Autonomous gasification has two significant columns in the estimate: installation of a gas tank and annual fuel consumption. We will tell you how much you will spend on liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) when living in an area of 50 to 800 m2.
The entire article in 1 table
| Popular house sizes | Gas consumption per month | Gas consumption during the heating season (7 months) | Gas consumption per year |
| 100 m2 | 316 l | 2,212 l | 3,802 l |
| RUB 5,624 | RUB 39,368 | 67,000 rub. | |
| 150 m2 | 475 l | 3,325 l | 5,703 l |
| RUB 8,455 | RUB 59,185 | 101,000 rub. | |
| 200 m2 | 633 l | 4,431 l | 7,603 l |
| RUB 11,267 | RUR 78,869 | 135,000 rub. |
LPG at a price of 17.80 rubles/l as of 01/29/2019.
How to calculate the need for thermal energy
The simplified formula for this calculation looks very simple - 1 kW of thermal energy is spent on heating 10 m2 of building area.
A more accurate formula operates not with areas, but with the cubic capacity of the house, also taking into account the height of the ceilings in the room. But for standard-type dwellings with a ceiling height of 2.5-2.7 meters, the above simplified proportion is valid. An accurate calculation of the need for thermal energy operates not only on the volume of heated space, but also on the heat resistance of walls, openings and ceilings. In addition, in this case, the average annual temperature and other nuances are taken into account. Boiler room
However, in order to calculate the volume of fuel, a simple formula will be enough for us: 1 kilowatt = 10 square meters. As a result, heating a building with an area of 150 or 200 square meters requires spending 15 or 20 kW, respectively. And this is only an hour. But the boiler does not consume gas every minute. The work/downtime period here is divided in the proportion of 50/50 percent. Therefore, per day, a house with an area of 150 square meters will spend 180 kW (15x24/2), and a home with an area of two hundred square meters will spend 240 kW.
The cold season in our latitudes lasts from October to April - 7 months or 210 days. Therefore, annual thermal energy consumption will be 37,800 and 50,400 kW. We will focus on these values in our further calculations.
How to reduce fuel consumption for the owner of a private house
The amounts mentioned above can stun an impressionable tenant or an ordinary citizen. Well, what can you do - “your own home” was an expensive pleasure at all times. However, unlike a city dweller living in an apartment, the owner of a private home can change heating costs in his favor.
Insulating your home will help reduce heating costs
To do this, he will need to do the following:
- Insulate the facade, foundation, roof, attic and basement floors - even a thin layer of thermal insulation material can make up at least a couple thousand, or even a whole ten, from the gas bill.
- Replacing old windows with modern double-glazed windows, installing a heat-resistant panel in the doorway is another 5-10 thousand minus. Moreover, doors and windows should be tackled first, since they generate at least 40 percent of heat losses.
- Install a heat accumulator in the basement or boiler room, change the wiring diagram to a double-circuit or manifold version, which provides the possibility of point thermoregulation of radiators, purchase a boiler with high efficiency. Now there are excellent 95% devices on sale. In this case, savings can be up to 10-15 percent of the total bill.
In short, it is necessary, firstly, to increase the heat resistance of the house, and secondly, to use more energy-efficient equipment. And no one is forcing you to make these changes in one season. You can start with windows, then improve the boiler and get to the walls and ceilings. As a result, you can save up to a quarter of the stated costs.
How much heat does liquefied or natural gas give off?
We already know the annual consumption of the heating system. Now we must calculate the calorific value of the energy source itself - liquefied and natural gas. Using these values, we can come up with the amount of substance burned in the firebox of a gas boiler per year.
Calorific value is the ratio of the amount of kilowatt of energy released during fuel oxidation to a unit of mass or volume. Since we are interested in main (natural) or liquefied gas used for heating the house as an energy source, we will use cubic meters or liters as a measure of the substance. According to the tabular data, the calorific value of natural gas is 33.5 MJ/m3 or 9.3 kW/m3 (a coefficient of 1 kW = 3.6 MJ is used for conversion). That is, when a cube of gas is burned, 9.3 kW of thermal energy is released.
Liquefied gas is a mixture of propane, ethylene and other flammable carbohydrates. And it is more “caloric” than dietary natural fuel. According to tabular data, the calorific value of a kilogram of such a substance is 45.20 MJ or 12.5 kW. But the generally accepted “unit of measurement” for liquefied fuel is liters, and its density is 0.524 kg/l. Therefore, we can say that when a liter of liquefied mixture is burned, 6.55 kW of thermal energy is released.
Calculation methods with illustrative example
Boiler Zhukovsky AOGV
The amount of gas spent on heating a house depends mainly on the characteristics of the gas boiler and its operating conditions.
Therefore, for calculations you will need to know:
- technical parameters of the boiler;
- its power and efficiency;
- gas consumption specified in the technical passport;
- room area.
Our example will involve a gas boiler AOGV-17.4-3 (JSC Zhukovsky) with a capacity of 17.4 kW with an efficiency of 88%.
Natural gas consumption – 1.87 cubic meters/h, liquefied gas – 1.3 kg/h.
The boiler will heat up to 140 sq. meters of total premises area.
It is necessary to take into account that the values indicated in the passport correspond to the continuous operation of the boiler at full power, but in fact the boiler operates 12-14 hours a day, so we will divide the calculated values by two.
Tariffs and fuel prices
Let’s assume that the cost of the natural gas tariff is 3.9 rubles. for 1 cubic meter.
The cost of refilling a standard 50-liter cylinder with liquefied gas is 600 rubles. Such a cylinder is usually filled to 80% (42.5 l), which is about 21 kg of propane-butane mixture.
Accordingly, the price of 1 kilogram of liquefied gas will be equal to 600 / 21 = 28.6 rubles (excluding the cost of transporting the cylinder to the gas station and back).
According to the device datasheet
This is the simplest and most approximate method of calculation.
For natural gas, the consumption is 1.87 cubic meters per hour, hence:
For liquefied gas, the boiler consumption is 1.3 kg/h, hence:
Educational program on gas boilers using liquefied gas.
According to the specific heat of combustion of gas
The specific heat of combustion (calorific value) of gas depends on the type of natural fuel and the quality of the mixture. This value can be found in reference books on heating engineering.
For natural gas, the lowest value of specific heat of combustion is 34.02 MJ/cub.m or 9.45 kW/h of thermal energy. With a device efficiency of 88%, this figure will be adjusted to 9.5*0.88=8.3 kW/h.
How much does a gas boiler consume:
For liquefied gas, the specific heat of combustion is 50.38 MJ/kg or 13.99 kW/h. With an efficiency of 88%, this figure will be adjusted to 13.99*0.88=12.3 kW/h.
LPG boiler consumption:
The gas consumption of a double-circuit boiler is 20-25% higher (add this difference to the final amount).
When comparing the results, it is noticeable that if we calculate by the specific heat of combustion of gas, then the costs and cost of heating are higher. This happens because the minimum value of the specific heat of combustion is taken, which in fact may be higher.
In any case, the cost of heating with natural gas will be approximately 5 times cheaper than heating a room with bottled gas. However, liquefied fuel is still cheaper than autonomous electric heating.
At the same time, one should take into account the possibility of connecting to the gas pipeline and the cost of such a connection, which amounts to a fairly significant amount.
It is also worth noting that such calculations are very rough and approximate, since they do not take into account a number of circumstances that can significantly affect the final amount of expenses. In this case, the amount of calculations can vary significantly up or down
It is best to entrust an accurate calculation, taking into account all the circumstances, to heating engineering specialists.
Which gas to choose - which is more profitable?
To connect to the main gas pipeline, the user will have to pay for the project and installation work. And these expenses cannot be called insignificant. The growing appetites of gas services make gasification of homes a very expensive undertaking. However, all these expenses pay off during operation. As of March 2022, the cost of a cubic meter of gas, depending on the region of the Russian Federation, ranges from 4.44 to 8.66 rubles. The average price is 6.55 rubles. As a result, heating a house with natural gas of 150 or two hundred square meters, taking into account the estimated consumption rate for the season, will cost 29,825 and 39,038 rubles.
Liquefied fuel does not require insertion into the main line, but to store it it is necessary to build a gas tank - a container that accepts the required volume of fuel. In addition, this container will have to be periodically filled with gas, which is delivered to the site using special transport, and this service is not cheap. And the gas tank will have to be repaired and maintained. After all, the safety of all residents of a house heated by liquefied gas depends on its condition.
Liquefied fuel storage
At the beginning of spring 2022, a liter of liquefied gas at gas stations cost from 11 to 20 rubles, depending on the region of the Russian Federation. The average cost of this fuel was 15.5 rubles. Therefore, heating a 150-square-meter house with liquefied gas will cost 98,394 rubles. For housing with an area of two hundred square meters you will have to pay even more - 131,192 rubles. As you can see, liquefied fuel has surpassed natural gas in cost by 3.3 times. Therefore, conclusions regarding whether it is profitable or unprofitable suggest themselves - natural (main) gas, with all the bureaucracy and complexity of the connection process, will be much more profitable than liquefied fuel.
Installing a wall-mounted boiler instead of a floor-standing one
For heating a residential building with an area of up to 400 square meters. It is better to use a wall-mounted gas boiler. This will allow you to save more on gas. A wall installation can be considered a mini boiler room. It consists of structural elements:
- expansion tank;
- group responsible for security;
- circulation pump;
- electronic board.
Expensive models have additional elements:
- wireless weather-sensitive programmer;
- indirect heating boiler;
- circulation pump with frequency control.
Single-circuit mounted tanks are often equipped with a three-way valve. It is installed at the junction with an indirect heating boiler. Heat exchangers of mounted boilers are made of copper or stainless steel.
The main savings on gas can be achieved due to the stable efficiency of the boiler. Unlike floor-standing models, wall-mounted ones most often offer forced draft solutions. Forced draft provides the combustion chamber with the required amount of oxygen. With natural traction, this indicator is not always stable.
Types of gas
Heating private houses and cottages with an area of over 150 square meters requires a large amount of fuel. For this reason, when choosing a suitable coolant, one should take into account not only the degree of its heat transfer, but also the economic benefits of its use and the profitability of equipment installation. Gas best meets the listed parameters.
For a larger room area, more fuel is needed
Types of gas:
- Natural. It combines hydrocarbons of various types with a predominant proportion of methane CH4 and impurities of non-hydrocarbon origin. When one cubic meter of this mixture is burned, more than 9 kW of energy is released. Since gas is naturally located underground in certain rock layers, special pipelines are laid for its transportation and delivery to consumers. In order for natural gas to flow into the house and heat it, it is necessary to connect to such a pipeline. All connection work is carried out exclusively by gas service specialists. Their work is valued quite highly, so tapping into a gas main can cost a large sum.
- Liquefied. Includes substances such as ethylene, propane and other flammable additives. It is usually measured not in cubic meters, but in liters. One liter, when burned, produces about 6.5 kW of heat. Its use as a coolant does not imply an expensive connection to the main pipeline. But to store liquefied fuel, it is necessary to equip a special container. As gas is consumed, its volume will have to be replenished in a timely manner. The cost of transportation must be added to the cost of a permanent purchase.
Once the choice in favor of one or another type of fuel has been made, you can determine the gas consumption for heating a house of 150 m². A special formula should be used for calculation.
You will see the principles of heating with liquefied gas cylinders in this video:
Pros and cons of heating systems
And now, friends, let’s look at the most interesting thing - the pros and cons of these systems, so that each of you can decide and understand what to use for your country house, for your heating system.
The first option is natural gas. Natural gas is the cheapest form of heating. If you are lucky and managed to connect it, then you don’t even have to consider all other options. If you do not have the opportunity to connect natural gas, or it is very far away, and the cost of its supply costs a lot of money, or you are running out of time, and you need to connect to heating as quickly as possible, and connecting natural gas takes about 1 year to 1.5 years, then this option is not for you. When you need heating tomorrow, and you have to run through authorities, it does not cause any pleasure, even taking into account the subsequent savings.
Let's look at three heating options that can be used alternatively, autonomously, quickly.
Volume of consumption
Despite the fact that both coolants are gas, heating the same room will require different amounts of fuel. To calculate the amount of fuel consumed in 1 hour (A), it is necessary to take into account:
- equipment power (Q);
- specific heat of gas of a particular brand (q);
- efficiency factor of the gas installation (B).
Heating one room requires different amounts of natural and liquefied gas
We recommend: Instructions for operating and starting up gas boilers in a private home
To calculate, you should use the formula A = Q / q * B. If you substitute all the available values into it, it is easy to determine that for an area of 150 m² you will need 0.836 liters of natural gas per hour, for an area of 200 m² - 1.114 liters. In the case of liquefied gas, the amount of fuel will be 1.168 and 1.558 liters per hour, respectively. The average daily level of consumption is obtained by multiplying these figures by 24 hours, the monthly - by multiplying the average daily by 30 (31) days.
If a house heated by gas has several rooms, then the volume of its consumption should be calculated for each room separately. In this case, it is necessary to take into account the average temperature during the coldest time of the year.
Since the temperature regime will change from negative to positive throughout the year, during the calculation process its average will need to be divided in half.
Two-position thermostats - thermostats for a gas boiler
The electromechanical two-position room thermostat Protherm Exabasic for a gas boiler is simple, cheap, but temperature fluctuations in the heated room will be significant - about 2-3 ° C.
The electronic two-position room thermostat Protherm Exacontrol provides higher accuracy and stability of maintaining the temperature in the room, and has the function of protecting the heating system from freezing. The display shows the current room temperature.
Electronic two-position programmable room thermostat - Protherm Thermolink S thermostat
Thermolink S is an electronic two-position programmable controller that differs from previous models in that it allows you to adjust the temperature according to one weekly program with the possibility of combinations of three different time intervals (morning, afternoon, evening).
Weekly program for regulating heating temperature in a house or apartment using the Protherm Thermolink S room thermostat
In addition, it is possible to set one of three temperature modes: “Comfort”, “Eco” (economy) or “Vacation” mode.
The Thermolink S controller supports the function of protecting the heating system from freezing when the room temperature drops to 3°C.
The display shows the current room temperature, as well as the time and day of the week.
Features of operation of a boiler with a two-position thermostat
On-off thermostats have a relay with contacts at the output. The contacts can be in one of two positions: closed or open. Connected to the boiler, closed thermostat contacts switch on the boiler heating mode. When the contacts open, the heating mode is switched off. The boiler operates in cycles - on/off. There are no changes in the heating mode settings on the boiler itself.
The cyclical operation of the boiler under the control of a two-position room thermostat can hide the clocking of the boiler, which occurs due to a significant discrepancy between the capacities of the boiler and heating devices (read the beginning of the article about clocking).
Many even argue that boiler clocking can be eliminated not by adjusting the gas valve, but by installing a room thermostat.
However, if the boiler power significantly exceeds the power of the heating devices, then the frequency of operation cycles of the boiler with a two-position thermostat increases. The boiler turns on and off more often. In addition, the range of temperature fluctuations in the room expands.
Correct adjustment of the power of a gas boiler is also necessary when the boiler is operating under the control of a room thermostat.
The sensitivity of the electronic two-position room thermostat is 0.5 °C. The thermostat switches contacts when the room temperature changes by half a degree.
Calculation method for natural gas
The approximate gas consumption for heating is calculated based on half the power of the installed boiler. The thing is that when determining the power of a gas boiler, the lowest temperature is set. This is understandable - even when it is very cold outside, the house should be warm.
You can calculate gas consumption for heating yourself
But calculating gas consumption for heating using this maximum figure is completely incorrect - after all, the temperature is generally much higher, which means much less fuel is burned. That’s why it is generally accepted that the average fuel consumption for heating is about 50% of the heat loss or boiler power.
We calculate gas consumption by heat loss
If you don’t have a boiler yet, and you estimate the cost of heating in different ways, you can calculate it from the total heat loss of the building. They are most likely known to you. The technique here is this: they take 50% of the total heat loss, add 10% to provide hot water supply and 10% to remove heat during ventilation. As a result, we obtain the average consumption in kilowatts per hour.
Next, you can find out the fuel consumption per day (multiply by 24 hours), per month (by 30 days), and, if desired, for the entire heating season (multiply by the number of months during which the heating operates). All these figures can be converted into cubic meters (knowing the specific heat of combustion of gas), and then multiply the cubic meters by the price of gas and, thus, find out the heating costs.
| Natural gas | 1 m 3 | 8000 kcal | 9.2 kW | 33.5 MJ |
| Liquefied gas | 1 kg | 10800 kcal | 12.5 kW | 45.2 MJ |
| Coal (W=10%) | 1 kg | 6450 kcal | 7.5 kW | 27 MJ |
| Wood pellets | 1 kg | 4100 kcal | 4.7 kW | 17.17 MJ |
| Dried wood (W=20%) | 1 kg | 3400 kcal | 3.9 kW | 14.24 MJ |
Example of heat loss calculation
Let the heat loss of the house be 16 kW/hour. Let's start counting:
- average heat demand per hour - 8 kW/h + 1.6 kW/h + 1.6 kW/h = 11.2 kW/h;
- per day - 11.2 kW * 24 hours = 268.8 kW;
- per month - 268.8 kW * 30 days = 8064 kW.
The actual gas consumption for heating also depends on the type of burner - modulating ones are the most economical
Convert to cubic meters. If we use natural gas, we divide the gas consumption for heating per hour: 11.2 kW/h / 9.3 kW = 1.2 m3/h. In calculations, the figure 9.3 kW is the specific heat capacity of natural gas combustion (available in the table).
By the way, you can also calculate the required amount of fuel of any type - you just need to take the heat capacity for the required fuel.
Since the boiler has not 100% efficiency, but 88-92%, you will have to make further adjustments for this - add about 10% of the obtained figure. In total, we get gas consumption for heating per hour - 1.32 cubic meters per hour. Next you can calculate:
- consumption per day: 1.32 m3 * 24 hours = 28.8 m3/day
- monthly demand: 28.8 m3/day * 30 days = 864 m3/month.
The average consumption for the heating season depends on its duration - multiply by the number of months while the heating season lasts.
This calculation is approximate. In some months, gas consumption will be much less, in the coldest month - more, but on average the figure will be about the same.
Boiler power calculation
The calculations will be a little simpler if you have the calculated boiler power - all the necessary reserves (for hot water supply and ventilation) have already been taken into account. Therefore, we simply take 50% of the calculated capacity and then calculate the consumption per day, month, per season.
For example, the design power of the boiler is 24 kW. To calculate gas consumption for heating, we take half: 12 k/W. This will be the average heat demand per hour. To determine fuel consumption per hour, we divide by the calorific value, we get 12 kW/hour / 9.3 k/W = 1.3 m3. Then everything is calculated as in the example above:
- per day: 12 kW/h * 24 hours = 288 kW in terms of the amount of gas - 1.3 m3 * 24 = 31.2 m3
- per month: 288 kW * 30 days = 8640 m3, consumption in cubic meters 31.2 m3 * 30 = 936 m3.
You can calculate gas consumption for heating a house using the design capacity of the boiler
Next, add 10% for the imperfection of the boiler, we find that for this case the consumption will be slightly more than 1000 cubic meters per month (1029.3 cubic meters). As you can see, in this case everything is even simpler - fewer numbers, but the principle is the same.
By quadrature
Even more approximate calculations can be obtained based on the square footage of the house. There are two ways:
- You can calculate according to SNiP standards - on average, heating one square meter in Central Russia requires 80 W/m2. This figure can be used if your house is built according to all requirements and has good insulation.
- You can estimate based on average statistical data: with good insulation of the house, 2.5-3 cubic meters/m2 is required;
- with average insulation, gas consumption is 4-5 cubic meters/m2.
The better the house is insulated, the lower the gas consumption for heating will be.
Each owner can assess the degree of insulation of his home; accordingly, one can estimate what gas consumption will be in this case. For example, for a house of 100 sq. m. with average insulation, 400-500 cubic meters of gas will be required for heating, for a house of 150 square meters it will take 600-750 cubic meters per month, for heating a house with an area of 200 m2 - 800-100 cubic meters of blue fuel. All this is very approximate, but the figures are derived based on many factual data.
Heating of country cottages
When calculating the gas consumption needed to heat a house, the most difficult task will be calculating the heat loss, which the heating system must fully compensate for during operation.
The complex of heat losses depends on the climate, the design features of the building, the materials used and the operating parameters of the ventilation system.
Calculation of the compensated amount of heat
The heating system of any building must compensate for its heat loss Q (W) during the cold period. They happen for two reasons:
- heat exchange through the perimeter of the house;
- heat loss as a result of cold air entering through the ventilation system.
Formally, heat loss through the wall and roof Qtp can be calculated using the following formula:
Qtp = S * dT / R,
Where:
- S – surface area (m2);
- dT – temperature difference between room and street air (°C);
- R – indicator of heat transfer resistance of materials (m2 * °C / W).
The last indicator (which is also called the “thermal resistance coefficient”) can be taken from the tables attached to the building materials or products.
The heat loss rate of the house significantly depends on the type of double-glazed window. The high price of insulated windows will be justified due to fuel savings
Example. Let the outer wall of the room have an area of 12 m2, of which 2 m2 is occupied by the window.
The heat transfer resistance indicators are as follows:
- Aerated concrete blocks D400: R = 3.5.
- Double-glazed window with argon “4M1 – 16Ar – 4M1 – 16Ar – 4I”: R = 0.75.
In this case, at room temperature “+22°С”, and street temperature – “–30°С”, the heat loss from the outer wall of the room will be:
- Qtp (wall) = 10 * (22 – (– 30)) / 3.5 = 149 W:
- Qtp (window) = 2 * (22 – (– 30)) / 0.75 = 139 W:
- Qtp = Qtp (wall) + Qtp (window) = 288 W.
This calculation gives the correct result provided there is no uncontrolled air exchange (infiltration).
It may occur in the following cases:
- The presence of structural defects, such as loose fitting of window frames to the walls or peeling of insulating material. They need to be eliminated.
- Aging of a building, resulting in chips, cracks or voids in the masonry. In this case, it is necessary to introduce correction factors into the heat transfer resistance of materials.
In the same way, it is necessary to determine heat loss through the roof if the object is located on the top floor. Through the floor, any significant energy loss occurs only if there is an unheated, ventilated basement space, such as a garage. Almost no heat goes into the ground.
To calculate the heat transfer resistance index of multilayer materials, it is necessary to sum up the indicators of individual layers. Usually, only the most non-thermal conductive materials are taken for calculations
Let's consider the second reason for heat loss - building ventilation. Energy consumption for heating the supply air (Qв) can be calculated using the formula:
Qв = L * q * c * dT , where:
- L – air flow (m3/h);
- q – air density (kg/m3);
- c – specific heat capacity of incoming air (kJ/kg *°C);
- dT – temperature difference between room and street air (°C).
The specific heat capacity of air in the temperature range of interest to us [–50.. +30 °C] is equal to 1.01 kJ / kg * °C or, translated to the dimension we need: 0.28 W * h / kg * °C. Air density depends on temperature and pressure, but for calculations you can take a value of 1.3 kg / m3.
Example. For a room of 12 m2 with the same temperature difference as in the previous example, heat loss due to ventilation will be:
Qв = (12 * 3) * 1.3 * 0.28 * (22 – (– 30)) = 681 W.
Designers take air flow according to SNiP 41-01-2003 (in our example, 3 m3 / h per 1 m2 of living room area), but this value can be significantly reduced by the owner of the building.
In total, the total heat loss of the model room is:
Q = Qtp + Qb = 969 W.
To calculate heat loss per day, week or month, you need to know the average temperature for these periods.
From the above formulas it is clear that the calculation of the volume of gas consumed both for a short period of time and for the entire cold season must be carried out taking into account the climate of the area where the heated facility is located. Therefore, well-proven standard solutions can only be used for similar natural conditions.
To determine similar climatic parameters, you can use maps of average monthly temperatures in winter. They can be easily found on the Internet
With the complex geometry of the house and the variety of materials used in its construction and insulation, you can use the services of specialists to calculate the required amount of heat.
Ways to minimize heat loss
The cost of heating a home makes up a significant portion of the cost of maintaining it. Therefore, it is reasonable to carry out some types of work aimed at reducing heat loss by insulating the ceiling, walls of the house, insulating the floor and adjacent structures.
The use of insulation schemes outside and inside the house can significantly reduce this figure. This is especially true for old buildings with severe wear and tear on walls and ceilings. The same polystyrene foam boards can not only reduce or completely eliminate freezing, but also minimize air infiltration through the protected coating.
Significant savings can also be achieved if the summer areas of the house, such as verandas or the attic floor, are not connected to heating. In this case, there will be a significant reduction in the perimeter of the heated part of the house.
Using the attic floor only in the summer significantly saves the cost of heating the house in winter. However, in this case, the ceiling of the upper floor must be well insulated
If you strictly follow the standards for ventilation of premises, which are prescribed in SNiP 41-01-2003, then heat loss from air exchange will be higher than from freezing of the walls and roof of the building. These rules are mandatory for designers and any legal entities if the premises are used for production or provision of services. However, residents of the house can, at their discretion, reduce the values specified in the document.
In addition, to heat the cold air coming from the street, you can use heat exchangers, rather than devices that consume electricity or gas. Thus, an ordinary plate heat exchanger can save more than half of the energy, and a more complex device with coolant can save about 75%.
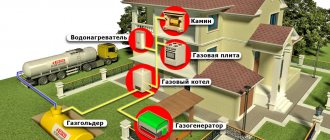
Heating a house with a gas holder
It is better to calculate the required amount of gas in relation to the barrel. That is, how long will each container last for different room sizes?
The gas tank is selected according to the number of refills. The optimal rate is 1-2 times a year. At a minimum, the tank should last for 7–8 months—the heating season.
Liquefied gas consumption per season
According to SP 131.13330.2012 Construction Climatology (updated edition of SNiP 23-01-99), the heating season in Russia is 207 days. This is approximately 7 months.
Also important information: the boiler does not operate around the clock. On average, heating operates 10 hours a day.
We carried out calculations based on the initial data:
- brick house without attic and basement;
- floor height 3.2 m;
- The efficiency of the gas boiler is 92%.
Indicators for refueling frequency are averaged. We assumed the same fuel costs for each month. In reality, residence may be seasonal or temporary, and consumption differs depending on the season.
The ratio of the area of the house and the volume of the gas tank (GG)
| GG volume (m3) | Full gas charge (l) | How long will gas last (months) | |||||||
| 50–100 m2 | 150 m2 | 200 m2 | 250 m2 | 300 m2 | 350–450 m2 | 500–600 m2 | 800 m2 | ||
| 3,802 l/year | 5,703 l/year | 7,603 l/year | 9,504 l/year | 11,405 l/year | 17,107 l/year | 22,809 l/year | 30,412 l/year | ||
| 2.5 | 2 125 | 6.7 | 4.5 | 3 | 2.7 | 2 | 1.5 | 1.1 | 0.8 |
| 2.7 | 2 295 | 7 | 5 | 3.6 | 3 | 2.4 | 1.6 | 1.2 | 0.9 |
| 4.6 | 3 910 | 12 | 8 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 2.7 | 2 | 1.5 |
| 4.8 | 4 080 | 12.8 | 8.5 | 6.4 | 5.1 | 4.2 | 2.8 | 2.1 | 1.6 |
| 4.85 | 4 112 | 13 | 8.6 | 6.5 | 5.2 | 4.3 | 2.9 | 2.2 | 1.6 |
| 5 | 4 250 | 13.4 | 9 | 7 | 5.4 | 4.5 | 3 | 2.2 | 1.7 |
| 6.4 | 5 440 | 17 | 11.4 | 8.5 | 6.8 | 5.7 | 3.8 | 2.8 | 2.1 |
| 6.5 | 5 525 | 17.4 | 11.6 | 8.7 | 6.9 | 5.8 | 3.9 | 2.9 | 2.2 |
| 6.6 | 5 610 | 17.6 | 12 | 9 | 7 | 6 | 4 | 3 | 2.2 |
| 8.6 | 7 310 | 23 | 15 | 11.5 | 9 | 7.7 | 5 | 3.8 | 2.9 |
| 9.1 | 7 735 | 24.4 | 16 | 12 | 9.7 | 8 | 5.4 | 4 | 3 |
| 9.15 | 7 777 | 24.5 | 16.4 | 12.3 | 9.8 | 8.2 | 5.5 | 4.1 | 3.1 |
| 9.6 | 8 160 | 25.7 | 17 | 13 | 10 | 8.6 | 5.7 | 4.3 | 3.2 |
| 10 | 8 500 | 27 | 18 | 13.4 | 10.7 | 9 | 6 | 4.5 | 3.4 |
Interpretation of colors in the table:
| irrational | Capacity supply is too large or too small |
| optimal | For seasonal or permanent residence with 2 refills per year |
| perfect | It is best to install for the heating season |
| with reserve | One-time refill is enough for a year |
Houses with an area of 800–1000 m2 are served by:
- gas tanks with industrial volumes of more than 10 m3 (installation is more complicated);
- two containers located side by side (8.6, 9.1 or 9.15 m3).
Calculation formula
To determine the amount of fuel consumed, you can use existing formulas.
Together they give a complete picture of the amount of fuel required for heating. First you need to determine the power of the boiler. It is calculated according to the principle of 1 kW of energy per 10 m2.
In this case, the power reserve should be about 20%, since it is not customary to operate the device at maximum performance. As a result, for a house with an area of 150 m2, the optimal boiler power can be about 13 kW. Based on this, the amount of fuel required is determined. If it is liquefied, then a week can take from one to four 50 liter cylinders.
Attention! It is customary to fill cylinders not completely, as propane and butane expand. Therefore, the amount of liquefied gas in the cylinder is usually about 80% of its volume. It is believed that on average 15 liters of liquefied gas per day are consumed per 100 m2
Accordingly, for a cottage of 150 m2 this figure increases to 22.5 liters per day. A 50 liter cylinder is usually filled with about 40 liters. Thus, with active use, you can use more than one cylinder in two days.
It is believed that on average 15 liters of liquefied gas per day are consumed per 100 m2. Accordingly, for a cottage of 150 m2 this figure increases to 22.5 liters per day. A 50 liter cylinder is usually filled with about 40 liters. Thus, with active use, you can use more than one cylinder in two days.
But these are approximate calculations, and you can make even more accurate ones using the formula: 169.95/12.88/0.98 x S premises x cost of 1 kg of liquefied gas. Here, 169.95 kW means the thermal energy for heating 1 m2, 12.88 kW/kg is the calorific value of liquefied propane and 98% is the efficiency of the boiler.
What is the average consumption per week
The figure demonstrating the consumption of liquefied gas for heating can be determined based on a number of parameters.
In addition to the area of the house, materials and weather conditions, this is also the mode of operation. Therefore, for each building the consumption will vary, even if it has the same area.
But according to home owners, in regions where in winter the temperature ranges from -5 to -20 C, 150 m2 on average can use 3 cylinders of 50 liters per week.
In this case, the boiler is turned on 2 times a day for 3 hours. Savings are increased through the use of advanced models of boilers and thermostats that regulate fuel consumption in proportion to changes in air temperature.
Seasonal consumption for heating a house with an area of 150 m2
The seasonal consumption of liquefied gas for heating a cottage with an area of 150 m2 is calculated based on weekly expenses. But it is worth remembering that this figure is approximate, since the weather will change repeatedly, and at the same time, fuel consumption. Meanwhile, along with the amount of fuel, financial costs can also be calculated.
To calculate the cost of consumption during the season, it is necessary to multiply the power of a particular device by 24 hours, then by 30 days. Since it is unlikely that the boiler is operating at maximum power all this time, the result must be divided by 2.
The resulting figure is multiplied by 7 months of the heating season, and this gives an indicator of power consumption per year.
Having found out the cost of 1 kW/hour, you need to multiply it by the annual amount of kW. The result obtained will demonstrate the financial costs of consumption. However, that’s not all, because cylinders with exhausted gas need to be refilled regularly, and this also costs money.
You can make refueling less frequently if you use fuel sparingly. For example, when you are away from home, it is enough to set the room heating temperature to a lower temperature, and then the financial costs of heating will be significantly reduced.
Liquefied gas consumption per month and year
Let's go over the costs of refilling a gas tank for houses of different sizes. We use the LPG price current at the beginning of 2022 - 17.80 rubles/l. This is the cost of refueling in our company.
House area (m2) Gas consumption per month (l) Gas price per month (rub.) Gas consumption per year (l) Gas price per year (rub.)
| 50–100 | 316 | 5 624 | 3 802 | 67 675 |
| 150 | 475 | 8 455 | 5 703 | 101 153 |
| 200 | 633 | 11 267 | 7 603 | 135 533 |
| 250 | 792 | 14 097 | 9 504 | 169 171 |
| 300 | 950 | 16 910 | 11 405 | 203 009 |
| 350–450 | 1 425 | 15 365 | 17 107 | 304 504 |
| 500–600 | 1 900 | 33 820 | 22 809 | 406 000 |
| 800 | 2 534 | 45 105 | 30 412 | 541 334 |
Thus:
- gas consumption for heating a house of 100 m2 is 68 thousand rubles per year;
- gas consumption for heating a house of 150 m2 is 101 thousand rubles per year;
- gas consumption for heating a house of 200 m2 is 136 thousand rubles per year.
Ways to reduce energy consumption
Electric heating is the most profitable, which is proven by calculation.
To reduce heating costs, we recommend using the following tips:
- The easiest way is to insulate the house. A lot of heat is wasted through old windows, which are often not sealed tightly. Modern plastic windows with several air chambers significantly reduce heating costs. The walls are insulated with various materials with low thermal conductivity - foam plastic, mineral wool, etc. There is also a need to insulate the foundation and roof.
- Payment according to multi-tariff accounting. Peak loads occur from 08:00 to 11:00 and from 20:00 to 22:00. Therefore, it is beneficial for the boiler to operate at night, when energy consumption, and therefore its price, is minimal.
- Installation of injection equipment to accelerate the movement of coolant. As a result of this, the hot coolant will be in contact for a minimum time with the walls of the boiler, which allows you to use the heat source longer.
- Installation of additional heating devices running on fuel.
- The use of ventilation with a recuperator. This device will return almost all the heat that escapes along with the heated air during ventilation of the premises. When using a system of sufficient power, there is no need to open windows for ventilation at all. At the same time, humidity and air purity will be maintained at an optimal level.
A hundred years ago, the consumer did not have to choose a heating system. It was either coal or firewood. Plus, a fireman was needed, whose duties were most often performed by the owner of the house. Currently, a large number of different energy carriers have appeared. Depending on the chosen energy source, you can select one or another equipment. However, how to choose an affordable source with a long-term future? Let's try to figure this out.
Let's take as a basis a residential building with an area of 100 square meters. If this house is insulated in accordance with SNIP standards, then its energy loss at the minimum outside temperature for a given region should not exceed 100 W per 1 sq. m. meter of area per hour. Accordingly, we need a heat source that allows us to produce 10 kW of thermal energy to compensate for these energy losses. Note that this figure does not depend on the choice of heating system, but is determined solely by the design of the building. Further, we agree that the heating season lasts 5 months or 150 days. During the heating season there are both cold and warm days. Therefore, we will accept one more condition - the average energy loss of a house during the heating season will be equal to half of the maximum (which, however, is practically true). Thus, during the heating season our house will require:
Q = 150*24*5 = 18000 kilowatts.
So, let's consider the following types of energy carriers:
- Electricity
- Electricity with a two-tariff meter
- Electricity with a two-tariff meter and a heat accumulator
- Main gas
- Bottled gas
- Gas from a gas tank
- Diesel fuel
- Firewood
- Coal
- Pellets
- Heat pump
- Heat pump with two-tariff meter
In passing, we note that the calculation of heating costs was made at prices in the Moscow region at the end of March 2012. Naturally, these numbers may vary depending on the region and time period.
For those who do not want to delve into the details, here is a final table of heating costs:
| Coolant type | Unit | price | consumption per season | total heating costs, rub. |
| Electricity | kW/h | 2r.37k. | 18000 | 42660 |
| Electricity with a two-tariff meter | kW/h | 2r.37k/92k. | 18000 | 38160 |
| Electricity with a two-tariff meter and a heat accumulator | 18000 | 16560 | ||
| Main gas | cube meter. | 3r.30k. | 1821 | 6012 |
| Bottled gas, gas from a gas tank (liquefied gas) | liter | 16 rub. | 2958 | 47340 |
| Diesel fuel | liter | 25 rub. 50k. | 1976 | 50400 |
| Firewood | cube meter | 1350 rub. | 11 | 15840 |
| Coal | kilogram | 9r. 50k. | 2046 | 19440 |
| Pellets | kilogram | 10 rub. | 4176 | 41760 |
| Heat pump | 79k. (47.4 k.) | 14220 (8532) | ||
| Heat pump with two-tariff meter | from 18k. up to 91k. | 18000 | 12756 (7632) |
Prices for little-used, but quite profitable heating systems are highlighted in green. Prices for frequently used, but quite meaningless from an economic point of view, energy resources are highlighted in red.
A gas boiler
Having made a preliminary calculation of the fuel consumed, many choose the liquefied type and install a gas boiler in their home. This choice is determined by the following factors:
- Long service life. Liquefied fuel does not destroy the material from which boilers are made, so they last for quite a long time.
- Easy installation. If we compare the process of connecting to a gas pipeline and the process of installing individual gas equipment, the second is much easier and faster.
- Economic benefit. Since heating the same room requires less liquefied gas than mains gas, its use will be more economical (especially in cases with large houses exceeding 200 m²).
- Properties. Fuel in cylinders has better characteristics. When it burns, no hazardous substances are released. The minimum sulfur content guarantees high combustion efficiency.
- Safety. Autonomous units are equipped with modern systems that prevent fuel leakage and explosion in the event of a breakdown.
A gas boiler is economical and safe.
With all its advantages, autonomous heating equipment is not without some disadvantages. These include the need to regularly refill cylinders, the influence of atmospheric pressure on the operation of the system, and the inability to operate during a power outage.
The main part of any autonomous gas heating system is a gas tank . This is a container into which liquefied gas is pumped. The amount of thermal energy released by the gas during combustion directly depends on the area for evaporation of the gas tank. This area inside the tank is called a mirror. If the 4.8 ton tank is fully filled, this volume will be enough for a period of about 200 days.
In addition to the size of the mirror, the volume of heat generated is affected by the design of the heating system, the number and area of the radiators included in it, climatic conditions and other factors.
Is it profitable to install autonomous heating?
The cost of purchasing, installing and setting up autonomous heating equipment that runs on a mixture of propane and butane is much lower than connecting to the main line.
This system also significantly reduces the risk of a sudden drop in pressure. Autonomous heating is equipped with tanks that keep the fuel available after it runs out in the main tank.
In the event of a power outage or gas supply, the safety system will block the solenoid valve. Once the supply is restored, the system must be restarted.
What increases gas consumption
Gas consumption for heating, in addition to its type, depends on the following factors :
- Climatic features of the area. The calculation is carried out for the lowest temperature indicators characteristic of these geographical coordinates;
- The area of the entire building, its number of floors, the height of the rooms;
- Type and presence of insulation of the roof, walls, floor;
- Type of building (brick, wood, stone, etc.);
- The type of profile on the windows, the presence of double-glazed windows;
- Organization of ventilation ;
- Power in the limit values of heating equipment.
The year the house was built and the location of the heating radiators are also important.
Save money by not heating all rooms equally
Not all rooms and volumes of the house need to be maintained at the same temperature. For example, storerooms, gyms, garages, workshops may have a slightly lower temperature, while children's rooms, showers or bathrooms may have a higher temperature.
To maintain the desired temperature in a particular room, you need to install regulators on each heating radiator. The principle of their operation is simple - they change the working cross-section of the heater pipe and reduce or increase the coolant circulation rate. It is enough to set the required temperature value on the regulator. This measure optimizes the total gas consumption for heating water in the boiler.
How to reduce gas consumption
A well-known rule: the better the house is insulated, the less fuel is used to heat the street. Therefore, before starting the installation of the heating system, you should perform high-quality thermal insulation of the house - roof/attic, floors, walls, replacement of windows, airtight sealing loop on the doors.
You can also save fuel due to the heating system itself. By using heated floors instead of radiators, you will get more efficient heating: since heat spreads by convection currents from bottom to top, the lower the heating device is located, the better.
In addition, the standard temperature of floors is 50 degrees, and radiators are on average 90. Obviously, floors are more economical.
Finally, you can save gas by adjusting the heating according to time. There is no point in actively heating a house when it is empty. It is enough to maintain a low positive temperature so that the pipes do not freeze.
Modern boiler automation (types of automation for gas heating boilers) allows remote control: you can give a command to change the mode through a mobile provider before returning home (what are Gsm modules for heating boilers). At night, the comfortable temperature is slightly lower than during the day, etc.
We use modern automation
Well, and the obvious things: you can save gas by correctly setting the heating time. For example, if you are away from home from morning to evening, then in the boiler (if it supports such a function) you can set the thermostat to a low temperature and program an increase in power at a certain time. And if you are away from home for weeks or even months, then ideally you need to set the coolant temperature to 3-5 degrees. And let it be cold in the house. The main thing is that the pipes do not freeze.
Modern technologies have gone far ahead in this regard. Many boilers can be equipped with modern automation, which allows you to control the device remotely. You can command the boiler to change mode from your smartphone while at work. For this purpose, special GSM modules are installed on the equipment. And there are many similar smart systems. If used correctly, actual heating costs can be reduced. Sometimes savings can reach 30, 40 and even 50%. Of course, this depends on how often you are at home and what the temperature is outside.
How to calculate main gas consumption
The calculation of gas consumption for heating a private home depends on the power of the equipment (which determines the gas consumption in gas heating boilers). Power calculation is performed when choosing a boiler. Based on the size of the heated area. They calculate for each room separately, focusing on the lowest average annual temperature outside.
To determine energy consumption, the resulting figure is divided approximately in half: because throughout the season, the temperature fluctuates from severe minus to plus, gas consumption varies in the same proportions.
When calculating power, the ratio is based on the ratio of kilowatts per ten square meters of heated area. Based on the above, we take half of this value - 50 watts per meter per hour. At 100 meters – 5 kilowatts.
Fuel is calculated using the formula A = Q / q * B, where:
- A – the required amount of gas, cubic meter per hour;
- Q – power required for heating (in our case 5 kilowatts);
- q – minimum specific heat (depending on the type of gas) in kilowatts. For G20 – 34.02 MJ per cubic meter = 9.45 kilowatts;
- B is the efficiency of our boiler. Let's say 95%. The required figure is 0.95.
We substitute numbers into the formula, and for 100 m2 we get 0.557 cubic meters per hour. Accordingly, the gas consumption for heating a house of 150 m2 (7.5 kilowatts) will be 0.836 cubic meters, the gas consumption for heating a house of 200 m2 (10 kilowatts) will be 1.114, etc. It remains to multiply the resulting figure by 24 - you get the average daily consumption, then by 30 - the average monthly.
Calculation formula for main fuel
The power of the boiler affects gas consumption in a private home, so the owner must first calculate the fuel consumption, focusing on gas equipment. The area of the cottage is also taken into account. Each room is calculated separately, based on the average annual street temperature and starting from the obtained minimum value.
To calculate gas consumption, the identified number must be divided by 2, since each winter season has different air temperatures. In the northern regions, it can reach serious disadvantages; accordingly, resource consumption will be higher than in the southern regions.
According to all the rules, it is calculated as follows: the ratio is 1 kW per 10 sq. m. area of the house. Divide the resulting number in half, resulting in 50 watts for 60 minutes of heating. A house with an area of 100 m² will consume approximately 5 kW. Formula for calculating gas consumption in a private home (A=Q/q*B):
- A - cubic meter of resource consumption in 60 minutes;
- Q is the power of equipment for heating the house, in this case 5 kW;
- q - determines the minimum specific heat, it all depends on the type of fuel, for example, for G20 - 34.02 MJ per 1 cubic meter comes out to almost 10 kW;
- B is the efficiency of the equipment, for example, it works at 90%, which means they take the figure at 0.90.
All that remains is to substitute the required numbers instead of the letters in the formula. In this case, gas consumption per 100 sq. m. will be like this: 0.560 cubic meters per 60 minutes of boiler operation. For heating a room with an area of 150 sq. m. it will turn out to be 0.840 cubic meters and 7.5 kW. For suburban real estate, 1,115 cubic meters and approximately 10 kW will be spent on 200 m².
For a room of 250 m² it will be 1,392 cubic meters. A house of 300 m² will use 1,662 cubic meters. resource. The resulting number is multiplied by 24 hours and the consumption per day is determined, and then multiplied by 30 days.
How to save money?
The financial costs of maintaining a comfortable microclimate in the house can be reduced by
:
- additional insulation of all structures, installation of windows with double-glazed windows and door structures without cold bridges;
- installation of high-quality supply and exhaust ventilation (an incorrectly executed system can cause increased heat loss);
- use of alternative energy sources - solar panels, etc.
Separately, it is worth paying attention to the advantages of the collector heating system and automation, thanks to which the optimal temperature level is maintained in each of the rooms. This allows you to reduce the load on the boiler and fuel consumption when the weather warms up outside, and reduce the heating of the coolant that is supplied to radiators or a heated floor system in unused rooms.
If the house has a standard radiator system, a sheet of thin foam heat insulator with an outer foil surface can be glued to the wall behind each heating device. Such a screen effectively reflects heat, preventing it from escaping through the wall to the street.
A set of measures aimed at increasing the thermal efficiency of a home will help minimize energy costs.
How to avoid heat loss
Fuel consumption for heating a house depends on the total area of the heated premises, as well as the heat loss coefficient. Any building loses heat through the roof, walls, window and door openings, and the floor of the lower floor.
Accordingly, the level of heat loss depends on the following factors
:
- climate features;
- wind roses and the location of the house relative to the cardinal directions;
- characteristics of the materials from which building structures and roofing are constructed;
- presence of a basement/ground floor;
- quality of insulation of floors, wall structures, attic floors and roofs;
- quantity and tightness of door and window structures.
Thermal calculation of the house allows you to select boiler equipment with optimal power parameters. In order to determine the heat requirement as accurately as possible, the calculation is performed for each heated room separately. For example, the heat loss coefficient is higher in rooms with two windows, in corner rooms, etc.
Note! The boiler power is selected with some margin relative to the calculated values obtained. The boiler unit wears out faster and fails if it regularly operates at its maximum capacity. At the same time, excessive power reserves result in increased financial costs for the purchase of a boiler and increased fuel consumption.
How much propane-butane do you need for the heating season?
Modern gas boilers are designed to use not only main gas, but also liquefied gas. To stock up on the required amount of fuel, they use not ordinary gas cylinders, but more capacious tanks - gas tanks.
The use of gas tanks solves the problem of storing liquefied hydrocarbon fuel sufficient to heat a house of 100 square meters. m, throughout the heating season in a temperate climate zone
When calculating the consumption of liquefied gas required to heat a 100m2 house, the same methodology is used, but the values of some variables in the formula change.
A liquefied propane-butane mixture is supplied for household needs.
Its calorific value is 12.8 kW/kg. We substitute this parameter into the formula and get:
V = 10 / (92.5 / 100 × 12.8). V = 0.8 kg/h.
When operating on liquefied fuel, the efficiency of the equipment decreases, so gas consumption increases by approximately 10% and amounts to 0.88 kg/h per day. The correction may be different for your boiler model. The specific value is indicated in the attached documentation.
Now we calculate the required amount of gas for the heating season: 0.88 × 24 × 183 = 3865 kg. This value must also be divided by 2 due to temperature fluctuations. Final result: 1932.5 kg of propane-butane is required for the heating season.
It will be useful to convert kilograms to liters. Based on reference data, 540 grams of liquefied propane-butane mixture corresponds to 1 liter. That is, for the entire heating season, 3578 liters of liquefied gas will be required.
Using a propane-butane mixture
Autonomous heating of private houses with liquefied propane or its mixture with butane has not yet lost its relevance in the Russian Federation, although in recent years it has noticeably increased in price
It is all the more important to calculate the future consumption of this type of fuel for those homeowners who are planning such heating. The same formula is used for the calculation, only instead of the lower calorific value of natural gas, the parameter value for propane is set: 12.5 kW with 1 kg of fuel
The efficiency of heat generators when burning propane remains unchanged.
Below is an example of a calculation for the same building of 150 m², only heated with liquefied fuel. Its consumption will be:
- for 1 hour - 15 / (12.5 x 92 / 100) = 1.3 kg, per day - 31.2 kg;
- on average per day - 31.2 / 2 = 15.6 kg;
- on average per month - 15.6 x 30 = 468 kg.
When calculating the consumption of liquefied gas for heating a house, it is necessary to take into account that fuel is usually sold in volumetric measures: liters and cubic meters, and not by weight. This is how propane is measured when filling cylinders or a gas tank. This means that it is necessary to convert mass into volume, knowing that 1 liter of liquefied gas weighs about 0.53 kg. The result for the example above will be:
468 / 0.53 = 883 liters, or 0.88 m³, propane will have to be burned on average per month for a building with an area of 150 m².
Considering that the retail cost of liquefied gas is on average 16 rubles. for 1 liter, heating will cost a considerable amount, about 14 thousand rubles. per month for the same cottage on one and a half hundred square meters. There is reason to think about how best to insulate walls and take other measures aimed at reducing gas consumption.
Many homeowners expect to use fuel not only for heating, but also to provide hot water supply
These are additional costs, they must be calculated, plus it is important to take into account the additional load on the heating equipment
The thermal power required for hot water supply is easy to calculate. You need to determine the required volume of water per day and use the formula:
- c is the heat capacity of water, equal to 4.187 kJ/kg °C;
- t1—initial water temperature, °C;
- t2—final temperature of heated water, °C;
- m is the amount of water consumed, kg.
As a rule, economical heating occurs to a temperature of 55 °C, and this must be substituted into the formula. The initial temperature varies and lies in the range of 4-10 °C. For a day, a family of 4 people requires approximately 80-100 liters for all needs, provided that it is used sparingly. It is not necessary to convert the volume into mass measures, since in the case of water they are almost the same (1 kg = 1 l). It remains to substitute the obtained value of QDHW into the above formula and determine the additional gas consumption for DHW.
Nuances and subtleties
It is important to understand what the liquefied gas consumption will be for heating a house of 150-200 m2 in order to take care of how the fuel is stored. You can hold it:
- in cylinders. Their volume is small - from 10 to 50 liters. Regular replacement or refilling is required, which is not very convenient. In fact, approximately 35 liters will be needed per day for heating with liquefied gas;
- gas holders. This is a special storage (reservoir) for blue fuel. Can hold from 200 to 1000 liters depending on the dimensions. Such a structure must be built in accordance with safety requirements and standards. To refill the gas tank, you will need to call specialists. Attempts on your own may result in fires and explosions.
A gas holder - a container for storing liquefied gas for heating - can hold up to 1000 liters of “blue fuel”
As for the prices for such heating, they depend on the region where you live.
The cost of a liter of liquefied gas varies from 12 to 20 rubles. Based on the average value of 15 rubles, during the heating season you will spend approximately 121 thousand rubles on a building with an area of 200 square meters.
Any other type of fuel will be cheaper. For natural blue fuel - approximately 40 thousand rubles, for firewood and coal - about 60 thousand rubles per heating season.
Method number 1: Insulate yourself
A warm house is a structure with a minimum number of spontaneous air escapes from the house. The easiest way is to insulate a house that is just under construction - modern technologies make it possible to achieve great success in this area. But the old house will have to be specially insulated.
Most heat is lost through the roof, floor, doors and windows.
Installing good doors and windows is not a problem. However, you can minimize costs with a special home layout. Windows and doors should be located where there is the most sun and the least wind. It is easy to assess where the sun will shine - in the northern hemisphere it is a combination of south and west. As for the prevailing winds, you need to study the wind rose, according to which you can place windows.
If you already live in a house where no one took into account geographical and climatic factors, then you can create additional barriers in the path of the winds from buildings such as a veranda or trees, mainly coniferous. They will not only create comfort, but will also significantly reduce heat loss from strong winds.
However, the use of green spaces as protective barriers is creative, since they cover windows not only from the wind, but also from the sun.
Experts' opinions
Gas consumption for heating a house of 150 m2, according to experts, depends on the efficiency of the boiler, the correctness of the installed system, and the equipment manufacturer. For the most detailed cost calculation, you should consider:
- cost of combustible materials;
- operating costs;
- cost of equipment, its delivery and installation;
- air temperature during cold periods;
- mode of residence in the house (temporary or permanent);
- degree of modernization of the building (material of construction, presence of insulation, etc.).
Example: Forumhouse user used the following as calculation data:
- house area – 150 m2;
- duration of the heating period – 6 months;
- System efficiency – 0.5;
- specific power of the climatic zone is 1.5 kW.
After calculations, the following results were obtained:
- the average volume of raw materials to produce 1 kW/h of heat is 0.1 m3;
- gas cost (approximate) – 5 rubles/m3;
- the cost of 1 kW/h of gas is 0.5 rubles;
- heating costs for the season - 11,000 rubles.
Performing Calculations
A preliminary calculation of gas consumption for heating is made using the formula:
V = Q / (q x efficiency / 100).
- q is the caloric content of fuel, the default is 8 kW/m³;
- V is the required main gas flow rate, m³/h;
- Efficiency is the efficiency of fuel combustion by a heat source, expressed in %;
- Q is the heating load of a private house, kW.
As an example, we offer the calculation of gas consumption in a small cottage with an area of 150 m² with a heating load of 15 kW. It is planned that the heating task will be performed by a heating unit with a closed combustion chamber (efficiency 92%). The theoretical fuel consumption per 1 hour in the coldest period will be:
15 / (8 x 92 / 100) = 2.04 m³/h.
During the day, the heat generator will consume 2.04 x 24 = 48.96 m³ (rounded - 49 cubic meters) of natural gas - this is the maximum consumption on the coldest days. But during the heating season, the temperature can fluctuate between 30-40°C (depending on the region of residence), so the average daily gas consumption will be half as much, about 25 cubic meters.
Then, on average, per month a turbocharged boiler uses 25 x 30 = 750 m³ of fuel to heat a house with an area of 150 m², located in central Russia. Consumption for cottages of other sizes is calculated in the same way. Based on preliminary calculations, it is possible to carry out measures aimed at reducing consumption even at the construction stage: insulation, selection of more efficient equipment and the use of automatic control devices.
History instead of conclusions
A user with the nickname Blonde 99 permanently lives in a frame house with an area of 100 m2. The temperature in the rooms is maintained at 25°C.
One refill of a 4,800 liter gas tank was enough for 3 years of use! The expense was 20 thousand per year.
We recommend doing the same: buy a larger gas tank and forget about refueling for a long time.
Gas is still the cheapest type of fuel, but the cost of connection is sometimes very high, so many people want to first assess how economically justified such expenses are. To do this, you need to know the gas consumption for heating, then you can estimate the total cost and compare it with other types of fuel.
Reducing consumption
This is known: if you insulate your house well, the fuel consumption for heating will be significantly reduced. Therefore, before selecting and installing equipment and laying main routes, it is necessary to properly insulate the house: walls, roof and attic, floor, replace windows, and make an airtight sealing loop on the doors.
Particular attention should be paid to the roof and windows. It is assumed that out of 100% of lost heat, 35% goes through the roof, about 25% is lost at the windows. Therefore, use the best thermal insulation materials and good double-glazed windows, which have a low thermal conductivity coefficient. Cheap double-glazed windows are immediately obvious: their aluminum or steel “skeleton” is always very cold in winter, and a lot of heat is lost directly through it. Even the glass itself does not transmit heat as much as the metal profile on which the glass is held does.
Selection of boiler power based on calculation results
Having determined the heat losses of walls, windows, ceilings and floors, all values must be summed up, and the result will be the total heat loss of the building, measured in kilowatts (kW). The same unit is used to measure the thermal power of heat generators. The boiler power is selected with a margin of 10-15% of the total heat loss capacity of the building. If there is a swimming pool, a large-volume hot tub, or heating of the ventilated air of the supply and exhaust system from heating, the thermal needs of this equipment are summed up with the figure obtained by calculating heat loss.