In any heating network there are foreign particles circulating along with water through pipes and radiators. This is rust, salt sediment from the boiler (scale), all sorts of solid impurities. If the amount of debris is large, the heat exchangers begin to clog, and silt deposits form in the batteries and pipelines. They interfere with the flow of coolant and normal heat transfer. The solution to the problem is flushing the heating system of a private home, which you can do yourself.
Instructions for flushing the heating system
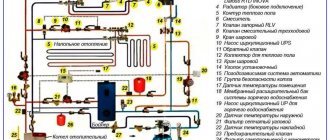
Pneumatic pulse cleaning scheme
There are 2 main methods for flushing the heating system, namely:
- using special hydropneumatic equipment;
- using chemical reagents.
Flushing using the hydropneumatic method
Hydropneumatic flushing of heating systems - instructionsHydropneumatic flushing of heating systems - instructions
This method is actively used by domestic housing offices and is quite effective. You just need to do everything in accordance with technology.
The principle is extremely simple: first, water is discharged from the system, then it is supplied back. A special pneumatic pump is used to “adjust” the water flow. As a result, under the influence of a fairly powerful pressure, scale and other deposits peel off, and when the water is drained, they are removed from the system.
To carry out this procedure yourself, you will need a pneumatic pump capable of pumping a pressure of more than 6 kg/cm2.
The sequence of actions is as follows.
Before starting work, you need to turn off all the taps. The end fittings are unscrewed using a wrench.
First step. We close the return valve.
Heating system line diagram
Second step. We connect the pneumatic pump to the valve installed after the valve.
Third step. We reset the return line.
Fourth step. Let the pneumatic pump build up pressure above 6 kg/cm2, and then open the valve to which it is connected.
Fifth step. We close off all the risers one by one. We do this so that no more than 10 risers are blocked at one time. Compliance with this rule will make the washing procedure as effective as possible.
Sixth step. We switch the system to reset in the opposite direction. To do this we do the following:
- close the discharge and close the valve connected to the pump, and turn off the device;
- close the open valve, and then open a similar one on the “return”;
- we reset the heating system. To do this, connect the pneumatic pump to the valve in the opposite direction, then open the valve and turn on the pump. The liquid will move in a different direction.
You can determine the required duration of rinsing by eye. Has clear clear liquid started coming out of the system? We can finish! Return the gates and valves to their original positions and turn off the pump.
Prepare a suitable container to collect dirty water. If you wish, you can connect a hose to the battery and ensure that the dirty coolant is discharged into the sewer.
Chemical wash
Chemical pipe flushing diagram
This method can be used only in two cases, namely:
- if it is necessary to clean a heating system with natural circulation, built using steel pipes. It is advisable to use chemical reagents in situations where, for any reason, there is no desire to flush the entire system. Most often, blockages are deposited in heat exchangers. The system can silt around the entire perimeter. In the second case, chemical washing will not be of much use;
- if it is necessary to restore the old heating system. Over decades of operation, pipes can become clogged and overgrown so much that the power of the pneumatic pump will not be enough for effective cleaning. It would, of course, be possible to use a more powerful pump, but no one can guarantee that the pipes will not burst under such pressure.
Wash reagent
The principle of flushing is simple: instead of coolant, a special solution containing acid and alkali is poured into the system. Then the mixture is circulated for 2-3 hours (if it is not the natural circulation line that is being cleaned, you will need to connect a pneumatic pump for this), after which it is drained and the pipes are filled with standard coolant.
Reagents for flushing and protecting heating systems
Never use such chemical mixtures to clean aluminum pipes. If the products remain intact after such washing, they will serve significantly less.
It is recommended to carry out mandatory flushing of the system of a private home at least once every 7 to 10 years.
SP-OM
The complex product of the SP-OM brand is used for flushing heating systems, heat exchangers, boilers and any other heat exchange equipment. Can be used in open and closed heat exchange circuits. "SP-OM" does not destroy aluminum and polymer elements of the system, as well as rubber gaskets. It has proven itself well on an industrial scale. There are various brands of SP-OM designed for specific operating conditions. Manufacturer's website - https://spomcom.ru/
SP-OM Pros
- effective removal of scale, rust and other deposits;
- wash-in-place;
- does not corrode rubber gaskets and seals;
- prevents corrosion of ferrous metals;
- may further include a corrosion inhibitor;
- Can be used with aluminum parts.
Minuses
Consultation and services of a flushing specialist may be required.
SP-OM
Metalin T is a product made on the basis of hydrochloric acid. Removes heavy lime deposits, rust products and organic matter in heating systems made of steel or non-ferrous metals. It is a non-flammable substance. After adding an alkaline neutralizer, the waste is allowed to be drained into the sewer. Packaged in concentrated form in containers from 1 to 30 liters.
Metalin T Pros
- non-flammable;
- quick cleansing.
Minuses
- after neutralization with alkali, discharge into the sewer system is allowed;
- not used for treating surfaces made of aluminum and its alloys.
Used in the treatment of pressure boilers, tubular heat exchange devices, boilers, condensers, pipelines in industry and domestic conditions. Removes various types of contaminants, in particular limestone and corrosive deposits. Ideal for washing plastic, metal and rubber pipes. Cleans carefully and does not have a negative effect on the structure of the seals. Not recommended for cleaning systems with surfaces made of aluminum and derivative alloys. Preliminary testing on treated stainless steel surfaces is also recommended.
SYNTILOR Watesup Pros
- does not affect the structure of metals;
- concentrated product;
- high efficiency even at low operating temperatures (20–35°C);
- does not damage seals and rubber gaskets;
- contains an inhibitor.
Minuses
Heating system cleaner SYNTILOR Watesup
Deoxyl-3
Deoxyl-3 is an acid-type product for chemical cleaning of pipelines in heating and water supply systems. It is packaged as a concentrate in 20 liter containers. The liquid is not flammable and belongs to toxicity class 3. For a greater cleaning effect, it is advisable to use the Deoxyl NO additive together with the drug. Foaming is neutralized by the Foral PG additive. The liquid is quite aggressive, so when working with it it is recommended to protect the skin and respiratory organs with protective equipment. Use strictly according to label instructions.
Deoxyl-3 Pros
- completely removes scale-corrosion deposits regardless of the design features of the equipment;
- biodegradable;
- after washing, the spent working solution can be drained into the sewer;
- The composition includes various inhibitors that prevent metal etching and the appearance of corrosion. Inhibitors not only remove deposits, but also protect the metal.
Minuses
The liquid is aggressive (work with it only with protective equipment).
Which system flushing products would you choose or would you recommend purchasing?
Deoxyl-3
44.44% ( 4 )
Save your voting results so you don't forget!
To see the results you need to vote
Cleaning and washing of floor-standing boilers
Removal of scale and soot is carried out without dismantling the heat exchanger. A flushing pump (booster) is used. An aqueous solution of citric acid is poured into its container. For 2 liters of warm water, 200 grams of powdered citric acid is required.
Before cleaning a floor-standing gas boiler, turn off the gas and water supply taps, drain the water from the heating and hot water circuits. Next you need to get to the heat exchanger. Remove the door, disconnect the wires connected to the piezoelectric element, remove the thermocouple and nozzle, dismantle the ignition system and burner.
Unscrew the nuts securing the top cover and remove it. You have gained access to the heat exchanger and can clean it of soot with a brush and brush.
Connect the leads of the booster to the heat exchanger pipes, which will pump a citric acid solution into the pipe under pressure. Circulating along the circuit for 4-6 hours, it will dissolve the scale. The rinsing time depends on the level of contamination.
To keep the process under control, use a pH meter. This device will show the change in acid concentration in the solution, which occurs as a result of the ongoing chemical reaction of dissolving carbonate deposits.
If the acid has neutralized and the meter displays a pH value of 1, you may have to repeat the process all over again. A stable pH level between 2 and 4 indicates descaling.
Finally, the pipes are washed with a baking soda solution to neutralize residual traces of the reagent. Next, it remains to install the parts in their places, check the unit for leaks by washing and visually inspecting the detachable connections, or using crimping. If there are no gas or water leaks, the boiler operates as usual.
Appendix 2
Consumption of reagents for boiler alkalization
| Boiler type | Water volume, m3 | Reagent consumption, kg, at dosage, kg/m3 | ||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | ||
| TP-80 | 115 | 115 | 230 | 345 | 460 | 575 | 690 | 805 |
| TP-82 | 115 | 115 | 230 | 345 | 460 | 575 | 690 | 805 |
| TP-10 | 88,2 | 88 | 176 | 265 | 358 | 441 | 529 | 617 |
| TP-12 | 85 | 85 | 170 | 255 | 340 | 425 | 510 | 595 |
| TP-15 | 87,4 | 87 | 175 | 262 | 350 | 437 | 524 | 612 |
| TP-230-2 | 71,6 | 72 | 143 | 215 | 286 | 385 | 430 | 501 |
| TP-170-1 | 56,7 | 57 | 113 | 170 | 227 | 284 | 340 | 397 |
| TP-200-2 | 67 | 67 | 134 | 201 | 268 | 335 | 402 | 469 |
| TP-150-1 | 52 | 52 | 104 | 156 | 208 | 260 | 312 | 364 |
| PK-10, PK-10-2 | 61 | 61 | 122 | 183 | 244 | 305 | 366 | 427 |
| PK-14, PK-14-2 | 63 | 63 | 126 | 189 | 252 | 315 | 378 | 441 |
| PK-19, PK-19-2 | 57 | 57 | 114 | 171 | 228 | 235 | 342 | 399 |
| PK-20, PK-20-2 | 58 | 58 | 116 | 174 | 232 | 290 | 348 | 406 |
| BKZ-220-100F | 66 | 66 | 132 | 198 | 264 | 330 | 396 | 462 |
| BKZ-210-100F | 64 | 64 | 128 | 192 | 256 | 320 | 384 | 448 |
| BKZ-160-100F | 48 | 48 | 96 | 144 | 192 | 240 | 288 | 336 |
| BKZ-75-89-FB | 30 | 30 | 60 | 90 | 120 | 150 | 180 | 210 |
| TsKTI-75-39F | 30,4 | 30 | 61 | 91 | 122 | 152 | 182 | 213 |
| BKZ-75-39SL | 32,6 | 33 | 65 | 98 | 130 | 163 | 196 | 228 |
| BKZ-50-39F | 21,2 | 21 | 42 | 64 | 85 | 106 | 127 | 143 |
| TP-35U | 13,3 | 13 | 27 | 40 | 53 | 67 | 80 | 93 |
| TS-35U | 13,07 | 13 | 27 | 39 | 52 | 65 | 78 | 92 |
| TP-20-U | 9,33 | 9 | 19 | 28 | 87 | 47 | 56 | 65 |
| TS-20-U | 10,73 | 11 | 21 | 32 | 43 | 54 | 64 | 75 |
| DKVR-10-15 | 8,6 | 9 | 17 | 26 | 34 | 43 | 52 | 77 |
| DKVR-6.5-13 | 7,5 | 8 | 15 | 33 | 30 | 38 | 45 | 60 |
| DKVR-4-13 | 5,4 | 5 | 11 | 16 | 22 | 27 | 32 | 49 |
| DKVR-2.5-13 | 3,6 | 4 | 7 | 11 | 14 | 18 | 22 | 32 |
Peculiarities
Flushing the heating system cannot be done “blindly”, because you need to know what you will encounter. Typically, batteries do not heat up well when the fluid circulation in them is weak due to debris clogging the internal walls. It is found in the water itself in the form of suspensions of alkali salts, heavy metals and rust. Utilities are required to flush the system annually to prevent a decrease in water flow. But often this task has to be performed by the residents themselves, inviting specialists to clean the radiators from the dirt compacted inside.
This problem is especially typical for cast iron batteries, where sometimes there is a channel for water circulation no more than 1 cm in diameter due to infrequent washing. The cause of clogging of steel radiators is stagnation of rust, due to which they are subject to not only clogging, but also destruction. Not every type of flushing is suitable for such batteries, since after some methods leaks may appear in them. Plastic radiators also become clogged, but cleaning them differs from cleaning their metal counterparts.
This process cannot be called universal, because it is selected specifically for each case. An example of a bad choice is the flushing of the heating system by housing and communal services workers, when they apply powerful pressure by abruptly opening the riser valve located in the basement of an apartment building. This leads to knockout of locking elements and leaks at the junctions of spans. But not every family owner can disassemble the battery into separate bends for the purpose of mechanical cleaning in order to solve the problem of a clogged heating system.
When flushing radiators in an apartment on the lower floors, one cannot always expect the efficiency of the coolant, since for high-quality cleaning it is necessary that the neighbors of all floors of the same branch do the flushing. Otherwise, after cleaning one apartment and washing the batteries by utility workers with high pressure, some of the garbage may fall behind the walls, and mud masses will fall into the newly cleaned batteries. However, it is unlikely that all neighbors will agree when it comes to flushing, but the insufficient internal cross-section creates high hydraulic resistance.
Every mm in thickness of deposits increases fuel consumption by 20-25%. In central heating systems, the water must be pre-treated to reduce clogging. But this is not always done, although residents pay decent amounts every month for house maintenance. In addition, radiators last for decades without replacement. According to the established regulations, flushing of centralized and autonomous systems must be carried out annually. This period is critical. If the pipes are not flushed before the start of the heating season, the pipeline becomes clogged, causing the heating equipment to break down.
If you ignore the blockage, the consequences can be disastrous:
- the heating system may freeze;
- you will have to buy new batteries;
- You will need an electric heater, which will increase the price of electricity.
Chemical descaling of boilers
The chemical cleaning method, which involves preliminary determination of the composition of the scale and its nature, will help to clean the boiler quickly and effectively. This method is considered the simplest, fastest and most effective. Before cleaning, you need to take a scale sample from different places, and then start determining the average sample.
Carbon dioxide promotes the rapid dissolution of carbonate and phosphate deposits. Hydrochloric acid interacts with carbon scale, forming chloride compounds of calcium, magnesium and carbon dioxide, which easily dissolve. Cleaning scale from phosphate and silicate scales is more difficult, but efficiency can be increased by adding fluorine acid to the cleaner.
Types of acids for cleansing:
- Solyanaya;
- Sulfuric;
- Sulfamine;
- Sorrel;
- Lemon.
When choosing acids, it is important to pay attention to their availability, cost, effectiveness and environmental friendliness. You can clean the boiler chemically with your own hands, but you need to be extremely careful. The most popular in the West are reagents that belong to the class of chemical acids
Chemical cleaning is the most reliable and effective type of descaling if all reagents are selected correctly
The most popular reagents in the West are those that belong to the class of chemical acids. Chemical cleaning is the most reliable and effective type of descaling if all reagents are selected correctly.
What is a heat exchanger
This was done so that the thermal energy obtained from burning gas passes through it and, accordingly, heats it up.
Thus, hot water passes through the heat exchanger, which may contain various impurities in the form of metal salts and lime particles. These chemicals constantly deposit on the inner walls of the pipes, forming a coating. (Read this article about cleaning a heating boiler from scale.)
Over time, this type of pollution only increases, as a result of which the movement of water through the heat exchanger becomes difficult, which leads to failures of the entire boiler unit as a whole.
Therefore, it is very important to flush the gas boiler regularly.
Single-circuit or double-circuit boiler - is there a difference?
Varieties of boilers do not in any way affect the time period after which it is necessary to flush the heat exchanger. It is much more important which liquid () circulates in the heating system and which is supplied for hot water supply.
When using process water that has undergone standard purification, the boiler can be flushed no more than once every four years. This removes a layer of scale (which still forms) and deposits that have a more complex structure. If you do not filter water before pouring it into the system, but use ordinary water from a centralized water supply, then flushing should occur more often, at least once every two years. This is due to the high content of chlorine in the liquid, which, upon contact with the heating element, settles in the form of scale.
Some users prefer to use antifreeze as a coolant. This liquid is of higher quality: it does not freeze even at low temperatures, releases heat more slowly, but heats up quickly. Unfortunately, antifreeze is poisonous
, and breaking down into components, leads to damage to metal structures. The heat exchanger through which antifreeze circulates should be cleaned at least once every 1.5-2 years.
Therefore, both single-circuit and double-circuit boilers require timely cleaning of the heat exchanger, the intervals between which are the same in all systems.
In order to clean the bithermal heat exchanger less often, it is necessary to take care not only of the quality of the coolant in the heating circuit, but also of the quality of the water in the DHW system. The water should be pre-purified and filtered. You should also take into account the fact that the process of scale deposition begins at a temperature of 70°C, its rate increases by 2 times with every 10°C increase in temperature. In this case, the process progresses, since the growing layer of calcium impairs heat transfer and the temperature of the heat exchange wall increases.
Why us
Our company is officially registered. We have the necessary documents to provide steam boiler cleaning services to enterprises of any form of ownership and field of activity. We cooperate with both private entrepreneurs and large factories. We work with all forms of payment: cash, non-cash, bank transfers.
To order or find out more about flushing our company’s steam boilers, just contact us in any convenient way specified in the contacts.
Flushing the boiler from scale: consequences of ignoring
Modern mains use ordinary hard water, which quickly leads to the inside of the equipment being covered with scale. Boilers must be cleaned on a regular basis. If cleaning is not done on time. The consequences can be the most unpredictable, but definitely unpleasant.
The design of the gas boiler is such that the coolant coming from the return line cools the cavities of the heating elements located inside. The coolant cannot effectively cool the elements if they are covered with a thick layer of scale. If the boiler constantly overheats, it will soon stop working altogether.
What will happen if you ignore flushing?
- Scale consists of mineral deposits that do not promote thermal conductivity. Scale causes the water to heat up slowly, which requires significantly more electricity. A thick layer of scale leads to increased gas consumption, which increases the price of using the boiler.
- Scale can lead to boiler failure due to difficult coolant passage. This increases the load on the circulation pump, which leads to its rapid breakdown.
Before flushing the boiler, it is important to pay attention to what kind of liquid flows through the line. The need for frequent flushing will be due to very hard and contaminated water. In order to reduce the frequency of cleaning, it is necessary to use antifreeze - it is important that it is not expired
In order to reduce the frequency of cleaning, it is necessary to use antifreeze - it is important that it is not expired
What stages do we go through when cleaning industrial boilers?
Hydrodynamic boiler flushing has a mandatory 9 stages. Here they are.
1. Draining water from the boiler
2. Opening the hatches of the upper and lower drums
3. Dismantling the steam separator
4. Cleaning of each boiler tube by a specialist located inside the upper drum
5. Final washing of the upper drum.
6. Cleaning screen and convection pipes
7. Opening and washing the collector
8. Washing the lower drum
9. Removing sludge and scale from the lower drum.
An effective way to descale
To carry out the highest quality cleaning of equipment, you can use a modern device - a booster. It will effectively solve the problem of how to flush a gas boiler from limescale.
What does the booster include:
- circulation pump;
- container for loading reagents;
- electric heating part.
The booster functions as follows:
- the reagent is heated in a special container (in order to increase its cleaning properties);
- the circulation pump pumps the heated reagent into the coil;
- chemicals circulate through the heat exchanger and clean the walls;
- the spent reagent with dirt pours out.
The heat exchanger must be cleaned regularly, at least once a year. However, this procedure can be repeated more often if the quality of the coolant is very low. If ordinary tap water is poured into the system, then it is very simple to determine this: observe how quickly scale forms on the kettle. Hard water “suffers” from this deficiency.
What is a heat exchanger
A gas boiler has an element in its design that is located above the firebox and consists of connected tubes. The coolant circulates in them. Its location is not accidental; combustion of gas in the boiler must heat the coolant, which is located in the heat exchanger.
The coolant is water. It heats up and passes further through the system. But untreated water contains many impurities that can settle in the tubes when heated. Most often these are salts and lime particles. If there is a lot of contamination, water has difficulty passing through the tubes, which leads to malfunctions.
How to clean
Many ordinary people who decide to flush the heat exchanger with their own hands, as a rule, ask two questions. How to clean this device? How to clean it? First, let's tell you what chemicals are used to flush the heat exchanger.
Cleaning products
Therefore, you need to be very careful when choosing a cleaning agent. First of all, you need to consider the following factors:
- degree of heat exchanger contamination;
- how the reagent will affect the material from which the heat exchanger is made.
At home, it is most advisable to use the following chemicals to flush this boiler element:
- citric acid, which is a fairly effective descaling agent;
- sulfamic and adipic acids are practical for regular washing of the heat exchanger, when the contamination is not so significant;
- hydrochloric acid is intended to remove fairly strong scale, but when using it, it is worth taking into account the properties of the heat exchanger material;
- gels that dissolve in water - they are not as aggressive as acidic reagents, but no less effective.
Washing methods
To clean this structural element of the boiler from scale with your own hands, it is optimal to use the following two methods:
- mechanical;
- chemical.
The essence of the mechanical method is as follows:
- the gas boiler is disconnected from the gas supply and power supply;
- the heat exchanger is disconnected from all lines and carefully removed;
- the device is soaked for 3–7 hours (depending on the degree of contamination) in a container with a low concentration acid solution;
- the heat exchanger is thoroughly washed with running water and installed in place.
Expert advice: when rinsing with running water, the device can be gently tapped with a mallet at the same time to increase the cleaning effect.
Here
The procedure for this is as follows:
- two pipes of the device are disconnected from the general boiler system;
- a booster hose is connected to one of them, through which liquid for flushing will be supplied;
- We also attach a hose to the second branch pipe, from which the reagent will flow out to the booster - thus, the cleaning agent will circulate between the heat exchanger and the booster;
- After cleaning, the spent chemical solution is drained and then washed well with water.
Specialist's note: to successfully clean the heat exchanger from scale using a booster, flushing should be done several times.
gas boiler cleaning
Watch the video in which an experienced user clearly explains the features of flushing the heat exchanger of a gas boiler:
Estimated cost of services
The cost of work is determined based on the boiler model, location, heat exchange surface area, water volume and degree of contamination.
The cost of work is determined based on the heat exchanger model, location, heat exchange surface area, and water volume.
What explains the need to flush boiler and heat exchange equipment with chemical reagents?
In practice, the quality of water for heating networks does not meet established standards. Failure to comply with the regulations when putting the system into operation starts the process of deposition of excess salt and other impurities on the surface of the pipes. In this regard, the hydraulic regime is disrupted, the useful volume of the networks is reduced, which leads to a complete imbalance and threatens the integrity of the system. It is not possible to carry out mechanical cleaning of pipes and equipment due to the lack of technical potential, so chemical flushing becomes perhaps the only and most effective method of cleaning the system.
Washing methods
Chemical
Chemical flushing of heating systems is used in two cases:
When it is necessary to restore the functionality of the heating system of an apartment building, which has been in operation for several decades. In combination with the inevitable siltation, the overgrowth of steel pipes leads to a catastrophic drop in efficiency during this time.
The actual flushing consists of pouring a special reagent into the heating circuit instead of water. This product is a solution of alkali (most often sodium hydroxide) or acid (phosphoric, orthophosphoric, and so on).
Then a special pump in the circuit ensures continuous circulation for several hours. Then the heating system flushing fluid is drained and the system is pressure tested before being put back into operation.
This device is a reagent tank and a pump in one housing.
The cost of the cleaning product starts from 5-6 thousand rubles for 25 liters. Housing maintenance rules prohibit disposing of used solution down the drain; however, if there is no other way of disposal, solutions for their neutralization are sold along with washing compounds.
Hydropneumatic flushing
This technology for flushing the heating system has been used for many decades in the Russian (and previously in the Union) housing and communal services and has long shown its effectiveness. But only and exclusively if performed correctly.
The instructions for flushing the heating system are quite simple: the circuit is discharged into the sewer system, first from the supply to the return, then vice versa. In this case, air is pumped into the water flow by a high-power pneumatic pump. The pulp, passing along the entire contour, partially destroys the scale and removes silt.
The heating system flushing scheme used in practice in housing and communal services is as follows:
- We close the house valve on the return pipeline.
- We connect the compressor to the supply metering valve after the house valve.
- We open the reset on the return line.
- When the pressure in the ballast tank of the compressor reaches 6 kgf/cm2, open the valve to which it is connected.
- We close off groups of risers one by one so that no more than a dozen are open at any given time. In this case, flushing heating risers and heating devices connected to them will be most effective.
The duration of flushing can be easily controlled by visually assessing the degree of contamination of the water being discharged. As soon as it has become transparent, we begin to wash a new group of risers.
After all the risers are washed, we switch the heating to reset in the opposite direction:
- We close the discharge and the valve to which the compressor is connected.
- We close the house valve on the supply and open it on the return.
- We open the reset from the supply. We connect the compressor to the metering valve on the return pipeline and open it.
Next, washing the groups of risers is repeated, but with the pulp flow in the opposite direction.