In private houses there are always several utility or technical rooms, where the requirements for the interior are low. But you still need to heat them, and in order not to spend money on buying modern radiators, you can install a steel register welded from pipes there. And, although everyone has seen such simple heating devices with their own eyes, not everyone knows their structure. This material is to help those homeowners who want to independently manufacture, install and connect heating registers to their system.
Construction of heating registers
Despite the fact that such heaters are considered outdated and do not have a very attractive appearance, they continue to be widely used in a variety of areas, for example:
- for heating production premises of industrial enterprises;
- as an autonomous heater in garages;
- as a water heating element built into a brick oven.
Note. A stove register made of smooth heating pipes is calculated and manufactured depending on the power and design of the stove.
By design, heating devices are divided into 2 types: sectional and in the form of a coil. In the first case, the role of 1 section is played by each horizontal pipe, the flow of coolant through them is ensured by vertical jumpers. They are made of smaller diameter pipes in order to create artificial resistance to flow and increase heat transfer from each section. The pipes from which the sectional heating register is made are plugged at the ends, and the coolant is supplied according to the “top to bottom” scheme.
The design of the heater in the form of a coil is clear from its name. Here the diameters do not narrow; water flows freely through the entire device, changing direction several times. The heat transfer of this register is lower than that of a sectional one, but the hydraulic resistance is less and it is somewhat simpler to manufacture.
Advice. It is preferable to make sectional heaters for utility rooms or garages, where uniform heating and comfortable air temperature are important. It is better to install coils as standby heaters at the very end of a two-pipe system. They work great there because of their low resistance.
Heating registers from smooth pipes of round and rectangular cross-section are welded. However, the generally accepted design is ordinary round pipes made of low-carbon steel such as St3, St10 and even St0. If the battery is intended to work with a steam system, then St20 steel is used. It is not recommended to make sections with a rectangular cross-section; they are less washed by the convective air flow, which means they will give off less heat. For garage heating, autonomous registers are made, filled with antifreeze or transformer oil, and an electric heating element is built into the lower section at the end.
Installation methods: welding or threading?
The biggest problem when carrying out installation work on assembling and installing heating registers is welding work. Heating appliances are assembled from individual parts outside the room, and then the heating system is installed from the prepared blanks using gas welding. Welded seams can be replaced with threaded connections, which are inferior in strength and durability, but if the work technology is followed and modern materials are used, they can ensure long-term operation of heating equipment.
A heating register in a garage or warehouse is an independent device that allows you to heat a technical room using electricity
Advantages and disadvantages
Before you start making heating registers, you need to evaluate all the pros and cons of these heaters, so that your expectations are not disappointed later. So, first about the advantages:
- low cost and ease of manufacture;
- low hydraulic resistance: thanks to this, the heater can be used in the “tail” of any system;
- reliability and durability: a register, qualitatively welded from ordinary pipes, will quietly serve for at least 20 years;
- resistance to pressure drops and water hammer;
- The smooth surface facilitates easy removal of dust when cleaning premises.
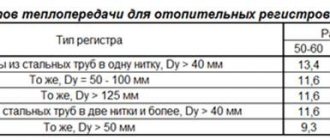
Unfortunately, a home-made heating register also has a lot of disadvantages. The main one is low heat transfer with a significant mass of the device. That is, in order to provide a comfortable temperature in a medium-sized room, the register must be of decent size. Let's give a simple example taken from technical literature. If the temperature difference between the coolant and the room is 65 ºС (DT), a register welded from 4 DN32 pipes 1 m long will deliver only 453 W, and from 4 DN100 pipes – 855 W. It turns out that, based on heat transfer per 1 m of length, any panel or sectional radiator is at least twice as powerful.
Note. The presented data were determined experimentally at a high coolant flow rate of 300 kg/h.
Other negative aspects of smooth-tube registers are not so critical, although significant:
- holds a large volume of water: the disadvantage does not play a big role if there are 1-2 such heating devices for the entire system;
- During operation, it is very difficult to increase or decrease the power of registers made of smooth pipes. You can’t do without dismantling the welding machine;
- are susceptible to corrosion and require periodic maintenance with painting;
- They have an unpresentable appearance: the defect can be corrected; if necessary, the heater is hidden behind a decorative screen.
Having analyzed the advantages and disadvantages of smooth-tube devices, we can conclude that their scope of application in private housing construction is very limited. As already mentioned, registers can be used for heating various rooms with low requirements for comfort and interior design.
How to calculate heat transfer?
The required amount of material can be calculated based on the temperature parameters that need to be obtained in the room. At the household level, this step is usually skipped - they make heating registers with their own hands “by eye” according to the principle “the more, the better.”
But it is better to make simple calculations of heat transfer, for which you do not need to be a mathematician. All you need is:
- Calculate the area of the room.
- Learn about the heat transfer properties of steel.
- Select the optimal pipe diameter.
The area of a room is calculated by multiplying its length by its width (S = L*W). However, for more accurate calculations, it is recommended to calculate the volumetric parameter by adding the height (H) value to the calculations.
So, the final calculation formula takes the form:
V = L*W*H
For example, you need to calculate V of a room where the length is 5 m, width is 3 m, height is 2.15 m. The volume of the room is obtained: V = 5*3*2.15 = 30.25 m3. Based on this basic value, further calculations should be made to determine the amount of heat, the size and number of heating registers to make with your own hands.
Self-welded heating registers are blocks consisting of six steel pipes with a diameter of over 100 mm. Such batteries, made without proper calculations, can overheat the room being served.
First of all, the required amount of heat per calculated volume of the room is calculated to achieve the required internal temperature (W):
Qп.т = V * k (Tin – Tout),
where V is the volume of the room; k – heat transfer coefficient of the building walls; Tin – temperature inside; Tout – outside temperature.
The amount of heat generated by one register can be calculated using the formula:
Qр = q * L * (1-n),
where: q – heat flow from each horizontal and vertical pipe of the register (approximately 20-30 W/m); L – length of vertical and horizontal pipes of the register (m); n – coefficient of unaccounted heat flows (for metal pipes – 0.1).
The category of unaccounted heat loss also includes the hood in the garage. If the mechanical type is installed, the coefficient n must be increased to at least 0.2.
The number of registers, accordingly, is determined by the formula:
Nр = Qп.т. / Qр
Such a calculation method will most likely be assessed by design specialists as a simplified and crude form. However, this approach still seems to be a more rational action than calculating and making registers with your own hands by eye, without any calculations.
Manufacturing recommendations
When selecting materials, you need to decide what pipe diameters to take and what their total length should be. All these parameters are arbitrary; you can make a heater from any pipes, and take its length convenient for placement in the room. But in order to supply the required amount of heat, it is necessary to ensure a sufficient heat exchange area. To do this, it is recommended to perform an approximate calculation of the register based on the surface area.
Making such a calculation is quite simple. It is necessary to calculate the outer surface area of all sections in m2 and multiply the resulting value by 330 W. Proposing this method, we proceed from the statement that 1 m2 of register surface will give off 330 W of heat at a coolant temperature of 60 ºС and room air temperature of 18 ºС.
Advice. You don’t have to do manual calculations, but use a simple EXEL program and then correctly weld the register according to the exact parameters. You can download the program in one click from the link: https://al-vo.ru/wp-content/uploads/2014/02/teplootdacha-registra-otopleniya.xls.
For a person who has welding skills, it will not be difficult to independently weld the register according to the available drawings. It is necessary to prepare and cut pipes into sections and lintels, and cut plugs from a steel sheet. The assembly sequence is arbitrary; after welding, the heater should be checked for leaks. When manufacturing and installing registers, consider the following recommendations:
- you should not take pipes with too thin or thick walls: the former will cool faster and last less, and the latter will take a long time to warm up and are difficult to adjust;
- do not forget to build a Mayevsky valve into the end of the upper section for bleeding air;
- when welding coils, the rotating section can be made from two ready-made elbows if it is not possible to use a pipe bender;
- Place a tap at the coolant inlet and a valve at the outlet;
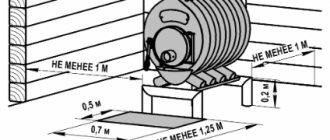
- remember that the registers are installed with an invisible bias towards the connection of the supply pipe. Then Mayevsky's crane will be at the highest point.
Application area
Currently, water heating registers are mostly used in industries (workshops, workshops, warehouses, hangars and other buildings with large areas). The large volume of coolant and large dimensions allow the registers to efficiently heat such rooms.
The use of heating registers in industrial buildings ensures the most optimal efficiency of the heating system. Compared to cast iron or steel batteries, registers are characterized by better hydraulics and heat dissipation. The relatively low cost of their manufacture reduces the cost of installing the entire factory heating system. In addition, they are not expensive to operate.
Registers are also recommended for use in premises with high sanitary safety requirements (medical institutions, kindergartens, etc.). The devices are easily washed from dirt and dust.
Despite this, the concept of efficiency does not apply to this type of heating device. As noted above, heating a large volume of coolant requires a lot of energy.
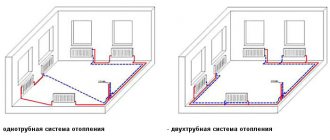
Heating registers made of steel electric-welded pipes can be used in both single-pipe and two-pipe heating systems with forced or gravity circulation of the coolant (based on water or steam).
How to weld heating registers with your own hands - Metals, equipment, instructions
Any device or device made by yourself is an economical approach to solving your plans. This fully applies to the heating system.
You won’t be able to make a radiator yourself, but a person who has the skills to work with a welding machine can assemble a register from smooth or profile pipes.
For manufacturing, you only need pipe sections, two bends and several electrodes.
ontakte
Odnoklassniki
These devices are rarely used in everyday life. They are usually installed in production and warehouse premises. This is a cheap alternative to expensive radiators.
A distinctive feature of the devices is the large volume of coolant inside, which heats up quickly and cools down slowly. Hence the high heat transfer .
They are installed in exactly the same way as conventional radiators, according to the same schemes, standards and rules.
Ratio of metal thickness to electrode diameter
| Metal thickness, mm | 1—2 | 3—5 | 4—10 | 12—24 | 30—60 |
| Electrode diameter, mm | 2—3 | 3—4 | 4—5 | 5—6 | 6 or more |
The current strength is selected depending on the diameter of the selected electrode. The dependence is as follows: I=Kd, where K is the coefficient of correlation with the diameter of the electrode.
| Electrode diameter, mm | >2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| Coefficient - "K" | 25—30 | 30—35 | 35—40 | 40—45 | 50—60 |
Calculation of the number of ribs
Heating registers must be calculated before purchasing them. The diameter of the pipes is very important: experts believe that pipes with a cross-sectional diameter in the range from 3 cm to 8 cm are suitable for a private house. This decision is determined by the fact that a conventional heating boiler is not capable of producing a larger amount of heat, so too large surfaces will not warm up completely .
When making calculations, you need to pay attention to the length of one register rib and the heat transfer per meter of this length. For example, a meter-long pipe with a 6-centimeter cross-section can heat one square meter of area. When calculating the required number of edges, the result must be rounded up. The calculation of the number of heating registers must also take into account the characteristics of the building. For example, if a building has a large number of windows and doors, or if the walls are thin and poorly insulated, then the number of registers can be increased by 20-50%.
Video
In private houses there are always several utility or technical rooms, where the requirements for the interior are low. But you still need to heat them, and in order not to spend money on buying modern radiators, you can install a steel register welded from pipes there. And, although everyone has seen such simple heating devices with their own eyes, not everyone knows their structure. This material is to help those homeowners who want to independently manufacture, install and connect heating registers to their system.
Selecting a welding machine
There are three types of welding machines. Which one to choose depends on the welding method and the material being processed. Device types:
- Step-down welding transformers. This is a reliable device that is used for welding carbon steel. The quality of the seam is average.
- Welding rectifiers. Suitable for carbon and aluminum materials, as well as stainless steel. The seam quality is high.
- Welding inverters. A universal device that is suitable for any material.
You cannot use damaged equipment when welding heating pipes using electric welding. Therefore, before starting work, the equipment is carefully checked.