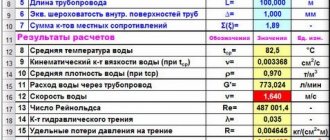
Regardless of the type of communications, whether it is an autonomous or centralized system, it is important to correctly determine the physical parameters of individual elements of the service network in advance. Let's consider how you can independently calculate the diameter of the pipeline based on water flow or the required heat transfer of the coolant liquid. Let's get acquainted with the basic formulas without taking into account engineering subtleties that may be missed in the private sector.
Autonomous system of different pipes Source promtu.ru
Calculation methods
When developing projects for large-scale facilities, professionals use special engineering programs to draw up diagrams and drawings of future heating networks and hot/cold water supply. For simpler problems at the private sector level, solutions can be found using calculators that are published on the websites of manufacturers and sellers. The third option is to carry out calculations using ready-made formulas and tabular data, for example, about the speed of water in pipes.
You can do it even simpler - start from common solutions that have been tested at different sites, there is evidence of their effectiveness. However, the recommended schemes in individual construction do not always work properly. So, if you allow the diameter of the pipeline to be exceeded during selection, then the heating will have low heat transfer, and water will flow with low pressure. On the contrary, the use of narrowed channels increases pressure and the heating system will warm the house well. But at the same time, a large load is placed on the pipes and fittings, which shortens the service life of communications due to accelerated wear.
Using fittings to optimize the location of different channels Source kanaliza.ru
Factors influencing choice
The choice of pipes is influenced by a number of factors, including the optimal temperature and water pressure. You need to choose the right coolant pressure and temperature when choosing autonomous heating. Which values will be used depends on the heat transfer rate of the batteries.
Cast iron radiators have the lowest heat transfer coefficient, while aluminum products have the highest. When the liquid temperature does not exceed +75°C (the most optimal indicator), the rated thermal power should be taken into account when calculating the required number of radiators and their sections. But with constantly changing air temperatures outside, it is necessary to adjust the heating of the coolant so that the room always has a comfortable temperature and there is no unnecessary energy consumption.
In addition to temperature, for normal operation it is necessary to control the pressure in the pipes and calculate their suitable diameter. A pressure of 1.5-2 atmospheres is the most optimal. When it increases to 3 units, the entire circuit may malfunction and leaks and ruptures may occur. Therefore, to periodically check the pressure in the circuit during installation, you need to leave a free gap for installing pressure gauges. By using expansion tanks, it is possible to reduce the pressure.
The heating system can be installed using one- or two-pipe schemes. To make the room comfortable, the most suitable option should be chosen when drawing up the project.
Single-pipe wiring will be cheaper, but if price does not affect the choice and you need high operating efficiency, then a two-pipe circuit will be suitable.
What to consider when calculating water supply
Engineering programs and calculators already contain all the necessary data that must be used to obtain the desired results. Therefore, let us consider in more detail the third method of calculations using ready-made formulas. Thus, the diameter of the pipe is calculated taking into account the throughput of the pipeline and the speed of fluid flow in the pipe:
Here the symbols mean:
- d – the desired cross-sectional size of the channel relative to the internal walls;
- q – flow rate of transported liquid in liters or kg per second or per hour;
- v – flow velocity in m/s;
- π is a constant value (the ratio of the circumference to the diameter).
To determine water flow or pipeline capacity, the following formula is used: q = 5 × q(0) × k .
Here, q(0) means a normative value that can be found in the current SNiP. For example, for a bathroom it is 0.25, for a faucet in the kitchen - 0.12, and for a flush cistern on a toilet, 0.1 units are enough. Coefficient k is needed when several consumption points are connected to the main line under study.
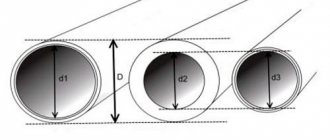
Multichannel network for servicing various points of consumption Source planlook.ru
It can be defined as follows: k = N × P. Here:
- f – volume of water consumed;
- N – number of liquid consumption points;
- P – the probability value of the simultaneous operation of several plumbing fixtures.
In turn, to determine the probability there is a formula: P = qhrμ × u/(q(0) × 3600 × N) . Without going into details, the product qhrμ is the maximum water consumption per hour. This indicator is normative, information is available in SNiP. As an example: The volume of cold water consumption should be within 5.6 liters, and the total with hot water should be about 15.6 l/s. By u in the formula we mean the number of people who constantly use the water supply.
An example of the location of water consumption points in a house for a small family Source jaxtr.com
Pipe patency
According to sanitary standards, which are taken into account by organizations when drawing up receipts without meters, there is about 360 liters of water per person per day. However, the flow rate, depending on the installed channels with a round cross-section, may differ from the standard. The actual result is influenced by several factors, among which the following are considered basic:
- Line length. Throughout the entire path, the moving liquid is subject to resistance from the inner walls of the pipe. Otherwise, this phenomenon is called pressure loss. That is, as you move, the speed of water in the pipeline decreases. As a result, the greater the difference between the pressure at the beginning and the end of a particular straight section, the more time will pass before a new portion of liquid enters the water supply. This is especially noticeable in old systems, where rust and growths gradually appear on the inside of the metal surface.
An example of different straight segments in the system Source septik-centr76.ru
- Diameter. The moment of resistance also matters here. On the one hand, in pipes with a small cross-section, the braking effect turns out to be a small surface area. On the other hand, the indicators are higher than in wider channels due to the proportionally different volume of transported liquid. That is, in the second case, with similar consumption, a person will receive the required displacement faster than through a thin pipeline.
- Compound. The modern market is represented by products for communication systems for water transportation, which are made of various materials. Thus, polypropylene walls have a noticeably less effect on reducing the flow rate than steel ones.
- Durability. There is a significant difference in the duration of maintaining the initially specified operating conditions. Corrosion and growths may appear on rough metal, which helps to reduce the cross-section of the line. That is, the initial calculations of the pipe diameter based on flow rate will ultimately turn out to be unfair. There are no such phenomena on smooth polymer walls. Their service life can exceed older analogues by up to 200 times.
Example of a clogged metal pipe Source ytimg.com
- Nodal connections. Any areas with fittings, regardless of installation method, rotations and separations provide additional resistance.
The summary tables indicate the throughput of water supply channels depending on the cross-section of the pipe (DN - nominal or nominal diameter) and the speed of fluid movement in the pipeline under one or another pressure.
| Pressure | Throughput or water flow (kg/h) at flow speed below 0.15 m/s | |||
| Pa/m | Mbar/m | 15 mm | 20 mm | 25 mm |
| 90 | 0,9 | 173 | 403 | 745 |
| 92,5 | 0,925 | 176 | 407 | 756 |
| 95 | 0,95 | 176 | 414 | 767 |
| 97,5 | 0,975 | 180 | 421 | 778 |
| 100 | 1 | 184 | 425 | 788 |
| 120 | 1,2 | 202 | 511 | 943 |
| 140 | 1,4 | 220 | 511 | 943 |
| 160 | 1,6 | 234 | 547 | 1015 |
| 180 | 1,8 | 252 | 583 | 1080 |
| 200 | 2 | 266 | 619 | 1151 |
| 220 | 2,2 | 281 | 652 | 1202 |
| 240 | 2,4 | 288 | 660 | 1256 |
| 260 | 2,6 | 306 | 713 | 1310 |
| 280 | 2,8 | 317 | 742 | 1364 |
| 300 | 3 | 331 | 767 | 1415 |
See also: Catalog of companies that specialize in engineering systems (heating, water supply, sewerage and others) and related work
| Pressure | Throughput or water flow (kg/h) at a flow speed within 0.15 m/s | |||||
| Pa/m | Mbar/m | 32 mm | 40 mm | 50 mm | 65 mm | 80 mm |
| 90 | 0,9 | 1627 | 2488 | 4716 | 9612 | 14940 |
| 92,5 | 0,925 | 1652 | 2524 | 4788 | 9756 | 15156 |
| 95 | 0,95 | 1678 | 2560 | 4860 | 9900 | 15372 |
| 97,5 | 0,975 | 1699 | 2596 | 4932 | 10044 | 15552 |
| 100 | 1 | 1724 | 2632 | 5004 | 10152 | 15768 |
| 120 | 1,2 | 1897 | 2898 | 5508 | 11196 | 17352 |
| 140 | 1,4 | 2059 | 3143 | 5976 | 12132 | 18792 |
| 160 | 1,6 | 2210 | 3373 | 6408 | 12996 | 20160 |
| 180 | 1,8 | 2354 | 3589 | 6804 | 13824 | 21420 |
| 200 | 2 | 2486 | 3780 | 7200 | 14580 | 22644 |
| 220 | 2,2 | 2617 | 3996 | 7560 | 15336 | 23760 |
| 240 | 2,4 | 2740 | 4176 | 7920 | 16056 | 24876 |
| 260 | 2,6 | 2855 | 4356 | 8244 | 16740 | 25920 |
| 280 | 2,8 | 2970 | 4356 | 8566 | 17338 | 26928 |
| 300 | 3 | 3076 | 4680 | 8992 | 18000 | 27900 |
| Pressure | Throughput or water flow (kg/h) at flow speeds above 0.3 m/s | |
| Pa/m | Mbar/m | 100 mm |
| 90 | 0,9 | 30240 |
| 92,5 | 0,925 | 30672 |
| 95 | 0,95 | 31104 |
| 97,5 | 0,975 | 31500 |
| 100 | 1 | 31932 |
| 120 | 1,2 | 35100 |
| 140 | 1,4 | 38160 |
| 160 | 1,6 | 40680 |
| 180 | 1,8 | 43200 |
| 200 | 2 | 45720 |
| 220 | 2,2 | 47880 |
| 240 | 2,4 | 50400 |
| 260 | 2,6 | 52200 |
| 280 | 2,8 | 54360 |
| 300 | 3 | |
The flow rate in channels with a circular cross-section depends, among other things, on the nature of the transported liquid. For example, for a viscous gravity medium, 0.1-0.5 m/s is considered optimal, and for a more liquid medium, 0.5-1 m/s. Indicators increase if devices for forced transportation are used. Thus, under discharge conditions, the speed can reach 0.8-2 m/s, and during suction - 1.5-3 m/s.
An example of performing independent calculations
Let's look at how to calculate the diameter of a pipe for a cottage inhabited by 4 people. The list of consumption points includes a bathtub, shower stall and toilet; the kitchen has a washing machine and dishwashing equipment. Since there are several users and the fact that different equipment is operating simultaneously, we first need to determine the probability. Based on the available data, this would result in P = 5.6 × 4/(0.25 × 3600 × 6) = 0.00415 .
The water consumption in each room will be as follows:
- bathroom – q = 5 × 0.25 × 0.00415 = 0.00519 l/s;
- kitchen – q = 5 × 0.12 × 0.00415 = 0.00249 l/s;
- toilet – q = 5 × 0.1 × 0.00415 = 0.00208 l/s.
The next step is to determine the required pipeline diameter.
You can check the pipe cross-section with a regular ruler Source kipmu.ru
The flow rate in the pipe can be accurately calculated with parallel calculation of losses, coefficient of hydraulic friction and other required values. It is easier, despite the errors, to take information from ready-made tables. After all, there are no blanks on the construction market that differ from standardized sections.
If we take pressure water supply and the movement of liquid at a speed of 3 m/s as a guide, then according to calculations we will get the following options for optimal pipe diameters.
Bathroom - approximately 45 mm:
Kitchen - approximately 33 mm:
Toilet – approximately 30 mm:
Characteristics of water pipes
The design of a water supply system cannot work without pipes, so it would not be a mistake to say that they are the most important element of this system. In construction, plastic, metal-plastic and metal pipes are most often used.
Despite the differences due to different materials of manufacture, all pipes have the same dimensional characteristics, the list of which looks like this:
- Inner diameter, which must be the same at all joints so that the structure is solid;
- Nominal diameter is the nominal value required for the installation of a water supply system;
- Wall thickness;
- Pipe length.
The correct selection of pipes in terms of dimensional characteristics is needed not only for their installation - elements suitable for arranging a water supply system will allow you to create a structure that will not have problems during operation. If the diameter of the plastic water pipe is too small, water turbulence will occur in it, causing the structure to make noise and periodically fail.
Heating system
Here the main task that needs to be solved with the help of a coolant liquid is to provide the heating devices with the required amount of heat. Before calculating the diameter of the pipe, you will need to determine the heat loss of the house and select radiators with optimal power. You will also need data on the length of the pipeline and the design of the working system (method of water circulation, with one or two channels).
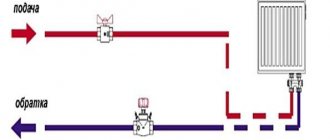
Two-pipe autonomous heating scheme Source kupisantehniky.ru
To calculate the diameter of heating pipes, you can use the following formula:
Here:
- d – the required value of the internal diameter;
- Q – load on a specific section of the system relative to the required amount of supplied heat;
- Δt° – difference between supply and return temperatures;
- V – coolant flow rate in the serviced area.
In autonomous heating systems, liquid can move at a speed of 0.2 to 1.5 m/s. In this case, the optimal values in practice are 0.3-0.7 m/s. At lower speeds, the likelihood of airing the system increases; at higher speeds, the system operates noisier.
Below is a table with the optimal values of hot water speed in polypropylene pipes depending on the amount of heat up to 20 kW (in kW) and the outer diameter of the channel (in mm). This takes into account the 80/60 operating mode and a temperature difference of 20 degrees Celsius.
| Warm | 20 | 25 | 23 | 40 | 50 | 63 | 75 |
| 3 | 0,2 | 0,1 | 0 | ||||
| 4 | 0,3 | 0,2 | 0,1 | 0 | |||
| 5 | 0,4 | 0,2 | 0,1 | 0 | |||
| 6 | 0,4 | 0,3 | 0,2 | 0,1 | 0 | ||
| 7 | 0,5 | 0,3 | 0,2 | 0,1 | 0 | ||
| 8 | 0,6 | 0,4 | 0,2 | 0,1 | 0 | ||
| 9 | 0,7 | 0,4 | 0,3 | 0,2 | 0,1 | 0 | |
| 10 | 0,7 | 0,5 | 0,3 | 0,2 | 0,1 | ||
| 11 | 0,8 | 0,5 | 0,3 | 0,2 | 0,1 | ||
| 12 | 0,9 | 0,6 | 0,3 | 0,2 | 0,1 | ||
| 13 | 1 | 0,6 | 0,4 | 0,2 | 0,1 | ||
| 14 | 1 | 0,7 | 0,4 | 0,3 | 0,2 | 0,1 | |
| 15 | 1,1 | 0,7 | 0,4 | 0,3 | 0,2 | 0,1 | |
| 16 | 1,2 | 0,8 | 0,5 | 0,3 | 0,2 | 0,1 | |
| 17 | 1,2 | 0,8 | 0,5 | 0,3 | 0,2 | 0,1 | |
| 18 | 1,3 | 0,8 | 0,5 | 0,3 | 0,2 | 0,1 | |
| 19 | 1,4 | 0,9 | 0,5 | 0,3 | 0,2 | 0,1 | |
| 20 | 1,5 | 0,9 | 0,6 | 0,4 | 0,2 | 0,1 | |
Total information
Today there are several options for heating systems, but water heating has been the most popular method for decades.
The option in which forced circulation of the coolant occurs is considered especially effective. When choosing it, you can speak with confidence about the quality of heating of a room even of large footage.
Before designing a heating system, it is worth deciding on the material from which the pipes and components will be made.
Today, steel, polypropylene, metal-plastic and copper products are widely used.
A correctly calculated diameter affects the optimal length of the pipeline, the number of possible radiators to connect and the forecast of heat losses during operation.
Briefly about the main thing
The diameter of the pipeline determines the rate of supply of contents over the reporting period of time and the service life of communications.
You can calculate the optimal cross-section size for a particular section of the system using special engineering programs, calculators on the Internet, or using several formulas yourself.
When calculating the diameter of channels for water supply, the flow speed, pressure, required water consumption for servicing plumbing equipment and people living in the house, watering the garden or flower garden are taken into account.
When determining the diameter of the pipes for assembling the heating system, it is necessary to find out the load or the amount of heat needed to compensate for heat loss, the temperature difference between the supply and return, and the speed of movement of the coolant.
What pipe diameter to choose for water supply in a private house
As shown above, the pipe diameter is specified by fixed values from a standardized number series with a significant variation. This makes accurate calculation using formulas, tables and online calculators a meaningless procedure in the vast majority of cases. Even the simplest option of determining the diameter based on the throughput of pipes and summing up the water consumption of simultaneously turned on plumbing equipment (Table 3.) is not worth the time spent and was carried out long ago by specialist installers.
Outside
If an individual water supply system is installed for a private house, then water from a submersible or surface electric pump enters it through an underground pipeline made of low-density polyethylene HDPE.
The outlet pipes of most pumps are designed to accept pipes with a diameter of 1 or 1 1/4 inches, that is, outer diameters of 25 and 32 mm. Since the pipeline from electric pumps is prohibited from being narrowed, installers have no choice which pipes to use.
Sometimes, if the outlet of the electric pump has a 1-inch (25 mm) outlet pipe, and the distance to the house is too great, a larger diameter 1 1/4-inch (32 mm) pipeline is used to reduce hydraulic losses.
The same applies when connecting from a centralized water main. In the vast majority of cases, installers do not face the question of which pipe to choose. It is enough to use two types - 25th or 32nd HDPE pipes.
Rice. 5 One of the options for manifold wiring and corresponding pipes made of thin-walled metal-plastic (for PP, all diameters should be increased by one standard size)