of combustion of various types of wood:
- Birch wood fires quickly and can burn even when damp. Disadvantage - they contain a lot of resin, which settles in the form of tar on the chimney.
- Aspen and alder - burn out without releasing soot, and in addition they help clean the chimney from burning. Aspen fires burn slowly, produce little heat, and burn quickly. Alders burn quickly, releasing a lot of heat.
- Poplar - burns well, but burns out quickly.
- Pine burns hotter than spruce due to the larger amount of resin. Easy to prick. Disadvantage: resinousness. Beech and ash are difficult to melt, but can burn when wet. They split easily (except beech wood).
- Linden ones burn well and for a long time, but they are difficult to light.
- Apple and pear trees are easy to split and burn well.
- Cedar trees take a long time to smolder.
- Cherry and elm ones smoke.
- Sycamores burn well, but are difficult to prick.
- Oak wood is one of the leaders in terms of calorific value and combustion duration. The calorific qualities of middle-aged oaks are better than those of old and young ones. A significant drawback is that it is very difficult to stab.
It is necessary to take into account the fact that the calorific characteristics of different types of wood vary significantly. Therefore, it is possible to observe fluctuations in the density of different tree species and fluctuations in the calculated coefficients
Table of calorific values of various types of wood
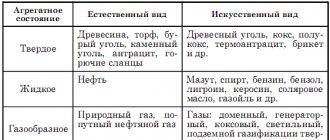
Specific heat of combustion of solid fuels (coal, firewood, peat, coke)
Of the solid fuels considered, coking coal has the highest calorific value - its specific heat of combustion is 36.3 MJ/kg (or in SI units 36.3·106 J/kg). In addition, high calorific value is characteristic of hard coal, anthracite, charcoal and brown coal.
Fuels with low energy efficiency include wood, firewood, gunpowder, milling peat, and oil shale.
For example, the specific heat of combustion of firewood is 8.4...12.5, and that of gunpowder is only 3.8 MJ/kg. Specific heat of combustion of solid fuels (coal, firewood, peat, coke)
| Fuel | Specific heat of combustion, MJ/kg |
| Anthracite | 26,8…34,8 |
| Wood pellets (pellets) | 18,5 |
| Dry firewood | 8,4…11 |
| Dry birch firewood | 12,5 |
| Gas coke | 26,9 |
| Blast coke | 30,4 |
| Semi-coke | 27,3 |
| Powder | 3,8 |
| Slate | 4,6…9 |
| Oil shale | 5,9…15 |
| Solid rocket fuel | 4,2…10,5 |
| Peat | 16,3 |
| Fibrous peat | 21,8 |
| Milled peat | 8,1…10,5 |
| Peat crumb | 10,8 |
| Brown coal | 13…25 |
| Brown coal (briquettes) | 20,2 |
| Brown coal (dust) | 25 |
| Donetsk coal | 19,7…24 |
| Charcoal | 31,5…34,4 |
| Coal | 27 |
| Coking coal | 36,3 |
| Kuznetsk coal | 22,8…25,1 |
| Chelyabinsk coal | 12,8 |
| Ekibastuz coal | 16,7 |
| Frestorf | 8,1 |
| Slag | 27,5 |
Coal
It is a natural material of plant origin, extracted from sedimentary rock.
This type of solid fuel contains carbon and other chemical elements. There is a division of material into types depending on its age. Brown coal is considered the youngest, followed by hard coal, and anthracite is older than all other types. The age of a combustible substance also determines its moisture content, which is more present in young material.
During the combustion of coal, environmental pollution occurs, and slag is formed on the boiler grates, which to a certain extent creates an obstacle to normal combustion. The presence of sulfur in the material is also an unfavorable factor for the atmosphere, since in the air space this element is converted into sulfuric acid.
However, consumers should not fear for their health. Manufacturers of this material, taking care of private customers, strive to reduce the sulfur content in it. The heating value of coal can vary even within the same type. The difference depends on the characteristics of the subspecies and its mineral content, as well as the geography of production. As a solid fuel, not only pure coal is found, but also low-enriched coal slag, pressed into briquettes.
| Type of coal | Specific heat of combustion of the material | |
| kJ/kg | kcal/kg | |
| Brown | 14 700 | 3 500 |
| Stone | 29 300 | 7 000 |
| Anthracite | 31 000 | 7 400 |
Pellets
Pellets (fuel granules) are solid fuels created industrially from wood and plant waste: shavings, bark, cardboard, straw.
The raw material, crushed to dust, is dried and poured into a granulator, from where it comes out in the form of granules of a certain shape. To add viscosity to the mass, a plant polymer, lignin, is used. The complexity of the production process and high demand determine the cost of pellets. The material is used in specially equipped boilers.
This is important to know!
Regardless of the type of trees that will be used for firewood, you need to know about some features:
- Deadlines. Of course, those logs that have already served their “allotted” time will also burn (provided that they are dry and there is no mold on them). However, most trees retain their aroma only for two years. Alder and aspen are a pleasant exception in this regard - 3 years.
- Everything has its time. In winter, the humidity of trees is at a minimum level. In this regard, the preparation of firewood must be done during this period. Drying usually takes about 12 months. However, the timing depends on the type of forest, harvesting time, storage conditions and a number of other factors. In this case, the duration may increase significantly or, conversely, decrease.
- Dimensions. Which firewood is more profitable? Of course, those with optimal sizes. And these are 40-50 cm in length and 8-10 cm in thickness. This is how they are convenient to store and are suitable for any firebox.
- Rot. Under no circumstances should you use rotten firewood. Keeping logs on the ground for a long time results in the accumulation of toxic substances released during combustion, which is not beneficial to humans. For this reason, when cutting down branches, you should immediately take the correct measures to store them. When choosing raw materials for heating among dead wood, you should not take into account long-fallen branches.
- Storage issues. Logs should be laid with the bark facing up. This will protect the firewood from accidentally entering moisture, which evaporates faster from the surface of the bark. And if you show your imagination, you can build an original woodpile to the delight and surprise of your guests.
As you can see from this material, it’s not enough to know which firewood is best for the stove
It is equally important to ensure that they are stored correctly.
Characteristics of firewood
In order to choose the right type of wood for the firebox, you need to know some of its characteristics. Firewood is distinguished by heat transfer, flammability, ash content and the amount of smoke it produces when burning.
High-quality firewood is distinguished by good flammability and heat transfer, the ability to produce a minimal amount of ash and avoid excessive smoke.
To choose exactly these, you need to pay attention not only to the type of wood, but also to its dryness, since it must contain a certain percentage of moisture. Everyone knows that logs cut from a freshly cut tree will burn poorly due to excess moisture in them.
Therefore, the preparation of firewood, and wood for outbuildings, furniture making and other needs, is usually carried out in the middle of the winter period. At this time, the trees “sleep”, and their trunks do not have such intense sap flow as, for example, in spring or summer.
Alternative fuel materials
The calorific value of specific types of firewood is very high, but far from the maximum potential. In order not to lose funds and space for storing heating material, today more and more attention is being paid to other options. The use of pressed briquettes is considered good.
The effectiveness of using briquettes is many times higher than that of firewood.
With similar loading volumes, solid wood ovens generate much more heat. A similar effect is possible by increasing the density of the material. In addition, there is a much, much lower percentage of moisture. Another plus is a slight formation of ash.
Briquettes and fuel pellets are made from sawdust and wood chips. By pressing waste, it is possible to create an incredibly dense fuel material that even the most suitable types of wood cannot match. At a high price per cubic meter of briquettes, the final savings will be a very large amount.
It is necessary to prepare and purchase combustion materials based on a meticulous analysis of their parameters. Only high-quality firewood can provide you with the essential heat without causing damage to your health or the heating structure itself.
USEFUL INFORMATION ON THE PROPERTIES OF WOOD
Accounting is carried out by the volume of firewood in stacks (woodpiles). The quality of the woodpile depends on the layout used, being considered optimal if the mass of wood is approximately 70% of the cubic capacity. The higher the specific gravity of firewood in the woodpile, the more profitable the purchase.
Below is the ratio of a cubic meter of birch firewood to competing wood:
- 1.5 cubic meters of aspen;
- 1.3 cubic meters of spruce.
- 1.2 cubic meters of pine;
- 1.1 cubic meter of alder;
- 0.75 cubic meters of oak;
Let's assume that the logs will occupy the entire volume of the woodpile, in which case the mass of a cubic meter of wood (relative humidity is taken as 20%) will be:
- oak - 725 kg;
- birch - 671 kg;
- pine - 530 kg;
- aspen - 505 kg;
- spruce - 475 kg.
The chemical components of different species are similar; wood is approximately half carbon. Therefore, the heat of combustion of wood of different species (provided the same humidity) is close and amounts to approximately 18,700 kJ (about 4,500 kcal). Fluctuations between breeds do not exceed 3-5%. At the same time, the calorific properties of logs per cubic decimeter differ and on average show the following figures:
- birch - 11000 kJ (2700 kcal);
- alder - 8500 kJ (2100 kcal);
- aspen - 7200 kJ (1750 kcal);
- pine – 7600 kJ (1850 kcal);
- spruce – 7200 kJ (1750 kcal);
- oak – 13500 kJ (3100 kcal).
The heat of combustion of 100 kg of dry firewood is approximately equal to:
- 31 kg of oil;
- 42 kg of coal;
- 54 kg of dry peat;
- 121 kg of semi-dry peat.
The main recommendation is to avoid wood that contains too much resin, so as not to clog the boiler and chimney. Otherwise, the question of what kind of wood to heat the boiler with depends on the availability of a particular wood in the place of residence of the owner of the solid fuel boiler. published econet.ru
Join us on Odnoklassniki
Main criteria
The most basic indicators for combustion material: density, humidity and heat transfer. They are all closely related to each other and determine to what extent wood burning is considered practical and useful. It is necessary to consider any of them in more detail, taking into account the various types of wood and methods of its preparation.
Firstly, what the right consumer pays attention to when ordering wood heating material is its density. The higher this indicator, the higher quality the breed is considered.
All tree species are divided into three key categories:
- low-density (soft);
- medium-dense (moderately hard);
- high-density (solid).
We recommend reading the publication about what types of firewood there are. Plus everything about this material.
Categories of wood varieties according to their density (kg/m3)
Each of them has a different density, which means the specific heat of combustion of wood. Hard varieties are considered the highest quality. They burn longer and bring out more heat. They also create a lot of coals, which keep the combustion chamber hot.
We suggest you learn information about how to chop wood correctly on this site.
Due to its own hardness, such firewood is difficult to finish, which is why some consumers prefer medium-density wood, for example, birch or ash. Their structure makes it possible to chop logs manually without much effort.
The second indicator is humidity, in other words, the percentage of water content in the wood structure. The higher this value, the greater the density, while the resource used will generate less heat with the same effort expended.
The specific heat of combustion of dry birch firewood is more productive than wet wood. It is necessary to note this characteristic of birch: it can be placed in the combustion chamber almost immediately after felling, because it is distinguished by moderate humidity. To maximize the beneficial effect, it is better to prepare the material appropriately.
The relationship between the drying level of firewood and its density for a wide variety of species
To increase the quality of wood by reducing the percentage of moisture content in it, these approaches are used:
- Fresh firewood is left under the roof overhang for a specific period of time to dry. The number of days depends on the season and ranges from 80 to 310 days.
- Some firewood is dried indoors, which increases its calorific value.
- A good option is artificial drying. The calorific value is brought to the highest level by bringing the percentage of moisture to zero, and a minimum of time is required to prepare the wood.
Heat release
Such an indicator as the heat transfer of firewood seems to summarize the previous two characteristics. Specifically, it indicates how much heat the material chosen can provide under certain conditions.
The highest heat of combustion of firewood is considered to be from hardwoods. Based on this, the situation is opposite with soft wood. Under equal conditions and natural shrinkage, the difference in readings reaches almost 100%. This is why, in order to save money, it makes sense to purchase high-quality firewood, which is much more expensive to purchase, since its production is more productive.
Calorific value of various types of wood and their density during natural drying
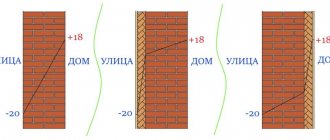
Here it is necessary to mention this property as the burning temperature of wood. It is considered the highest for hornbeam, beech and ash, more than 1000 degrees Celsius, while a lot of heat is applied at the level of 85-87%. Oak and larch are close to them, and poplar and alder stand out with the lowest indicators with a production of 39-47% at temperatures around 500 degrees.
Rare types of firewood
Good oak firewood comes from middle-aged trees; when burned, they release a pleasant tart aroma. Oak firewood is ideal not only for stoves, but also for fireplaces.
Excellent, but also one of the most expensive, is alder firewood. They burn hot, without smoke or soot, spreading a pleasant aroma.
Alder cannot be confused with any other firewood; when cut, it has a color from yellow to deep red. Perhaps this is the best firewood for a fireplace; it burns with a mesmerizing, even flame of a beautiful color. A big plus is that alder firewood lasts a long time and can be stored for future use for 5-6 years.
Rare firewood includes linden. Although linden is common, linden firewood is rare. The wood is hot, although it takes a long time to burn, but then the stove heats up very quickly. The aroma that comes from linden when burned has healing properties. A bathhouse heated with linden firewood is useful for colds, diseases of the bronchi and lungs, and has a beneficial effect on the condition of the skin.
Regardless of what type of firewood you purchase, make sure that the wood is not rotten. The benefits of rotten mushrooms are zero. In order for the wood to burn, giving off maximum heat, it must be dry. Undried wood burns poorly, produces a lot of smoke and little heat.
At the dacha or in the countryside you can’t do without them. Wood from different trees can be used as fuel. They all have their own characteristics.
Alder - a royal gift
If you just want to feel like a member of the king’s family, it’s worth getting hold of alder logs, because it’s not for nothing that people call them royal logs. They flare up quickly, emphasizing just a large amount of heat, practically no smoke appears, which also eliminates the occurrence of soot and soot. In addition, the logs burn for a very long time. In other words, the question of what kind of firewood is best to heat the stove in the house has already been resolved!
But the most important piquancy lies in the original aroma, which has a healing effect. It has long been accepted that if you heat a bathhouse using alder wood, you can once and for all forget about colds. In addition, even in the old days, alder logs were placed in the royal furnaces, as well as in the combustion chambers of other estates of poor peasants or nobles.
Freshly cut alder of a red-orange hue, thanks to which the woodpile has an original and light appearance. There is one interesting feature that everyone should know about. All the advantages described apply to trees that grew in dry areas. If the plants bloomed in the swamp, then there will be soot and unbearable heat.
Alder is very popular among fans of smoking meat or fish. Under traditional conditions, wood dries very quickly, and it retains its own healing natural properties for 3 years.
Calorific value of firewood
November 23, 2016 Vulcan-Teploenergo LLC
Fuel combustion
- This is the chemical destruction and oxidation of combustible fuel, accompanied by the release of heat and light. When fuel burns, carbon dioxide and water vapor are formed, oxygen is part of both products, water evaporates, and when the fuel is completely burned, only ash (non-hot mineral substances) remains.
The calorific value of firewood is the amount of thermal energy that one weight unit of fuel can produce during combustion. The calorific value of firewood is measured in heat units. A unit of heat is the heat that can heat 1 kilogram of water by 1 degree Celsius. The table shows the results of testing the calorific value of various types of firewood (firewood dried artificially to a constant weight).
| Breeds | Calorific value of firewood in calories |
| Birch | 4968 |
| Pine | 4907 and 4952 |
| Spruce | 4857 |
| Alder | 5047 |
| Aspen | 4953 |
| Average | 4947 |
The presence of moisture in wood reduces the calorific value of firewood (calorific value). When burning wood with 15% moisture, its productivity is approximately 3633 calories. Thus, 1 kilogram of firewood, theoretically delivering 3633 units of heat, can heat 36.3 liters of water from 0 to 100 degrees Celsius, or evaporate about 5.7 kilograms of water. In practice, however, the result is somewhat smaller.
For room heating, back in the 18th century, the Irish scientist tester Guyer proposed the following classification of firewood of different wood species when burning firewood in the same volume:
- The hottest firewood is provided by
: hornbeam, beech, winter oak, birch, mountain pine, acacia, black pine. - Hot firewood is provided by
: maple, ash, red elm, resinous larch, common pine, summer oak. - Medium
-hot: spruce, fir, noble chestnut, Siberian cedar. - Not enough
- hot firewood is provided: linden, alder, aspen, poplar, willow.
Fuel combustion is distinguished between complete and incomplete. Complete combustion occurs when there is a sufficient amount of oxidizer and ends with complete oxidation of the combustible fuel elements. If there is insufficient amount of oxidizer, incomplete combustion of carbon occurs.
The absolute heat output of a fuel is the amount of heat that is obtained during complete combustion of wood. The calorific value of firewood greatly depends on the degree of dampness.
Artificial drying of firewood increases the calorific value twice as much, depending on the amount of moisture contained in the firewood before drying. The calorific value of different types of firewood is generally almost the same, and for air-dried firewood with 10-12% moisture it is about 3850 calories, which means that one kilogram of such fuel can heat about 3850 kilograms of water by 1 degree Celsius.
In addition to assessing firewood in terms of its calorific value, it is often very important in practice to know the combustion temperature of firewood and its heat output. The temperature that wood can develop when burned
Some fuels develop thermal energy slowly when burned, while others burn quickly with a strong flame, producing high-temperature combustion products.
In addition to the type of wood, the combustion temperature of firewood also depends on other reasons.
:
- on the completeness of combustion, i.e. the amount of air flowing into the fuel;
- from losses to the surrounding space.
The combustion temperature of firewood is measured using special instruments called pyrometers. In practice, the pyrometric effect of firewood ranges from 770 to 1200 °C. A comparative test of the heat-producing ability of firewood establishes the following order, taking the maximum combustion temperature of maple as (1200 degrees).
| Breed | Heating capacity, % (100% - maximum) | Temperature °C |
| mountain maple | 100 | 1200 |
| Beech | 87 | 1044 |
| Ash | 87 | 1044 |
| Hornbeam | 85 | 1020 |
| Hawthorn | 82 | 984 |
| Winter oak | 75 | 900 |
| Larch | 72 | 864 |
| Elm | 72 | 864 |
| Summer oak | 70 | 840 |
| Birch | 68 | 816 |
| Fir | 63 | 756 |
| Acacia | 59 | 708 |
| Linden | 55 | 660 |
| Pine | 52 | 624 |
| Aspen | 51 | 612 |
| Alder | 46 | 552 |
| Willow | 40 | 480 |
| Poplar | 39 | 468 |
In practice, the following relationship was established. With limited air access, incomplete combustion produces less heat but a higher temperature; during complete combustion with the same volume of air, the amount of heat is greater at a lower temperature.
The essence of the combustion process
If you heat wood, at 120–150 ˚C it becomes dark in color. This is a slow charring, turning into charcoal. Raising the temperature to 350–350 ˚С, we will see thermal decomposition, blackening with the release of white or brown smoke. When heated further, the released pyrolysis gases (CO and volatile hydrocarbons) will ignite, turning into flames. After burning for some time, the amount of volatile substances will decrease, and the coals will continue to burn, but without a flame. In practice, to ignite and maintain combustion, the wood must be heated to 450–650 ˚C.
Wood burning process
Subsequently, the combustion temperature of heating oil in the firebox ranges from approximately 500 ˚С (poplar) to 1000 and higher (ash, beech). This value greatly depends on the draft, the design of the furnace and many other factors.
The color of wood when burning may change depending on the temperature
Birch - traditions should not be broken
Most people are inclined to believe that such firewood is the best fuel for starting a fire in a fireplace, stove or sauna. And all due to invaluable advantages:
- easy to light;
- burn for a long time;
- the flame turns out beautiful and even;
- no sparks;
- copious heat generation.
But the advantages don't end there. Since ancient times, the healing properties of birch have been known. The pleasant aroma has a beneficial effect on the human body, protecting it from colds and chronic diseases. In other words, birch firewood has a disinfecting effect, which causes approval among those who like to take a steam bath.
When burning, logs emit a small amount of carbon dioxide, and this is certainly a plus. But there is also a minus - a high concentration of tar. And this combustion product is no longer beneficial to health. In addition, soot and soot form on the walls of the stove and in the chimney. As a result, over time, not only is traction lost, but the risk of fire or carbon monoxide poisoning increases. Therefore, when choosing this firewood, it is also worth mastering the profession of a chimney sweep, as well as maintaining safety.
This is the queen of the Norwegian forests. Birch has a deservedly high rank in Norway, so high that other good varieties of trees are found in the shade and many prefer it alone.
Nevertheless, the status of the national firewood tree has a good justification: there is a lot of birch (it makes up 74% of all deciduous trees), and it grows large and even. The exception is mountain birch, which can be tortuous and difficult to fit into small ovens. But birch, growing in valleys and lowlands, if the trees are dense, forms a long trunk without branches.
But birch also has its own requirements: it needs to be well dried and quickly deteriorates if it is attacked by fungus and mold. If an undried birch tree is left lying on the ground, it will quickly rot.
Birch grows most actively until 50 years old and rarely lives more than 200 years. Downy birch can grow up to 20 meters, silver birch - up to 30 meters. The average density of wood is 500 kilograms of dry raw materials per cubic meter.
Heat removal optimization
You can increase the efficiency of your heating system by removing a large amount of heat and transferring it into the room. You can do this in two ways:
- Infrared radiation - from a burning flame or hot walls.
- Heating air or water in the firebox.
Hearths were traditionally heated with open flames in Europe. A fashionable fireplace has a low efficiency, but it only uses infrared radiation. The light of a burning flame in conventional stoves is used to heat the walls of the firebox. In most cases, heating the firebox is not beneficial. You can use part of the heat emitted during bright combustion with a transparent door of a large firebox. You won't be able to use plain glass - it might break. Heat-resistant glass is inserted into the doors.
Heating-type stoves have proven to be effective. The Winter Palace, the Hermitage, and the Arsenal were heated by Uttermark stoves. The burning fuel heated the pipes in which the air moved. Such heating made it possible to obtain fantastic results in terms of speed and efficiency. By laying dry pipes in the firebox, you can quickly warm up the room with dry warm air. In residential premises, you can use forced air supply, influx from the street and humidification. This way you can control not only the temperature, but also the humidity, as well as the amount of carbon dioxide. The downside is the difficulty of implementation in ready-made brick kilns.
By inserting a central heating circuit into the furnace, you can increase heat output and effectively transfer heat throughout the building. In this case, an increase in heating efficiency is achieved by increasing the heat exchange area; less heat escapes into the pipe.
Exotic
As you know, there are quite a lot of tree species, and to list all their types, you could write a thick book, or even more than one.
Therefore, in addition to the varieties listed, it is worth touching on at least a few more:
- Elm. It produces a lot of smoke, is difficult to split and takes a long time to ignite.
- Poplar. Like firewood for a stove - nothing at all. They prick easily, just scatter sparks and burn quickly.
- Beech. It is also difficult to light and split, but can be used raw.
- Fir. Like poplar, it is easy to prick and ignite, but you cannot do without a lot of smoke and sparks.
- Sycamore. Wood is easy to kindle, but difficult to split.