Expanded polystyrene boards, colloquially referred to as polystyrene foam, are an insulating material, usually white. It is made from thermally expanded polystyrene. In appearance, the foam is presented in the form of small moisture-resistant granules; during the melting process at high temperatures, it is smelted into one whole, a slab. The sizes of the granule parts are considered to be from 5 to 15 mm. The outstanding thermal conductivity of 150 mm thick foam is achieved due to a unique structure - granules.
Each granule has a huge number of thin-walled micro-cells, which in turn increase the area of contact with air many times over. We can say with confidence that almost all polystyrene foam consists of atmospheric air, approximately 98%, in turn, this fact is their purpose - thermal insulation of buildings both outside and inside.
Everyone knows, even from physics courses, that atmospheric air is the main insulator of heat in all thermal insulation materials; it is in a normal and rarefied state, in the thickness of the material. Heat-saving, the main quality of polystyrene foam.
As mentioned earlier, polystyrene foam is almost 100% air, and this in turn determines the high ability of polystyrene foam to retain heat. This is due to the fact that air has the lowest thermal conductivity. If we look at the numbers, we will see that the thermal conductivity of polystyrene foam is expressed in the range of values from 0.037 W/mK to 0.043 W/mK. This can be compared with the thermal conductivity of air - 0.027 W/mK.
While the thermal conductivity of popular materials such as wood (0.12 W/mK), red brick (0.7 W/mK), expanded clay (0.12 W/mK) and others used for construction is much higher.
Polystyrene foam provides a high level of energy saving due to its low thermal conductivity. For example, if you build a wall of brick with a thickness of 201 cm or use a wood material with a thickness of 45 cm, then for foam plastic the thickness will be only 12 cm for a certain amount of energy savings.
Therefore, polystyrene foam is considered to be the most effective material among the few for thermal insulation of external and internal walls of a building. Residential heating and cooling costs are significantly reduced through the use of polystyrene foam in construction.
The excellent qualities of polystyrene foam boards have found their application in other types of protection, for example: polystyrene foam, which also serves to protect underground and external communications from freezing, due to which their service life increases significantly. Polystyrene foam is also used in industrial equipment (refrigerators, refrigerators) and in warehouses.
Why is thermal insulation needed?
The relevance of thermal insulation is as follows:
- Keeps you warm in winter and cool in summer.
Heat loss through the walls of a typical multi-storey residential building is 30-40% . To reduce heat loss, special thermal insulation materials are needed. The use of electric heaters in winter contributes to additional energy costs. It is more profitable to compensate for these costs by using high-quality thermal insulation material, which ensures heat retention in winter and coolness in the summer heat. At the same time, the cost of cooling the room with air conditioning will also be minimized.
- Increasing the durability of building structures.
In the case of industrial buildings using a metal frame, insulation helps protect the metal surface from corrosion, which is the most detrimental defect for this type of structure. And the service life of a brick building is determined by the number of freeze/thaw cycles. The impact of these cycles is perceived by the insulation, because the dew point is located in the thermal insulation material, and not in the wall material.
Such insulation allows you to increase the service life of the building many times.
- Noise insulation.
Protection against increasing noise levels is achieved by using such noise-absorbing materials (thick mattresses, sound-reflecting wall panels).
- Increasing the usable area of buildings.
The use of a thermal insulation system makes it possible to reduce the thickness of external walls, while increasing the internal area of the building.
Insulation technology
The ease of cutting and laying the material has ensured its unprecedented popularity among all developers. If you make proper calculations, you can create a comfortable indoor microclimate.
Which sides to mount on?
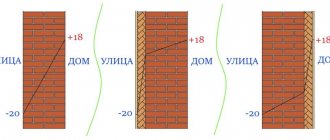
Before starting insulation, you should immediately determine where and on which side the insulation will be located. It is not profitable to install slabs indoors. This is due to the fact that the wall will cool down greatly, and much more insulation will be required to achieve a normal result. In addition, the dew point in this case will be at the junction of the wall/foam, and this is fraught with the development of mold.
If you install the insulation material outside, the dew point will fall on the insulation material. But there is no moisture in it, and therefore condensation will not form. The wall will warm up from the inside and will not get wet, and this will increase the service life of the structure insulated with polystyrene foam. When the material is used to insulate an attic, condensation will form in the attic space, as it will be between the roofing material and the insulation.
Calculation of the required thickness
Every region has its own standard of thermal resistance. The indicator is a constant value and is denoted by R. For a sample calculation, take the value as 2.8 m2*K/W. The foam thickness is calculated using the following formula:
R=R1+R2
R1 represents the wall, and the foam is taken to be R2. For brick walls, the optimal thickness of polystyrene foam is from 50 to 60 cm with external and internal finishing, as well as a layer of waterproofing.
Cutting
The material should be cut only with a well-sharpened painting knife. The tool must be properly prepared for use. If the blade is dull, you will have a lot of debris and it will be difficult to remove it - the polystyrene particles create a static charge and will “stick” to various surfaces. The sheets should be cut along a ruler. You can replace the ruler with a building level. Use a wooden plane for cutting.
Installation of polystyrene foam under plaster
When insulating and finishing the facade of a house, they use the technology of installing slabs on glue and umbrella dowels. The top of the material can be finished with ordinary or decorative plaster. Pre-seal the gaps and use gluing plaster mesh.
It is also important to level the walls before installing the panels. As a result, the material, which is correctly laid, will create a perfectly flat surface. Sometimes, before laying polystyrene foam PSB-S-25, the wall is first finished with plaster, and then the slabs are fixed.
Creating a frame
Sometimes they use the technology of installing foam plastic panels between the beams, which are located horizontally, and a vertical sheathing is created on them. If gaps appear between the bars and slabs, they need to be blown out with foam.
This method is also used for gypsum plasterboard partitions, in which insulation is placed between the profiles. But in this case, the material should be used as a heat insulator. Since wood itself is an ideal heat insulator, installing foam plastic between the beams will be the optimal solution to eliminate heat loss at home.
When choosing metal sheathing, this option will not work. In this case, the insulation should be laid under the frame. To do this, we screw the brackets that will secure the metal profiles to the surfaces of the ceiling or walls.
How to choose the right insulation?
When choosing insulation, you need to pay attention to: affordability, scope of application, expert opinion and technical characteristics, which are the most important criterion.
Basic requirements for thermal insulation materials:
- Thermal conductivity.
Thermal conductivity refers to the ability of a material to transfer heat. This property is characterized by the coefficient of thermal conductivity, on the basis of which the required thickness of the insulation is taken. Thermal insulation material with low thermal conductivity is the best choice.
Also, thermal conductivity is closely related to the concepts of density and thickness of insulation, so when choosing, you need to pay attention to these factors. The thermal conductivity of the same material can vary depending on density.
Density insulation material. Based on density, materials are divided into: extra light, light, medium, dense (hard). Lightweight materials include porous materials suitable for insulating walls, partitions, and ceilings. Thick insulation materials are better suited for insulating the outside.
Foam composition
To make expanded polystyrene, polystyrene itself or styrene copolymers are used. Here you need to take into account these substances are environmentally friendly and chemically neutral. This allows you to use polystyrene foam even as food containers! Also, fire retardants are added to SPB-S foam, which makes the material difficult to burn, significantly increasing its fire safety without compromising the physical properties of the insulation.
Despite its impressive history, foam plastics are excellent modern thermal insulation building materials, which in their practical physical and chemical characteristics are an order of magnitude superior to materials for similar purposes.
Table of thermal conductivity of materials
| Material | Thermal conductivity of materials, W/m*⸰С | Density, kg/m³ |
| Polyurethane foam | 0,020 | 30 |
| 0,029 | 40 | |
| 0,035 | 60 | |
| 0,041 | 80 | |
| Expanded polystyrene | 0,037 | 10-11 |
| 0,035 | 15-16 | |
| 0,037 | 16-17 | |
| 0,033 | 25-27 | |
| 0,041 | 35-37 | |
| Expanded polystyrene (extruded) | 0,028-0,034 | 28-45 |
| Basalt wool | 0,039 | 30-35 |
| 0,036 | 34-38 | |
| 0,035 | 38-45 | |
| 0,035 | 40-50 | |
| 0,036 | 80-90 | |
| 0,038 | 145 | |
| 0,038 | 120-190 | |
| Ecowool | 0,032 | 35 |
| 0,038 | 50 | |
| 0,04 | 65 | |
| 0,041 | 70 | |
| Izolon | 0,031 | 33 |
| 0,033 | 50 | |
| 0,036 | 66 | |
| 0,039 | 100 | |
| Penofol | 0,037-0,051 | 45 |
| 0,038-0,052 | 54 | |
| 0,038-0,052 | 74 |
- Environmentally friendly.
This factor is significant, especially in the case of insulating a residential building, since many materials emit formaldehyde, which affects the growth of cancerous tumors. Therefore, it is necessary to make a choice towards non-toxic and biologically neutral materials. From an environmental point of view, stone wool is considered the best thermal insulation material.
- Fire safety.
The material must be non-flammable and safe. Any material can burn, the difference is at what temperature it ignites. It is important that the insulation is self-extinguishing.
- Steam and waterproof.
Those materials that are waterproof have an advantage, since moisture absorption leads to the fact that the effectiveness of the material becomes low and the useful characteristics of the insulation after a year of use are reduced by 50% or more.
- Durability.
Comparison with PSB-S-25F (0), PSB-S-25F
So, in order to compare the quality of materials, let's determine what each subspecies is needed for. PSB-S-25 is the most popular and common material, suitable for almost everything. Option PSB-S-25F (0) is a lightweight façade option. PSB-S-25F is an ideal solution for facade finishing. There is no way to compare the material in the laboratory, so it will be based on visual and tactile differences.
- Sample No. 1 (PSB-S-25) - breaks easily, grains are large (0.2-06 cm).
- Sample No. 2 (PSB-S-25F (0)) is a lightweight version of the first sample. The break occurs without much effort, but it is felt that the material is denser than the previous sample. The grains are medium in size (0.1-0.2 cm).
- Sample No. 3 (PSB-S-25F) is an option that is intended exclusively for the facade, only it is used in high-quality SIP panels. The sample is denser than the previous two, breaks more easily, and has small grains.
As you can see, no matter what anyone says, all 3 brands are even visually and torn apart.
Advantages and disadvantages of insulation
- Polyurethane foam – by far the most effective insulation.
Types of polyurethane foam
Advantages: seamless foam installation, durability, better heat and water insulation.
Disadvantages: high cost of material, instability to UV radiation.
- Expanded polystyrene (foam) – in demand for use as insulation for various types of premises.
Advantages: low thermal conductivity, low cost, ease of installation, water resistance.
Disadvantages: fragility, easy flammability, condensation.
- Extruded polystyrene foam – durable and comfortable material, if necessary, elements of the required size can be easily cut with a knife.
Advantages: very low thermal conductivity, water resistance, compressive strength, ease of installation, absence of mold and rot, ability to operate from -50⸰С to +75⸰С .
Disadvantages: much more expensive than polystyrene foam, susceptibility to organic solvents, condensation formation.
- Basalt (stone) wool – mineral wool made on a basalt base.
Advantages: resistance to the formation of fungi, sound insulation, mechanical strength, fire resistance, non-flammability.
Disadvantages: higher cost compared to analogues.
- Ecowool – insulation made from natural materials (wood fibers and minerals). Today it is used quite often.
Advantages: sound insulation, environmental friendliness, moisture resistance, affordable cost.
Disadvantages: thermal conductivity increases during operation, the need for special equipment for installation, and the possibility of shrinkage.
- Izolon – modern insulation made by foaming polyethylene. It is one of the most popular.
Advantages: low thermal conductivity, low vapor permeability, high noise insulation, ease of cutting and installation, environmental friendliness, flexibility, light weight.
Disadvantages: low strength, need for a ventilation gap.
- Penofol - insulation that meets many requirements for the quality of insulation and insulation of various premises, as well as structures, etc.
Advantages: environmental friendliness, high ability to reflect heat, high noise insulation, moisture resistance, non-flammability, ease of transportation and installation, reflection of radiation exposure.
Disadvantages: low rigidity, difficulty in fastening the material; penofol alone is not enough as thermal insulation.
Water absorption of polystyrene foam
A rather important property of foam insulation is its non-hygroscopicity or, as they say, water absorption of foam .
Unlike mineral wool, polystyrene can be completely immersed in water for hours and still not lose its thermal insulation properties. Unfortunately, the hygroscopicity of this material is not absolute; in twenty-eight days of complete immersion, water absorption can reach up to three percent of the volume. This is, of course, a trifle, and in no way affects thermal conductivity, but water that has penetrated into the insulation can freeze at low temperatures, thereby destroying the material itself. Therefore, facades covered with polystyrene foam boards must be plastered with special reinforcing mixtures, followed by priming and painting.
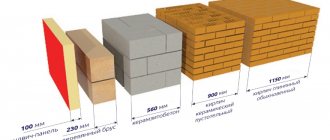
Dimensions of polystyrene foam boards produced by production
Foam sheets are produced in accordance with GOST standards. Not only the composition of the foam is regulated, but also the size of the slabs. The length of a standard foam sheet can be 100 cm, 12 cm or 200 cm. The width of the sheet is 100 cm, the thickness can be 2-5 cm.
The most popular foam is 50 mm thick. The thermal conductivity of polystyrene foam is often compared with the characteristics of other insulating materials. A foam plastic board 50 mm thick, according to SNiP of Russia, is equivalent in thermal insulation to 85 cm thick brickwork. Consequently, the use of foam plastic insulation allows you to save considerable money during construction.