Wester WRV-8 – membrane tank for heating systems.
An expansion membrane tank is an element of a closed heating system designed to compensate for the thermal expansion of the coolant and maintain the required pressure.
Note! In addition to being used in heating systems, membrane tanks are also used in water supply systems. They “soften” water hammer that occurs when pumping stations are turned on/off, and also maintain constant pressure in the system.
Expansion tank installation process
Now let's figure out how to install an expansion tank in a heating system.
There is an important rule for connecting the device: the tank must be connected to the heating system main using a shut-off ball valve with an American connection. This installation principle makes it possible, if necessary, to shut off the flow of water in the system at any time, remove the faulty membrane tank and install a new one
Otherwise, you would have to wait for the coolant to cool down and dismantle part of the piping. Ideally, a tee is installed on the supply line, as well as a second tap - in this case, before removing the expansion tank, it can be emptied into a substitute container.
How to correctly orient a membrane expansion tank in space? The tank is installed with the air chamber up or down, and the container is placed “on its side”. From the point of view of operational characteristics, this does not matter much, since in any case the device will perform its functions properly.
However, it is worth considering this point: if the air compartment is located at the bottom, then the coolant is supplied from above, and the bubbles of air dissolved in it will rise into the pipeline and be removed using an air valve. Otherwise, an air bubble will form in the “water” compartment of the membrane tank over time.
In turn, when the tank is positioned with the air chamber upward, its service life is extended. Over time, from constant contact with hot water, the polymer membrane loses its tightness and cracks appear in it. If the air chamber is located at the bottom, then water will immediately begin to seep into the air compartment, which will quickly damage the expansion tank, while air will penetrate into the coolant. When the air chamber is located on top, the diffusion of water through cracks occurs many times slower, and the device can operate much longer.
- If you install a pressure gauge next to the expansion tank and the valve, thanks to which the heating system is fed from the water supply, it will allow you to control the pressure in the system in order to bleed off excess in time if the safety valve spool is stuck and does not operate automatically.
- Frequently repeated release of pressure by the valve indicates that the capacity of the expansion tank is selected incorrectly. Instead of changing it to a larger tank, just connect a second tank in parallel.
- Replacing the existing expansion tank with a larger one or connecting a second one will also be required if it is decided to replace the water in the system with antifreeze. This is due to the fact that non-freezing coolants have a higher coefficient of thermal expansion.
Before connecting the tank and filling it with coolant, you need to check the pressure level in the air chamber of the tank - it must correspond to the pressure in the heating system. For this purpose, you should remove or unscrew the plastic plug that covers the spool valve (similar to those installed in car cameras). Using a pressure gauge, it is necessary to measure the pressure and adjust it to the indicators of the heating system. To do this, air is pumped up by a pump or, vice versa, it is bleed by pressing the spool rod.
Note! The tank should be adjusted so that the pressure in its air chamber is 0.2 bar less than the design pressure in the system filled with coolant. If the pear-shaped membrane is not pressed on the water injection side, the coolant, compressing during the cooling process, will be able to draw in air through automatic air vents
After completing the settings, open the tap and fill the entire system with coolant. Then the boiler unit starts up.
The adjustment step is not required if the factory pressure in the air compartment of the expansion tank corresponds to the required parameters. Manufacturers of some brands of equipment indicate the pressure level in the tank on the packaging, which makes it possible to select the optimal option when purchasing.
Conclusion
You can correctly install the expansion tank and prepare the customized membrane tank for operation yourself, without the help of a specialist. The experience gained may be useful in the future if you need to quickly determine the source of problems associated with a decrease or surge in pressure in the system, due to which the burner flame goes out. In such cases, it is recommended that you first carefully inspect the system for coolant leaks and measure the pressure in the air chamber of the membrane reservoir.
Types of tanks
Compensation tanks for heating networks differ in shape, design, and internal size.
Open type equipment
They are a rectangular or cylindrical container with an open top, where you can always add water if necessary. Most often, such tanks are made of sheet steel and are thermally insulated. They are installed at the highest level of heating networks with natural circulation.
The design includes the following elements:
- containers of various sizes;
- inlet pipe for supplying coolant;
- outlet pipe for water return;
- control pipe that prevents overflow.
The main disadvantages of open expansion tanks are their large size, tendency to corrosion, the need to add water and constant monitoring.
Closed type device and its functions
Suitable for heating networks where the movement of coolant is provided by pumps. Externally it looks like a closed oval or spherical container with a pipe for connecting to the heating network and a nipple on the reverse side. A membrane is installed inside the tank, dividing the cavity into two chambers: one is filled with gas (air or nitrogen), the other is intended for liquid.
If the circuit is not heated, the tank is empty; when the temperature rises, the excess coolant is directed into the tank, increasing pressure in another chamber. When this parameter reaches the limit level, the valve is activated and excess gas is released. As the liquid cools, it contracts and is pushed back into the circuit. All processes occur automatically.
Photo 1. Closed expansion tank, volume 50 l, steel, without replaceable membrane, .
Closed devices are available in two designs.
With flanged replaceable diaphragm
The main features of expansion devices of this type:
- Water does not come into contact with the walls of the device, remaining inside the membrane cavity - eliminating the risk of corrosion and contamination of the coolant.
- Possibility of replacing the elastic chamber through a bolted flange.
- They have higher maximum pressure values than models with a non-replaceable diaphragm.
- Horizontal and vertical design - convenient to place in boiler rooms of different configurations.
With stationary membrane
The internal space is divided in two by an elastic butyl diaphragm, which is rigidly attached to the walls of the chamber.
Initially, the entire cavity is occupied by gas, so the membrane is pressed against the walls. During heating, the liquid enters the tank, the gas is compressed, and the pressure increases.
80ffce45030ada9c3069748facadb954.jpe
Water comes into direct contact with the inner surface, which creates a risk of corrosion. To prevent the destruction of the metal, a moisture-resistant coating is applied to the inside of the tank walls.
The main advantages of devices with a non-replaceable membrane are their affordable price and variety of design options.
Attention! The main disadvantage is that if the diaphragm fails, the tank will have to be replaced with a new one. Closed expansion equipment is allowed to be installed close to the heating boiler - on the side of the pump inlet pipe
Closed expansion equipment is allowed to be installed close to the heating boiler - on the side of the pump inlet pipe.
How and where to install the expansion tank
So, we are going to design and assemble a heating system with our own hands. If it also starts working, our joy will know no bounds. Are there instructions for installing the expansion tank?
Open system
In this case, the answer will be prompted by simple common sense.
An open heating system is, in essence, one large vessel of complex shape with specific convection currents in it.
The installation of a boiler and heating devices in it, as well as the installation of pipelines, must ensure two things:
- Rapid rise of water heated by the boiler to the top point of the heating system and its drainage through the heating devices by gravity;
- Unhindered movement of air bubbles to where they will rush in any vessel with any liquid. Up.
- Installation of a heating expansion tank in an open system is always carried out at its highest point. Most often - at the top of the accelerating manifold of a single-pipe system. In the case of top-fill houses (although you hardly have to design them) - at the top filling point in the attic.
- The tank itself for an open system does not need shut-off valves, a rubber membrane, or even a lid (except to protect it from debris). This is a simple water tank open at the top, into which you can always add a bucket of water to replace the evaporated water. The price of such a product is equal to the cost of several welding electrodes and a square meter of steel sheet 3-4 millimeters thick.
This is what an expansion tank for an open heating system looks like. If desired, a water tap from the water supply can be brought into the hatch in it. But much more often, as the water evaporates, it is topped up with an ordinary bucket.
Closed system
Here both the choice of tank and its installation will have to be taken quite seriously.
Let's collect and systematize the basic information available on thematic resources.
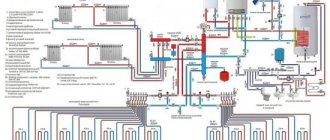
Installation of the expansion tank of the heating system is optimal in the place where the water flow is closest to laminar, where there is a minimum of turbulence in the heating system. The most obvious solution is to place it in the direct filling area in front of the circulation pump. In this case, the height relative to the floor or boiler does not matter: the purpose of the tank is to compensate for thermal expansion and dampen water hammer, and we can bleed the air through the air valves.
Typical tank installation diagram. Its location in a single-pipe system will be the same - in front of the pump along the flow of water.
- Factory equipped tanks are sometimes equipped with a safety valve that relieves excess pressure. However, it is better to play it safe and make sure that your product has it. If not, buy one and install it next to the tank.
- Electric and gas boilers with electronic thermostats are often supplied with a built-in circulation pump and heating expansion tank. Before you go shopping, make sure you need them.
- The fundamental difference between membrane expansion tanks and those used in open systems is their orientation in space. Ideally, the coolant should enter the tank from above. This subtlety of installation is designed to completely remove air from the compartment of the tank that is intended for liquid.
- The minimum volume of the expansion tank for a water heating system is taken approximately equal to 1/10 of the volume of coolant in the system. More is acceptable. Less is dangerous. The volume of water in the heating system can be roughly calculated based on the thermal power of the boiler: as a rule, 15 liters of coolant per kilowatt is taken.
- A pressure gauge mounted next to the expansion tank and the feed valve (connecting the heating to the water supply) can provide you with an invaluable service. The situation with a stuck safety valve spool, alas, is not so rare.
- If the valve releases pressure too often, this is a clear sign that you have miscalculated the volume of the expansion tank. There is no need to change it at all. It is enough to purchase another one and connect it in parallel.
- Water has a relatively low coefficient of thermal expansion. If you switch from it to a non-freezing coolant (for example, ethylene glycol), you will again need to increase the volume of the expansion tank or install an additional one.
The expansion tank in the photo is installed according to all the rules: the coolant is supplied from above, the tank is equipped with a pressure gauge and a safety valve.
Design and principle of operation
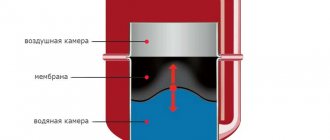
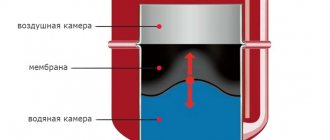
A membrane tank is a hermetically sealed metal container divided into two compartments (chambers) by an elastic membrane. One such chamber is a pneumatic chamber, which contains gas or air under pressure. The coolant enters the second chamber, the hydraulic chamber.
The device operates as follows:
- the air pressure, which is in a state of equilibrium, in the pneumatic chamber compensates for the fluid pressure in the heating system, the volume of the coolant and the hydraulic chamber is reduced to a minimum;
- when the fluid pressure increases in the system, including during heating, the pressure also increases in the hydraulic chamber, where excess coolant flows;
- due to the elasticity of the membrane, the volume of the pneumatic chamber decreases, which is accompanied by an increase in gas pressure;
- when the pressure in the pneumatic chamber increases, the increase in pressure in the hydraulic chamber is compensated, and the system returns to a state of equilibrium.
When the coolant pressure in the system decreases, the opposite occurs. Gas (air), compressed in the pneumatic chamber, expands and displaces liquid from the hydraulic chamber into the system until the pressure difference is restored. The design eliminates the possibility of contact between the coolant and air, reducing the likelihood of rust not only in the tank, but also in other parts of the heating system - piping, boiler. Sealed expansion tanks are equipped with safety valves that allow you to limit the maximum pressure in the heating system to an acceptable level. This characterizes the tank as a protection device for the heating system.
Let's compare closed and open heating systems
The operation of an open heating system is based on the laws of thermodynamics, due to which the coolant moves. From an area of high pressure and corresponding temperature at the boiler outlet, water moves through pipes to an area of lower pressure, and its temperature decreases. The cooled coolant is sent back to the boiler and the process is repeated. Thus, natural circulation of liquid occurs, according to the laws of physics.
Since when water is heated, its volume increases, an expansion tank is provided in the design of an open heating system. For efficient movement of open-type coolant, the expansion tank is installed at the highest point of the system, and the heating boiler at the lowest. Installing an expansion tank in the attic seems to be the best option. Its device is not complicated.
Over time, water evaporates, so its level must be replenished in a timely manner. During breaks in the use of heating and at negative ambient temperatures, the water must be drained, otherwise it will freeze in the pipes and burst them. An open heating system has the following advantages:
- independence from electrical energy sources;
- no noise;
- ease of maintenance;
- quick start and stop.
You can select radiators for any type of heating system based on the recommendations of the article “Which radiators are best to choose for heating a private home: photos, dimensions and technical characteristics.”
In a closed heating system, water does not evaporate because it is sealed. The movement of the coolant is carried out using a pressure or circulation pump, which can be found in the article “Which circulation pump to choose for a water heating system for a private house, technical characteristics.” At the same time, for effective operation, an expansion tank made of durable metal is also required. A closed heating system consists of a heating boiler, a circulation pump, a pipeline network, radiators and an expansion tank. A closed heating system has the following advantages:
- no need to constantly monitor the coolant level;
- possibility of using antifreeze;
- internal pressure adjustment;
- possibility of connecting additional devices.
Closed heating system
With proper installation of heating equipment, both options will work perfectly. The choice between them is determined by operating conditions and placement features. The differences between the two systems are as follows:
In an open heating system, the expansion tank is located at the highest point. In a closed heating system it can be located almost anywhere. The likelihood of air locks forming in a closed heating system is much lower. This is due to increased internal pressure and lack of direct contact with the atmosphere. To operate an open heating system, large diameter pipes are required. Installation work is complicated by the need to take into account hydraulic rules when distributing flows, making turns, slopes, and so on. Small diameter pipes used in a closed heating system reduce its cost
Here it is important to correctly install the circulation pump so that during its operation it creates as little noise as possible.
Types of membrane expanders
To compensate for the volume of coolant in the network at the time of temperature changes, two types of containers are used: open and closed. The first type is very popular among consumers, but has a number of disadvantages:
- installation requires significant costs, since such devices are installed in the upper zone of the system in order to set the required atmospheric parameters;
- it is necessary to constantly monitor the level of the liquid medium;
- there is a possibility of rust due to prolonged contact of water with air.
The second type of expansion tanks is devoid of such disadvantages. Their design provides for the presence of a special membrane (balloon or diaphragm).
SF-mix Clack up to 0.8 m3/h
SF-mix Runxin up to 0.8 m3/h
SF-mix manual up to 0.8 m3/h
general information
What is an expansion tank and what is it for?
Its very name gives a hint: for expansion. With a fixed mass of coolant in the heating circuit and pipes, the elasticity of which tends to zero, with a change in coolant temperature the pressure in the system will inevitably change. Thermal expansion, remember? Water or any other coolant expands when heated.
As soon as the force exceeds the tensile strength of the pipe or radiator... Boom!
The reason for a possible accident is that water, changing its volume when heated, remains practically incompressible. Hence the concept of water hammer: elastic interactions in a liquid medium, to put it simply, are absent.
The obvious solution is to create a reservoir in the system with an easily compressible substance - air. As the volume of water increases in the presence of such a reservoir, the pressure will increase slightly.
Useful: to prevent oxygen from the air tank from contributing to pipe corrosion by dissolving in water, in tanks for closed systems it is separated from the water by a rubber membrane.
This is what this simple device looks like in cross-section.
However, we have described only one of the functions of the expansion tank.
In addition to closed heating systems of private houses with fixed volumes of both the circuit and the coolant in it, an expansion tank can be found:
- In open systems in contact with atmospheric air;
- In central heating systems with top filling. There, the expansion tank is located in the attic and connects directly to the supply pipe of the house heating system.
In both described cases, installation of a heating expansion tank is necessary in order to get rid of air pockets. The difference between the two threads in the case of central heating is only about two meters. In heating systems of private houses with natural circulation - even less.
Clarification: the author can almost hear the exclamations of more or less knowledgeable people who, at the height of the heating season, saw a 10 times greater difference in the elevator unit. Typically 6 kgf/cm2 on the supply pipeline and 4 on the return pipeline (1 atmosphere of excess pressure corresponds to a water column of 10 meters). Do not confuse warm with soft: it is not supply water that enters the heating system, but a mixture. The elevator draws return water into a repeated cycle through the heating system, injecting a stream of hotter water with higher pressure into it through a nozzle from the supply pipeline. As a result, as stated, the difference between the mixture and the return does not exceed 2 meters, or 0.2 kgf/cm2.
With such a difference, the water pressure will not be able to squeeze the air plug out of the upper part of the heating system. Hence the simple solution: put some kind of container to collect air where it will accumulate, and bleed it out when the system starts. In the case of an open system, of course, no active actions are needed.
All air in the system will be forced up and into the expansion tank. In an open system, it will immediately reunite with the atmosphere. When closed, it will wait until the owner of the house opens the air valve.
What does the system consist of and how does it work?
In order for heat to flow from the boiler room to the heating devices, a mediator is used in the water system - liquid. This type of coolant moves through a pipeline and heats rooms in the house, all of which can have different areas. This factor makes such a heating system popular.
The coolant can move naturally; circulation is based on the principles of thermodynamics. Due to the different densities of cold and heated water and the slope of the pipeline, water moves through the system.
One of the important elements of the heating system is the open expansion tank; excess heated liquid enters here. It is this element that stabilizes the coolant pressure. The main condition is that the tank should be located at the highest point of the heating system.
Open heating operates according to the following scheme:
- The boiler heats water and supplies it to heating devices in every room of the house.
- On the way back, excess liquid goes into an open-type expansion tank, its temperature drops, and the water returns to the boiler.
Single-pipe heating systems involve the use of one line for supply and return. Two-pipe systems have independent supply and return pipes. When deciding to install a dependent heating system yourself, it is better to choose a single-pipe scheme; it is simpler, more accessible and has a basic design.
Single-pipe heat supply consists of the following elements:
- Heating boiler.
- Batteries or radiators.
- Expansion tank.
- Pipes.
A simplified scheme involves using pipes with a cross-section of 80-100 mm instead of radiators, but it should be borne in mind that such a system is less efficient in operation.
Benefits of using closed appliances
- Small dimensions of the tank, easy installation and maintenance of the tank.
- Tightness (evaporation is excluded, replacement of water with antifreeze is acceptable).
- There is no danger of underfilling (overfilling) or freezing.
- Accelerated heating, automatic regulation.
- Regulation of pressure surges.
- Slight temperature fluctuations in the boiler connection areas.
- No heat losses.
- Adding or decreasing room temperature.
- Installation in a place free for access.
- Narrow pipe diameter – cheaper cost.
The main advantage is versatility: it is possible to include a boiler, convector heater, heated floor, and radiators of different configurations into the system.
Volume calculation
There is a very simple method for determining the volume of an expansion tank for heating: 10% of the volume of coolant in the system is calculated. You should have calculated it when developing the project. If this data is not available, you can determine the volume experimentally - drain the coolant, and then fill in a new one, measuring it at the same time (put it through a meter). The second way is to calculate. Determine the volume of pipes in the system, add the volume of radiators. This will be the volume of the heating system. From this figure we find 10%.
Shape may vary
The second way to determine the volume of an expansion tank for heating is to calculate it using the formula. Here you will also need the system volume (indicated by the letter C), but other data will also be needed:
- the maximum pressure Pmax at which the system can operate (usually the maximum boiler pressure is taken);
- initial pressure Pmin - from which the system begins operation (this is the pressure in the expansion tank, indicated in the passport);
- coolant expansion coefficient E (for water 0.04 or 0.05, for antifreeze it is indicated on the label, but usually in the range of 0.1-0.13);
Having all these values, we calculate the exact volume of the expansion tank for the heating system using the formula:
Formula for calculating the volume of an expansion tank for heating
The calculations are not very complicated, but is it worth bothering with them? If the system is open, the answer is clear - no. The cost of the container does not depend very much on the volume, plus you can make it yourself.
Expansion tanks for closed type heating are worth counting. Their price depends greatly on volume. But, in this case, it is better to take it with a reserve, since insufficient volume leads to rapid wear of the system or even its failure.
If the boiler has an expansion tank, but its capacity is not enough for your system, install a second one. In total, they should give the required volume (the installation is no different).
What will result from insufficient expansion tank volume?
When heated, the coolant expands, its excess ends up in the expansion tank for heating. If all the excess does not fit, it is released through the emergency pressure relief valve. That is, the coolant goes into the sewer.
Working principle in graphical representation
Then, when the temperature drops, the volume of coolant decreases. But since there is already less of it in the system than there was, the pressure in the system drops. If the lack of volume is insignificant, such a decrease may not be critical, but if it is too small, the boiler may not work. This equipment has a lower pressure limit at which it is operational. When the lower limit is reached, the equipment is locked. If you are at home at this time, you can correct the situation by adding coolant. If you are not there, the system may unfreeze. By the way, working at the limit also does not lead to anything good - the equipment quickly breaks down. Therefore, it is better to play it safe and take a slightly larger volume.
How to make it yourself from plastic containers or stainless steel
You can make an expansion tank yourself. A tank of 10-12 liters is suitable for this (depending on the exact calculations of the coolant volume of the general system).
If you have a ready-made base, for example, a plastic container, you should check its capacity (with regular 3-liter jars), and then attach the missing elements.
Usually the tank is made of stainless steel sheet 2-4 mm thick.
Tools:
- welding machine, electrodes for welding;
- grinder with corresponding circles;
- sheet metal (stainless steel);
- pipes;
- various bolts, a set of fittings;
- rubber gaskets;
- brush, gloves, protective mask;
- Oil paint;
- thermal insulation materials;
- metal file;
- roulette;
- tank diagram with all dimensions.
Marking a sheet of metal
First of all, you need to make markings on the sheet metal. To do this, you can use a cutting card with paper parts, which allows you to use metal with the least waste. When joining two parts on a sheet, you must take into account the thickness of the grinder circle, which can “eat” several millimeters.
Important! All work should be carried out carefully, followed by cleaning the edges
Cutting blanks
The tank body consists of five or six rectangles (depending on the presence of a lid). If desired, you can divide the upper part of the lid into two parts in a way that is convenient, welding one part to the base and attaching the second to the curtains.
Welding a homemade device
The cut pieces must be placed at right angles and welded. The method of fastening can be different - gas is perfect for 2 mm steel sheets, and electric welding works well with 3-4 mm sheets.
It is necessary to make a hole in the bottom of the housing and weld a pipe there through which the coolant will enter the tank. The pipe itself, accordingly, is connected to the circuit of the general heating system.
Insulation
The open heating structure is characterized by the installation of an expansion tank at the highest point of the system. Typically, this is an unheated attic, where in winter the temperature is often sub-zero. Under such conditions, the water in the tank may freeze, damaging the entire system. To avoid this problem, the tank should be insulated with special materials, for example, basalt wool.
This thermal insulation material is resistant to high temperatures, which is a necessary condition, since the water in the tank boils at elevated degrees.
Adding oil
In addition to the main pipe connecting the tank to the system, additional elements are welded into the design of a homemade tank:
- to recharge the system or add coolant (water, oil);
- for emergency drainage of excess coolant into the sewer system.
Important! The drain pipe must be located above the maximum filling level of the tank to avoid liquid overflowing from the top. Through the hole in the lid, water from the tank evaporates and air can enter the system
This leads to overheating of the pipes and poor coolant circulation. To solve this problem, professionals recommend pouring a little oil into the tank. It will cover the surface of the coolant with a thin film, thus creating a protective layer against air penetration
Through the hole in the lid, water from the tank evaporates and air can enter the system. This leads to overheating of the pipes and poor coolant circulation. To solve this problem, professionals recommend pouring a little oil into the tank. It will cover the surface of the coolant with a thin film, thus creating a protective layer against air penetration.
Setting the optimal pressure in the tank
Before connecting the expansion tank and filling it with coolant, it is necessary to set the optimal pressure in its air chamber corresponding to this parameter in the heating network. To perform this procedure, a plastic cover is removed from the air compartment, under which there is a nipple, the same as in car tires. The pressure measured by the pressure gauge is adjusted to the desired value by pumping it up using a pump or by bleeding it by pressing the nipple rod.
The optimal pressure in the tank is obtained by adjusting the internal pressure in a closed heating system downwards. This is done so that the rubber diaphragm is pressed on the coolant side. Otherwise, when it cools down, air will be drawn through the automatic vents, which should not be allowed under any circumstances. For example, if the internal pressure in the network is 1.2 atmospheres, then its optimal value in the expansion tank will be one atmosphere. After setting this value, you can open the tap and fill the system with coolant.
Recommendations for selection
When choosing a tank, special attention should be paid to its design. If critical pressure drops are not expected, then it is better to choose an inexpensive fixed tank. Otherwise, you will need to install a collapsible expansion tank, since replacing the membrane will cost much less than replacing the entire structure completely.
Additional factors to consider when choosing:
- wall thickness: must be at least 1 mm;
- type of external and internal coating: the body made of metal should not be subject to corrosion;
- volume of the liquid compartment: should not be too large to avoid reducing the temperature of the coolant in the pipes;
- container design: it can be horizontal or vertical; in other positions its installation is prohibited.
Expansion tank in the room
Despite the apparent simplicity of such an element of the heating system as a water tank, its selection and installation require a lot of attention and scrupulousness, even in small things. A serious attitude will help you avoid any troubles and make heating a private home effective and safe.
Video on the topic:
Design features
The purpose of the membrane expansion tank is that at all operating stages the device must maintain a balance between the pressure of both parts and, if necessary, level off excessive pressure or regulate its differences in the heating structure. Thus, the installation of a membrane expansion tank prevents the occurrence of increased loads in the heating circuit and in emergency situations in the event of malfunctions.
The device comes with a replaceable or non-replaceable membrane. In the first case, the coolant is completely contained in the flexible membrane container and cannot interact with the steel inner surface. All work associated with dismantling and subsequent installation of a new product is carried out through a flange secured with bolts.
If you purchase a device with a fixed diaphragm, it has an internal cavity consisting of two parts. In this case, a non-replaceable diaphragm membrane is used, which is rigidly fixed. A membrane tank for the heating system is selected directly for a specific heating structure, taking into account the amount of coolant. If the volume of the device turns out to be insufficient, the consequences can be very negative - cracks often appear and water can leak through the threads. In addition, the pressure in the system often drops below the permissible norm, as a result of which air gets inside the tank. Therefore, the choice of device must correspond to the necessary design parameters (for more details: “We are making the selection of an expansion tank for heating”).
An expansion membrane tank for heating systems is used to create closed-type coolant circulation in order to compensate for its thermal expansion as a result of an increase or decrease in fluid temperature, thereby preventing water hammer. In constant mode, both chambers of the device - water and gas - have the same pressure, which makes it possible to maintain the tightness of the system. This arrangement of the expansion tank of the heating system has been time-tested and recognized as the most practical.
The water circulating through the circuit does not contain aggressive gases and therefore corrosion will not render the tank unusable, which allows it to be used for a long time. The pressure expansion device is placed in the boiler room, and for this reason there is no need to protect it from freezing.
Despite the fact that the selection of a tank for a heating structure is individual, one should not forget that:
- the initial pressure in the membrane tank for heat supply connected to the cold water supply must exceed the static pressure in the system by 30-50 kPa;
- The device must have a reserve amount of coolant to compensate for possible leaks.
To protect a closed-loop system with an expansion tank from too high pressure, safety valves are installed.
System components
Open-type heating in a private house requires the installation of a boiler that runs on solid fuel or fuel oil. The fact is that this type of heating is characterized by the periodic formation of air pockets, which can cause an accident when using electric and gas boilers.
You can calculate the power of a heating boiler using a standard scheme, according to which heating 10 m2 of room area requires 1 kW of energy plus 10-30%, depending on the quality of the thermal insulation.
You should not use polymers as a material for the expansion tank; steel would be the best option in this case. The volume of the tank depends on the area of the heated room; for example, in the heating system of a small building one floor high, an expansion tank of 8-15 liters can be used.
As for the pipes for the heating system circuit with a circulation pump, in this case the following materials can be used:
- Steel. This pipeline is characterized by high thermal conductivity and resistance to high pressure. However, installation has some difficulties and requires the use of welding equipment.
- Polypropylene. This system is characterized by easy installation, durability and tightness; it can withstand temperature fluctuations. Polypropylene pipes have been characterized by flawless operation for a quarter of a century.
- Metal-plastic. Pipes made of this material are resistant to corrosion; deposits do not form on their internal walls, which would impede the natural movement of the coolant. However, the cost of such a system is quite high, and its service life is only 15 years.
- Copper. A copper pipeline is considered the most expensive, but it can withstand high temperatures, up to +500 degrees, and is characterized by maximum heat transfer.
How to install a membrane type expansion tank
A membrane tank is needed to protect the engineering system from water hammer and fully ensure its high-quality operation. After purchasing the equipment, you need to carefully consider how to install the membrane tank so that it works without failures. A hydraulic accumulator in a water supply performs several functions: it accumulates a supply of water, maintains the required pressure in the system, and serves as a reserve to reduce the frequency of turning the pump on and off.
Without installing a membrane tank, the service life of the pump is significantly reduced. In a system equipped with a hydraulic accumulator, water can be collected even during a power outage. When the pump is started for the first time, the water chamber of the tank is filled with water. The larger the volume of water in the tank, the smaller the volume of air and the higher the pressure.
Having reached the preset pressure required to turn off the pump, it automatically turns off. As soon as the pressure in the system drops to an acceptable level, the water supply will immediately turn on. To check the pressure, a pressure gauge is installed on the accumulator. It is also necessary to configure the required operating range of the equipment.
Common faults
Typically, most problems are not related to the container itself. Not so often there are cases when the tank itself cracks and begins to leak for no obvious reason. However, even taking into account the simple design, the problem part may well be the cap of the expansion tank of the engine cooling system.
The valve built into the lid may fail. Insufficient sealing may also occur due to deformation of the rubber ring. As a result of such malfunctions, the cap may begin to leak antifreeze, the system may become airy, etc.
If the valve in the cover begins to work incorrectly, then in such a case deviations in the operation of the internal combustion engine cooling system are inevitable. In addition to the formation of air locks, this situation in some cases leads to a critical increase in pressure and rupture of the expansion tank. In such a situation, the tank needs to be replaced with a new one. It is not recommended to attempt to restore a damaged container by sealing cracks.
If we talk about the cover, its damage and defects, as well as malfunctions of the valves due to clogging or deterioration, are a reason to replace the cover. In some cases, the lid is cleaned in an attempt to restore functionality, but this method does not always work. Given the low cost, it is better to replace the element immediately.