A traditional water system transfers thermal energy into rooms using water or an antifreeze liquid (antifreeze). But there is another solution - pure air heating of the house, in which the air in the rooms is heated directly, without hydraulics and radiators. Since this topic is being actively promoted by interested manufacturers of heating equipment, we decided to figure out how much better (or worse) air heating is than classic heating and whether it can be installed with your own hands.
Calculation of an air heating system for do-it-yourself design and installation
The calculation is of great importance if you want the system to function smoothly, efficiently and last for decades.
If you do not plan your heating system correctly, you may fail, which will lead to unplanned expenses. So, what can happen if you don’t pay enough attention to the preparatory stage:
- The heater may overheat. The result is a breakdown.
- unexpected vibrations, and as a result, noise during system operation. The result is constant noise that most likely cannot be eliminated.
- drafts. The result is constant colds and colds.
Calculation parameters
Firstly, the power of the air heater. Depending on the quality of operation of the air heater, it will be clear how much area it can heat with air.
Secondly, feed speed. The faster the heated air is supplied to the intended places, the less heat loss will be.
Thirdly, the diameter of the air ducts. This indicator affects the calculation of the aerodynamic characteristics of the system as a whole. The diameter must be consistent with the flow rate, otherwise air will be lost in the duct, resulting in heat loss.
Specifications
Currently, two models of Volcano heating equipment have been produced - VR1 and VR2. There are also models of fan heaters Volcano VR MINI and Volcano VR3, but they are not widely used.
Models VR1 and VR2 have a body that is resistant to temperatures and corrosive processes, which is made of special plastic that meets all control standards when testing for environmental friendliness. These copies use only reliable automation, which is very easy to operate.
The Volcano VR1 heater is a single-row device and has a power of 30 kW at maximum load. The second model has two rows, and the power indicator is increased by 2 times.
Water acts as a coolant. The maximum possible heating temperature of the working fluid for both models is 1300C with a heated air jet distance of 25 m. In the first model, namely VR1, 1.7 dm3 of water is used, and in the second - 3.1 dm3.
The maximum permissible operating pressure is considered to be 1.6 MPa.
We must not forget that the use of water under pressure as a coolant requires additional protection with a possible increase in this indicator. But the conditions are also taken into account that when temperatures drop to negative values, the heat exchanger may rupture if there is water in the system.
Principle of operation
Many of our fellow citizens imagine a heating system as nothing more than a circuit of pipes and radiators filled with water or antifreeze. Meanwhile, the use of a coolant liquid in an autonomous heating system of a private house is nonsense, a vivid example of thoughtless adherence to established stereotypes. After all, we are building such a complex and expensive system only because centralized systems are designed on this principle.
At the same time, no one thinks that they operate in completely different conditions: the heating unit is located at a considerable distance from consumers (large heat losses), and the consumers themselves - public and residential buildings - have a very extensive distribution network. To convey heat to the most distant radiator, you need a coolant with a very high heat capacity, and water is best suited for this.
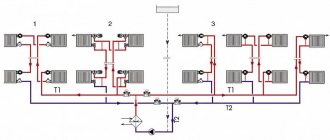
Schematic diagram of air heating
In an autonomous system, nothing like this is observed: the boiler room is located directly in the house, therefore there are no heat losses as such; in this case, the maximum distance to the most distant room usually does not exceed several tens of meters. In such conditions, the medium for the sake of heating everything is started, that is, air, can be used as a coolant.
The heat capacity of air is 800 times less than that of water, but it will be quite sufficient to distribute heat within the house.
This distribution is the principle of operation of the air heating system. The air is heated by a convection-tube furnace (common name - heater), running on gas, wood with coal or diesel fuel, and is distributed through a network of air ducts to all rooms. In each of them, you can set your own temperature regime by blocking part of the air duct outlet with a damper.
Features of installation and operation of equipment
Since these devices belong to the air-heating group, their power comes from a 380 V network. An electrician who has the appropriate permit to carry out technical work can be invited to connect them. The only condition before connecting is the correctly calculated power consumption, which must be taken into account to protect the wires from damage and prevent fire due to a short circuit.
Devices used in heating are connected only with steel pipes. Experts recommend using a pre-galvanized type of pipe to increase its service life, because during operation the metal may be exposed to corrosion, as well as the appearance of deposits and subsequent “overgrowth.” Pipes that are made of metal-plastic and polymers are unsuitable, because during the work they will use water heated to 1300C.
There are two installation methods:
- wall;
- vertical.
When using the wall method, it is necessary to take into account a free distance of at least 30 cm from the wall. It must be left to ensure air flow.
In workshops or warehouses where volatile, explosive or aggressive substances are stored, the use of installations using electric current is prohibited
Particular attention should also be paid when used in metalworking shops because graphite, which can be used as a lubricant, as well as fine sawdust released during operation, are capable of conducting current.
Application of air heating systems
But where can air heating systems be effectively used?
Firstly, at industrial enterprises due to the peculiarities of their work. In some places it is impossible to do without such a system, since others are not suitable.
Secondly, in areas where it is necessary to ensure the safety of children. For example, in kindergarten. Touching hot water radiators may cause burns.
Thirdly, to create an isolated air system in the house. This option is suitable for people suffering from allergies or lung diseases, especially if there are industrial emissions nearby.
However, today many enterprises prefer a hydraulic heating system, since it is cheaper and modern technologies have made it possible to apply solutions that can get rid of the shortcomings of older hydraulic systems.
Features of installation and operation
What features will you have to face if you decide to choose air heating for a private home?
First, you will need to place air ducts everywhere. For this purpose, you will have to order a separate architectural project in order to correctly fit them into the architectural appearance of the house and create convenience and comfort inside.
Placing air ducts under the ceiling and in the floor will require increasing the height of the house by about a meter. If they are not hidden, the air ducts will look unsightly and take away space that could be used for other needs.
Secondly, there is the problem of cleaning the air ducts. From time to time, dirt and dust will accumulate in them. And to remove them from there, you will need a whole system of hatches along the entire length of the air duct.
If you do not clean them, then after a while a creature called Staphylococcus aureus will begin to live in the accumulations of dust. Its presence in the air can lead to an allergic reaction.
It is useless to install any filters, since dust and dirt will still settle inside. There are special services for cleaning air ducts that also clean air conditioners.
Thirdly, the air heating system of a private house requires the placement of diffusers, that is, special fans that will rotate and create an air flow inside. They make a lot of noise and should not be placed near the bedroom. This also requires additional hassle, since a place needs to be prepared for the diffusers.
The fan diameter is most often 600 mm, but can be 400 mm.
When choosing diffusers, pay attention to the fan rotation speed. The faster it spins, the more air moves through the air heating system. . Fourthly, a competent and responsible approach to the installation of this system is required due to the complexity of the process
Finding a good ventilation specialist who will think through everything and make an effective working system is extremely difficult. And most specialists can make various mistakes. For example, improper air extraction from the room.
Fourthly, a competent and responsible approach to the installation of this system is required due to the complexity of the process. Finding a good ventilation specialist who will think through everything and make an effective working system is extremely difficult. And most specialists can make various mistakes. For example, improper air extraction from the room.
Fifthly, installation and maintenance of air heating can be 10 times higher than the cost of similar procedures in relation to water heating. After all, you need to spend money on an architectural project, increase the height of the house, regularly clean the air ducts, and so on. There are much more effective, cheaper and suitable options for private homeownership.
What are the advantages of such a system?
The air control system has the following characteristics:
- Extremely high efficiency rate - as much as 93%
- Can be put into operation even on buildings that are already in use
In case of emergency, it can always be turned off by a person to avoid subsequent malfunctions. The water system is invariably susceptible to damage; there is no way to protect it from an accident.
- Storage water heater - installation methods and review of the most economical options (85 photos)
Circulation pump - 90 photos of popular models and their connection options
Electrode boiler - the best models from world manufacturers and DIY construction (110 photos)
- Cheap installation and operation. All materials used require low costs
- Can heat rooms quickly and evenly
- Long wear of spare parts
Possibility of adaptation in repairs (in some interior design works, emphasis is even placed on air ducts, this fact is proven by numerous photos with examples of laying air heating ducts)
Drafting
Like any other air heating system, it also needs a primary design, which for a private home can be done with your own hands. The design and calculations must take into account the following:
Gas heater device
- A heating boiler of appropriate power, which, taking into account heat losses, is capable of heating all rooms.
- The speed of movement of warm air masses.
- The amount of heat a building loses through walls, roof, floors, windows and doors.
- Aerodynamic characteristic, which depends on the cross-section of the air ducts, and is calculated to determine the reduction in air flow pressure.
Before you undertake a thermal engineering calculation, make sure that your knowledge is sufficient for this work, since an incorrectly done project can bring such phenomena as an eternal draft in residential premises, and this is fraught with colds, the constant noise of a working fan and vibration, which will invariably be created in air ducts. And overheating of the heat exchanger can lead to failure of the heating unit itself.
Air heating of a private house involves a ventilation device to replenish the internal space with fresh air and remove exhaust air.
When making thermal engineering calculations, it should be taken into account that the ventilation system supplies about 25% of cooled air from outside to the room.
After the calculations have been carried out, you need to select the location for installing the air ducts. As previously mentioned, they can be located under the ceiling or made in a baseboard design. There are no rules or regulations here. Everyone is free to choose what suits them best. In any case, the air duct sleeves should be located both at the bottom and at the top. Since air masses must circulate, covering the entire space of the room. It is recommended that the outlets of the channels supplying warm air be located where people are most often and for the longest time.
Mistakes when choosing an air-heated fireplace
The generally accepted scheme for selecting heating equipment is unacceptable in this case. Most believe that the power of the firebox is adjusted to the area of the room at the rate of 1 kW per 10 m2. Time has shown that choosing a firebox for fireplaces for a country house with air heating requires an integrated approach.
Gas stoves that are too powerful lead to overheating of the apartment. Residents have to open windows or reduce the amount of heating fuel they use. Frequent temperature fluctuations provoke colds and other unpleasant symptoms - weakness, dizziness and insomnia.
Fireplace area calculation table
How to calculate the required firebox power for an air-heated fireplace? Experts advise contacting sales consultants with this question. It is necessary to contact a specialist correctly, that is, by providing information on the area of the room, type of ventilation and number of rooms. Only in this case will the seller select the required power of the equipment.
How to make air heating in a private house with your own hands
Design and calculation of an air heating system
Before installing air heating with your own hands, you need to think through its layout and design for a specific private home. To do this, an approximate design of such a system is drawn up on paper.
Then, depending on the heating requirements in a particular building, parameters such as:
- intensity of heated air injection;
- optimal power of the heat-generating installation to heat a room of the corresponding area to the required temperature;
- air duct cross-section;
- aerodynamic features;
- volume of heat loss on room surfaces.
It is advisable to agree on a preliminary scheme with a full set of components that meets all requirements with a specialist in order to avoid any errors or omissions that could lead to drafts, noise or vibration in the room.
Professionals can also help you choose the optimal heat generator model so that it provides a comfortable temperature and does not overheat.
It is best to install the equipment in a separate, pre-designated room.
Air heating systems
Air heating structures come in several types depending on their parameters.
According to air circulation they are:
- with the natural flow of air masses;
- with forced air movement under the influence of pressure created by a fan.
By size and scale:
- local, designed for heating one or two rooms in a small private house;
- central - for heating multi-storey buildings and large warehouse or factory hangars.
According to the heat exchange implementation scheme:
- supply air, which draws street air into the room and heats it;
- recirculation, that is, the same air moves, cooling and heating inside the room;
- with combined recirculation, when indoor air and fresh air from the street are combined.
By location in the room:
- hanging;
- floor units.
- Selecting a heat generator.
The source of thermal energy is always the heart of the entire heating system, therefore, the comfortable temperature of the premises of a private house depends on its type, power and design. There are two types of heat generators: mobile and stationary.
The first are represented by gas mobile heat generators, which are distinguished by their large dimensions. They are used to heat large industrial premises, for example, factory floors.
The latter have an isolated combustion chamber and are intended for installation in special rooms with a smoke exhaust system. They are produced by manufacturers in two versions: as floor-mounted or suspended equipment. The second type of design is called heater, that is, it performs the function of heating only one room.
They are installed in country cottages, since such a device can warm up a small rear area in just a few hours.
The suspended structure is compact and produces minimal noise during operation. It is made from materials that do not conduct heat well, so it is safe to use even next to wooden walls.
The floor-mounted unit is much more powerful and larger, so it can be used to heat even a wooden cottage with several floors.
Air source heat pumps for heating
Today, the use of heat pumps instead of boilers as heat sources in the house is becoming increasingly important. The cost of such installations that extract thermal energy from the environment is becoming more affordable, although it is still very far from ideal.
The principle of this kind of heating devices is similar to the operation of split heating systems. Air having a temperature above absolute zero, in any case, has thermal energy, which such a pump takes away from it, making it even colder outside.
The heat thus obtained is transferred to the internal air of the room, distributed over its entire area.
This is a fairly efficient system because the electricity costs for operating the fans and compressor are only 1/3 of the heat obtained from the air. Therefore, a heat pump is one of the best options for heating a private home, although it is the most expensive.
Installation equipment
Personal installation of an air heating system in a private house requires the purchase of the equipment included in it: air ducts or tin pipes, a heat generator unit, a fan, hoses for taking in outside air and decorative grilles.
Stove-based water heating device
The operating principles of any water heating are based on the distribution of heat from a local source throughout the room, using the movement of water along the heating circuit.
Basic elements of water heating
For a stove heating scheme with a water circuit, the main elements are:
- stove or fireplace with a heat exchanger in which water is heated;
- heating circuit where heat is transferred to the room;
- expansion tank to prevent damage to the system due to increased pressure;
- circulation pump to ensure water movement along the circuit.
There are general rules for the operation of water heating, such as wiring diagrams, that are well known and must be followed. However, when using a stove as a heat source, there are specific requirements related to the temperature regime.
The operating principle of water heating based on a stove or fireplace is simple, but it is necessary to accurately calculate the parameters of all elements of the system
Furnaces do not heat up quickly and cool down slowly, uneven heat release occurs, and only the correct installation of all system components will avoid problems with high-quality heating of the premises of the house.
Types of heat exchanger and placement methods
For the manufacture of heat exchangers for furnaces, sheet “black” steel or heat-resistant stainless steel is used. The use of cast iron as a production material is difficult, but ready-made cast iron products, such as cast iron radiators, can be used.
It is possible to use copper, which has better thermal conductivity compared to steel, but the price of such a device will be high. It is recommended to make the heat exchanger from steel with a thickness of 3 mm. At high furnace temperatures that arise when using coal or, especially, coke, it is necessary to use steel 5 mm thick.
Heat exchangers can be divided into three types:
- registers, coils and radiators , consisting of a set of pipes;
- jackets (boilers) welded from sheet steel;
- a combined version in the form of vertical walls connected by pipes (the so-called “books”).
Sheet steel jackets are easier to manufacture and easier to clean from fuel combustion products, but tubular structures have a larger heating area. When making a jacket, it is necessary to take into account the excess water pressure that occurs when using a membrane expansion tank or raising water to a great height.
A heat exchanger for water heating based on a stove can be constructed from scrap materials:
Image gallery
Photo from
Brick kiln heat exchanger
Heat exchanger made of cast iron battery
Forced heating type
Heat exchanger in a cooking furnace
In this case, it is necessary to use steel with a thickness of at least 5 mm and additionally reinforce the walls with stiffeners to avoid their deformation.
The shapes of tubular structures can be different, but it is necessary to comply with the condition that the internal size of the pipes is at least 3 cm in diameter. Otherwise, if the circulation speed is slow or the temperature is too high, the water may boil.
Registers are made, as a rule, from profile rather than round pipes to facilitate welding work.
You can make a heat exchanger of the required size yourself. In this case, increased attention should be paid to the quality of welding. If the heat exchanger leaks, all the water will pour into the furnace.
In addition, to fix the problem, you will have to do a lot of work: disassemble the stove, remove, weld and put back the heat exchanger, and then reassemble the stove.
There are two options for the location of the heat exchanger. In the first case, it is placed directly in the firebox, significantly narrowing its space. In the second, the registers are installed in the hood of non-revolving furnaces, but the furnace itself in this case has a more complex design.
If you have a bell-type stove, it is better to place the heat exchanger in the bell: it is also hot there, and the firebox space will remain unchanged
When installing a tubular type heat exchanger, it is necessary to leave a gap between it and the wall of the stove. This is necessary for better heating of the coolant, as well as the possibility of cleaning the register. It is necessary to clean both shirts and registers periodically, since in case of severe clogging with ash, the efficiency of heat transfer decreases.
If there is a hob, cleaning occurs after removing it. If the stove has only a heating function, then cleaning occurs through the combustion door.
Water circulation in the heating circuit
The basic principles of organizing the natural circulation of water in the system are to model the “acceleration collector” at the outlet of the heat exchanger and to create a constant slope of the heating circuit pipes of 3-5°.
The general meaning of the “acceleration manifold” is that heated water from the stove rises vertically upward, and then is distributed along the heating circuit.
Circulation occurs due to the difference in specific gravity of cold and hot water. Cold water is heavier than hot water, and flowing to the heat exchanger, displaces hot water up the pipe. The “return” entry point must be lower than the water outlets from the heating radiators, otherwise the water circulation will be very slow or not at all.
An acceleration manifold is necessary even for small-length heating circuits when natural circulation is used
To increase the speed of water movement along the heating circuit, a circulation pump is installed. Thus, there is a faster and more uniform distribution of heat throughout the house. Several pumps can be used simultaneously for different heating circuits.
In the presence of power surges, it is necessary to use a voltage stabilizer, since failure of the pump can have serious consequences for the entire system.
Pumps can be divided into two groups relative to the position of the engine: with a “dry” rotor and a “wet” rotor. By voltage type: models operating from a 220 V network and pumps operating from 12 V power sources.
The motor in pumps with a dry rotor is isolated from the impeller submerged in water by sealing rings. Compared to pumps with a submerged motor, dry pumps have higher efficiency.
However, the disadvantages include high noise levels, the need for regular maintenance and shorter engine life. Therefore, in a private home, as a rule, circulation pumps with a “wet” rotor are used.
The choice of pump power type depends on the possibility of natural circulation of water in the system. If it is impossible without the participation of a pump, then the choice should be made in favor of an option that supports 12 V voltage and an uninterruptible power supply.
Otherwise, in the event of a power outage, the water may boil and the system may fail. If natural circulation is possible, then it is better to purchase a more common and cheaper option powered by 220 V.
By connecting a 12-volt pump to an uninterruptible power supply, you can not worry about the functioning of the heating system
When installing a pump with a 220 V power supply, it is necessary to ensure that the heating system can operate during a power outage. To do this, install a shut-off valve on the pipe, and bypass it by installing a bypass pipe with a pump (the so-called “bypass”).
A filter tap is installed on the bypass pipe in front of the pump, and then a shut-off valve. By adjusting the position of the shut-off valves on the main and bypass pipes, you can turn on the forced and natural circulation mode.
As a rule, the pump is installed on the “return” near the furnace so that the temperature of the liquid that will pass through the device is the lowest. This will significantly extend the life of the pump.
In addition, it is necessary to place the maximum possible number of heating system controls in one place, so that in the event of emergency situations, measures can be quickly taken to eliminate them.
Installation of a bypass pipe (by pass) allows the heating system to operate during a power outage, and also makes it possible to remove the pump without draining the water
Rules for using the expansion tank
When heated, a liquid expands, and if this happens in a closed system, the pressure inside it will greatly increase, and an increase in pressure is fraught with water breakthrough. Using a safety valve is not advisable, since after the water cools and its volume decreases, air will be introduced into the system.
Therefore, in heating circuits with forced water movement, special expansion tanks are used, which are of open or closed type. Their volume is calculated based not only on the maximum thermal expansion of the liquid (5-7%), but also taking into account the possibility of boiling of the system.
An open-type tank equips the water circuit of a gravity-type stove heating system, that is, with natural transportation of the coolant. It is a metal container of arbitrary shape located at the very top of the heating circuit. It communicates directly with the atmosphere, due to which the coolant partially evaporates.
The pipeline is connected to the bottom or lower quarter of the tank, and a pipe is welded to the top of it to drain water in case of overflow and allow air to escape from the system. Practice shows that the volume of an open tank should be at least 15% of the volume of water in the heating system.
An open type expander tank is usually located in a technical room and its appearance does not matter at all
A closed or membrane type tank is a closed vessel with a membrane inside. When the water heats up, it increases the pressure, stretches the membrane and enters the tank. If the pressure exceeds, the automatic system is activated and the excess coolant is discharged into the sewer.
After the first discharge, there is usually no longer any reason to produce it again, since the volume of coolant becomes equal to the volume of the system.
A closed membrane tank is mounted in front of the pump. Such a container, unlike an open-type tank, cannot get rid of air on its own, so at the top of the heating circuit it is necessary to install a Mayevsky valve (mechanical air vent) or its automatic equivalent.
The only element of a membrane tank that can fail over time is the membrane, so it is better to buy a tank with the ability to replace it.
When purchasing a closed-type tank, which is sometimes called a hydraulic accumulator, the main thing is not to confuse it with a hydraulic accumulator for water supply.
For a membrane tank used in heating, the operating temperature is up to 120°C and the pressure is up to 3 Bar. For water supply, tanks with temperatures up to 70°C and pressure up to 10 Bar are used.
Choosing between pipes and radiators
As a water circuit for stove heating, you can use a system of plastic pipes with radiators (batteries) or a system of metal pipes. The main advantage of using radiators is that they look more beautiful compared to massive air ducts.
Plastic wiring can be easily hidden in the floor, as it does not give off heat. Although according to the rules, the water heating wiring must be open. However, polymer pipelines have limitations: they cannot be laid where there is a risk of melting and direct UV exposure.
The advantage of metal pipes is the lower price of the entire heating circuit, ease of installation and fewer problems encountered during operation of the system.
The use of metal heating pipes instead of a radiator system with metal-plastic connections is justified if the aesthetic component of the room design is not important
A significant advantage of a system with radiators is the ease of temperature adjustment. Even the most accurate calculations of room temperature can be adjusted. For example, a temperature of 19-21°C is recommended for a small child under 6 months, while a comfortable temperature in the rest of the house is considered to be 25°C.
To ensure this temperature for a long period of time in the room, you must completely or partially close the heat supply valve to one of the radiators. In the case of a metal pipe, the issue can also be solved, but in a more complex way: reduce the heat transfer of a pipe segment using polyurethane foam or foil shell.
Another heating circuit option can be a water heated floor. This is a very comfortable type of heat supply for a person, but installing a heated floor is much more labor-intensive than the previously discussed options.
In addition, when using a heated floor, it is not possible to provide a slope for the natural circulation of water, which, in combination with the small diameter of the underfloor heating pipes, leads to a mandatory condition for the use of a circulation pump.
To push water through the underfloor heating pipes, you must use a pump; natural circulation will not work with this geometry of the heating system
Types of air heating
The use of hot air to heat rooms has been known to people since ancient times. During excavations in Pompeii, “preserved” by the ashes of Vesuvius, walls and foundations of buildings were found, the design of which clearly indicated the use of “hypocausts” - ancient centralized air heating systems.
With the fall of Rome, air heating was forgotten in Europe for many centuries, like many other things that were the legacy of the Empire. The second birth of centralized heating systems occurred in the 14th and 15th centuries. It is curious that heating the walls and floors with warm air was used to heat the chambers of the Moscow Kremlin long before such a heating method was remembered in Western Europe. Surprised foreign ambassadors told their fellow countrymen about the Moscow wonder, and for some time central air heating in Europe was called ... “Russian heating.”
Air heating became widespread in modern times, when the industrial revolution moved large masses of people to cities. It was this type that was used for the first central heating of apartment buildings in London, the then industrial capital of the world.
Direct-flow heating system
The basic design of the first air heating systems was quite simple. In the lower part of the building, usually in the basement, the air was heated by burning wood, charcoal or coal. The heated air rose by gravity through cavities in the floor and walls, and came out through special outlet openings on the roof. The air inside the room was heated indirectly - from the floors and walls heated by hot air.
Scheme of the Roman hypocaust
The effectiveness of such a system, called direct-flow, was very modest, b o
The majority of the energy was spent on heating the entire depth of the walls and floor, as well as on “heating the street” - still hot air was thrown out through the outlet openings. It was impossible to avoid this: it was the temperature difference in the system and outside that created the draft, due to which the air moved.
Recirculation heating system
The revolution in air heating was made by the use of a new type of fuel - natural gas. Heating the air with cleaner fuel, coupled with the advent of advanced air filters, made it possible to pump heated air directly into the room, thus creating a closed cycle of air circulation in the room.
Air heated by gas or electric heaters rises through air ducts and is supplied to the upper part of the building. Giving off heat, the air cools down and, gradually being replaced by new masses of heated air, falls down, again falling into the heater.
Recirculating air heating system
This recirculation heating scheme is called gravity, because air circulation is carried out without the use of any special devices only due to gravity.
If the building structure prevents the free circulation of air, a recirculation scheme with forced ventilation is used. In this case, hot air is pumped into the premises and taken into the heater using special fans.
Heating a building with air recirculation is the simplest and most inexpensive option, which is ideal for use in non-residential premises, workshops, and warehouses. The fact is that repeated passage of air through the heating system negatively affects its quality. Air heating of a private house or apartment using a recirculation scheme requires additional costs for humidification and ionization of the air.
Therefore, to heat residential premises, recirculation with a partial influx of outside air is more often used. With this scheme, the “exhaust” air is gradually removed outside with its gradual replacement with fresh air.
Recirculation with partial supply of outside air
There are also various combined air-water or air-oil heating schemes, which are mainly used for central heating of several buildings. The coolant carries energy from the central boiler room to the buildings, where a powerful radiator plays the role of a heating element in the air heating system.
The main advantages of air heating units of the Vulcan brand
If you need a heating unit, then you can consider one of the models described above as an option. The main advantages of these devices are:
- high efficiency of the fan heater;
- low operating costs;
- optimal air jet range;
- reduced noise level;
- high thermal power;
- full regulation of technical parameters;
- simple and quick installation and assembly.
With the help of this equipment you will be able to heat and then automatically maintain the desired level of air temperature in a room or building. In this case, the coolant will heat up to 90 °C. The Vulcan heating unit does not use air masses from the outside in its operation, since it is designed to recirculate the air that is inside the building.
As an additional feature, we can highlight the fact that the units have the ability to redistribute air masses; this is ensured by built-in axial fans and guide grilles in the form of blinds. With the help of the latter, flows can be directed to almost any part of the structure or room.
How does this system work?
Air heating is very practical. Happy owners who heat their homes in this way note undeniable advantages:
- Absolute safety. Highly sensitive automation clearly controls all processes. At the slightest threat of leakage or other danger, it instantly blocks the equipment. In addition, there are no pipes filled with coolant in the system, therefore, in principle, their ruptures, leaks, etc. are impossible. troubles.
- High heating speed. It takes from 20 to 40 minutes to completely warm up the room, even if the initial temperature in the house was negative.
- Economical. Low energy consumption, high efficiency and the absence of intermediate coolants make air heating of a private home extremely profitable.
- Reliability and durability. Subject to proper design, installation, regular maintenance and necessary repairs, the system will last at least 20 years.
- Easy to use. Automatic control of the processes of starting, stopping and changing modes allows you to easily regulate the temperature in the house and at the same time protects against possible errors.
- Affordable installation cost and fairly quick return on investment.
- Aesthetics. The absence of conventional radiators in the room makes it possible to install windows of almost any size, frees up space and opens up opportunities for design experiments.
Traditionally, air heating systems involve the use of a heat generator. The air pumped into the heat exchanger warms up to 45-60° and, moving through the air ducts, heats the room. The cooled air is returned to the heat generator through grates in the floor or through return air ducts.
The main parts of the heat generator are the heat exchanger and the air-directing fan
Air heating can be done using several options:
- heat pump;
- gas burner using both bottled and main gas;
- hot water from a centralized boiler room;
- diesel burner.
The average air flow in the system is from 1,000 to 3,800 cubic meters. m per hour, the pressure is 150 Pa. In large rooms, heat loss may occur from long air ducts. In such cases, it is worth thinking about installing several heat generators that operate without air ducts. According to experts, the length of the main air duct should not be more than 30, and the branches - 15 m.
Using the system exclusively for heating rooms is somewhat irrational, so most often an air cooling unit is introduced into the device, from which an external air conditioning unit is diverted. Thus, the system combines heating and air conditioning, allowing you to maintain a comfortable temperature in the house at any time of the year. In addition, you can use additional equipment: a humidifier and an air sterilizer, creating a unique healthy microclimate in the rooms.
You can arrange air heating for your cottage using:
- Natural ventilation. The simplest option is when the air rises due to initial heating. It enters the rooms through air ducts, heats them and returns to the heat exchanger. The main disadvantages of natural ventilation are clearly manifested in the case of additional cool air entering through doors or windows. In this case, cold air, of which there is more, accumulates in the lower part of the room, creating a temperature imbalance and interfering with the normal functioning of the system.
- Forced ventilation. Air circulation is provided by a fan that creates pressure in the system. The room warms up much faster due to the higher speed of air movement. Also, in devices with forced ventilation it is easier to regulate the temperature in the rooms. A minor design flaw may be the noise coming from the air ducts.
Basic elements of the heating system
Before making air heating at home with your own hands, you need to review all the elements, components and significant details of the structure.
Devices for heating air flows
The equipment is designed to heat flows to the required temperature. Heat sources are used that heat the masses by passing them through a heat exchanger with heated steam, or heat the flows inside the heating element.
There are 4 types of heat generators used for air heating systems:
- Direct heating fuel systems, where the flows are heated due to the combustion of any fuel. This can be coal, diesel fuel, firewood; this type includes air-fired gas heating - when burned, the gas warms up the air, which is transported through air ducts throughout the premises.
- Electric units with direct heating are powerful fan heaters mounted to air ducts.
- Indirect heating units. The system involves installing a heat exchanger where hot liquid constantly circulates. The liquid is heated by any known method, and as an option, you can consider connecting the coolant from the central water supply system.
- Combined system. This is a universal option that combines several types of air heating, for example, liquid and electric options. The combined system is suitable for installation in private homes. In this case, the rooms will be heated even when the power supply is turned off.
Channels for transporting air masses
Air ducts are a mandatory element of the system. Through them, the coolant enters the room and returns back for heating. Most often, a circular transportation circuit is installed, which has more functionality than single-pipe circuits.
A circular structure is made of two main pipelines made of galvanized metal. One line is supply, the second is return. Air ducts of a smaller cross-section are connected to the pipes, which are laid in the rooms. Flexible air ducts must be sealed and insulated. Aluminum tape is used for sealing, and foil heat insulators 25-30 mm thick are used for insulation. The mains also need to be insulated with foil insulation 3-10 mm thick.
Fans
Duct fans are needed for forced transportation of a flow of heated air. Installation on the supply and return lines is selected taking into account the possibility of adjustment, operation at different speeds, resistance to voltage surges, and smooth start-up. The technical parameters of the units must exactly match the specific heating system in order to maintain the pressure performance of all equipment.
Grilles and diffusers for flow distribution
All air ducts located in the room are connected to these elements. Grilles and diffusers are needed to provide air conditioning and heating systems by uniformly mixing air flows. Wall-mounted and floor-mounted models with adjustable and non-adjustable blinds are available for sale.
In-channel dampers and valves
Details are important to ensure the throughput of the entire structure. Throttle dampers are fixed in the supply lines to regulate air flows to different rooms. Valves are needed for different sections of air ducts, for example, a supply element is required to regulate the flow of air from the street.
Air preparation equipment
When setting up homemade air heating combined with air conditioning, the system must be equipped with filters. These can be carbon, mechanical or electrostatic devices that clean air flows from impurities. The scheme is also complemented by ionizers, humidifiers and other types of units.
Automatic control systems
To simplify the coordination of the entire circuit, it is recommended to select a control unit. The choice is made according to the type of heating functionality, allows you to control the operation of devices, change the program of actions, distribute air flows across zones depending on the needs of the user.
Advantages and disadvantages of air heating
When arranging such heating in a separate house, there are advantages and disadvantages. Its advantages are such features as:
- high efficiency, in some cases exceeding 90%;
- not burdened with a large number of complex, expensive and heavy parts such as radiators and steel pipes;
- you can set optimal microclimate conditions for each room;
- almost instantaneous response to temperature control;
- due to the fact that the fans are compatible even with solid fuel stoves, you can heat absolutely all rooms of the house without restrictions;
- a filter system along the path of circulating air, cleans it of allergens, dust and other particles;
- a humidifying filter built into the design;
- in the summer, with forced air circulation and the heat generator turned off, it works as a powerful cooling system;
This heating design does not pretend to be perfect, as it also has disadvantages:
- this heating method must be provided for by the design of the house during its construction;
- its installation is relatively complicated;
- needs regular maintenance;
- difficult to modernize;
- this heating method makes it necessary to take care of the cleanliness of the filters and regulate the saturation of the atmosphere with moisture;
- needs a backup source of electricity to operate efficiently during interruptions in its supply from the main network.
Air heating units
8, 366-84-44, 366-85-29
In air heating units AO2, hot water or steam at a temperature of 95-150°C is used as a coolant. The AO-2 unit heats recirculated, external or mixed air.
It can also be used as an air cooler when cold water is supplied and there is a tray for collecting condensate.
The fan of the AO2 unit is a general-purpose axial fan with a supply voltage of 380 V.
The heaters are bimetallic, spiral-knurled. KSk water heaters are used if the coolant is hot water, and if steam is used, KPSk steam heaters are used (heat exchangers are also bimetallic, spiral-roll type VNV-113 and VNP-113 with 3-4 rows of tubes in the direction of air movement. If the coolant water, then use type VNV-113, if the coolant is steam, then VNP-113).
The air passage and air distribution valve are made of 2 mm sheet steel.
The efficiency of using the supplied heat, the size and configuration of the air flow, and the degree of comfort depend on the configuration of the valve of the AO-2 unit. As standard, the valve blades have a horizontal position, which allows you to regulate the heat flow in the vertical plane. The valve blades are made of 2 - 3 mm unformed steel and are bolted to fix the position of the blade and the direction of the outgoing air flow. Each blade is individually manually adjustable.
The base of the air heating unit AO2 has 4 mounting holes that allow you to fix the unit on the installation site or in another place.
– ambient air temperature from minus 10 to + 35°С;
– relative air humidity up to 80% at a temperature of 25°C;
– environment – non-explosive, with permissible content of aggressive gases, vapors and dust in concentrations not exceeding the values established by GOST 12.1.005-88.
The air supplied by the fan is heated, passing through the heater, and supplied to the room.
AO-2 units have high thermal performance and efficiency, which are ensured by the optimal distance between the fan and the heater, eliminating stagnant zones when air moves in the unit, as well as the use of high-quality heaters and axial fans.
air heating units
How to perform a preliminary calculation
In fact, it is very difficult to independently calculate air heating. Often only specialists can do this. The calculation determines:
- heat losses for each room in a heated house;
- type of heater and its power, which should be comparable to the amount of heat loss;
- the required amount of heated air, taking into account the heater power;
- required diameter of air channels;
- pressure loss in the air installation, etc.
The right decision would be to order an example of calculating air heating at home from specialists. It is likely that as a result, engineers will offer several options; all that remains is to choose the most acceptable one.
Heating with air is economical, safe, extremely easy to use and at the same time durable and reliable. It is not surprising that it is gaining more and more popularity. However, it is quite difficult to arrange air heating with your own hands. Possible errors can lead to unpleasant consequences in the form of drafts in rooms, noise, overheating of equipment, etc. Those who choose this practical system should seek help from professionals. A well-designed and high-quality installed system will provide warmth in your home for decades.
Air heating is actually an ancient thing. And it goes without saying that, again, Europe and America are ahead of the rest. Because it's not like that! After all, an ordinary Russian stove is also one of the options for air heating! How many villages are there in Russia where they still use this heating method? There are enough of them! And yes, I would not classify such a stove as environmentally friendly. Still, when burning fuel - whether wood or gas - it harms our planet. But air heating can be done completely without harm to nature. After all, you can use the energy of the sun! This idea is not so new anymore, and there are even people who brought it to life!
Installation standards
The installation conditions for VK are simple, but for specialists, there are many nuances that need to be known so that the user is not disappointed in choosing an air-heating boiler.
The boiler looks great in the interior. Photo source: ogodom.ru
Features of VK installation:
- The boiler is installed indoors during the construction of the building.
- Specialists must first complete an installation project, taking into account the actual heating and structural characteristics of the building, in accordance with which the main and auxiliary equipment will be selected.
- The system must be equipped with a backup power source.
- To increase efficiency, the boiler should be installed in a room with well-insulated walls.
- The combustion room must have a good ventilation system for ventilation.
- Air ducts make sense if you are installing them in multi-level houses with an area of more than 100 m2.
To select a VC you will need the following data:
- AC power taking into account heat losses in the building;
- the rate at which heated air enters the room;
- technical data of the air duct system;
- VK installation location.
If installing a boiler seems to be a difficult and impossible task for consumers, it is better to entrust it to a company that will perform the entire set of installation and adjustment work for the home heating system; in this case, inconsistencies can be avoided and reliable and safe operation of the equipment can be ensured for many years.
Heat pumps and ducted air conditioners
Sometimes you can find combined climate control systems, which include components such as:
- Duct air conditioner, which, depending on the weather, is capable of heating, cooling and drying the air.
- Dust filter.
- Ultraviolet filter that disinfects the air.
- Supply and exhaust ventilation system.
Duct air conditioners
In this case, the source of thermal energy is electrical energy. Studying the reviews, it can be noted that this scheme of work is very convenient. After all, you have only one control unit that controls absolutely all characteristics from one point. If we compare it with a traditional system, where the fan is somewhere in the attic, air conditioners are in the rooms, heating with air through pipes is somewhere else, then such a system seems more thoughtful and improved.
In addition, with such a combined system, you can preserve the interior of the premises. Indeed, in this case, only the ventilation grilles will be visible, since air heating, as can be seen in the photo, does not require the installation of wiring and radiators.
Warm air outlet for air heating system
Of course, there are several disadvantages to this type of scheme. The cost of the finished system is quite high. For example, if you take Chinese duct air conditioners with a heating power of 15 kW-hours, then they will cost about 70,000 rubles.
The outdoor unit, which takes heat from the atmospheric air, can operate at temperatures no lower than -15 - -25 degrees Celsius. And as the temperature outside drops, the efficiency of the system will only decrease.
An alternative to such a system is a geothermal heat pump. So, if in winter the air cools to a very low temperature, then below the freezing depth the earth is constantly warmed up to 8-12 degrees. A heat exchanger with a sufficient area is immersed in the ground - and you will have an almost endless resource of heat that needs to be pumped into your home.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Interesting information on calculations and design of air heating is shown here:
In this video you can see two options for relatively inexpensive installation of air heating systems using Russian-made devices and materials:
Air heating is a worthy and profitable option for heating a private home. It is more efficient than traditional water systems and can significantly improve the quality of life in your home. But to ensure the successful implementation of this idea, the system must be correctly calculated and professionally designed.
Do you have any questions? Or do you have personal experience using air heating for your home? Please share your own opinion on this issue. Leave comments, ask questions, share tips in the block below.
Types of wood stoves by material of manufacture
Wood-burning stoves, while still remaining an excellent source of heat, fit well into modern heating systems for private households. Wood-burning stoves can be divided according to the material of manufacture into the following main groups:
- brick (stone);
- cast iron;
- steel.
Brick wood stoves
Brick kilns are the most durable and expensive to build. A good stove is not cheap, and it is not easy to find an experienced installation technician. To build such a stove, fireclay and refractory red bricks are used, as when laying a wood-burning fireplace, special mastics for masonry, cast iron doors, grates, and valves for the chimney pipe. A brick oven takes a long time to heat up, but also retains heat in the room for a long time.
Cast iron wood stoves
Cast iron stoves are usually used as an additional heat source. Manufacturers create not only heat sources from cast iron, but also beautiful products that fit perfectly into the interior of any home. Heated cast iron retains heat excellently, and the presence of a hob allows you to cook food or heat water for domestic needs.
Metal wood stove
A metal wood stove can quickly raise a room's temperature using minimal fuel, but the thin steel they're made of doesn't allow the heat to last long. The simplest type of metal stove is the well-known “potbelly stove,” which is often used to heat small country houses or garages.
As mentioned above, the stove itself only heats the room in which it is located. In order to transfer heat to other rooms, there are two ways - organizing air heating with an air duct system, or water heating from a stove with a heat exchanger, piping and heating radiators. Air heating is easier to install, but has a number of disadvantages, which together outweigh the use of a traditional water heating circuit.
The disadvantages of air heating include:
- installation of air ducts through which warm air is distributed must be carried out at the stage of building a house, since they are quite bulky;
- the need to install fans with a flow rate regulator, which improve air circulation but produce noise. Installing a furnace with fans in the basement of the house can solve this problem.
- The need to install additional air filters to prevent dust transfer.
The advantage of air heating, which at the same time is also a disadvantage, is low inertia. That is, the rooms begin to warm up immediately after the stove is lit, but they also cool down quickly.
Another advantage of air heating is the absence of heating radiators. Air ducts, as a rule, are hidden under the ceiling of the building, and the space under the windows remains free.
In most cases, owners of houses with stove heating opt for a water heating circuit for a private home, so we will analyze this option in detail.
Where can combined systems be made?
The area and number of floors in our example are very arbitrary. It is also necessary to coordinate their operating modes.
It’s one thing: connecting a radiator heating system to a boiler when all the functionality for this is already included in the boiler. They propose to install polypropylene supply and return pipes in a layer of sand under the screed along the foundation. It can be single-pipe or double-pipe.
In some situations, when all the radiators are closed and the heated floor is running, the boiler pump and the underfloor heating pump work sequentially, interfering with each other. Installation of combined heating in a system with a gas boiler The most difficult moment in the process of installing combined heating is the need to supply coolant with different temperatures from the manifold for the heated floor and radiators through two pipes. Depending on the temperature at the outlet of the in-floor circuit, the mixing valve opens or closes, increasing or decreasing the amount of hot coolant from the supply in the recirculation circuit.
This is necessary to ensure the tightness of all joints made. Air heat pump is the main source of heat Air heat pump Before considering the positive and negative aspects of existing heating units, let's talk a little about air heat pumps.
Where can combined systems be made?
The collector is mounted in a special box made of galvanized steel that matches its size. In this case, the type of coolant or heat source does not matter.
Designation of the main elements of the circuit: wall-mounted gas boiler with built-in circulation pump and expansion tank; hydraulic separator thermo-hydraulic separator or hydraulic arrow ; collector - collector beam for connecting heating circuits; radiator heating circuit circulation unit; mixing unit kennel water thermoplastic floor; safety thermostat. The three-way thermostatic valve of the second type is distinguished by the fact that it provides regulation of the supply intensity of only the hot flow. In more complex systems, the controller is also guided by a weather sensor, making a preventive change in the heating power.
4 Proven water heated floor connection diagrams
As a result, the coolants are mixed as follows: liquid from the return pipe is supplied continuously, and hot liquid is supplied only when necessary. In this case, the in-floor structures will be durable, reliable and durable.
A special heat-sensitive device is used. Heating with a solid fuel boiler Combined heating with a solid fuel boiler is a closed gravity system with a heat storage device. We combine heating. Warm floor + radiators. A simple solution
How to draw up a heating project
If you decide to install a VO system, it’s worth understanding and developing a detailed project. Key points to consider when planning:
- heating speed (warm air supply) and room area;
- heat generator power, which is calculated based on the characteristics of the house and possible heat losses (condition of doors, windows, walls);
- dimensions of air ducts and the subsequent value of air pressure losses.
Please note that for optimal operation of the system, all calculations are carried out by competent specialists. Due to miscalculations and attempts to independently “figure out” the operation of the system, intense heat loss, strong noise and vibration during operation are possible.
What is combined heating
Combined (mixed) is a heating system that contains both traditional high-temperature (conventional radiators, convectors) and low-temperature (warm floors, less often warm walls) heating devices.
Water floors in a combined system are connected in two ways:
- For existing heating boilers. The advantages of this solution are a reduction in the estimated cost of equipment and a reduction in installation time. Disadvantage - additional heating cannot function in autonomous mode. This causes an increase in thermal energy consumption, and the efficiency of using heated floors decreases.
- Install hotel boilers for floor heating. The disadvantage is a significant increase in cost. Advantages: complete autonomy; water floors can be used independently of radiators. This may be necessary for a small heating of the room when the batteries are already turned off, for example, in the autumn-spring period.
1st floor - heated floor, 2nd floor - radiators