A safety group in a heating system is a control and measuring unit designed to remove air masses and automatically prevent emergency situations associated with an increase in pressure in the heating system to critical values. The safety group is used exclusively in closed heating systems. In an open type CO with natural coolant circulation, it is simply not needed: the air is discharged through an expansion tank located at the top of the system, and the pressure, even under the most extreme conditions, cannot approach at least 1 bar.
The average cost of a ready-to-install unit is 1,100-3,000 rubles; if desired, you can assemble it yourself by purchasing all the components separately.
What is included in the heating system safety group
Composition of a classic security group.
The safety group consists of three elements connected by a collector (a technical element that divides the flow into several parallel branches).
Automatic air vent
The automatic air valve is designed to relieve air masses from the heating system. An earlier alternative is Mayevsky’s manual taps on radiators. The air in the pipes and radiators of the heating system slows down the heating and circulation rate of the coolant, reduces efficiency, and when heated above 90°C, it seriously increases the pressure, which can lead to damage and depressurization of the heating system.
Air may appear even with competent and careful operation of the CO. The most common reasons:
- initial filling of the heating system with coolant allowing air;
- release of air bubbles when heating water used as a coolant above 90°C;
- improper use of the make-up tap;
- wear of the elements and components of the heating system, which violates its tightness.
The automatic air vent does not require adjustment or human intervention. As soon as air forms in the system, it enters the air vent channel. The float located in this cylindrical channel lowers, lowering the locking rod: the valve opens and bleeds all the air from the channel.
Pressure gauge
The purpose of the pressure gauge is to display the exact pressure inside the heating system to monitor performance. Typically, bars are used as units of measurement. Having adjusted a certain level of pressure, looking at the pressure gauge, you can make sure that the system is working properly, all components are completely sealed, and other elements of the safety group are performing their functions.
Safety relief valve
The operating principle of a spring safety valve designed for an individual heating system.
The safety valve ensures automatic release of air, steam or coolant when a critical point is reached, thereby freeing up space in the system for further expansion of the coolant. An increase in pressure in the heating system can be caused not only by the formation of air (which is handled by the air vent), but also by the expansion of the coolant itself during strong heating, which can lead to damage and leakage.
If radiators and pipes can usually withstand a pressure of 7-9 bar without problems, then the most vulnerable element of the heating system is the boiler heat exchanger, often designed for 3 or even 2 bar.
It is based on the maximum permissible operating pressure that the safety valve is selected: there are models designed for a specific pressure and models with an adjustable value, which is set during installation and configuration. The most common and best in terms of price-quality ratio is the spring mechanism, which is what is used in almost all versions of security groups.
The principle of operation of a spring safety valve is the balance of pressure inside the system and the clamping force of the valve spring:
- from the inside, the coolant exerts pressure on the valve shutter;
- on the other hand, the spool is pressed by a rod, on which a spring presses, thereby holding the valve in the closed position;
- as soon as the pressure in the system exceeds a critical value, it outweighs the clamping force of the spring and the valve opens slightly, releasing excess air, steam or coolant;
- as soon as the pressure drops below a critical point, the spring force is sufficient to move the valve to its original closed position.
Device structure
As a rule, the reasons for disrupting the normal functioning of a closed boiler are an increase in pressure or a significant overflow of the pipeline with a coolant, that is, water.
The heat exchanger is the first section in the boiler that reacts to these deviations, and therefore it quickly fails.
To avoid these problems in the heating system, a boiler safety group is used.
Using this unit, the required coolant pressure in pipes and radiator batteries is achieved.
During periods of excessive pressure, excess heated water is discharged.
Various emergency situations that arise, for example excessive heating of the heating boiler, increase the pressure in the pipeline.
During strong heating, the water begins to expand; a closed water heating system is not designed for this - no additional reserve is provided here.
The result of increased pressure is a breakdown of boiler equipment or a rupture of the pipeline. To regulate the pressure and, during a potential threat, reduce it to the required value, you will need to install a boiler safety group.
The design consists of the following elements: safety valve, pressure gauge and automatic air release. All these devices are housed in a metal case with threaded connections.
Air vent
Most often, automatic air vents for boiler safety systems are made of brass.
Air bubbles in the heating system are formed for the following reasons:
- seals of poor quality or failure of old ones;
- initial filling of the heating line with water with air bubbles;
- incorrect installation or incorrect commissioning of the heating system;
- water replenishment;
- clogged or deposited pipes.
The water entering the heating circuit contains a large amount of air, which, when heated, expands and creates plugs.
Due to their formation, pressure increases and the speed of movement of the coolant decreases.
Therefore, it is advisable to install an automatic air release valve, which is characterized by ease of operation - it does not require human intervention during adjustment.
The operating principle of this device will depend entirely on its design.
Typically, an automatic valve includes a valve and a channel. The first element controls the release of excessive air. If there is no significant liquid pressure in the pipes, the float is in the raised position and the valve is in the “closed” position.
During the formation of a plug, the float lowers, and the rocker opens the outlet valve - this is how air is released from the heating pipes. After excess air is released, the float returns to its original position and the valve closes.
Trigger algorithm
Let us briefly summarize the principle of operation of the entire group. From the very beginning of commissioning, an automatic air vent operates, removing all air from the system. However, if it overheats and reaches critical pressure levels, it is powerless. To avoid an emergency, the safety valve is activated, releasing excess coolant, thereby reducing the pressure in the system.
To monitor the operation of the system, the safety group includes a pressure gauge that shows the pressure at the moment: low pressure indicates depressurization, a malfunction of the expansion tank or make-up valve; increased - about expansion of the coolant or excessive release of steam due to overheating.
Principle of operation
If an open expansion tank is installed in the boiler equipment system, then installation of a safety group is not required - the pressure in the pipes is equal to atmospheric pressure, and an excessive amount of air leaves the system through the tank.
The safety group for a heating boiler works according to a very simple scheme, when each block is responsible for maintaining the norms of the specified indicators:
- The main job of the air vent is to discharge air that enters the pipes during operation.
- The safety valve prevents significant pressure levels from appearing in the heat generator.
- Thanks to the pressure gauge, the owner of a private house will be able to regulate the pressure level while filling the pipeline with coolant, as well as later during operation of the boiler.
All modules are a single unit and are located in a special housing - a manifold.
How to choose a security group for the heating system of a private home
Choosing the right model is not difficult, you need to look at:
- The maximum permissible system power (kW) for which the unit is designed. Typically this is 44, 50 or 55 kW. If the system has less power, great, but if it has more power, you need to look for a more durable option.
- Safety valve response pressure . As a rule, valves with a fixed value are installed in finished units - 1.5 bar, 3 bar, 4 or 6 bar. The response pressure must correspond to the maximum permissible operating pressure of the most vulnerable element of the heating systems - usually a steel boiler heat exchanger designed for 2 or 3 bar. Safety valves for 2 bar, despite sufficient demand, are difficult to find on sale; the way out of the situation is to assemble the unit yourself by purchasing the safety valve and other elements separately (see below for more on this).
- The operating temperature is the permissible temperature of the coolant; for almost all modern models it is within the range of -10°C – 110°C, which is more than enough.
- Compatibility with coolant - if antifreeze is used as a coolant instead of water.
- Threaded connection diameter – it can be 1″, 1/2″ or 1.4″ in diameter. You can also select a unit that does not match the thread diameter, but then you will have to take care of selecting an adapter, which is not always easy.
It is important to pay attention to the material of manufacture; galvanized steel or stainless steel is a good, but not the best option. More expensive, but more durable, wear-resistant and even more resistant to corrosion are brass products. The material of manufacture is not always indicated in the characteristics; in addition, the collector can be made of steel, and the remaining elements - of brass. You can distinguish brass by its characteristic monochromatic, matte color (bronze-golden or silver, depending on the alloy).
How to choose a room thermostat and save up to 30% per month on heating
Features of choice
For any model of protective group, the instructions indicate acceptable parameters. The main criteria that influence the choice of device:
- maximum coolant temperature;
- thermal performance indicators of boiler equipment;
- thread diameter for connection (if necessary, you can buy an additional adapter);
- compatibility with thermal fluid;
- nominal pressure.
A competent choice of unit power can provide reliable protection of boiler equipment from various disturbances during operation of the heating circuit.
The best known manufacturers and models: characteristics and prices
TIM JH-1024-1.5
One of the most inexpensive but proven models. Despite the low cost, it has a brass manifold. The maximum power of CO is 50 kW, the response threshold of the safety valve is 1.5 bar, the connection diameter is 1″ BP. Country of origin: China.
VALTEC VT.460.0
One of the best ready-made safety groups for the boiler and heating system of the famous Italian manufacturer VALTEC. The unit is entirely made of nickel-plated brass and has an additional threaded outlet for connecting an expansion tank. It is distinguished by high reliability and quality of all connections and technical elements. The permissible power of the CO is up to 44 kW, the response threshold is 3 bar, the diameter of the connection to the network is 1 V.
Watts KSG 30
Security group of another well-known German company with production in Italy. There is a whole range of models on the market, where there are models designed for power up to 100 and even up to 200 kW. The collector body is made of galvanized steel, which, given the cost, is a disadvantage. However, the technical elements are made of brass, and there is a thermal insulation casing. Maximum CO power – 50 kW, response pressure – 3 bar, connection diameter – 1″ (internal thread).
Caleffi 302631
Another reliable and high-quality (in terms of materials and assembly) Italian-made model, entirely made of brass, with a heat-insulating polystyrene casing included. The maximum power of the CO is 50 kW, the response pressure is 3 bar, the diameter of the threaded connection is 1″ female.
Cost: 4,500-4,750 rubles.
Varieties
Let's look at the types of security groups. They differ:
Appearance: classic - in the photo above, compact - in the photo below:
The presence of thermal insulation: there are models with and without insulation:
Installation method: on the pipeline (all the above models) or on the wall:
Boiler safety group WATTS GAG/KAV with wall console. By the way, on the left side of this boiler safety group there is pre-installed fittings for connecting an expansion tank (models up to 33 liters are suitable)
Maximum boiler power: the most common sizes are up to 50 kW, up to 100 kW, up to 200 kW:
Boiler safety group WATTS KSG 30/25M-ISO insulated for boilers up to 200 kW
Prices: summary table
| Manufacturer and model | Maximum CO power, kW | Response pressure, bar | Thread diameter, inch | price, rub. |
| TIM JH-1024-1.5 | 50 | 1,5 | 1″ BP | 990-1 200 |
| VALTEC VT.460.0 | 44 | 3 | 1″ BP | 1 650-1 800 |
| Watts KSG 30 | 50 | 3 | 1″ BP | 2 600-3 400 |
| Caleffi 302631 | 50 | 3 | 1″ BP | 4 500-4 750 |
Technological requirements
The following technical requirements must be observed:
- A special area must be provided to disperse the smoke. It is a vertical pipe installed behind the nozzle of a solid fuel boiler. The acceleration section is made one meter high.
- The chimney is installed only vertically. Deviation of no more than 30 degrees is allowed.
- Deflections are prohibited.
- The length is very important (3 - 6 meters).
- Three horizontal sections are allowed. Moreover, the length of each should not exceed half a meter.
- The height of the head above the roof must exceed 100 cm.
- The pipe is attached to the wall in 1.5 meter increments.
- To create a sealed joint, the pipes are generously lubricated with heat-resistant sealant.
To obtain ideal draft, it is necessary that the chimney design has a minimum number of turns. A straight pipe is considered best.
The chimney can be installed inside or outside the building. For the first option, it is necessary to protect the pipe so that it does not come into contact with flammable materials. A special metal screen is used, installed where the pipe passes through the ceiling. The chimney must be located at a distance of more than 25 cm from the wall.
External structures look much safer. They are much easier to maintain. Masters consider this method the most preferable.
Where is the security group placed?
The safety group is placed on the supply line of the heating boiler, as close as possible to the boiler unit, but above its level. It is prohibited to install any shut-off valves, filters or other elements that narrow the pipeline between the boiler and the safety group. The safety group must be installed strictly in a vertical plane so that the air vent and safety valve are in a vertical position; in the horizontal plane the unit can be rotated as desired.
Please note that if there is an appropriate outlet pipe, it is recommended to connect the expansion tank through it. If this is not done, the outlet pipe for the expansion tank must be plugged.
Water heater protection
Indirect heating boilers and electrical storage devices that prepare water for household needs also require protection. In this case, the danger is represented by pressure surges in the water supply and expansion of the liquid in the tank due to heating. To prevent the tank from leaking, a boiler safety group is installed at the water supply, consisting of the following parts:
- brass body;
- a check valve that does not allow water to flow from the container back into the pipe;
- safety valve that relieves excess pressure;
- ball valve to close the hot water supply line.
Storage water heater safety group from the VALTEC brand
In addition, indirect heating boilers are equipped with an automatic air vent mounted in the upper part of the tank and a dial temperature meter. A pressure gauge is optionally installed on the unit.
Connection to the heating system
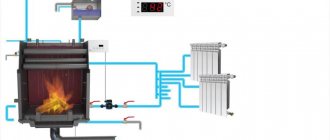
The entire process of connecting the safety group to the heating system consists of a threaded connection to the vertical pipe previously allocated for it (the diameter of the pipe thread = the diameter of the thread of the safety group) and checking the functionality of its modules. An example of installing a security group is shown in the diagram below.
An example of installing a security group in a closed heating system.
After a tight connection, you need to check the operation of the air vent by forcibly opening it: turning the valve handle (top cap) until it clicks. Leave the air vent open. It is better to close the automatic air vent while the system is filling with coolant. A drain tube must be placed on the relief valve, leading either to the floor (into a prepared container) or to the sewer. In the first case, the consequences of the accident will be visible; when draining into the sewer, you may not even know what happened.
Installation of homemade automation
High-quality products from well-known manufacturers are quite expensive. For example, the cost of a safety group for boilers of the Italian brand Icma is 40-43 USD. e. If you buy components from the same manufacturer and assemble the safety automatics yourself, the price will be significantly lower:
- safety valve – 6 cu. e.;
- pressure gauge - 10 cu. e.;
- automatic air vent – 5 cu. e.;
- brass crosspiece DN 15 as a collector – 2.2 cu. e.
The total amount for a security group assembled with your own hands is 23.2 USD. That is, the benefit is obvious.
When choosing components, be sure to take into account the advice of our expert, based on many years of practice:
- Do not go for absolute cheapness when purchasing safety valves. Chinese products begin to leak after the first actuation or do not release pressure at all.
- Pressure gauges “originally” from the Middle Kingdom often lie. If, when filling the system with coolant, the device underestimates the readings, then after heating the pressure in the network will jump to critical and an accident will occur.
Assembling a homemade block - Select a safety valve according to the boiler operating pressure specified in the technical data sheet.
- Do not buy an angular type air vent, only a straight one. The first creates increased resistance to the outgoing air.
- The crosspiece should be made of high-quality thick-walled brass. When choosing, compare the weight of a cheap and expensive part in the palm of your hand and feel the difference.
For reference. The vast majority of gas and wood heat generators operate with a maximum water pressure of 3 bar. The exception is Stropuva long-burning cylindrical heaters (max - 2 Bar) and completely cheap boilers with thin walls (max - 1.5 Bar).
Setting up a homemade security group is quite simple. Screw the air vent into the upper terminal of the cross, and install a pressure gauge and safety valve on the side terminals in any order. Cut the finished element into the main line next to the boiler according to the diagram (see the previous section).
If you want to maximize the safety of your solid fuel heating unit, pay attention to thermal relief valves. They work in tandem with the main group and, in case of overheating, release the coolant from the water jacket of the boiler, running cold water from the water supply inside. Product types and connection diagrams are described in our earlier publication.
How to properly assemble a knot with your own hands
A correctly configured safety group should be in the shape of a trident, so that the air vent is located in the middle, directly above the pipe under the safety group. This way air will be guaranteed to flow into it, without any obstacles.
A homemade security group includes the following elements:
- pressure gauge, automatic air vent and safety valve;
- 2 steel or brass squares at 90° with external and internal threads (the diameter is selected to match the diameter of the threads of the modules and the crosspiece);
- 1 steel or brass cross;
- 1 coupling/nipple for connecting the finished unit with the heating system tee;
- tow or silicone for sealing joints (FUM tape is not recommended because it deforms at temperatures above 70-80°C).
We connect the elements in accordance with the photo below, connect them to the heating system and check their functionality.
An example of a knot assembled by yourself.
Self-assembly
There should be no difficulties during the manufacture of the security unit. To start the process, you need to prepare the following tools and materials:
- pressure gauge;
- relief valve;
- wrench and gas wrench;
- air vent;
- two squares;
- crosspiece;
- union;
- sanitary linen;
- sealant;
- adapters.
The angles are screwed into the cross. For a tight connection, plumbing flax is wound onto the thread, evenly distributing it over the surface. A small layer of sealant must be applied on top. Then, using a wrench, screw the squares into the crosspiece perpendicular to each other.
Then you need to install an air vent, a safety valve and a pressure gauge. If the parts have different thread sections, adapters are used. After the final assembly of all elements, the operation of the product must be tested under pressure - the unit should not leak, and all parts must be in working position.
Maintenance
- It is advisable to check the status of all modules of the security group every 2-3 months.
- The safety valve must be cleaned every 6 months to prevent leaks and contamination. To do this, it must be opened by turning the valve cap in the direction of the arrow.
- After 5-7 operations, it is recommended to replace the safety valve due to wear on the spring, which can lead to leakage and operation at lower pressures in the system.
Instructions Boilers Boiler room equipment Safety valves