The microclimate in the house is influenced by many factors. One of them, perhaps the most important, is the presence of clean indoor air. A person’s well-being depends on the quality of air. Excessively dry or humid air leads to damage to furniture and interior decoration. Properly equipped ventilation in a private home regulates the air and its composition and prevents potential problems associated with it.
How to properly install ventilation with your own hands in a private home to ensure optimal air exchange? Which system will be most effective? How does the system differ in different residential areas? We hope that after reading this material you will receive answers not only to these questions, but also to many related topics on the installation of ventilation in a private home. Installing a ventilation system may be too difficult a task to handle on your own. However, understanding the basic principles will allow you to determine the scope of work and calculate the required budget .
Why is ventilation needed in a private house?
Ventilation is essentially airing. The task of the ventilation system is to remove air that has already been exhausted and replace it with clean air. The incoming air is processed, preparing it for the needs of the residents.
The air in a private home, as in any other residential premises, must correspond to human living standards. Its parameters are regulated by SNiPs, GOSTs and other building codes. The microclimate then becomes comfortable for living when the following conditions are met:
- the air must be clean and fresh;
- temperature and humidity indicators are within normal limits.
The ventilation system is designed to create these conditions in the living space. Its scheme is developed individually for each house, taking into account its data.
The ventilation system in a private house performs the following tasks:
- removes air containing dust and carbon dioxide to the outside environment;
- provides a flow of clean air from the street, saturating the premises with oxygen.
Thus, ventilation creates conditions for a comfortable stay of residents in the house, ensures the safe use of furniture, building structures and all interior items. It allows you to store food in pantries and things in dressing rooms. In the kitchen, ventilation provides the conditions necessary for cooking.
Types of residential buildings
Considering residential buildings, we can divide them into standard and individual. Typical are sample templates that demonstrate ready-made solutions where key points have been developed. They are used for large-scale developments.
In such blanks, minor adjustments are made according to local conditions. For example, orientation to the terrain or location of connection to networks.
A special house, with unique layouts and facades, with personal wishes and ideas is called individual.
There is also a division into multi-apartment and single-apartment buildings.
Multi-apartment buildings are those that have shared premises and utilities outside the apartment boundaries.
This also includes boarding schools, hostels and hotel complexes. Often in high-rise buildings there are other non-residential objects: parking lots, retail outlets, service organizations and others.
Air flow rates are the basic requirement for ventilation
SNiPs set specific standards for air flow and air exchange rates, which form the basis for ventilation design. The air exchange rate refers to the ratio of the volume of air that enters per unit of time (1 hour) and the volume of the room. Thus, the multiplicity becomes an indicator of the hourly renewal of air, how many times per hour it is renewed.
Let us outline the basic requirements and standards for ventilation of a private home.
- the amount of air provided by the ventilation system must be sufficient to ensure that all residents present in the room feel free and comfortable. The air norm per person is 30 cm3/hour for an area of more than 20 m3. If there is less than 20 m2 of space per person, 3 m3/hour is sufficient.
- Based on the purpose of a particular living room, the following air flow rates are determined:
— for a living room: 3 m3/hour per 1 m2 of area;
— for separate toilets and bathrooms: 25 m3/hour;
— for a combined bathroom: more than 50 m3/hour;
— for the kitchen: in accordance with the type of stove and the number of burners, 2-burner electric and gas require 60 m3/hour, 4-burner gas 90 m3/hour.
- The air exchange rates are as follows:
- for rooms where there are always people - one volume per hour;
- for technical premises - from one volume per 5 hours (that is, there should be 0.2 volumes per hour).
The standard indicator is affected by the air temperature indoors and outdoors. So, for these standards to be considered valid, it should be +18° inside and +5° outside.
Moments of exhaust structures
The hood plays an important role in a finished house. It also serves as a chimney. Exhaust ventilation ducts should be installed in the kitchen. This arrangement of the channel is completely no coincidence because the air in the kitchen is the most polluted. The exhaust system channel should be shorter, unlike the supply system. This way you can significantly reduce the likelihood of condensation in unheated areas.
For the least resistance to air movement through the exhaust duct, in other words, to increase draft, the following conditions must be met: one duct size, without narrowing; the direction of the pipes is rectilinear without horizontal sections.
Exhaust duct with minimum length
You can achieve greater air extraction efficiency by installing a fan in the central air duct, which will subsequently extract air from the rooms.
For the hood above the gas stove, as well as for the heating boiler pipes, taps into the main duct are used, but only above the fan, otherwise it will quickly fail.
Methods for calculating ventilation parameters
To accurately calculate how to properly install ventilation in a private home, you will need special software. Such calculations will be carried out by specialists who have the necessary equipment and the necessary experience. However, there are basic techniques that allow you to get an idea of ventilation parameters .
- based on consumption standards. If the rate of air consumption per person is 60 m3/hour, then calculating the required ventilation performance is quite simple: multiplying the rate by the number of people living. But in this case, it is impossible to take into account whether all residents are in the same room or dispersed across several rooms. Therefore, this technique is used for air heating calculations when air circulates inside the building;
- in accordance with the air exchange rate. According to SNiP standards, the air must be renewed at least once every hour. If this frequency is not enough to feel good, the following calculations are made: the frequency is multiplied by the total area of the entire house and by the height of the ceilings in the house. Moreover, the multiplicity is taken 1-3. This technique is more popular than the previous one, but deals with larger volumes of air.
Natural and forced ventilation
Any ventilation system is inherently natural or artificial.
Natural (also convective or natural) ventilation in a private house is carried out due to draft arising from the difference in temperature and, as a result, air pressure inside and outside the building.
Artificial (or forced) ventilation in a private house occurs using air blowers. Their role is played by compressors or fans.
Design
The ventilation structure of the house must ensure air circulation in the following way: air circulation should occur in the direction from the cleanest to the most polluted rooms. This should be taken into account when drawing up diagrams and design drawings for the placement of valves and fans.
Typical ventilation designs place exhaust air in bathrooms and kitchens. In turn, power mechanisms are located in each room, with the exception of rooms equipped with an exhaust hood.
Natural ventilation: principles of operation and features
Natural ventilation occurs due to the upward movement of warm air currents and their replacement of cold masses coming from below . The speed of circulation depends on the temperature difference and how fast the wind is moving.
Modern windows do not let air in from the street. As it was before. Therefore, ventilation valves are installed in window systems. The used air is removed through special channels in the kitchen, bathroom and other rooms.
Benefits of natural ventilation:
- absence of noise;
- work without accidents;
- cheap installation;
- energy independence;
- high reliability;
- mild microclimate;
- efficiency.
Disadvantages of this type of air exchange:
- poor circulation, not always sufficient for effective air change in the room;
- the draft depends on the time of year and the altitude of the house;
- intensity regulation is not possible;
- almost complete absence of movement in the summer, when temperatures outside and inside the house are equalized;
- heat goes outside, increasing the cost of heating the premises. At the same time, in winter the draft increases, creating heat losses of up to 40%;
- ventilation stops completely when double-glazed windows with a high level of tightness are installed;
- no air treatment;
- To continue circulation, the installation of supply valves is required.
This system depends on seasonality and daily temperature changes. Suitable for brick, wooden, cinder block, foam concrete houses.
Insufficient ventilation is determined by the following signs:
- windows fog up;
- a greasy coating or fungus forms on the kitchen walls;
- high humidity in winter.
Alternative way vacuum valves
The vacuum valve is installed at the end of the second floor riser
Another way to ensure sewer ventilation is to install valves. But it is worth choosing this option in the case when it is technically impossible or cost-ineffective to install a fan pipe.
How does he work? The valve is equipped with a flap that is connected to a spring that has a slight resistance. When the device is closed, the airtight seal prevents air from entering. When a vacuum forms in the system, which can occur when flushing the toilet, flushing water under pressure, or draining water from the washing machine with a pump, the valve automatically opens. Then the air in the room passes through the valve into the sewage system, restoring pressure. When the balance is restored, the flap takes the reverse position, hermetically blocking the access of air. In this condition, sewer “odors” will not be able to penetrate your premises. And when the valve opens, the air flow that is sucked into the system prevents odor from leaking out.
But there are some nuances that should be taken into account when installing and using such equipment:
- unlike drain pipes, vacuum valves cannot ensure a complete absence of sewage odor when the siphons dry out;
- such equipment is installed on sockets, but if for some reason it is difficult to install it there, this can be done on any horizontal section of pipes of the sewer system;
- the main disadvantage of valves is the wear of the rubber seals, which make it airtight;
- The device requires periodic maintenance: if you smell a smell, you need to open it and fix the problem.
Vacuum valve behind the bathtub
If we talk about installation, the process is simple, and, unlike installing a drain pipe, no additional repair work is required. It is enough to simply connect the valve to the sewage system and ensure good sealing of the joint. A regular rubber cuff is suitable for this purpose.
Features of artificial ventilation
Artificial ventilation is created by the work of special electromechanical equipment in a forced manner. Ventilation equipment consists of the following elements :
- fan;
- a filter that purifies air masses;
- noise muffler;
- air heater that heats the air;
- air valve.
If the system is modern, it may include a recuperator, which takes heat from the air exhausted outside and thereby heats the incoming one.
Advantages of artificial ventilation:
- the operation of the system does not depend on circumstances and environmental conditions;
- you can adjust the characteristics for each room;
- no manual control of the equipment is required;
- the air can be processed, creating the most comfortable microclimate. For example, you can moisten it or, on the contrary, dry it, change the temperature, and clean it from dust.
Disadvantages of artificial ventilation:
- the operation of the system depends on the source of electricity and increases energy consumption, especially in winter;
- the equipment itself is quite expensive to purchase and requires constant maintenance;
- the project must be carefully calculated.
Ventilation operating diagrams. Recuperator
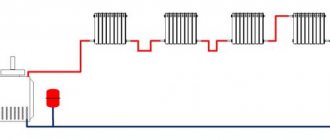
There are several types of ventilation schemes in a private house:
- supply: works to supply air;
- exhaust: works to extract air from the house;
- combined supply and exhaust.
Supply ventilation in a private house consists of an air duct, fittings, and a supply chamber. The air must be supplied at a temperature not lower than 18°, otherwise it must be heated so as not to disturb the comfort of the residents. This can be done using a recuperator. Its power should be enough to provide air to all housing, taking into account the characteristics of each room. Controlled remotely or manually. It is important that it takes into account seasonal differences in temperature and works for cooling in the summer and heating in the winter.
Exhaust ventilation in a private house works with the help of hoods and should be located where there are the most unpleasant or very intense odors: in the kitchen, in the bathrooms, in the boiler room. Consists of a powerful fan and an exhaust hood that goes outside. According to the standards, there is one hood for two heating devices, unless the regulatory authorities require it for each device. It is strictly forbidden to use plastic pipes: they are easily susceptible to combustion, which releases harmful fumes.
A combined supply and exhaust system for a private home is considered the most productive system: it removes exhaust air and pumps in new air at the same time. Can be installed in two ways :
- two air ducts are installed under the ceiling itself: one removes air, the other takes it in through a fan;
- one air duct, for the supply, is installed at the bottom of the wall, and the other under the ceiling, where the exhaust air goes.
The principle of operation of the recuperator is the heat exchange of air flows using plates and filters. The heat from the exhaust flow is recovered in the device and used to heat the supply air from outside. The process takes place in heat exchangers or in separate heat exchange devices, which can even be installed in different rooms, connected by an additional coolant (usually glycol or ethylene glycol). However, such structures are less efficient than those located in a single housing. In general, the operation of the recuperator in the supply and exhaust system retains 70-90% of the heat of the exhaust air.
Features of ventilation of premises of a private house
Air flows must be distributed so that air from the street penetrates first into the living room, bedrooms, office and other living spaces, and only then through the corridors - into the technical and ventilation shafts. Thus, where people are constantly (more than 6 hours a day), excess pressure will arise, which will not allow unpleasant odors and dust to enter.
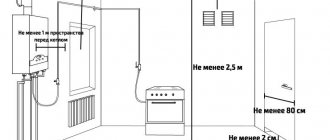
Kitchen ventilation
Natural and artificial systems are used for kitchen ventilation. The zone most in need of increased air circulation is the zone above the stove. It is important to consider the number of burners and the volume of air space. The following norms for the ratio of space and burners have been approved:
- kitchen more than 8 m3 - the stove must have two burners;
- 12 m3 – no more than 3 burners;
- 15 m3 – 4 burners.
It is better to purchase a hood for a private home with an aluminum body. Clean filters at least 2-3 times a year. If you install a device in which the fan speed is controlled, the air can be purified in different ways. You can check whether the hood is in working condition by holding a lit match or a burning sheet of paper to the grille: the flame should be drawn inward and the paper should stick.
If the kitchen is more than 15 m2, there should be several exhaust ducts.
Ventilation in the bathroom and toilet
An effective ventilation system is especially necessary in the bathroom and toilet: high humidity, strong odors, bacteria. Only an even, straight ventilation duct of 1-2 m can provide the necessary air circulation. Placed opposite the entrance door to create maximum traction. From the outside, it should be protected from moisture and precipitation by an inclined grille. The grate should have an adjustable flap inside. The compulsory system will be more effective in these conditions.
All components of the air duct are installed at a distance from heating devices. The power of the equipment is selected according to the intensity of operation and room parameters. It would be useful to install motion sensors, air humidity sensors, and timers in the bathroom.
Basement ventilation
Basement rooms are characterized by increased dampness, difficulty in ventilation, and insufficient sunlight, which leads to the spread of fungi and mold. For natural air circulation, ventilated openings (vents) are created along the base of the entire perimeter. They are located at a height of 300 mm from the ground. To protect from rain and moisture, they must have canopies and a drainage area. Forced circulation is carried out using fans located on opposite sides. The intensity of their work depends on the room conditions.
If partitions are installed in the basement, vents are also created in them, placing them under the ceiling and protecting them from rodents with bars.
Ventilation of upper floors and attic
In low-rise cottages, stairwells become ventilation ducts, allowing exhaust air to rise to the top, creating a difference in temperature and humidity between floors. The solution is to block access to the floors or isolate each room, which is more complex and requires a separate ventilation system. To ventilate the attic, a forced ventilation system is needed.
To avoid the formation of condensation in the under-roof space in the attic, it is necessary to organize proper air exchange. The roof will become more durable and will not need constant repairs. It is important to protect the ventilation in the attic from dust and moisture, and the vents from birds and leaves. The channels must be smooth, otherwise their efficiency will decrease.
DIY ventilation system
Installation of ventilation begins only after careful drawing up of the diagram, taking into account all the rules and regulations. Correct ventilation in a private house with your own hands is based on the following data:
- air exchange and microclimate parameters;
- standards defined for equipment of this type;
- features of equipment use.
When installing the system, the fewer parts used, the better. It is worth paying attention to the following points during installation:
- so that you can configure and repair yourself;
- there must be backup nodes;
- management is as simple as possible;
- the system must be reliable under different operating conditions;
- ventilation should be combined with the interior, fitting into the complex;
- installation and operation are economical.
Sewer pipes: main characteristics
Modern manufacturers offer three main options for sewer pipes:
- Made from polyvinyl chloride (PVC).
- Made from polypropylene.
- Made of polyethylene (corrugated).
Each of them has its own specifics and characteristics, but they all have a certain list of advantages:
- Affordability. Sewer pipes most often have the most affordable price for the general public, which allows them to be in significant demand among the population.
- Easy to install. To install sewer pipes you do not need to have any special knowledge, equipment or tools - they are laid using the socket method. Therefore, installation can be carried out on your own without incurring additional costs.
- Ease of dismantling and repair. There are always a significant number of different types of mounting elements on sale, which allow you to carry out repair work or replace the necessary section of the system without significant effort.
- High level of resistance to the influence of aggressive external environment.
- Smooth surface of the inner walls.
In connection with such a huge list of advantages, the question may logically arise: why then are ventilation and other types of pipes produced at all, if they can be profitably replaced with sewerage pipes? It turns out that not everything is so simple and the advantages of the described pipes are important when installing sewer systems. What is so special about ventilation pipes?
Recommendations and nuances
Ventilating a private home is a responsible and important process that should be approached with utmost care. Often, due to additional expenses, they try to save on it, subsequently getting a lot of problems. Experts give recommendations on ventilation that are worth listening to:
- Having an air conditioner will not solve the ventilation issue. Having the ability to change the characteristics of air, it cannot create its circulation. The air conditioner will create the desired temperature, but will not add oxygen or eliminate excess carbon dioxide.
- The exhaust fan will not cope with the ventilation of the building. Sealed double-glazed windows prevent the flow of air and, as a result, its exhaust. After some time, the hood will stop working due to the built-up pressure.
- Ventilation and an open window are not enough for ventilation. This air supply will not be constant, and micro-ventilation in winter is fraught with drafts and, as a result, colds.
- Equipment with a heater is not used under all conditions. The recuperator has restrictions on the minimum temperature up to (-25)-(-30)°. At lower temperatures, condensation freezes on the device.
When selecting pipes for the ventilation system, consider their cross-sectional size, heat resistance and tightness. In addition, they must comply with sanitary standards.
Metal air ducts
- Made of black steel.
- Made from galvanized steel.
- Stainless steel.
Looking ahead, we can immediately say that for small private buildings, metal air ducts are not often used.
Let's conduct a comparative analysis of metal and plastic pipes for ventilation.
Metal pipes are heavy, which means they are more difficult to install. They are more difficult to connect.
The service life of steel is short (on the scale of building structures that are theoretically built to last for centuries). Steel is susceptible to corrosion. A layer of zinc slows down this process, but does not cancel it completely. The weak points of galvanizing are the joints. And even when rusting just begins, the pipes emit a characteristic odor, which is unpleasant in a residential building.
Stainless steel stands out noticeably from previous options. Its service life is noticeably longer, but the price is disproportionately higher than its plastic counterpart.
In addition, any metal pipes create resistance to air flow. This means that the owner will have to buy a more powerful ventilation unit than for the plastic version.
Metal cannot be called a soundproofing material. Any sounds, fan operation, vibrations, etc., will echo throughout the ventilation shaft.
Metal pipes are resistant to high temperatures, aggressive environments and, most importantly, of any shape and size (this explains their use in ventilation systems of large factories and enterprises).
But if you have a private home, and not a hot shop, then you are lucky that plastic was invented!