Of course, if you are faced with the task of installing heating, then specialists will come to you and tell you how much and what you need. But you want to protect yourself from mistakes, voluntary or involuntary, and to be confident in the correctness of what you are paying a lot of money for. It is necessary to make the house warm, and at the same time save as much as possible on installation and in the future on use. We will try to understand in this material how to achieve what you want without losses.
Heating installation is a job that can only be performed by qualified specialists Source climatext.es
Single-pipe system
This scheme is a cheaper and simpler solution to the problem of how to properly install a heating system. The installation is carried out in the form of a closed ring, where all batteries are connected in series to each other, and the coolant moves through the batteries and returns to the boiler.
This scheme allows for some savings due to simple installation and design. However, one significant drawback very often forces one to choose a two-pipe system. The fact is that the coolant gradually cools down as it moves through pipes and radiators. This results in the water in the last radiator having a lower temperature. Increasing the boiler power leads to strong heating of the first batteries. Adding a certain number of sections to the last battery also cannot be called effective. This causes some inconvenience, so very often homeowners refuse simple and cheap single-pipe wiring.
A pump for forced circulation of coolant helps solve this problem. The device is connected to the boiler, and the liquid moves through the system, practically without changing the temperature.
However, this case also has its drawbacks:
- Firstly, purchasing a pump is an additional expense, which leads to increased costs for installing a heating system in a private home.
- The pump must be connected to the power supply, which causes an increase in electricity consumption.
- Dependence on electricity makes the pump ineffective when there is a power outage, therefore, no light - no heat in the room.
Thus, a single-pipe heating system can be used in small houses where no more than three heat exchangers are connected in series. Therefore, for large premises where the installation of a large number of radiators is required, a simple and reliable single-pipe system is not suitable.
Classification of polypropylene hoses (4 classes)
Often four classes of hoses are indicated, since the third is practically not used, but GOST specifies five classes for polymer products.
Polypropylene hoses are divided into classes according to heat resistance and operating pressure values:
- Class 1 - hot water distribution systems up to 60 °C;
- Class 2 - hot water distribution systems up to 70 °C;
- Class 3 - underfloor heating, low-temperature radiators up to 50 °C;
- Class 4 - underfloor heating, low-temperature radiators up to 70 °C;
- Class 5 - high-temperature radiators up to 90 °C;
There is also a class “XB” - intended for cold water supply.
It is assumed that the system will operate in certain temperature conditions, which differ for each season and off-season. For example, for high temperature radiators, the system should last 50 years: 14 years at 20°C, 25 years at 60°C, 10 years at 80°C and 1 year at 90°C. This means that in a region with an extended heating season, the service life will be reduced.
The emergency temperature for classes 1-2 is 95 °C, for class 3 - 65 °C, for classes 4-5 - 100 °C. That is, pipes can withstand significant excess operating loads for a short time, up to 100 hours over the entire period.
The maximum working pressure of thermoplastics should be:
- 0.4 MPa;
- 0.6 MPa;
- 0.8 MPa;
- 1.0 MPa.
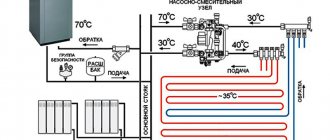
Two-pipe heating system
Do-it-yourself installation of solid fuel heating in a private house using this scheme is considered more effective than the previous option. Despite the complexity of execution and high cost, the system has a significant advantage: uniform distribution of heat across all batteries and the creation of comfortable living conditions.
A two-pipe system involves connecting a pipe with hot water to each heat exchanger and discharging the cooled coolant through a separate return pipe. In this case, the simultaneous supply of coolant allows each radiator to be evenly heated, regardless of its location relative to the boiler.
This scheme requires more materials due to the complexity of the pipe layout.
The operation of a two-pipe system can be organized according to a collector or beam scheme. In any case, heating installation from a boiler in a private house should be carried out by an experienced specialist.
In the first case, a collector is installed in the attic, thanks to which the working medium is evenly distributed throughout the pipes of the heating system. Cranes designed to cut off circuits are also installed here. This allows you to repair any area without affecting the operation of the entire system.
However, such a reliable and efficient system still has a drawback. It consists in the need to use a large number of materials, including shut-off valves, pipes, sensors and control devices.
The radial wiring option involves installing a supply pipe at the highest point of the room and installing bends to each radiator.
A two-pipe heating system can operate without a circulation pump due to its design, while operating efficiency is at a high level.
Conclusion
As you can see, today there are a large number of types of circuits and wiring. For each specific case it is necessary to choose the appropriate one. However, the principles for installing all systems discussed in the first part of this article always remain the same. It must be said that do-it-yourself installation is carried out on the basis of the same rules.
The most important thing in this matter is to draw up a competent scheme that will be effective in this case. To do this, some rather complex calculations must be made. The correct connection of all structural elements is also of no small importance.
Rules for choosing equipment for a heating system in a private house
To answer the question of how to properly install heating, it is important to choose the right equipment.
The main element of any heating system is the boiler. His choice depends on the preferences of the consumer and his financial capabilities.
Hybrid boilers can be safely called universal, since they operate on gas or solid fuel with equal efficiency.
Boilers equipped with a set of automation systems show a higher efficiency.
Each boiler model is characterized by a certain power, so you should choose the device that is most suitable for specific conditions. In this case, the material side should also be taken into account.
Drafting
Before installing heating in a private house, it is necessary to draw up a heating project. For this purpose, perform the following actions:
- They make a sketch of the house.
- The house is divided into zones depending on the degree of comfort in each room.
- Thermal energy loss indicators are determined separately for each room.
- The number of sections is calculated individually for each battery.
- Select the type of heating system.
- Calculate the boiler power and the required amount of materials.
Preparation
DIY screen installation for heating pipes
Before you begin heating installation, you will need to perform preliminary work and prepare the necessary material:
- The tool is prepared, the type and heating scheme is determined, and a boiler is purchased according to the calculation.
- The type of radiators and their volume in each room are determined.
- The need for materials (pipes, fittings, taps, fasteners, etc.) is calculated.
- Everything you need is purchased at the retail outlet.
Zoning
In order for your stay in the house to be comfortable and cozy, and the consumption of thermal energy to be economical, it is necessary to correctly distribute heat throughout the rooms. In this case, the following rules can be taken as a basis:
- The average comfortable temperature in the premises should not exceed 240C.
- In the bedroom, comfort is felt at a temperature of 220C -250C.
- For the bathroom and toilet, the figures drop to 210C. The same indicator is set for guest rooms.
- In the kitchen, dining room and work areas, you can reduce the temperature to 18-22 degrees.
- For a comfortable stay in the hallway, garage and passage area, you can set the temperature within 120C.
Heat loss calculation
At this stage, all external walls and corners are taken into account, since large heat losses are observed in these places. The calculation takes into account the thickness of the walls and the thermal resistance of the material from which they are made.
Each element of the house fencing has its own heat loss values. For example, at a temperature of -300C, up to 135 W per 1 m2 goes through a double-glazed window. At the same temperature levels, heat losses through solid double wooden doors amount to up to 234 W per 1 m2. Through the attic floor at -30 degrees, up to 35 W of heat per square meter is lost. 1 m2 of wooden floor above the basement deprives the room of 26 W of thermal energy.
Selection of radiators and number of sections
Radiators are a fairly important part of the heating system, as they determine the amount of heat required in the room and affect the durability of the entire system.
Batteries can be:
- Cast iron.
- Steel.
- Aluminum.
- Bimetallic.
Cast iron batteries are characterized by high heat transfer, but at the same time they have a fairly large mass.
Bimetallic radiators are characterized by durability and good heat transfer. However, the cost of such elements is too high, which forces most consumers to abandon this option.
Aluminum radiators have a short service life, and steel heat exchangers do not heat the room well in severe frosts.
The number of sections is calculated as follows: heat losses are determined and multiplied by the safety factor, which is equal to 1.2. Then the resulting value is divided by the thermal power of one radiator section. When receiving a fractional number, round up.
A simplified version of determining the number of battery sections involves using the following scheme: one radiator section is capable of heating about two square meters of a room up to 3 meters high. If heat losses are high, it is necessary to purchase sections with a small margin.
The optimal place to install heating system radiators is the area under the window. In this case, less heat is lost through the window opening. However, it is possible that some of the heat from the battery will be spent on heating the wall. Installing a foil “screen” on the section of the wall behind the radiator helps prevent this. Reflecting from the foil, the heat flow returns to the room, and it is not the wall that is heated, but the air in the room.
Pipe soldering
To connect pipeline elements, a special soldering iron is used, which has two nozzles. Each pair of nozzles corresponds to a specific pipe diameter. One nozzle heats the outer surface of the pipe, and the other heats the inner surface of the fitting at the same time. The heating process takes no more than 7 seconds. The elements are then connected.
During heating and connection, it is prohibited to rotate the mounted pipeline elements.
After joining, it is necessary to hold the parts for up to 30 seconds so that they cool down and the soldering is completed evenly. By sequentially connecting the pipeline elements, its turnkey installation is carried out.
Determining boiler parameters for installation
In order for the boiler to cope with any emergency, it is necessary to choose equipment with a power reserve. In this case, the room temperature will be comfortable even in severe frosts.
The required power is calculated as follows:
- The power of each device connected to the boiler, including radiators, is determined.
- The obtained values are summed up.
- The amount is multiplied by the ventilation heat loss coefficient equal to 1.4.
- The result is divided into power utilization factor and boiler efficiency.
- Based on the obtained value, the appropriate equipment is selected.
Carrying out installation work
Every homeowner wonders how to properly heat the house. Do-it-yourself installation of a heating system in a private house is carried out in several stages:
- First, they arrange the room where the boiler will be installed. The interior decoration of this part of the house should be made of fire-resistant materials. You should also ensure good ventilation.
- When installing the boiler, remember that the equipment should not stand tightly on the floor, press against the wall or reach the ceiling. A small offset must be maintained in all measurements. In addition, it is important to ensure free access to the boiler.
- After installing the boiler, you can connect a circulation pump to the system or install a collector. The actions depend on the type of heating system selected.
- Next, the necessary control sensors and metering devices are mounted and secured, as well as elements that allow regulating the operation of the entire system or a specific section of it.
- At the next stage, the installation of main pipelines is carried out. To fix the pipe elements, holes are made in the walls using a hammer drill. During the work, you should adhere to the basic rule for installing a heating system: for each linear meter, make a slope of 5 mm. Neglecting this rule can reduce the efficiency of the entire heating system, so you need to approach this stage responsibly.
- The completion of installation work can be called the installation of radiators. To fix them on the wall, make marks with a pencil or marker and use a puncher to punch holes into which the brackets are inserted. When making markings, adhere to the following: the distance from the floor to the lower level of the radiator should be 10 cm, from the wall to the rear surface - 2 cm, from the window sill - 10 cm. The inlet and outlet of each radiator is equipped with a valve for easier replacement or repair.
- After installing all system elements, a check is performed. When installing a gas boiler, the presence of a gas service representative is required.
From all of the above, we can conclude that installing heating systems in a private house is not a complicated process, which allows you to do most of the work yourself. The main condition is compliance with the rules and leisurely installation. However, this is possible if you have a lot of free time. If the time frame for completing installation work is short, then you can entrust some stages to specialists. In some situations, this can save both time and money.
In order for the heating system to function flawlessly for a sufficiently long period of time, it is necessary to purchase only high quality materials. By purchasing high-quality radiators, you can achieve maximum efficiency of the heating system and reduce fuel costs.
What is SNiP?
The rules for the design and installation of heat supply, ventilation, and air conditioning systems are described in detail in SNiP, which is a set of normative documentation for construction. In addition to building codes and regulations, SNiP also describes sanitary, fireproof and environmental measures that should be observed when operating such systems.
Of course, in addition to SNiP heating, ventilation and air conditioning, there is a whole list of SNiPs, SanPiNs, GOSTs, as well as other documents that describe the requirements for compliance with the required dimensions, tolerances, safety measures, and some hygienic conditions. When drawing up a project for a particular system, it is very important to comply with the norms and rules given in the documents. Therefore, you should familiarize yourself with SNiP in more detail. There are various SNiPs, which disclose important rules for the design and installation of heating, air conditioning and ventilation systems.
For example, there are such versions of documents:
- 2.04 05 91 heating, ventilation and air conditioning: contains fire safety requirements for these systems.
- 01/41/2003: sanitary, environmental, and fire safety standards for heat supply systems are described. This is a newer version.
By observing joint venture heating, ventilation and air conditioning when developing a project and carrying out installation work, you can be confident in the quality and reliability of the equipped system. But designing a system correctly is not enough. It is also important to use it correctly. For these purposes, operating instructions for the heating and ventilation system have been developed, which establishes a number of requirements for the use of the heating network, testing, startup, and adjustment of the structure.