Unfortunately, for many owners, using solid fuel to heat their homes still remains the only option. However, why “unfortunately”? According to some owners, no other type of heating can compare with, say, wood heating in its ability to create a truly comfortable atmosphere in the premises. And even if it is possible to switch to another energy source, they are in no hurry to do so.
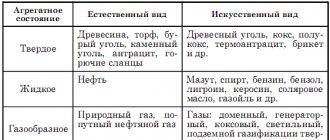
Solid fuel for a stove or boiler
So, solid fuel equipment has been and will continue to be in widespread demand. This means that its owners, real and even more so potential, should understand the diversity of this fuel. Know the advantages and disadvantages of each type available for use in your conditions. Be able to at least roughly predict consumption.
This publication is devoted to these issues. And let’s start our consideration, of course, with the most popular solid fuel in our area - ordinary firewood.
Long-burning pyrolysis boilers with a water circuit
Long-burning pyrolysis boilers with a water circuit are an excellent alternative source of energy in private homes in conditions of frequent gas supply interruptions.
A long-burning solid fuel boiler with a water circuit can operate on wood and other types of solid fuel: coal, wood waste, etc.
The main disadvantage of this type of boiler is the high price. In addition, unlike many other types of boiler equipment, a long-burning pyrolysis boiler with a water circuit is most often energy-dependent.
Not only the circulation pump and control devices are powered by electricity, but also the built-in fan: this equipment, as a rule, does not work on natural draft.
Solid fuel wood and coal boilers are second only to gas boilers in popularity. However, they have one serious drawback - fuel must be loaded several times a day.
During normal combustion of wood, the efficiency of boilers does not exceed 75%, and some of the flammable substances simply fly away into the chimney.
Long-burning pyrolysis boilers with a water circuit are much more practical and efficient.
It will not be a secret to anyone that pyrolysis heating boilers are currently very necessary and in demand heating system devices. It is for this reason that many of our people have become interested in these particular units.
A pyrolysis boiler is a special heating boiler that can use pallets, coal, wood, and other materials as fuel.
One of the main criteria, depending on which heating boilers are divided, is the type of fuel on which they operate. Thus, in today’s market you can find boilers based on pallets, coal, and wood. You can also find so-called universal boilers for yourself.
The most common at the moment are wood-burning solid fuel boilers, which have many advantages. The first is that fuel is considered the most affordable. It should also be noted that such boilers are sold at reasonable prices.
A distinctive feature of pyrolysis boilers is control of the oxygen level in the combustion chamber, and accordingly control of the temperature and rate of fuel combustion. A solid fuel pyrolysis boiler will ensure your independence from gas and electricity, since the costs of these energy sources significantly exceed the cost of solid fuel.
CALCULATION OF THE COST OF EXPENSES FOR SOLID FUEL
As an example of calculating costs for solid fuel, let’s take firewood from wood, whose calorific value is 2716. The calculation will be carried out using a simplified formula:
V = 24 * Q / (q * 0.01efficiency)
- 24 – number of hours per day;
- V – amount of fuel per day;
- Q – heat load (kilowatt-hour) required for heating 300 m2;
- q is the calorific value of 1 cubic meter of wood (kW/m3), in our case 2716;
- Efficiency is the efficiency factor (%) of the boiler; for example, let’s take 80%.
V = 24*24/(2716*0.8) = 0.26 m3
Thus, to heat 300 m3 per day you will need 0.26 m3 of wood. For the heating season, which is 183 days (from October 15 to April 15), taking into account temperature fluctuations, you will need:
(0.26 m3 (daily gas consumption) x 183 days (heating season)) / 2 (taking into account temperature fluctuations) = 24 m3.
Design Features
Pyrolysis boilers are one of the types of solid fuel boilers, which have recently been in increased demand due to constantly rising prices for gas and electricity; they are also called gas generator boilers.
The main fuel for a pyrolysis solid fuel boiler is:
- wood;
- briquettes;
- wood chips;
- wood waste.
Very rarely, coal or coke is used as fuel. Pyrolysis boilers are easy to use, reliable and have a long service life. Before buying a pyrolysis boiler, you need to study the possibility of meeting strict requirements for the quality of the fuel used.
In the vast majority of cases, it is allowed to use wood with a moisture content of no more than 20%. When using wood with a large amount of moisture, efficiency decreases sharply.
The pyrolysis boiler operates on the principle of dry distillation of fuel.
With a lack of oxygen, under the influence of high temperature, dry wood decomposes into a solid residue and a volatile part (pyrolysis gas, which is subsequently mixed with hot air).
This air-gas mixture, which was formed during the pyrolysis process, is the fuel of the pyrolysis boiler. The pyrolysis combustion process is exothermic (accompanied by the release of heat).
It occurs at temperatures from 200 to 800 °C and provides heating of the air entering the combustion chamber. In this case, the fuel in the unit chamber is heated and dried, thereby minimizing the release of soot and ash.
A pyrolysis or gas generator boiler is characterized by a higher efficiency compared to traditional solid fuel equipment.
When burning high-quality fuel, the efficiency of a pyrolysis boiler is at the level of pellet boilers and long-burning boilers and reaches 90%.
Pyrolysis solid fuel boilers are used both in private houses and apartments, and for heating industrial premises.
Pyrolysis boilers are a very cost-effective type of heating equipment. The fairly high price of a pyrolysis boiler is covered by low fuel consumption.
In a conventional long-burning solid fuel unit, the coolant is heated by the heat released during fuel combustion, but pyrolysis boilers operate on a different principle.
When burning organic fuel (wood, pellets, wood briquettes and even coal) at a temperature of 400-800°C, gas is released, burning which can produce much more heat than when burning fuel.
The process of gas formation from solid fuel and subsequent combustion of the resulting gas is called pyrolysis, and units using this operating principle are called pyrolysis, or gas generator boilers.
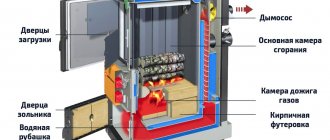
There are two chambers in the pyrolysis boiler, and combustion takes place in both:
- Combustion chamber – wood or other fuel is burned (charred).
- Afterburner – the gas emitted by the fuel is burned.
Fuel is located and ignited in the combustion chamber. Primary air is supplied to the combustion zone. When the fuel warms up to a certain temperature, gas evolution begins.
Using a smoke exhauster, gas, together with secondary air, is sucked into the afterburner chamber (it is located below the fuel level) and burns there, releasing heat.
Combustion products enter the smoke duct (flue) and enter the chimney, passing through the water jacket of the unit and heating the coolant.
As a result, firewood turns into charcoal, burning almost completely, and the smoke is cleared of unpleasant odors and carbon monoxide.
GAS
Natural gas is a mixture of gases that are formed underground during the decomposition of organic matter, which is why it is a mineral.
At 101.325 kPa and 20 °C, natural gas acquires a gaseous state, which is why, as a rule, natural gas underground is in a gaseous state, i.e. in the form of separate accumulations, gas deposits. But it is also found in the form of gas caps in oil and gas fields or in a dissolved state, for example, in oil or water. 92-98% of natural gas is methane (CH4), while its composition may also include heavier hydrocarbons, such as ethane (C2H6), propane (C3H8), butane (C4H10) and other non-hydrocarbon substances such as hydrogen (H2), hydrogen sulfide (H2S), carbon dioxide (CO2), nitrogen (N2), helium (He).
It is worth mentioning that natural gas, in its pure form, has no odor or color, which increases the risk of poisoning if it leaks. In order to determine the source of the gas leak, experts began adding special substances to it - odorants, for example, ethyl mercaptan, which has a strong unpleasant odor of rotten cabbage, rotten hay and rotten eggs.
ADVANTAGES
ENVIRONMENTAL SAFETY
Low amount of emissions of harmful substances into the atmosphere during combustion.
Low cost
Compared to other types of fuel, gas is the cheapest type of fuel, taking into account the costs of transportation, storage and associated labor costs.
High calorific value
High calorific value compared to other types of fuels.
Neutral:
Autonomy
If you have a gas main, when gas pipes are already connected to your house from the street, you just have to connect them to the boiler and no longer worry about replenishing fuel. But in the absence of a gas main, you will be forced to purchase gas using gas cylinders (gas holders) of 50 liters, which in turn will need to be changed every 1-2 days.
Labor costs
If there is a gas main, labor costs are minimal. If there is no gas line, you will have to take care of transportation, storage and replacement of gas cylinders.
Warehouse space
If there is no gas main, you will have to allocate premises for storing gas cylinders. To create an autonomous heating system, reduce labor costs and eliminate a separate storage room, large-volume gas tanks should be installed underground and filled before the start of the heating season.
Chimney
If the boiler has an open combustion chamber, then the installation of a full-fledged chimney system will be required to remove the exhaust gases, and if the combustion chamber is closed, then a coaxial chimney will be sufficient.
Danger to others
If gas boilers have an open combustion chamber, then a certain amount of exhaust gases can enter the room in which the boiler is located, which can lead to carbon monoxide poisoning in surrounding people. In contrast to gas boilers with a closed chamber, where the likelihood of exhaust gases entering is minimal.
Energy independence
All gas boilers with a closed combustion chamber require constant power supply, unlike gas boilers with an open combustion chamber.
Cons
Explosion hazard
High probability of explosion if safety precautions, operation, installation and maintenance are violated.
Difficulty of installation
Due to the high risk of explosion, the installation of a heating system requires appropriate permits and qualified personnel.
Separate space
The room in which the gas boiler will be located increases the level of fire and explosion hazard, which imposes certain restrictions on the design of the house.
Noise
Compared to electric boilers, gas boilers create noise when operating.
Installation cost
High installation cost for creating an autonomous heating system in the absence of a gas main.
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages of use:
- when burning firewood, it is impossible to obtain such a high temperature as during the combustion of pyrolysis gas (especially if the firewood contains a lot of moisture);
- With the help of a control controller, we can automate the operation of a pyrolysis boiler without much difficulty, since the combustion process of pyrolysis gas is easy to control and regulate;
- burning wood or coal requires much more secondary air than burning wood gas. Therefore, with the same volume of secondary air, the combustion efficiency of wood gas, the duration and temperature of combustion will be greater;
- the emission of harmful substances from pyrolysis boilers into the atmosphere is reduced to a minimum, therefore a pyrolysis boiler is an almost environmentally friendly source of heat;
- solid fuel pyrolysis combustion boilers need to be cleaned from ash extremely rarely;
- pyrolysis boilers can operate for a very long time (up to 15 hours) on one load of firewood, while conventional solid fuel boilers need to be reloaded every 3-4 hours.
If we talk about the disadvantages of this type of unit, then, in addition to the price, which is the price for increased efficiency, and a more complex design, because pyrolysis boilers are 30-35% heavier than conventional ones, since more metal is required for their manufacture, other “disadvantages” insignificant.
For maximum operating efficiency, the moisture content of firewood should be no more than 20%. If the wood is wet, when it burns, steam is generated, which reduces gas emissions and leads to the deposition of tar and soot. As a result, the efficiency of the boiler decreases, and there is a need to clean it.
Most pyrolysis units are electronically controlled.
Consequently, it becomes necessary to use electricity to operate the controller, which controls the fan and smoke exhauster.
Pyrolysis boilers with natural draft exist, but they require a very high and powerful chimney, so such models are unpopular.
The need to fill the firebox by 50-100% - only in this case will the high efficiency of the boiler be maintained.
Long-burning pyrolysis solid fuel boilers, although twice as expensive as a conventional solid fuel boiler, are distinguished by the possibility of economical use of fuel with maximum efficiency, which is significantly higher than from the combustion of coal and wood in conventional units.
What are the dangers of using unsorted coal?
The use of this type of fuel in TKDG can lead to equipment failure. Unsorted coal contains a lot of dust, and its combustion efficiency is low.
In addition, large pieces are often found. When using automatic fuel supply, their entry into the mechanism leads to jamming and breakdown.
In our country, sorted coal is rarely sold, and it is expensive. Therefore, for boilers operating on solid fuel, it is better to buy “seeds” - the fraction of such a product is 6-13 mm.
Most often it is anthracite, but it has a high calorific value and combustion temperature, as a result of which equipment often fails.
The use of fine coal in TKDG will lead to the following results:
- the fuel is not burned out, it will have to be sifted and reused;
- the rated power is reduced (for example, in the technical characteristics of the equipment it is 25 kW, but the unit will be able to generate no more than 15 kW).
Which coal is best for a solid fuel boiler? For efficient operation of a unit with automatic feeding, it is recommended to use long-flame coal. In Russia, such raw materials are produced with a fraction of 13-50 mm, while for this equipment it is allowed that the size of individual pieces does not exceed 30 mm.
Types of pyrolysis boilers with a water circuit
There are many models on the market that can be divided into groups.
- The location of the chamber in which the contents are burned.
Most boilers are designed so that this compartment is located at the bottom. This is more convenient for laying the material, but after its combustion, the ash enters the chamber where the resulting gas burns.
This obliges the owner to frequently clean the equipment. The top location of the camera eliminates this need, but has a number of disadvantages. The main disadvantages of such a system include the inconvenience of placing the chimney and the larger amount of materials for its manufacture.
- Traction type.
It can be carried out either by force or by supercharging. Boilers in which the draft power can be manually adjusted require the installation of a reinforced chimney and do not depend on the power supply. Such models are few and far between.
Devices of the second type are equipped with automatic systems that determine the blowing time. Maintaining power requires the energy dependence of the unit, but the rate of pyrolysis output in it is quite high. These models are the most popular.
- Type of fuel.
When determining the possibility of using a particular type of fuel, one should start from the moisture level of the material. If it is higher than 20%, then the first operating time of the boiler will be spent drying the material, which leads to a decrease in the efficiency of the device.
If the humidity of the fuel used is initially high, then the pyrolysis process will take no more than 1/5 of the entire combustion cycle. This is extremely ineffective and irrational.
It will be difficult to recoup the high cost of the boiler. Therefore, the conclusion is obvious: the best material for combustion in pyrolysis boilers is firewood, coal or briquettes, the moisture level of which is minimal.
Each material has its own burning time. The smoldering time determines the quality and uniformity of heating of a living space. The best option is dry wood with a moisture level of no more than 10–15%.
Today, there are two main types of pyrolysis units, differing in design.
- Boilers with forced air supply.
In the first version of the boiler design, the primary combustion chamber, where solid fuel is placed, is located above the secondary combustion chamber, where afterburning of pyrolysis gases is organized. A special nozzle is installed between the chambers, having a straight cross-section and made of a refractory composition similar to fireclay bricks.
In this design, air is forced into the main firebox using an installed fan, and partly enters the firebox with solid fuel, and partly into the afterburning chamber of the released gases.
In this case, it is obvious that the principle of pyrolysis is violated initially, since the fan creates an excess of oxygen instead of limiting it.
But, despite this, efficient and complete combustion of firewood occurs, with virtually no residue of even fine ash, since dry wood or products based on it burn to fine ash, and it is easily blown out through the nozzle by a fan into the chimney pipe.
Knowing the features of this design, it can be called a “top blowing device”, since the air pumped by the fan enters mainly into the upper main combustion chamber.
Due to the influx of oxygen, the temperature during combustion increases and gas production increases, but it burns quite quickly, escaping through the nozzle.
In this regard, firewood quickly burns out, and it has to be added quite often in the process of heating the house. This principle of boiler operation cannot be called pyrolysis in the full sense of the word, although similar devices are sold quite often under this name.
It’s another matter if the fan standing on the outlet pipe (often called a “smoke exhauster”) creates air movement, which is proportionally divided into primary and main - secondary using the usual mechanical method or using automation.
In this case, the primary air damper is located so that it is supplied precisely to the lower part of the fuel filler.
The smoldering of firewood occurs from below, and the temperature released during this process promotes heating - in the middle layers of the stack, and final drying - in the upper ones.
The main air flow will be supplied only to the nozzle area, so that the final combustion of the pyrolysis gases with the maximum amount of heat generated takes place in the lower chamber. Such a boiler can rightfully be classified as a long-burning pyrolysis boiler.
- Boiler with natural air supply.
In such a boiler design, the combustion chamber for storing firewood is located in the lower part of the device, and the combustion section of the pyrolysis gases released by the fuel is in the upper area of the body.
A fan is not installed in this design, and the air for lighting the boiler and afterburning pyrolysis gases is supplied naturally through dampers for primary and secondary air.
In this version of the arrangement of the chambers and the dosed supply of air flows, the pyrolysis process is carried out properly, since instead of intense combustion, with the primary air supply damper closed, wood smoldering occurs in the combustion chamber with the release of a large amount of pyrolysis gases.
However, this design also has its own problem. And it lies in the fact that the correct debugging of the combustion process is extremely important.
When the main chamber damper is completely closed, the temperature in it decreases, as well as the formation of gases. The concentration and temperature of the gases becomes insufficient for their complete afterburning and the upper chamber turns into a regular gas outlet.
The combustion products that rise into it do not burn out, but simply give off heat to the walls of the water circuit and go into the chimney. The efficiency of the boiler during such operation is sharply reduced. If the damper is opened more than required to create the conditions necessary for pyrolysis, then the intensity of combustion in the main firebox will increase, which leads to completely irrational fuel consumption and the need for frequent refills.
To achieve ideal operation of a pyrolysis boiler of this design, it is necessary to correctly adjust the supply of primary and secondary air, which is quite difficult to do, since this requires practical experience.
Modern models have automated process monitoring and control systems, and if the automatic fuel loading system works correctly, it lasts for 12-14 hours of operation at maximum heat transfer.
Calculation of required power
Table for calculating the required boiler power
To determine the performance of the boiler you are purchasing, you will need to thoroughly prepare and take into account the following indicators:
- area of heated premises in a country house or in a private house;
- quality of insulation of building walls;
- type of fuel constantly used;
- number of thermal circuits for heating the house.
After preparing all the listed data, including detailed drawings of the circuits, calculating the required boiler power for heating a private house will become much easier. In this case, the well-known ratio will help, according to which per 1 sq. meter of room will require 1 kW of useful power. This rule is valid only if the height of the ceilings in the building does not exceed 3 meters.
To make it easier to determine this indicator, special tables have been developed in which a room of a given area is assigned the power sufficient to heat it.
Fuel for pyrolysis boiler
Solid fuel pyrolysis boilers are practically omnivorous. Various types of solid fuel can be used as fuel: from ordinary firewood to peat.
Based on this, a boiler can be heated with any type of solid fuel, but still each type has its own inherent qualities and properties, so the operation of the boiler will also differ.
Therefore, fuel selection is a very important process.
- Using regular firewood.
Firewood for solid fuel pyrolysis boilers must be dry (it is allowed to use firewood with a moisture content of no more than 20%). The heat transfer of the boiler depends on dryness.
When loading logs into the firebox, they should be placed tightly together, and a free space of at least 20 cm should be left at the top. It is worth noting that unsplit firewood can also be used.
When loading for the first time, it is necessary to use approximately half of the portion of firewood, the rest is placed as it burns out in the boiler. Firewood burns unevenly - it must be carefully laid out on the surface of the firebox all the time, while preventing the solid fuel pyrolysis boiler from cooling.
The disadvantage of using firewood is that heating with this type of fuel cannot be automated. An advantage is the fact that this is a very environmentally friendly way of heating a room.
- Use of peat.
When using peat as fuel for a solid fuel pyrolysis boiler, certain rules must be followed. Firstly, the firebox must always be cleared of ash, and secondly, the ash door must be closed.
Peat should be placed on a grate. For better kindling, you can put some firewood on this layer and cover it all with another layer of peat. Then open the chimney valve and start lighting.
During operation of solid fuel heating equipment, it is necessary to ensure that the peat always lies in an even layer. This arrangement of peat will ensure maximum heat transfer.
- Use of coal.
To obtain the best level of heat using coal as fuel, it is necessary to use a special firebox - a shaft with a grate and vertical walls.
The firebox must be high enough, the distance between the arch and the grate must be at least 50 cm. The combustion and ash doors must be made of cast iron, the optimal distance between the doors is 21 cm.
In addition, it is recommended to strictly seal the doors. It should be remembered that when using coal, a new portion of fuel should be added only when the first one has flared up well. In this case, you need to constantly maintain an even layer and prevent the coal from burning to the grate.
- Use of fuel briquettes.
Today, fuel briquettes are the most optimal means for heating solid fuel pyrolysis boilers. You can use both coal and peat briquettes.
Thanks to the use of briquettes, you will receive high calorific value, an even combustion process (no need to interfere with the combustion process itself and adjust the layers), high density of the burning layer, a small amount of flame and a minimal amount of smoke.
Another advantage is the combustion of the briquette without any residue and the convenience of packing the briquettes. The combustion chamber of a solid fuel pyrolysis boiler is carried out until the fuel briquettes are completely burned. If unburned briquettes remain, they are reused.
The dimensions of a standard boiler firebox regulate the dimensions of the fuel used (dimensions of firewood or briquettes). As a rule, logs with a length of 400 mm and a diameter of up to 200 mm are used for fuel in gas generator boilers. The size of fuel briquettes is 300x30.
Along with firewood or briquettes, sawdust can also be used as fuel. But they should be taken no more than a third of the main part of the fuel by volume.
The operating instructions stipulate that the fuel moisture content should not be higher than 45%. The lower the moisture content of the wood, the greater the power of the boiler and the longer it can operate without repair.
For example, a kilogram of wood with 20% humidity when burned produces heat equivalent to 4 kWh, and firewood with 50% humidity produces only 2 kWh. In addition to the fact that with an increase in moisture content in the fuel, the specific heat of combustion decreases, fuel consumption increases significantly.
CALCULATION OF LIQUID FUEL COSTS
As an example of calculating heating costs, let’s take diesel fuel (diesel fuel). The approximate consumption of diesel fuel per hour of boiler operation can be found by multiplying 0.1 by the boiler power according to the passport. For example, if we chose a 25 kW boiler to heat 300 m3, then it will consume 0.1 * 25 = 2.5 liters of diesel fuel per hour.
Thus, to heat 300 m3 per day you will need:
2.5 liters (consumption per hour) * 24 (hours in a day) = 60 liters of diesel fuel.
For the heating season, which is 183 days (from October 15 to April 15), taking into account temperature fluctuations, you will need:
(60 liters (daily consumption of diesel fuel) x 183 days (heating season)) / 2 (taking into account temperature fluctuations) = 5490 liters.
Why is it better to choose a pyrolysis boiler and the basic rules for its operation
- Firstly, during the combustion of firewood it is impossible to reach such a high temperature as during the combustion of the gas obtained from them.
- Secondly, to maintain the combustion of gas, less secondary air is required than for burning wood; accordingly, the combustion temperature will be higher, and with it the efficiency.
- Thirdly, the procedure for burning pyrolysis gas is easier to control, thus, the operation of a gas generator boiler is automated in the same way as a liquid fuel or gas boiler.
This equipment is based on pyrolysis fuel combustion technology. Its essence lies in the fact that under the influence of elevated temperature and in conditions of lack of oxygen, wood begins to decompose into a solid residue and a volatile part - pyrolysis gas.
Pyrolysis occurs at temperatures ranging from 270 – 700 degrees. This process is exothermic, in other words, it is characterized by the release of heat, which increases the drying and heating of the fuel in the boiler.
Subsequently, the mixing of oxygen with pyrolysis gas at a high temperature leads to combustion of the latter, which is used to obtain thermal energy.
Pyrolysis gas actively interacts with carbon, due to which the flue gases leaving the boiler almost do not include harmful impurities, being considered, to a greater extent, a mixture of water vapor and carbon dioxide.
Numerous studies have shown that carbon dioxide will be released into the environment up to three times less than from an ordinary wood-burning and, even more so, coal-fired boiler.
The pyrolysis combustion procedure is characterized by the formation of a small amount of ash and soot, which is why this equipment rarely requires cleaning.
The advantages of long-burning pyrolysis boilers with a water circuit are environmental friendliness.
The efficiency declared by the manufacturers is only 4–10% higher than the productivity of a conventional solid fuel boiler. Obviously, the choice should be based on taking into account the individual characteristics of the heating system and the preferences of the owners.
The main features of a quality model that is worth purchasing:
- Good, neat welds and sufficient material thickness (at least 4 mm). Thin metal in cheap boilers burns out quickly and is more susceptible to corrosion. Buying such products is a bad decision!
- Ceramic nozzle and gas combustion chamber lining (this model will last longer). This material has excellent fire-resistant properties. Make sure that ceramics is used, as the most reliable material for these parts of the boiler.
- Two working chambers with the ability to smoothly adjust the air supply. Two chambers are the main feature of an effective pyrolysis model! If you need high-performance and at the same time economical long-burning boilers, choose long-burning pyrolysis boilers with a water circuit.
- The coolant is in contact only with the chimney and gas combustion chamber. If this technical point is not observed, the boiler will lose heat, since the main combustion chamber has a lower temperature (the coolant cools on contact).
- Availability of an automatic control unit and a corresponding warranty for it. Repairing this very important unit for regulating the air supply in some cases costs up to 50% of the total cost of the equipment. Take this part of the boiler seriously.
Some more tips for choosing a boiler:
- The required power can be calculated based on the area of the room and the degree of insulation. Approximately you need to take 1 kW per 10 m2, while adding a few kW, also taking into account the functions of the boiler as a boiler. So, if you have an area of 80 m2, then a 10 kW option is suitable, but if the area is 100 m2 and the walls are not insulated, then 10 kW will not be enough;
- The size of the firebox is important, if you burn with wood, the larger it is, the larger the size of firewood that can be placed there;
- Burning time without additional loading is usually indicated taking into account excellent quality fuel, so take 2/3 of these data. For example, if 10 hours are stated, you can count on 6;
- Energy independence is very important when choosing a boiler for a dacha or a place remote from electricity; in addition, it also saves electricity.
For normal operation of the equipment, it is necessary to maintain a certain range of fuel combustion temperatures. This range is from 2000 to 8000 C.
It is necessary to configure the device quite accurately. To prevent emergency situations at high temperatures, the water circuit of the unit is used.
The housing plays the role of a heat exchanger; water passes between its walls. This feature and the built-in coil in one of the walls prevents the creation of prohibitive temperatures.
When the water temperature is insufficient, the formation of pyrolysis gas stops, air is supplied to the combustion chamber and the boiler operates like a conventional solid fuel stove. It is not allowed to cool the water below a temperature below 600 C. In this case, the combustion process without oxygen stops in any type of pyrolysis boilers.
To ensure a small water circuit and transfer the equipment to an operating state, an additional jumper (bypass) is installed in the water circuit. The bypass is adjusted manually; temperature sensors are installed to control the temperature.
This type of equipment can work on all types of firewood, briquettes, pallets.
In reality, a type of fuel such as coal can be used. Provision is made for the processing of flammable household and industrial waste. But this can backfire due to their high polymer and rubber content.
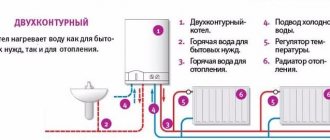
Pyrolysis boilers are produced only as single-circuit boilers and cannot be used for heating water. But, in the absence of natural gas, to create comfortable conditions in the building, this type of equipment is the best solution to the problem.
Conditions and rules for fuel storage
Each type of raw material has its own characteristics. Coal and peat are placed in a warehouse only after a 2-week stay in the open air, with 2- or 3-fold mixing. Firewood is dried and stored in stacks, and is treated with antiseptics and insecticides.
Pellets and briquettes initially have low humidity, but can absorb it from the environment. They require a dry place to store them.
Such fuel is placed on pallets to provide air access from all sides. Most of these products come in sealed bags, but there is always a risk of damage.
DIY pyrolysis boiler
Make a pyrolysis boiler with your own hands according to the drawings, or order production from specialists (which is still cheaper than buying a ready-made one).
To make such a complex device, you will need a fairly wide range of tools and materials.
Here is an approximate list of them:
- Plan diagram. Without an accurate calculation, you are unlikely to be able to do everything correctly. You don’t have to make the drawings yourself, if you don’t have the appropriate skills, you can simply download it on the Internet.
- Welding machine.
- Grinding machine.
- Metal pipes of different diameters and lengths (120, 130 and 150 centimeters, with a diameter of 50, 45 and 6-8 centimeters) and the boiler frame itself and the chimney will be made from the pipes.
- Sheet of metal for making a door.
- Hinges and handles for installing dampers.
Manufacturing a pyrolysis boiler includes the following steps:
- Making the frame.
The frame of the pyrolysis boiler consists of two parts: a casing and a firebox. A frame is made from two pipes of a larger and smaller diameter. One pipe is inserted into another and welded. In this case, the larger pipe acts as a casing, and the smaller one as a firebox.
The bottom and top of the pipes are welded in circles cut from a metal sheet. The space between the pipes is filled with a heat-conducting agent.
- The second stage is the division of the firebox by putting on the chambers.
Firewood will be loaded into one of them, and gas will burn out in the second. The air distributor acts as a separator. This is a pipe of the smallest diameter onto which a sheet of metal with blades is welded.
- Next, in the lower part of the frame - the firebox, you need to cut a hole-door; the door itself is made from a sheet of metal. It is very important that the door fits as tightly as possible to prevent excess air from entering the boiler.
- The last stage of manufacturing a pyrolysis boiler will be the installation of a chimney and an outlet pipe through which unburned gas will be discharged into the chimney and outside.
In addition to the fact that the pyrolysis boiler must be manufactured correctly, it must also be installed correctly:
- As a rule, a pyrolysis boiler is installed in a separate room - a boiler room; this is the safest option.
- Install the pyrolysis boiler at a distance of at least thirty centimeters from the walls.
- The floor on which the boiler will stand must be made of non-combustible materials.
- The boiler room must be equipped with good ventilation.
- The boiler chimney must be well insulated to avoid the release of combustion products into the room.
Recommendations:
- The fuel loading hole for home-made models is usually placed slightly higher than that of conventional solid fuel boilers.
- It is imperative to install a limiter that will allow you to control the amount of air entering the fuel chamber, as well as add firewood or briquettes in a timely manner.
- To make a limiter, you can use a pipe with a diameter of about 70 mm, slightly longer than the body of the device.
- A steel disk should be welded to the bottom of the limiter, forming a gap of about 40 mm with the pipe walls.
- To install the limiter, a corresponding hole must be made in the boiler lid.
- The loading hole for firewood should be made rectangular. This hole is closed with a door with a special steel plate that ensures a secure fit.
- Below you need to make a hole to remove ash.
- The pipe through which the coolant moves inside the boiler must be bent to maximize heat transfer. The amount of coolant entering the boiler can be adjusted using a valve installed outside.
- If after the first start-up of the boiler there is no carbon monoxide in the combustion products, it means that the design is made accurately and functions correctly. In the future, you should regularly monitor the condition of the boiler welds and promptly clean it of accumulated ash and soot.
Wood briquettes for the boiler
At the moment, the production technology has been changed. Consumers began to be offered cylindrical fuel, up to several centimeters long, which made it possible to use wood fuel briquettes in automatic boilers.
How and from what are wood briquettes made?
Heating wood briquettes for boilers are produced in three different ways, each of which has its own characteristics and markings:
- Rectangular RUF briquettes - received the marking due to the fact that the first compressed fuel was created on equipment manufactured by the German manufacturer RUF. In shape, the finished product resembles a small brick. The production principle is based on pressing sawdust and waste using hydraulic presses at a pressure of 300-400 bar.
Cylindrical briquette – pressing of briquettes for solid fuel boilers of this type is carried out using hydraulic or shock-mechanical equipment. When pressing, the pressure increases to 600 bar. The disadvantage of the cylindrical type of fuel is the fear of moisture and susceptibility to mechanical damage.
Pini&Kay – pressing of wood briquettes for heating boilers is carried out using mechanical screw equipment. The difference between production is the simultaneous use of high pressure (up to 1100 bar) and thermal firing. The resulting “logs” have edges and a characteristic dark brown color.
The washers are similar in structure to Pini&Kay, have four or six edges and a radial hole in the center. The length of the briquette is only a few centimeters.
The briquette production technology used affects the quality and cost of fuel. Pini&Kay have the highest calorific value; they are resistant to moisture and mechanical stress, and also burn longer when fired.
Briquette consumption in the boiler
Solid fuel for boilers in briquettes is made from various types of wood. The burning time and fuel consumption depend on the type and type of wood:
- Coniferous briquettes flare up quickly and create a high temperature in the firebox, but quickly burn out due to the large amount of resin released. Heating with pine briquettes is not profitable due to high fuel consumption, but it is advisable to use them to light the boiler.
- Pressed hardwood slabs have a high calorific value, are difficult to ignite and burn out slowly. The average consumption is 10 kg for 6-7 hours.
Another type of briquettes that has not found widespread use are slabs made exclusively from bark. This type of fuel burns hard, but during combustion it has practically no flame and smolders slowly. At the same time, the temperature is maintained until the slabs burn out. The average burning time is 12 hours.
Cost of wood briquettes
It is economically profitable to use fuel briquettes due to their high calorific value and low content of non-combustible residue.
What fuel should you choose to heat your home?
This question is asked by every owner of suburban residential real estate today.
After all, the choice of fuel will determine what kind of boiler equipment you will install in your boiler room and whether it is necessary to do it at all, how profitable the use of this fuel will be and whether it will be freely available? With modern market development, you can choose a boiler using any of the fuels on the market today. But the more choice, the more doubts. And what is better to choose a boiler or fuel first? So, egg or chicken?
We recommend and insist that you start your choice with fuel!
To begin with, we will highlight the main criteria by which we will evaluate the selected fuel.
- The price for 1 kW of heat is the most important point for you
- Availability – the type of fuel you choose should not be a rare, scarce commodity
- Ease of storage – monthly or seasonal fuel needs can take up quite a lot of space, and some types of fuel also require special premises
- Efficiency of the heating boiler - the selected fuel should bring maximum benefit when burned in the boiler
- Automated supply - fuel supply to the boiler should be carried out automatically, without your participation
- Fire safety – the fuel you store must be fireproof. In this case, a low price cannot in any way be for the sake of safety.
- Environmental safety - there are still those who use fuel that pollutes the environment. But we and our descendants still have time to live on this planet!
Let's immediately exclude fuel oil and oil from candidates - it is unlikely that you will use fuel in your home that is used in large factories, industrial boiler houses or processing stations.