The house is still under construction, all the troubles relate to the construction of the building and other equally important problems. However, sooner or later, every owner of both a private house and an apartment thinks about a heating system. Like any other utility network, the heating system requires increased attention to detail. The heart of the heating system is the boiler. It is very important to choose the right boilers so that no problems arise in the future.
There are a huge number of different types of boilers
First, let's note the advantages of creating an autonomous heating system over a central one:
- The ability to turn heating on and off as needed/desired - there is no schedule here.
- The ability to regulate the temperature inside heated rooms.
- If you install a double-circuit boiler, you can also install hot water supply.
Areas of application of steam boilers and purpose
Steam boilers are actively used in the following industries:
- Heating systems . There are industrial and domestic models of steam boilers that allow the use of steam as a coolant. The steam passes through the heating circuits and/or enters the heat exchangers of hot water supply devices, thereby transporting thermal energy. A household steam heating boiler is often combined with solid fuel heating devices. Industrial facilities use more powerful and reliable devices that produce superheated steam with increased heat transfer.
- Energy . Steam engines allow you to convert heated steam into electrical energy. The working process looks quite simple: steam moves into the turbine and rotates the shaft, due to which electricity is generated. This principle has been successfully used in many power plants.
- Industry . Steam devices may well provide mechanical movement of various system elements. The operating principle of an industrial steam boiler looks the same as in the previous case, but the generated energy is aimed at exerting a mechanical effect on the elements that must move.
Knowing what a steam boiler is for and where it is used allows you to use the device with utmost efficiency.
Etymology
The word cauldron first appears in Middle English as caudrun
(13th century).
This was borrowed from Normand caudron
[1] (Picard
caudron
, French: Chaudron).
It represents a phonetic evolution of Vulgar Latin *caldario
per Classical Latin
caldarium
"hot bath", derived from
cal(i)dus
"hot".[1]
Norman French word replaces Old English ċetel
(German
(Koch) Kessel
"cauldron", Dutch
(eccentric) ketel
"cauldron"), Middle English
Chetel
.
The word "kettle" is borrowed from the Old Norse variant Ketill
"cauldron".[2]
Operating principle of a steam boiler
First of all, you need to understand what is called a steam boiler. A steam boiler is a device that generates steam. There are two types of steam produced - saturated and superheated. The saturated temperature is 100 degrees and the pressure is 100 kPa. Superheated steam heats up to 500 degrees, and the pressure can exceed 26 MPa. Saturated steam is used in household units, and superheated steam, due to its characteristics, is applicable only at industrial-scale facilities.
The raw material for creating steam is water, which is processed in a boiler running on any type of fuel. During operation, the generated steam is converted into a coolant that delivers thermal energy to the area where it is used.
Regardless of the design features of a particular device, the general principle of operation of a steam boiler always remains the same:
- First, the water goes through a purification stage and is sent to a reservoir (usually located at the top of the device) using an electric pump;
- The water accumulated in the reservoir flows into pipes leading to the collector located below;
- From the collector, water is directed upward, entering the heating zone;
- In the pipe, water is converted into steam, which escapes upward due to the difference in pressure between the liquid and gas;
- At the top of the structure there is a separator that allows you to separate steam from water and drain excess water into the tank;
- The steam is directed into the pipeline and sent to consumers;
- In steam generators, the heating stage is carried out again to achieve the required steam state.
To understand well how a steam boiler works, you also need to consider the features of its design, which will be discussed further.
In Ozhegov's dictionary
BOILER, -tla, m. 1. Large metal round vessel for heating water and cooking food. Cast iron k. 2. Closed container, device for converting liquid into steam. Steam room 3. transfer. Complete encirclement of the military group. Get to the camp * Common boiler - food, allowances from the common kitchen. The artel has a common boiler. Boil in some kind of cauldron (disapproved) - constantly be in some kind of cauldron. actively operating environment, surroundings. || decrease bowler, -lka, m. (k. 1 value). || adj. boiler room, -aya, -oe (to 1 and 2 values) and boiler room, -aya, -oe (to 1 and 2 values). Boiler installation. Boiler allowance (from a common boiler; official).
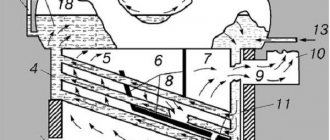
Steam boiler structure
Structurally, a steam boiler is a container in which the process of converting water into steam occurs. The container is usually made of a pipe, the diameter of which can vary within a fairly wide range. In addition to the filled pipe, the steam boiler circuit includes a combustion chamber designed for burning fuel.
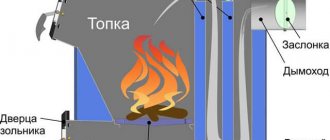
The firebox may have certain features that directly depend on the type of fuel used. For example, solid fuel combustion chambers are equipped with a grate in the lower part, through which oxygen enters the chamber. A traditional chimney is installed at the top of the structure, creating draft and ensuring normal combustion. In the case of using liquid energy carriers or gas, the combustion chamber is equipped with a burner.
In any case, the gas released during fuel combustion approaches the container filled with water, gives off its heat to it and is discharged into the atmosphere through the chimney. At a certain moment, the water begins to boil and turn into steam, which is directed to the upper part of the container, and then into the pipes.
In Vasmer Max's dictionary
genus. p. -tla, ukr. boiler, kind. n. kitla, other Russian, old Slav. kotl χαλκίον, Bulgarian cauldron, Serbohorv. kotao, b. n. kotla, Slovenian kótǝl, Czech. kotel, b. n. kotla, slvts. kotol, Polish kosiоɫ, gen. kotɫa, v.-luzh. kotoɫ, n.-luzh. kóśeɫ. Borrowing to Praslav Gothic era *katils or *katilus (attested form of the genus plural katilē), which comes from Lat. catīnus or catīllus “dish, bowl”; see Bernecker 1, 591; Uhlenbeck, AfslPh 15, 488; Schwartz, AfslPh 41, 125; Bruch, Kretschmer-Festschr. 10 et seq.; Frenkel, ZfslPh 8, 419. Hardly directly from Latin, contrary to Meillet (Ét. 186), Sobolevsky (ZhMNP, 1911, May, p. 163; AflsPh 33, 478); see Kiparsky 203 et seq. Old Balt.-Slav. the origin of the borrowing, contrary to Trautman (ВSW 121), cannot be proven, since lit. kãtilas, Old Prussian katils, lts. katls could be obtained through slav. mediation; see Bernecker, ibid.; M.–E. 2, 171; Buga, “Švietimo darbas”, 1921, No. 5–6, p. 20. From kotelnik came the local. n. Kotelnich, former Vyatsk lips; old the name Koksharov (according to Naumov, Memoir of the Prince of Vyatka Gubernia, 1904, p. 209 et seq.; as quoted in FUF 9, 122). Koksharov is a derivative of kovshar “master who makes ladles, boilers”, from kovsh (see).
Types of steam boilers
The first parameter by which steam boilers are classified is the type of fuel used, depending on which the following types of boilers are distinguished:
- Gas;
- Coal;
- Fuel oil;
- Electrical.
Depending on their purpose, the following types of steam boilers are distinguished:
- Household;
- Industrial;
- Energy;
- Recycling.
The last parameter is the design, which allows us to distinguish two types of boilers:
- Gas pipes;
- Water tube.
The design of a steam boiler is quite important, so it is worth understanding what the differences are between these types of devices.
Differences between gas and water tube boilers according to the operating scheme
A container that allows you to create steam is usually made of one or more pipes. The water found in them is heated by the heated gases released during the combustion of fuel. This design implies that the gas itself rises to water-filled pipes, and devices operating on this principle are called gas-tube boilers.
In another type of boiler, gas moves through a pipe in the water tank itself. The container in this case is called a drum, and the boiler itself belongs to the water-tube category. Drums filled with water can be positioned horizontally, vertically, radially, or in combination, depending on which the corresponding types of water-tube boilers are distinguished.
Comparison of the features of the types of boilers under consideration allows us to draw the following conclusions:
- The first difference is the different sizes of pipes used. Gas-tube devices are equipped with fairly large pipes compared to the products used in water-tube boilers.
- The next difference is the difference in power. The power limit for gas-tube boilers is 360 kW, and the maximum pressure cannot exceed 1 MPa. High pressure and volume of steam require an increase in the thickness of the walls of the device, which negatively affects the final cost of the boiler. Water-tube boilers do not have this drawback - they can easily use thin pipes, which allow them to achieve higher temperatures and pressures compared to gas-tube analogues.
- Water tube boilers differ not only in power and higher temperature. Their advantages also include the ability to withstand serious overloads, which indicates a greater degree of safety of such devices.
Gallery
- Honeycomb
, a Korean cauldron used to cook rice
- Witches cauldron table
- Three-legged iron pots used to serve a Liwa school party in Botswana. Everyday cooking takes place in the school kitchens.
- Garden of Earthly Delights
, the bird-headed monster or "Prince of Hell" (head close-up), the name comes from the cauldron he wears on his head.
- Mush boiler. Roman bronze cauldron found in 1988 in the tomb of Germanic leaders in Mušov, Czech Republic, dating to the 2nd century AD.
- African American woman and child on the street, standing by a pot of boiling water, c. 1901
- Execution execution in Deventer (Netherlands)
Additional boiler elements
The design of a steam boiler is not limited to the basic elements that have already been described above. Sometimes a steam boiler can be equipped with additional devices to increase the efficiency or functionality of the system.
We are talking about the following elements:
- Superheater . This element allows you to heat steam to a temperature of over 100 degrees, which allows you to achieve greater efficiency by increasing the efficiency of the unit. When using a superheater, steam can reach a temperature of 500 degrees, and its heating is carried out already in the pipes, that is, after the stage of evaporation of water. The superheater can be either built-in or in the format of a separate device. There are convection and radiation devices (the second type has 2-3 times more power).
- Steam separator . This element of the steam boiler allows you to remove all excess moisture from the steam and dry it as much as possible. When using a separator, the efficiency of the entire boiler increases significantly.
- Steam accumulator . This device allows you to stabilize the system. The battery absorbs excess steam generated and returns it to the system if it becomes too low.
- Water purification device . This device allows you to reduce the saturation of water with oxygen and various chemicals. Timely water preparation makes it possible to reduce the impact of corrosion on the internal elements of the boiler and minimize the amount of deposits in the system.
The steam boiler device also includes a valve for draining condensate, air heaters and a unit control unit, which includes a combustion switch and regulators for the consumption of raw materials and energy resources. Understanding what a steam boiler consists of allows you to tailor its configuration to solve specific problems.
In Dahl's dictionary
m. cast iron or sheet vessel for cooking, usually with a rounded bottom, a small socket at the top, with ears or with an overhang; cast iron, cauldron Large boilers are riveted, made from sheets of boiler iron; steam or steam engines are made in the form of tightly closed cylinders. A travel, soldier's bowler hat is suspended from a tripod. Copper cat. Burnt cat. Brewing boiler. A mortar cauldron, a void into which, in addition to the charge in the chamber, a bomb is placed. | There is a peasant game cauldron; | A cauldron is also a name for a basin, any depression, pit, or failure with steep walls. Salt boiler, frying pan, cren, cren. | Old boilers timpani. The pot is no friend to the cauldron. He cooks a man in a cauldron for seven years. The head is like a beer pot, but the mind (brain) doesn’t have a spoon. A woman's heart is like a boiling pot. Two sheep's heads don't fit into one pot, something sticks out. I walked past and saw a miracle: hanging a cauldron of ninety buckets? month. Kotelka, tul. ordinary pretzel boiled in a cauldron. (Shane). Cauldrons, -lochka, cauldron. plant Anemone pulatilla, anemone, anemone. | Water plant Trapa natans, slingshot, marsh, water chestnuts, flyers, bagel, devil's nuts, chilim, batlachik; | plant Satranula persicifolia, chenille, birdwort, bluebells. Pot, plant. Satranula patula, bells, balabolkas, flower pies. Boiler room, belonging to the boiler, related. Boiler bottom, -ears, -beer, not tavern, factory-made. - iron, thick sheet, for riveting factory boilers. -vault, round, capped. Boiler room, workshop where boilers operate. Boiler, boiler, related to the boiler. Boiler brick, the best, fire-resistant, for laying boilers; There is also a bent one for this purpose. Boilermaker, boiler master, working riveter (see also roll). Kotelnikov, belongs to him; boilermaker, relating to him or his skill. Boilermaker, trade in boiler making, riveting and boiler craftsmanship. Cauldron-shaped, cauldron-shaped, cauldron-shaped, cauldron-like, cauldron-like, i.e. deep, steep, with a rounded bottom and a slight camber. Kotlyar and. tul. boilermaker or coppersmith; Kotlyars also make samovars. Here are the girls, the girls, the daughters and their wives, walking. Kotlyarny, boilermaker. Kotlyarstvo cf. craft, skill of kotlyar; to make and play with it, to engage in it, to play around with it. Kotlina deep depression, pit, basin; | the deepest place in a lake, pond; | wild boar haulout, where a herd of wild boars lies down for the day; | a spacious cave in a fox hole, in the very depths. Basin, rounded deep hole, depression, failure; the same deepening of the earth of a vast volume, a roundish ravine, a valley, an earthen pool. The basin of the sea, its entire volume; the basin of a fire mountain, the depth of a vent or vent. Kotlovinny, related to the hollow. Kotlovinnik m. provalya, peshernik, the entire place is occupied by many sinkholes, usually in plaster. Kotluban eastern small, deep lake, pit. Kotlubanina a hollow filled with water, a pothole, a pothole. A pit, a place in the water enclosed in a tongue-and-groove pile driver, for digging and laying a bridge pier, abutment, etc. in it. Kotlyana railway. artel, slurping from one cauldron; in the arch. artel of maritime industrialists. A tight pot if the shareholders come from themselves, not from the owner; The main one in the kotlyan is called the korshchik, followed by the semi-korshchik, the third semi-uzhenschik (uzhna, pai), the rest are the korshchik, the pokrucheniki. Two-thirds of the harvest goes to the owner; the korshchik, from a third, receives 5-6 dinners, the half-korshchik receives half of this, etc. Kotlyany, related to the kotlyan.