The pressure in heating equipment is unstable and changes for various reasons. The readings are displayed on the pressure gauge. A normal reading is 1-2.5 bar. If they are above 3 bar, urgent measures should be taken to reduce the readings. The safety valve will indicate the difference.
It will release water to release excess. In electronically controlled units, such problems are displayed as an error on the display and the boiler will stop operating. In devices without built-in electronics, the difference leads to malfunctions and explosions.
Reasons for increased pressure. Ways to solve the problem
You can tell if there is too much pressure in the system by looking at the pressure gauges.
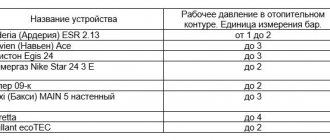
Normal readings are 1-2.5 Bar. If the pressure gauge needle reaches 3 Bar, sound the alarm. If the increase is constant, it is urgent to find the cause and reduce the pressure. Also pay attention to the safety valve: it will constantly release water to relieve pressure
The problem is in the expansion tank
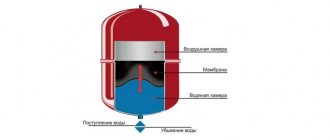
This tank can be located separately from the boiler or be part of the structure. Its function is to collect excess water when heating. Hot liquid expands, it becomes 4% larger. This excess is sent to the expansion tank.
The size of the tank is affected by the power of the boiler. For gas equipment, its volume is 10% of the total amount of coolant. For solid fuel - 20%.
Membrane rupture. If a part is damaged, the coolant is not restrained by anything, so it completely fills the compensation tank. Then the pressure begins to drop. If you decide to open the tap to add water to the system, the pressure will rise above normal. The connections will leak.
The tank or membrane needs to be replaced to reduce the pressure.
The pressure is below or above normal. A machine pump will help to achieve normal values (nominal) in a gas boiler.
- Drain all water from the system.
- Close the valves.
- Pump the circuit until you are sure there is no water.
- How to bleed air? Through the nipple on the other side of the inlet.
- Download again until the indicators reach the norm specified in the instructions for Ariston, Beretta, Navien and other brands.
The location of the tank after the pump provokes water hammer. It's about how the pump works. When it starts, the pressure rises sharply and then drops as well. To avoid such problems, in a closed heating system, install the tank on the return pipe. The next one to cut in is the pump in front of the boiler.
Why does pressure increase in closed systems?
Air accumulates in a double-circuit boiler. Why does this happen:
- Incorrect water filling. The fence is carried out from above, too quickly.
- After the repair work, excess air was not released.
- Mayevsky's air release valves are broken.
The pump impeller is worn out. Adjust or replace the part.
To relieve or reduce pressure, fill the fluid correctly. The intake is carried out from below, slowly, while the Mayevsky valves are open to bleed off excess air.
Open system problems
The problems are the same as described above
It is important to fill water and bleed air correctly. If after this the pressure does not return to normal, it is necessary to drain the system
Secondary heat exchanger
The unit is used to heat hot water. Its design consists of two insulated tubes. Cold water flows through one, and already heated water flows through the other. If the walls are damaged or a fistula appears, the liquids mix and enter the heating part. Then the pressure increases.
If you do not want to repair and solder the heat exchanger, you can replace it. To do this, buy a repair kit and get to work:
- Close the supply valves.
- Drain the water.
- Open the case and find the radiator.
The unit is secured with two bolts. Unscrew them.
- Remove the faulty part.
- Install new gaskets at the fastening points and connect the heat exchanger.
Other reasons
There are other reasons for such problems:
- The fittings are blocked. When collecting, the pressure increases and protective sensors block the equipment. Inspect the taps and valves, unscrew them until they stop. Make sure the valves are working properly.
- The mesh filter is clogged. It becomes clogged with debris, rust, and dirt. Remove and clean the part. If you do not want to clean regularly, install a magnetic or flush filter.
- The feed tap has failed. Perhaps its gaskets are worn out, then you can get by with a replacement. Otherwise, you will have to change the tap.
- Problems with automation. Faulty thermostat or controller. The reason is wear and tear, manufacturing defects, or incorrect connection. Diagnostics and repairs are carried out.
Check whether the boiler protection parts are in good working order: pressure gauge, valve, air vent. Clean radiators and other components from dust, soot, and scale. Prevention helps prevent serious breakdowns of gas equipment.
Pressure loss during cooling. What to do if it goes missing
An equally common problem is pressure surges depending on the operation of the boiler. When it is turned off or switched to DHW mode, the indicators may drop to 1 or 0 atm.
In such cases, its normalization in the expansion tank is required, which includes the following steps:
- Shut off the taps on the tank and then drain the coolant. After this stage the pressure should drop completely.
- Open the drain fitting and measure the pressure in the tank using a pressure gauge.
- Use a pump to pump air into the tank until water stops dripping from the fitting.
- Release the pre-inflated air.
- Pump the tank with air again until the pressure is 80% of the operating value.
- Close the fitting and energize the boiler.
Pressure drop
An increase in pressure in closed heating systems is not the only problem; in some cases there is a sharp drop in operating pressure, and among the reasons why the pressure level drops, the following should be highlighted:
- hidden system leaks, corrosion, loose connections, leaking fittings;
- rupture of the tank membrane, which requires replacement or repair of equipment;
- pressure drops in the system are observed, if the nipple poisons, such an air leak leads to deflation of the tank, and this causes damage to the membrane;
- there are cracks on the boiler heat exchanger, which leads to coolant leakage;
- pressure drops associated with the appearance of air bubbles lead to a decrease in the overall temperature in the system and its shutdown;
- One of the reasons for the decrease in pressure may be a soured or slightly open tap used to discharge water into the sewer system.
Leaks
Gaps are determined visually by pumping water into the pipeline to a predetermined level, and the cycle is stopped. The most susceptible to leaks are the joints of pipes, shut-off valves, radiator connections and the boiler itself.
One of the reasons for the pressure drop is a leak at the junction of the pipe and the radiator
- The presence of corrosion on metal pipes and connections;
- Poor quality pipeline installation;
- Weakening of joints;
- Damage to the pipe due to mechanical impact.
Troubleshooting
If the connection is damaged, replace the fitting or the connection itself. If a leak is detected (by a special scanner) in a pipe behind a decorative partition, wall or under the floor, it is necessary to dismantle the surfaces and make repairs.
How to increase the pressure in the boiler
If the pressure drops due to the expansion tank, it means that its volume is incorrectly calculated or the internal membrane is damaged. The situation can be corrected by more accurately calculating the required volume or by replacing the tank.
If the pressure in the heating system drops immediately after it is first started, then this is normal. The newly filled circuit, if it was filled with ordinary tap water, is full of air. As soon as it is converted into bubbles and removed from the pipes, the circuit parameters are normalized. You can also try removing the bubbles manually by using a manual air release.
The worst thing is if the pressure in the system laid inside the walls and floors has dropped - the pipes are often masked and completely recessed in building structures. If something happens to them, you will have to suffer thoroughly to localize the problem. The situation can be prevented by more careful selection of materials for the construction of the heating circuit.
Before increasing the pressure, it is necessary to check the tightness of the system. To do this you need to inspect:
- All heating devices - often leaks form where they connect to the pipes. Leaks between individual sections are also possible;
- Pipes - microcracks often lead to leakage of coolant, due to which the pressure gradually drops;
- Fittings are another common place for coolant leaks to occur;
- Boilers - double-circuit models have a complex internal structure; it is necessary to inspect the circulation pump, three-way valve and heat exchanger.
It is best if a specialist inspects the double-circuit boiler.
Increased pressure in the heating system causes unbalanced operation of the equipment and frequent boiler blockages. As a result, individual elements are subjected to increased load, which leads to circuit breakdowns and equipment failure. Why does the pressure in the heating system increase? There are several reasons for this phenomenon, most often these are leaks, unbalanced operation of individual elements, failure of automation or incorrect settings.
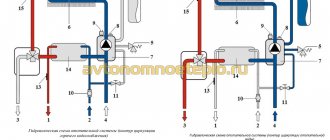
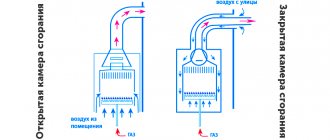
Movement of coolant in the heating system
When organizing heating systems, various options can be used, but recently closed systems have become more popular, in which the coolant moves due to the operation of a circulation pump. A gas burner heats water (or antifreeze) in a primary heat exchanger, and a pump pumps it through a radiator system, transferring heat to the premises.
At the same time, for normal circulation of the coolant, the system must be completely filled with water, and since the liquid tends to expand when heated, it is necessary to somehow compensate for the increase in volume. This is why expansion tanks are provided in heating systems.
The diagram shows a system in which the boiler acts exclusively as a heater. In household wall-mounted boilers ECOFOUR, the expansion tank and circulation pump are already built-in, which is why such boilers are convenient to use in small apartments.
Norm and control
We have already said that in a gas boiler the pressure should be within 1.5-2 atmospheres - this is the norm for a system that is put into operation and is in a heated state. In multi-storey buildings heated by centralized boiler houses, this figure is higher. Here, pipes and batteries must withstand not only high pressure, but also water hammer - this is an abrupt increase in pressure.
If drops are typical for centralized systems, then for autonomous heating they are rare - the volume of coolant here is not so large that serious jumps can be observed. In a cold state, the normal indicator is 1-1.2 atm., and in a warm state - slightly higher.
In private households, autonomous heating systems are used, powered by single-circuit and double-circuit boilers. The latter are becoming increasingly widespread. In addition to heating, they solve the problem of preparing hot water. One circuit in them heats the coolant circulating through the pipes, and the other ensures the operation of the hot water supply system.
Installation of expansion element
Boiler equipment is designed to operate at a certain water pressure. This means that there must also be a certain pressure in the expansion tank for it to work properly. It is supported by air or nitrogen, which fills the housing. Air is pumped into the container at the factory. During installation, care must be taken to ensure that no air is released. Otherwise, the device will not be able to function.
The pressure is monitored using a pressure gauge. The running arrow of the device indicates that air has escaped from the expander. In general, this situation is not a serious problem, since air can be pumped through the nipple. The average water pressure in the tank is 1.5 atm. However, they may not be suitable for your particular system. In this case, the pressure must be adjusted independently.
Normal values are 0.2 atm. less than in the system. It is strictly forbidden to exceed the pressure in the expansion tank compared to this indicator in the network. In such situations, the increased coolant volume will not be able to enter the tank. The tank is connected to the pipeline through the connecting size.
It is important not only to connect the expansion tank correctly, but also to choose the right location for its installation. Despite the fact that modern models can be mounted anywhere, experts advise installing this element of the system on the return line between the boiler and the pump
To ensure the maintainability of the structure, a ball valve is installed on the pipe through which the expander tank is connected. In the event of equipment failure, shut-off valves will allow it to be removed without pumping coolant out of the system. The tap must be open while the system is operating. Otherwise, the pressure in it will increase sharply, and it will leak at its weakest point.
Installation in a boiler room
In open systems with natural coolant circulation, tanks of other types are installed. Such a tank is an open container, usually welded from sheet steel. It must be installed at the highest point of the utility network.
The principle of operation of such an element is very simple. As the volume increases, the liquid is forced out of the pipes, rising through them along with the air. When cooled, the coolant returns to the pipeline under the influence of gravitational forces and natural air pressure.
If there is no expansion tank
The expansion tank for a home heating network is the second most important element (after the boiler). Water, when temperature changes, changes in volume. The volume inside the circuit is always constant, so an expansion tank is additionally connected to the circuit, where excess coolant can be diverted, i.e. acts as a compensator. Consequently, the RB is a safety device that prevents emergency situations - increased pressure, depressurization of pipes, etc.
The use of boiler equipment without an expansion tank is highly not recommended.
For stable operation, the pressure of the RB must correspond to the system volume, because when replacing radiators with pipes, the volume of coolant must be increased. At the same time, a too large RB will not maintain the operating pressure in the circuit.
The standard is an expansion tank designed for 120 liters of coolant in the circuit (typical two-room apartment). If the tank is too small, then the water will be discharged when heating and expanding the volume through a safety valve. When the boiler is turned off, when the liquid temperature decreases, starting the boiler will be impossible, because its volume, and, consequently, the pressure will be insufficient. In such cases, additional network feeding is necessary.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=tgwLKEVRgYk%3F
Pipe diameter and degree of wear
It is necessary to remember that the size of the pipe must also be taken into account. Often, residents set the diameter they need, which is almost always slightly larger than the standard sizes. This leads to the fact that the pressure in the system decreases slightly, which is due to the large amount of coolant that will fit into the system. Do not forget that in corner rooms the pressure in the pipes is always less, since this is the most remote point of the pipeline. The degree of wear of pipes and radiators also influences the pressure in the heating system of the house. As practice shows, the older the batteries, the worse. Of course, not everyone can change them every 5-10 years, and it is not advisable to do this, but it doesn’t hurt to carry out preventive maintenance from time to time. If you are moving to a new place of residence and you know that the heating system there is old, then it is better to change it immediately, so you will avoid many troubles.
Best answers
amateur:
You must have a vent, an air vent. Put a hose on it so as not to get it wet, and quietly open the tap and try to relieve the pressure. (this is my opinion, but it’s better to call a specialist.)
Boss Heat:
Anywhere in the heating system where there is a drain valve (Mayevsky tap, radiator drain, etc.), open and drain into a jar or bucket. It is most convenient to turn on the relief valve on a wall-mounted boiler.
Eliseikin:
Look for a drain valve... there must be one!
alexm66:
The boiler has a drain valve (usually from the bottom). It usually opens with a key - there is no flywheel on it. The instructions for the boiler indicate its location. In this case, it is advisable to stop the boiler.
So I say:
Before releasing the pressure, check that the valve on the expansion tank is open. If it is closed, open it, the pressure should drop. If it was open, bleed it from the battery in any convenient place. Under no circumstances should you bleed off the pressure from the boiler safety group yourself - if a speck gets under the valve seat, it can be very difficult to wash it off - this is how the valve drips.
Victor:
Install an expansion tank and forget about pressure surges.
L@rchik:
Bleed the air from the heating radiators, the pressure will immediately drop. Do not interfere with a well-functioning mechanism (boiler).
Features of the Navien boiler
In these units, the problem most often lies in leaks , especially when using fluids with a high glycol content. Antifreeze is very fluid, so it penetrates into the smallest cracks. Sometimes they are not easy to detect, so it is recommended to invite a specialist who will carefully check the entire harness. Detected leaks must be corrected, then the expansion tank must be refilled and the pipes must be cleared of air.
And also the pressure decreases slightly as the coolant cools. Usually, after turning on the boiler, this problem solves itself. If the fluctuations are significant, diagnostics are required. The latter may lead to repair or replacement of equipment.
To fix it, just follow steps similar to those described above. In rare cases, if it is impossible to solve the problem, you will have to purchase and install a new heating device.
Photo 1. Wall-mounted gas boiler model Deluxe 13A, open combustion chamber, South Korea.
What can lead to traffic jams in the circuit?
The importance of air vents cannot be overstated. Traffic jams in the circuit can lead to different processes:
- circulation disturbance;
- pressure surges;
- reduction in the efficiency of heating equipment;
- corrosion of metal.
Autonomous air vent
Installing an air vent in the heating system prevents the formation of plugs and pockets. When bumping into them, the coolant stops. Sometimes plugs cut off entire sections with radiators from the circuit. At the same time, the pressure in the system increases. When it reaches a critical level, an emergency release of coolant occurs. This, in turn, leads to a drop in pressure. At the same time, there are many cases when air collected in the batteries, the circuit continued to work, only half of the radiator became cold. This significantly reduces the heating efficiency and slightly increases the cost of its operation.
For open systems, one of the most serious threats is rust. At the same time, the question of how to remove air from the heating system arises only at the design stage. Such circuits are assembled at an angle from pipes with a large diameter, so there is a lot of water in the system. Considering the fact that the coolant is in contact with air and draws it into circulation, the oxygen level in the pipes is more than sufficient. Since it takes a long time to remove air from the heating system, oxygen reacts intensively with the metal. The result of the interaction is the formation of corrosion on the inner walls of the pipes. Rust sometimes eats up the tank so much that you have to replace it.
The direct consequences of traffic jams in the circuit entail indirect ones, which are no less dangerous:
Occurs if the valve for bleeding air from the heating system and all sensors are in good working order and working correctly. Due to the increase in pressure, an emergency release of the coolant occurs, which leads to a decrease in its quantity in the circuit. After cooling, there will not be enough fluid in the system, and the pressure will drop sharply. If it does not correspond to the minimum required to turn on the boiler, the heater will not turn on. And from this moment in winter, the countdown begins when the pipes defrost. Depends on how insulated the house is. Sometimes this happens in just three hours. In this case, unpleasant news awaits you at home from work;
This occurs if there is a malfunction of the valve for bleeding air from the heating system, or the temperature-controlling equipment. An unlikely situation, although possible. The results of this are very disastrous. At best, repair or replacement of the boiler; at worst, injury;
rupture of the circuit and release of the hot water fountain.
A very likely situation is that the joints may not be tightened enough. As the pressure increases, they cannot withstand and crack. At the same time, hot coolant flows from the pipe like a fountain. Not only does the circuit need to be repaired, but the neighbors also need to repair the ceiling, since you flooded it thoroughly. This is the kind of chain that can be caused by simply airing the system.
Automatic system recharge
The second unit that ensures the maintenance of excess pressure in the system is an automatic replenishment device. Of course, you can pump water into the system manually, but this is inconvenient to do with large volumes of leakage. For example, if the system has many fittings or there are gaps through which microscopic doses of coolant regularly leak. Also, automatic replenishment is practically irreplaceable for closed systems with a special coolant - without a pressure pump it simply will not be possible to provide a sufficiently high pressure.
The first type of automatic replenishment devices operates on the principle of a compressor automation group. High and low pressure switches turn the make-up on and off if the pressure in the system is lower or, respectively, higher than the set threshold. Such devices are the simplest and cheapest, but have a main drawback - they do not take into account the temperature of the liquid and the degree of its expansion.
Let's say that during system operation the pressure drops 20–30% below operating pressure, but does not reach the minimum threshold to which the relay is set. This is not surprising, because the relay calibration occurs in a cold state of the system. Another special case: when the relay is triggered, make-up is turned on, adding a portion of cold, that is, not yet expanded, liquid to the system. If the expansion tank has insufficient capacity, eventually the expansion of the coolant will cause the safety valve to operate, part of the coolant will be discharged, the pressure will drop again, the make-up will turn on again, and so on in a circle.
The described nuance is important for heating systems that contain over 300 liters of water. In such cases, it is optimal to use digital make-up dispensers, which are equipped with most advanced boiler equipment. The controller will make the necessary adjustments and add a strictly defined amount of coolant to the system, taking into account its temperature and expansion ability. Like conventional mechanical make-up valves, it is better to connect the electronic dispenser to the supply line immediately after inserting the bypass tube into it in order to avoid temperature shock of the heat exchanger. It is recommended to install a dirt or cartridge filter on the inlet pipe for the coolant; the injection unit is connected through a ball valve.
Optimal value for a private house or cottage
Any boiler operates at certain system settings, in particular, it is necessary to correctly calculate the water pressure. This value is influenced by the number of floors of the building, the type of system, the number of radiators and the total length of the pipes. Usually for a private house the pressure level is 1.5-2 atm, but for a five-story apartment building this value is 2-4 atm, and for a ten-story building it is 5-7 atm. For higher buildings, the pressure level is 7-10 atm, the maximum value is achieved in heating mains, here it is 12 atm.
For radiators that operate at different heights and at quite a decent distance from the boiler, constant pressure adjustment is required. In this case, special regulators are used to reduce it, and pumps to increase it. But the regulator must always be in good working order, otherwise sharp fluctuations and drops in coolant temperature will be observed in certain areas. The system must be adjusted so that the shut-off valves are never completely closed.
Control devices
To control the water pressure in the heating boiler and heating system, pressure gauges and thermomanometers are used. The latter are combined devices for monitoring two parameters at once. After starting the circuit, it is necessary to monitor the indicators so that they do not go beyond normal limits.
Some double-circuit floor-standing and wall-mounted boilers do not have traditional dial pressure gauges. Instead, electronic sensors are installed here, information from which is transmitted to the electronic unit, after which it is processed and displayed on the display. Another approach is also possible - if the heating unit does not have a pressure gauge, it is provided by the safety group.
The security group itself includes the following nodes:
- Pressure gauge or thermomanometer - for monitoring temperature and pressure in the heating circuit;
- Automatic air bleeder – prevents the circuit from becoming airy;
- Safety valve - relieves coolant pressure when it increases excessively.
Be sure to provide this unit in a closed heating system.
Some general information
Even at the design stage of the heating system, pressure gauges are installed in different places. This is necessary in order to control blood pressure. When the device detects a deviation from the norm, it is necessary to take some action; a little later we will talk about what to do in a specific situation. If no measures are taken, the heating efficiency drops and the service life of the same boiler is reduced. Many people know that the most detrimental effect on closed systems is caused by water hammer, for damping which expansion tanks are provided. So, before each heating season, it is advisable to check the system for weak points. This is done quite simply. You need to create excess pressure and see where it shows up.
How to bleed air from the boiler
Modern heat sources are equipped with automatic air ventilators or Mayevsky taps located in the upper part of the unit.
This design solution allows you to bleed air during operating mode without stopping the process of heating the room, just like with any radiator on which a similar valve is installed. To do this, periodically open and close the Mayevsky tap, with an interval of several minutes. The procedure is repeated until a hiss or whistle appears, indicating the release of the air lock. The appearance of sound requires holding the bleeder in the open position until the coolant appears.
The lack of special devices for removing plugs on the boiler requires the use of the same devices on pipelines located above the heat source.
The ideal conditions for freeing the air lock in the boiler is the possibility of separately shutting off the heat source circuit with the return pipe and circulation pump. When turned on, the coolant is pumped, and periodic opening of the Mayevsky tap or monitoring the operation of the automatic air vent by pressing the spool allows the blocked circuit to be released from the plug.
If there is no circulation pump in the closed circuit that cuts off the boiler with the return pipeline, then turn on the energy source: gas, electricity, and in the case of solid fuel, light the firebox. After heating the “supply” pipeline, the deaerator is periodically opened. The coolant, heating up, will rise from the boiler along the main line due to heating and return through the connecting pipeline - back to the heat exchanger. This technique requires careful monitoring of the temperature, especially when servicing a heat source other than solid fuel. The movement of coolant along such a circuit will be very slow and this is taken into account when performing work.
If it is not possible to shut off the boiler water circuit and there are air vent devices only in the upper part of the line, it is necessary to drain the coolant and then fill in the entire required volume of water. Before embarking on such global measures, it is recommended to turn off all devices (except the boiler) and, turning on the pump, release the pressure through the nearest air vent on the main line until sound or bubbles appear. The absence of a result indicates the need to completely drain the coolant.