What is an accumulator tank for a heating system?
An accumulator tank in a heating system is a reservoir to accumulate excess heat for use in the event that the boiler equipment stops. The device is used in a circuit with a solid fuel type boiler.
In some cases, it is installed together with other energy equipment, for example, they are equipped with solar collectors, heat pumps, and electric heaters. Otherwise, these units are called heat accumulators, buffer tanks, or storage tanks.
What should be the pressure in the accumulator?
One part of the accumulator contains compressed air, and water is pumped into the second. The air in the tank is under pressure - factory settings - 1.5 atm. This pressure does not depend on the volume - it is the same on a tank with a capacity of 24 liters and 150 liters. The maximum permissible maximum pressure may be more or less, but it does not depend on the volume, but on the membrane and is indicated in the technical specifications.
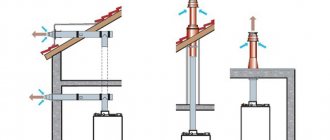
Accumulator design (image of flanges)
Preliminary check and pressure correction
Before connecting the accumulator to the system, it is advisable to check the pressure in it. The settings of the pressure switch depend on this indicator, and during transportation and storage the pressure could drop, so monitoring is very desirable. You can control the pressure in the hydraulic tank using a pressure gauge connected to a special inlet in the upper part of the tank (capacity of 100 liters or more) or installed in its lower part as one of the piping parts. Temporarily, for control, you can connect a car pressure gauge. Its error is usually small and it is convenient to work with. If this is not the case, you can use the standard one for water pipes, but they are usually not very accurate.
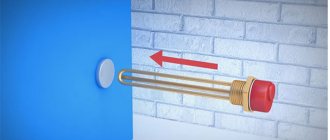
Connect the pressure gauge to the nipple
If necessary, the pressure in the accumulator can be increased or decreased. There is a nipple at the top of the tank for this purpose. A car or bicycle pump is connected through the nipple and the pressure is increased if necessary. If it needs to be vented, the nipple valve is bent with some thin object, releasing the air.
What air pressure should be
So should the pressure in the accumulator be the same? For normal operation of household appliances, a pressure of 1.4-2.8 atm is required. To prevent the tank membrane from tearing, the pressure in the system should be slightly higher than the pressure of the tank - by 0.1-0.2 atm. If the pressure in the tank is 1.5 atm, then the pressure in the system should not be lower than 1.6 atm. This value is set on the water pressure switch, which works in tandem with the hydraulic accumulator. These are the optimal settings for a small one-story house.
If the house is two-story, you will have to increase the pressure. There is a formula for calculating the pressure in the hydraulic tank:
Vatm.=(Hmax+6)/10
Where Hmax is the height of the highest point of water intake. Most often this is a shower. You measure (calculate) at what height relative to the hydraulic accumulator its watering can is located, substitute it into the formula, and get the pressure that should be in the tank.
Connecting a hydraulic accumulator to a surface pump
If the house has a jacuzzi, everything is more complicated. You will have to select it empirically - changing the relay settings and observing the operation of water points and household appliances. But at the same time, the operating pressure should not be greater than the maximum permissible for other household appliances and plumbing fixtures (indicated in the technical specifications).
Why is the sharpening angle so important?
The cutting wedge angle (the distance between the edges of the blade) is an important characteristic of any knife. It is set during production, depends on what function the cutting tool performs and varies from 55º (machete) to 10º (scalpel).
- for splitting and cutting hard materials - splitting bone, chopping bamboo, splitting coconut - you need a durable cutter with an angle between the edges of the blades of 45-55º;
- knives for separating meat from bones and cutting fibers with veins are sharpened at an angle of 40º;
- for a blade similar in functionality to an ax (it can be used to chop wood, chop meat, cut straw), an angle of 35-40º is typical;
- universal knives (hunting or fishing) are sharpened at an angle of 30-35º;
- for standard kitchen work (cutting bread, vegetables, cheese), an angle of 25-30º is suitable;
- for cutting fillets, the tool is sharpened at an angle of 10-15º;
- an angle of 8-12º is provided for the blade of a straight razor and scalpel.
In order for the knife to work correctly and serve for a long time, it is important to sharpen it at the right angle.
Design and principle of operation
The peculiarity of hydraulic tanks is that the water does not come into direct contact with the metal body, but remains enclosed in an elastic cavity, also called a membrane. The membrane is made of butyl, a durable rubber material. Butyl provides the proper level of protection of water from bacteria, which metal cannot boast of.
There is an air gap between the elastic membrane and the metal body. Nitrogen is pumped into it, but the chamber can also be filled with ordinary air. The chamber is equipped with a special pneumatic valve, through which the pressure inside is regulated. You can fill the chamber through this valve or, conversely, bleed the air.
The hydraulic accumulator installation can be disassembled and reassembled at any time. It has a simple device. This simplicity is ensured so that it is always possible to identify problems and carry out timely repairs. In this case, the device can be repaired without pouring all the water out of it.
Large-volume hydraulic accumulators have an additional valve in the membrane, which also allows air to be released, but here we are talking about air that is released from the water. Small hydraulic tanks do not have this function, but then the valve must be on the pipeline.
The hydraulic accumulator operates as follows.
- First, water is pumped into the elastic cavity, stretching and filling it. A special relay is attached to the cavity.
- Once the pressure threshold is reached, the relay reacts to this and turns off the pump.
- Further, during operation of the accumulator, the pressure drops again, and the relay, reacting to this, turns on the water again. The relay can be set to any level. This type of device is called an automatic hydraulic accumulator.
Nowadays, such options are practically not found, but there are still outdated hydraulic tanks, the level of filling of which must be monitored and filled independently as needed.
Vertical hot water storage tank BAGV
The vertical tank BAGV is a steel cylindrical tank, which is equipped with a ladder, a fence on the roof, a manhole in the lower zone, as well as pipes according to the piping.
Hot water storage tanks are not designed to operate with excess pressure, so the maximum incoming water temperature should not exceed 95C.
Like steel tanks for petroleum products, the vertical storage tank BAGV is manufactured by rolling in a factory. Rolling is the process of welding the wall and bottom panels. The finished elements are rolled into rolls on a special stand, after which they are sent in the form of rolls to the installation site.
Welding of seams is carried out by automatic tractors under submerged arc, thereby achieving high quality and reliability of welds.
At the construction site, the bottom rolls and walls of the BAGV storage tanks are unrolled and mounted on a pre-prepared foundation.
To prevent loss of thermal energy, the outer surface of the storage tank is insulated. As a rule, the insulation is a mineral plate, covered on top with a thin galvanized profile sheet 0.5 - 0.7 mm thick.
The roof of a vertical storage tank with a volume of up to 5000 m3 is made in the shape of a cone. The roofing is supplied to the BAGV construction site in the form of flat steel panels, welded overlapping and supported on the tank wall and the central support ring.
For non-standard hot water storage tanks with a volume of more than 5000 m3, the roof is made in the shape of a spherical dome.
Rice. 1. Vertical hot water storage tanks
A – water inlet; B – water output; G – output to thermocouple; D – manhole.
External reinforcing structures consisting of horizontal circular belts (bandages) and vertical posts must be installed on vertical tanks. The distance between the bands is set by the project depending on the value of tensile forces and the location of hatches and pipeline entries (the designs of external protective structures were carried out by the Lenproektstalkonstruktsiya Institute). It is mandatory to install external reinforcing structures on BAGVs with a capacity of 400 m3 or more with seismicity up to 6 points, and for 100 m3 or more - 6 points or higher.
Technical characteristics of vertical hot water storage tanks
| Name | volume, m3 | Inner diameter, mm D | Wall height, mm L | Roof type |
| BAGV-100 | 100 | 4.73 m | 5.98 m | Conical |
| BAGV-200 | 200 | 6.63 m | 5.98 m | Conical |
| BAGV-300 | 300 | 7.58 m | 7.45 m | Conical |
| BAGV-400 | 400 | 8.35 m | 7.45 m | Conical |
| BAGV-700 | 700 | 10.43 m | 8.94 m | Conical |
| BAGV-1000 | 1000 | 10.43 m | 11.92 m | Conical |
| BAGV-2000 | 2000 | 15.18 m | 11.92 m | Conical |
| BAGV-3000 | 3000 | 18.98 m | 11.92 m | Conical |
| BAGV-5000 | 5000 | 22.80 m | 11.92 m | Dome sphere |
| BAGV-10000 | 10000 | 34.20 m | 11.92 m | Dome sphere |
| BAGV-15000 | 15000 | 39.90 m | 11.92 m | Dome sphere |
| BAGV-20000 | 20000 | 45.60 m | 11.92 m | Dome sphere |
What it is?
But what is this device? In essence, this is a source of electrical energy, but only a secondary one, since the main task, as already mentioned, is to start the engine.
Yes, the battery supports the electrical equipment found in any car, but only in a secondary role. In reality, they are powered by a generator while the car is moving. But when the vehicle is immobilized and the engine is not running, then the load from the on-board network falls on the battery. This is actually why it is not recommended to listen to music for a long time when the car is just standing still.
In the middle of the 20th century, internal combustion engines managed just fine without batteries. This mainly applied to motorcycle engines. Muscular force was used to launch them. Then the generator provided energy. Does each of us remember how the Izh family motorcycle started up?!
After some time, manufacturers began to equip vehicles with a large number of electrical appliances. And each time their number only increases. Therefore, recharge from the battery is very useful. Perhaps in a few years, most vehicles will switch to an on-board network with a nominal value of 24 volts, instead of the usual 12. Although some Mercedes cars have already done this.
Battery functions
The main source of current in a car is the generator. But this device is capable of delivering full power only when the engine is running, and at least at medium speeds. In idle mode, its output may not be enough even to provide part of the regular consumers. To eliminate the voltage drop in the on-board network associated with overload, a buffer source is needed that is capable of replenishing its reserves when there is excess generator power and delivering energy to consumers when its capabilities are insufficient. This will be one of the roles of the battery in the system.
The second function of the battery was to start the engine. The starter used for this consumes significant current at a relatively low voltage. Hence the requirement for the battery to be not just a backup generator assistant, but to have the ability to operate in starter mode, that is, to briefly produce currents of the order of several hundred amperes. Not every battery is capable of this, so the battery type designation always indicates that it is a starter battery. This imposes significant restrictions on the technologies used in its production.
The combination of requirements for a large operating range of output currents, acceptable capacity, low cost and extreme temperatures forces manufacturers to give preference to lead-acid batteries, although this type has long been considered obsolete. There have been attempts to use alkaline cells and many other options, including high-tech supercapacitors, but each technology, in addition to its advantages in one direction, has ineradicable disadvantages in others.
The role of the hydraulic accumulator in the water supply network
It would seem that the device simply passes water through itself. Could you do without it? In fact, it is with the help of a hydraulic tank that stable pressure is maintained in the water supply system.
If for any reason the voltage in the electrical network is lost, a small “emergency” supply of water in the tank will help solve priority economic problems.
Let us clarify the list of advantages that this fairly simple device provides:
- Premature pump wear. There is a certain supply of water in the membrane tank. It satisfies the primary needs of cottage owners. And only when the supply runs out will the pump turn on. It should be noted that all pumps have a turn-on rate of an hour. If there is a hydraulic accumulator, this figure will not be exceeded, and the unit will last longer.
- Stabilization of pressure in the system. If you turn on two taps at the same time, for example in the bathroom and in the kitchen, pressure changes can affect the water temperature. This is very unpleasant, especially for those household members who are taking a shower at this moment. Thanks to the hydraulic accumulator, such misunderstandings can be avoided.
- Water hammer. These phenomena, which can damage the pipeline, can occur when the pump is turned on. With a hydraulic tank, the risk of water hammer is virtually eliminated.
- Water supply. In a country house, the problem of water supply is especially acute. If there is a sudden power outage and the pump cannot perform its functions, then it is no longer necessary to store a supply of water in a bucket or other container to solve urgent problems. It is available in the hydraulic accumulator tank and is regularly updated.
Obviously, the presence of this device in a water supply system independent of centralized networks is not accidental. It is necessary and useful.
The hydraulic accumulator in the water supply circuit performs a number of significant functions: it protects equipment from water hammer, provides a supply of water, and creates conditions for automating its intake.
When a hydraulic tank is not needed
In irrigation systems, a hydraulic accumulator is not needed, since when the tap is constantly open, the pump will operate without turning off. If there is a storage capacity in this scheme, the equipment will be turned on frequently, which will lead to premature depletion of the resource.
When purchasing a pump with an automatic system that involves smooth engine starting, a hydraulic pump is also not needed. The pipes are not at risk of water hammer, since the fluid flow moves slowly.
When is a heat accumulator needed?
This simple element of the heating system in the form of an insulated water tank is recommended to be installed in the following cases:
- for the most efficient operation of a solid fuel boiler;
- together with an electric heat generator operating at a reduced night tariff.
For reference. There are also water heat accumulators for greenhouses, used to store solar energy received during the day.
The operation of solid fuel boilers has its own characteristics. The heat generator operates with high efficiency only when operating at maximum modes; if you cut off the air to it to lower the temperature in the furnace, then the operating efficiency also decreases. The homeowner also has a lot of worries about the frequency of heating, the firewood has burned out - he needs to load new ones, which is extremely inconvenient to do in the middle of the night. The solution is simple: you need a storage tank that accumulates previously generated heat for use after the firewood burns out in the firebox.
The opposite situation occurs with an electric boiler connected to the network through a multi-tariff meter. To save money, you need to get maximum heat at night, when the tariff is low, and not use electricity during the day. And here the heat accumulator in the heating system will allow you to organize an optimal operating schedule for the heat source, supplying hot water to the system while the heat generator is inactive.
Important. To work together with a heat accumulator, the boiler must have at least one and a half reserve thermal power. Otherwise, it will not be able to simultaneously heat the water in the heating system and the storage tank
Otherwise, it will not be able to simultaneously heat the water in the heating system and the storage tank.
A similar situation with excess heat occurs in greenhouses; they are even ventilated during the daytime. In order to accumulate solar energy for use at night, you can use the simplest heat accumulator Lezhebok to heat the ground. This is a black polymer sleeve filled with water and laid directly over the bed; it prevents the soil from cooling at night. To absorb more heat, barrels of water painted black are placed inside the greenhouse.
What is a heat accumulator used for and how does it work?
Those whose homes are heated with a solid fuel boiler know how difficult it is to achieve a stable temperature in the batteries. Since the temperature in the heater’s furnace is constantly changing and this process is practically impossible to influence. How to do this when the fuel is placed in the firebox and has already flared up? You can, of course, shut off the air supply, but the effect will be barely noticeable and long-term. In other words, it is not possible to take prompt measures.
The second problem is the time between fuel loading. Naturally, the less often you need to add firewood or coal to the boiler, the better, the less hassle. To solve both of these problems, you can install battery storage tanks for heating. What it is?
There is a coolant inside the heat accumulator. This can be water or antifreeze, but you need to understand that this is the same coolant that circulates throughout the entire circuit. The principle of operation of the battery tank in the heating system:
- the boiler heats the water, and it enters the heat exchanger, which is constantly filled with coolant;
- then the coolant goes into the heating circuit and gives off part of the heat to the total volume of liquid in the reservoir;
- gradually the temperature of the water in the heat accumulator increases;
- from the return circuit also comes to the TA;
- From the buffer tank, the return flow is transferred to the boiler.
TA connection diagram
The water supply to the storage tank for heating is carried out at the top, and the return flow comes out at the bottom. These flows move in different directions in the reservoir. The task is to ensure that they intersect and heat exchange takes place. Otherwise, no heat accumulation will occur. In this case, you need to not just mix the water in the container, but do it correctly.
What does it mean? The circulation must be adjusted in such a way that the supply flow goes down to the return flow, while the return flow does not rise up. Only in this case will the liquid layer located between the flows heat up.
The circulation is adjusted by selecting the power of the pumps before and after the storage tank for heating, as well as setting one of three operating speeds
It is important to install filters for the heating system in front of the pumps. Otherwise, the circulation pump may need to be repaired.
The heat accumulator stops taking part of the heat from the coolant supplied to it only if it is fully charged. That is, the water temperature is the same in all layers and is equal to the supply temperature from the boiler.
Installation of storage tank
Connection diagram of a heat accumulator to a heating system
The container is installed in front of the heating radiators. The best option is to connect the inlet pipe immediately after the boiler. According to this scheme, the water in it will be heated as quickly as possible.
- Shut-off valves on all pipes;
- Pressure gauges and thermometers. Temperature sensors must indicate the degree of heating of the water in the container and the coolant;
- Sets of 2-way valves for mixing heated water and coolant from the return pipe, so you can minimize energy costs.
Maintenance of the storage tank must be done before each heating season. It is best to disassemble it completely to remove scale and check the condition of the structure. If this is not possible, washing is done with special solutions.
The video describes the advantage of using a storage tank for an autonomous heating system:
Thanks to the author for an interesting article. I myself learned about heat accumulators after purchasing a solid fuel boiler; I had to buy more and install it in a ready-made system. I took a barrel of the Thermiko brand, made in Ukraine. So far the impressions are purely positive. Firewood consumption has decreased by 25 percent, after loading the boiler provides heat for another 6 hours. In general, it has become much more convenient to heat the house. In general, I advise you to immediately look in the direction of buffer containers when purchasing.
Advantages and disadvantages of heating with a heat accumulator
The advantages of such systems are:
- Reduced energy costs.
- Increasing the efficiency of the heating system.
- No overheating.
- Reducing the amount (frequency) of loading solid fuel into the boiler.
- Fine-tuning the temperature in the rooms.
- Possibility of modernization (combination with a hot water supply system, use of alternative energy sources instead of fuel).
With all the advantages, heating equipment of this type also has disadvantages:
- The power of the installed boiler allows you to heat an area twice as large as required (power reserve).
- The system takes a long time to start from a cold state before entering normal operating mode.
- Due to the bulkiness of the equipment and the large number of components, transportation, placement and installation are complicated.
- There remains a need for a fuel warehouse in close proximity to the boiler room.
- The cost of equipment and the lack of quick payback, especially when replacing the boiler.
The last drawback can be successfully solved by installing the heat accumulator with your own hands.
Types of heating systems with heat storage and different numbers of coils
The coil plays the role of a heat exchanger, that is, liquids of different systems do not mix with each other, and heat transfer occurs through the walls of this spiral. Made from copper or stainless steel. Sometimes ferrous metal is used to reduce the cost of the structure.
There are four main types of systems:
Without coil. Instead, an additional tank of smaller diameter can be installed, connected to a small circuit. Heat transfer occurs due to the physical properties in which it rises up and the cold coolant falls to the bottom of the container. This system is the simplest and works with only one consumer, for example a heating system and one source. This can be either a solid fuel boiler or a solar collector. Features: minimal cost, ease of installation.
With one coil. The spiral is located inside the main tank; coolant from the source circulates through it. The energy is transferred to a storage tank from where it is circulated further to the consumer. The peculiarity of such a system is that there is no mixing of different coolants
This may be important if they have different chemical compositions
The system can also work in the reverse order; the heating system or hot water supply can flow through the coil.
With two coils. An additional small heat exchanger circuit is fed into a system connected to an alternative energy source. This system allows the use of a wider range of equipment for heating the coolant.
With three spirals. It is assumed that a single heating complex includes a solid fuel boiler and two alternative sources, for example, solar and geothermal batteries. Maximum solid fuel savings. The boiler can be used as an additional (backup) boiler.
With additional tank. There are systems in which another circuit with a heat exchanger is turned on so that hot water appears in the tap immediately after starting the boiler, without waiting for the optimal heating mode to reach. However, in such systems, the supply of hot water is limited; after its expiration, further heating will proceed more slowly than through the coil.
Application of different types of systems
Heating systems, which include only solid fuel boilers, are used, as a rule, for heating private houses. The need to build a coal (wood) warehouse is inconvenient, but this configuration is sufficient for heating in the most severe frosts.
Heating systems that include solar collectors can save up to 30% on energy costs, but cannot replace a solid fuel boiler. Therefore, it is used as an auxiliary one, especially since the sun does not always shine. But to always have water at home, the power is enough (replaces 50-90%).
Combined configurations involve the use of gas and solid fuel boilers. This is convenient when starting the system in a frozen building. If the gas unit is connected to a hot water supply system, then there will always be water. In this case, there is no need to add firewood; just press the start button of the gas burner. and the main task of heating the water will be taken on by a solid fuel boiler.
Manufacturing recommendations
From the previous section it follows that you won’t be able to get away with an ordinary 200 liter barrel, unless its capacity is at least half a cube.
This is enough for a house with an area of 30 m2, and even then not for long. In order not to waste time and effort, it is better to make a rectangular container from the point of view of placement in the boiler room. The dimensions are arbitrary, the main thing is that their product is equal to the calculated volume. The ideal option is a stainless steel tank, but ordinary metal will also work.
At the top and bottom, a self-made heat accumulator must be equipped with pipes for connection to the system. To prevent the steel walls from bulging outward under water pressure, the structure must be strengthened with ribs or jumpers.
The battery tank must be properly insulated, including from below. For this purpose, foam plastic with a density of 15-25 kg/m3 or mineral wool in slabs with a density of at least 105 kg/m3 are suitable. The optimal thickness of the thermal insulation layer is 100 mm. The resulting device, filled with coolant, will have a decent weight, so a foundation will be required for its installation.
Advice. If you need a container for a gravity heating system, you should install it yourself on a metal stand, not forgetting to insulate the lower part. The goal is to raise the tank above the level of the batteries.
How to assemble a heat accumulator with your own hands
It is not necessary to buy a heat accumulator. You can do it yourself, saving almost twice, and the efficiency will be no worse than that of a purchased one. The simplest cylindrical heat accumulator is similar in operating principle to a thermos. Its walls retain the heat of water for a long time, so it is perfect for heating rooms. Before you start assembling the water heat accumulator you will need:
- A tank with a minimum volume of 200 liters, a tank smaller does not make sense. Select the volume based on the area to be heated.
- Material to thermally insulate the structure, for example, take mineral wool.
- Foil film.
- Adhesive tape.
- Copper tube coil for its manufacture.
- For formwork, you can use a concrete slab or boards; you will also need concrete for pouring.
An iron barrel is perfect for storage.
Once you have stocked up with all the necessary materials, you can begin to work.
Diagram of the heat accumulator SWaG 800
Exploitation
Hot water storage tanks are a high-risk design. Personnel working with them must know the basic operating rules and possible causes and consequences of accidents.
First of all, BAGVs are placed in an illuminated area that complies with fire safety standards. The area with tanks must have free access for construction, installation and repair work if necessary.
To prevent spreading over the territory, the tank must be equipped with a fence and drainage of waste into the sewerage system. Installation of BAGV near residential buildings, districts, and work offices is prohibited. The distance to residential areas must be at least 30 m.
When filling the storage tank with water, workers must monitor the condition of the structure and check it for leaks and wet spots on the outside. If such leaks are detected, filling should be stopped and the water drained completely. The remote level gauge of the storage tank has a red line, which is responsible for the maximum permitted water filling level. Exceeding this line can lead to emergency situations.
A working hot water storage tank must not be exposed to shock or repair work. A full or partial inspection of the device must be carried out after disconnecting, emptying and cleaning the BAGV. If there are any malfunctions, the operation of storage tanks is prohibited.
To prevent emergency situations, it is necessary to organize supervision of the operation of storage tanks, which includes:
- daily check of alarm circuits, power supply of pumping units, electrical wires;
- daily external inspection;
- annual internal inspection;
- full technical inspection (at least once every 15 years or after an accident or violation).
How to determine damage to the accumulator
As in a water supply system, a hydraulic accumulator has its own service life. So, for built-in tanks it is determined by the service life of the heating boiler, and a free-standing tank made of ferrous metal usually withstands a 5-6 year period of operation. When filling the system volume with antifreeze, you must carefully study the manufacturer's recommendations to make sure that the material will not react with the antifreeze chemical.
The first sign that the accumulator has failed is a sharp drop in pressure in the system. The fact is that the bottleneck of the accumulator is the membrane. Despite its elasticity and strength, during operation, particles of debris from the internal volume of batteries, pipes, shut-off valves enter its cavity, and insoluble sediments from the water itself often accumulate here. And then, during operation of the membrane, these particles play the role of an abrasive, gradually rubbing the rubber. When the membrane walls break, air from the air chamber penetrates into the heating system and is removed through the air vent, and the freed volume is filled with coolant. In this case, no visible coolant leaks are detected in the room.
If you do not pay attention to the sharp decrease in pressure in the system and simply restore the required fluid pressure, then despite the breakdown of the hydraulic accumulator, the system will continue to operate. But at the first emergency situation, the scale of the accident will be much larger
To systematically monitor the condition of the membrane, it is recommended to periodically check the pressure in the accumulator using a conventional pressure gauge from a road car kit.
To be sure that the equipment is working properly, it is recommended to press the nipple and release a little air 1-2 times every 6 months. A rapid whistling stream of air will indicate that the tank is leaking. But if you hear a faint hissing sound or water drips out instead of air, then you need to sound the alarm - the membrane will most likely be damaged and the device will need to be repaired.
The second common problem when operating hydraulic accumulators is the loss of housing tightness. Unlike water supply system receivers, this problem is relatively rare, but it cannot be discounted. Such damage occurs as a result of improper installation or as a result of improper repair of the device. The tank body is usually made of steel or iron sheet by stamping. The outer part of the tank is painted to protect it from corrosion, but the inside is usually left without an additional protective layer. During operation, pockets of corrosion form on the inner wall of the air compartment, which causes a hole to form over time, and the air simply escapes. It is easy to determine such a malfunction - you need to start deflating the air with a few presses; if you cannot hear a characteristic whistle when pressing, then you need to look for damage to the housing.
Another common type of failure is a spool valve malfunction. This usually happens when setting up the device, when there is a need to constantly pump it up with a pump and check the pressure with a pressure gauge. If the spool is damaged, the pressure usually drops gradually, and on the boiler pressure gauge you can notice that the pressure does not decrease immediately, but over time, in small portions. It should be noted that it decreases, and does not jump in a certain amplitude. Directly on the tank, you can check whether the valve is working or not by applying a small amount of soap solution to it. If the solution does not change its state, then the problem is not with the valve. And if the escaping air blows up soap bubbles, even small ones, then the valve core needs to be replaced. The easiest way to buy it is at an auto store or sporting goods store; the core in the valve is identical to that used in car and bicycle tires.
Application efficiency for electric boiler
Making a small digression, let's talk about the fact that a storage tank for a heating system is used not only in tandem with solid fuel boilers, although this is generally the case. The buffer tank can also be used in heating systems with an electric heater. But this is only acceptable if it is possible to use night electricity rates. As you know, the cost of a kilowatt of energy at night is significantly lower than during the day.
In order to save money, the boiler only works at night; it does this continuously, thereby heating the home and warming up the water in the buffer tank. During the night, the coolant in the heat exchanger accumulates a sufficient amount of heat and releases it into the circuit during the day. The boiler is not working at this time. During the day, the temperature outside the window is higher than at night, so the coolant does not cool down as much.
Advantages of using thermal accumulators
The installation of a heat accumulator is aimed at achieving the following goals:
- The boiler can be heated at any convenient time;
- The laying of each subsequent batch of fuel can be postponed for some period of time;
- The amount of fuel spent on heating the building will be reduced.
A buffer tank (heat accumulator) built into the boiler allows you to maintain a comfortable microclimate in the house and at the same time reduce fuel consumption for heating. If such a system is supplemented with sensors and thermostats, the savings will be maximum - when a certain temperature is reached, the heat supply to the heating circuit simply stops.
Calculation of container volume
How to calculate the volume of a heat accumulator
The main parameter when purchasing a buffer tank for a solid fuel boiler, as well as for making the device yourself, is the capacity of the heat accumulator, which directly depends on the power of the heating boiler.
There are various calculation methods based on determining the ability of a solid fuel boiler to heat the required volume of working fluid to a temperature of at least 40°C during the combustion of one full load of fuel (approximately 2-3.5 hours).
Compliance with this condition allows you to obtain maximum boiler efficiency with maximum fuel economy.
The simplest method of calculation provides that one kilowatt of boiler power must correspond to at least 25 liters of the volume of the buffer tank connected to it.
Thus, with a boiler power of 15 kW, the capacity of the storage tank should be at least: 15 * 25 = 375 liters. In this case, it is better to choose a capacity with a reserve, in this case – 400-500 liters.
There is also this version: the larger the tank capacity, the more efficiently the heating system will work and the more fuel you will save. However, this version imposes limitations: finding free space in the house for installing a large heat accumulator, as well as the technical capabilities of the heating boiler itself.
Coolant capacity volumes have an upper limit: no more than 50 liters per 1 kW. Thus, the maximum volume of the storage tank with a boiler power of 15 kW should not exceed: 15 * 50 = 750 liters.
Obviously, using a heat exchanger with a volume of 1000 liters or more for a 10 kW boiler will cause additional fuel consumption to heat such a volume of working fluid to the required temperature.
This will lead to a significant increase in the inertia of the entire heating system.
To provide your home boiler room with environmentally friendly fuel, we recommend learning how to make fuel briquettes with your own hands.
Solid fuel boilers are more difficult to switch to automatic operation. Smart electrical devices such as a GSM module help make the heating system more or less self-regulating. Go to description.
Connection diagram for hydraulic accumulator
Depending on the assigned functions, the connection diagram of the hydraulic accumulator to the water supply system may be different. The most popular connection diagrams for hydraulic accumulators are given below.
Booster pumping station wiring diagram
Such pumping stations are installed where there is high water consumption. As a rule, one of the pumps at such stations operates constantly.
At the booster pumping station, the hydraulic accumulator serves to reduce pressure surges when additional pumps are turned on and to compensate for small water withdrawals.
This scheme is also widely used when the water supply system frequently interrupts the supply of electricity to booster pumps, and the presence of water is vital. Then the water supply in the hydraulic accumulator saves the situation, playing the role of a backup source for this period.
The larger and more powerful the pumping station, and the greater the pressure it must maintain, the larger the volume of the hydraulic accumulator, which acts as a damper, must be. The buffer capacity of the hydraulic tank also depends on the volume of the required water supply, and on the difference in pressure when the pump is turned on and off.
Scheme for a submersible pump
For long-term and uninterrupted operation, the submersible pump must make from 5 to 20 starts per hour, which is indicated in its technical characteristics.
When the pressure in the water supply system drops to a minimum value, the pressure switch is automatically turned on, and when the maximum value is turned off, it is turned off. Even the most minimal water flow, especially in small water supply systems, can reduce the pressure to a minimum, which will instantly give a command to turn on the pump, because the water leakage is compensated by the pump instantly, and after a few seconds, when the water supply is replenished, the relay will turn off the pump. Thus, with minimal water consumption, the pump will run almost idle. This mode of operation adversely affects the operation of the pump and can quickly damage it. The situation can be corrected by a hydraulic accumulator, which always has the required supply of water and successfully compensates for its insignificant consumption, and also protects the pump from frequent activation.
In addition, a hydraulic accumulator connected to the circuit smoothes out a sharp increase in pressure in the system when the submersible pump is turned on.
The volume of the hydraulic tank is selected depending on the frequency of activation and power of the pump, water flow per hour and the height of its installation.
Connecting a hydraulic accumulator to a water heater
For a storage water heater in the connection diagram, the hydraulic accumulator plays the role of an expansion tank. When heated, water expands, increasing the volume in the water supply system, and since it does not have the ability to compress, the slightest increase in volume in a confined space increases the pressure and can lead to destruction of the water heater elements. The hydraulic tank will also come to the rescue here. Its volume will directly depend and increase from an increase in the volume of water in the water heater, an increase in the temperature of the heated water and an increase in the maximum permissible pressure in the water supply system.
Connecting the hydraulic accumulator to the pumping station
The hydraulic accumulator is connected in front of the booster pump along the water flow. It is needed to protect against a sharp decrease in pressure in the water supply network when the pump is turned on.
The capacity of the hydraulic accumulator for the pumping station will be greater, the more water is used in the water supply system and the smaller the difference between the upper and lower pressure scale in the water supply in front of the pump.
Coolant reserve consumption rate
It is impossible to say exactly how long it will take for the heating system to consume the coolant supply from the buffer tank.
This setting depends on the following factors:
- internal volume of the heat accumulator;
- time of year and outside air temperature;
- degree of heat loss;
- parameters on temperature sensors;
- dimensions of the heated house.
When the heating system is in a passive state, the coolant reserves in the reserve tank may last for several hours or days.
Selection of housing material
If the connection diagram provides for several circuits: heating, heated floors, solar collector, etc., then the ratio of diameter and height should be at least 1: 3.
Advantages and disadvantages of a circuit with a heat accumulator:
- Where the area is not gasified, the use of a battery tank in combination with a solid fuel boiler provides significant fuel savings - up to 30%. The heat accumulator for heating smooths out temperature fluctuations and reduces the overall system maintenance time.
- If the standard “solid fuel boiler - buffer tank” scheme is supplemented with a backup line with a gas boiler, then one of the main drawbacks in its operation is eliminated. The fact is that the tank will begin distributing hot water only after it has heated itself, and for such a large volume it will take at least 5-6 hours. In the same scheme, a gas boiler can operate independently from the main line, heating water for heating and DHW. When hot water starts flowing from the tank, the gas boiler will automatically turn off.
- Any scheme with a heat accumulator has one big drawback - the high cost of the battery tank and automation. The calculation is simple: larger tank means higher price. You can make a circuit without expensive controllers, but you will still have to spend a lot on a tank and mixing and pumping units. Of course, over time the equipment will pay for itself.
- Thermal storage is the optimal solution for owners of solar collectors and heat pumps. The consumer “drains” into the buffer tank all the irregularly received heat from these sources plus the excess heat of the boiler, receiving in return hot water for his needs.
When is a heat accumulator needed?
This simple element of the heating system in the form of an insulated water tank is recommended to be installed in the following cases:
- for the most efficient operation of a solid fuel boiler;
- together with an electric heat generator operating at a reduced night tariff.
For reference. There are also water heat accumulators for greenhouses, used to store solar energy received during the day.
The operation of solid fuel boilers has its own characteristics. The heat generator operates with high efficiency only when operating at maximum modes; if you cut off the air to it to lower the temperature in the furnace, then the operating efficiency also decreases. The homeowner also has a lot of worries about the frequency of heating, the firewood has burned out - he needs to load new ones, which is extremely inconvenient to do in the middle of the night. The solution is simple: you need a storage tank that accumulates previously generated heat for use after the firewood burns out in the firebox.
The opposite situation occurs with an electric boiler connected to the network through a multi-tariff meter. To save money, you need to get maximum heat at night, when the tariff is low, and not use electricity during the day. And here the heat accumulator in the heating system will allow you to organize an optimal operating schedule for the heat source, supplying hot water to the system while the heat generator is inactive.
Important. To work together with a heat accumulator, the boiler must have at least one and a half reserve thermal power. Otherwise, it will not be able to simultaneously heat the water in the heating system and the storage tank
Otherwise, it will not be able to simultaneously heat the water in the heating system and the storage tank.
A similar situation with excess heat occurs in greenhouses; they are even ventilated during the daytime. In order to accumulate solar energy for use at night, you can use the simplest heat accumulator Lezhebok to heat the ground. This is a black polymer sleeve filled with water and laid directly over the bed; it prevents the soil from cooling at night. To absorb more heat, barrels of water painted black are placed inside the greenhouse.