Self-manufacturing of a heat accumulator is possible for every person who has the skills to work with basic plumbing and household tools. To assemble such a unit you will not have to buy any expensive parts and materials. Components for the simplest model can be found in the garage or pantry of any thrifty and economical person.
Thermal accumulator
After studying the following guide, you will be able to make your own heat accumulator and connect it to the heating system.
What is a heat accumulator?
A heat accumulator is a buffer reservoir designed to accumulate excess heat volumes generated during boiler operation. The saved resource is then used in the heating system in the period between scheduled loads of the main fuel resource.
Connecting a properly selected battery allows you to reduce the cost of purchasing fuel (in some cases up to 50%) and makes it possible to switch to one load per day instead of two.
In addition to the function of accumulating the generated heat, the buffer tank protects cast iron units from cracking in the event of an unexpected and sharp change in the temperature of the operating network water
If you equip the equipment with intelligent regulators and temperature sensors, and automate the heat supply from the storage tank to the heating system, heat transfer will increase significantly, and the number of portions of fuel loaded into the combustion chamber of the heating unit will noticeably decrease.
What is a heating storage tank
A storage tank is an insulated container with leads for connecting water heating pipes. Serves to heat the home when the heat source is stopped.
A standard heat storage tank without unnecessary bells and whistles consists of:
- Tank in the form of a steel cylinder;
- Thermal insulation is approximately 50-100 mm;
- Sheathing;
- Fittings embedded in the container;
- Immersion sleeves for fixing the pressure gauge and thermometer.
Also, such a water storage increases the efficiency of a solid fuel boiler. After all, maximum thermal output occurs during active combustion of fuel, and this is impossible without a buffer that absorbs all excess heat. The more efficiently wood burns, the less of it is needed. The same applies to gas installations.
While the room is heated by the heat generator, the storage tank accumulates heat, and the water in it warms up to the maximum temperature. After the boiler has finished operating, hot liquid begins to flow into the batteries, providing heating for the home. The duration of heating depends on the volume of the tank and the outside temperature.
Features of internal and external devices
The heat accumulator is a vertical cylinder-shaped tank made of high-strength black or stainless steel sheet.
There is a layer of bakelite varnish on the inner surface of the device. It protects the buffer tank from the aggressive influence of industrial hot water, weak salt solutions and concentrated acids. Powder paint is applied to the outside of the unit, resistant to high thermal loads.
The tank volume varies from 100 to several thousand liters. The most capacious models have large linear dimensions, making it difficult to place equipment in the limited space of a home boiler room
External thermal insulation is made of recycled polyurethane foam. The thickness of the protective layer is about 10 cm. The material has a specific complex weave and an internal polyvinyl chloride coating.
This configuration prevents particles of dirt and small debris from accumulating between the fibers, provides a high level of water resistance and increases the overall wear resistance of the heat insulator.
The heat insulator is not always included in the heat accumulator kit. Sometimes you have to buy it separately and then install it on the unit yourself
The surface of the protective layer is covered with a cover made of good quality leatherette. Thanks to these conditions, the water in the buffer tank cools much more slowly, and the level of overall heat loss of the entire system is significantly reduced.
The operating principle of a heat-saving product
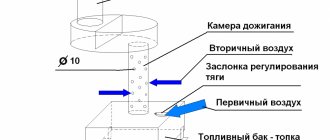
The heat accumulator operates according to the simplest scheme. A pipe from a gas, solid fuel or electric boiler is connected to the unit from above.
Hot water flows through it into the storage tank. Cooling down during the process, it falls down to the location of the circular pump and, with its help, is fed back into the main passage to return to the boiler for the next heating.
Installing a heat accumulator prevents overheating of the coolant when the boiler is operating at full power and ensures maximum heat transfer with economical fuel consumption. This reduces the load on the heating system and extends its service life
A boiler of any type, regardless of the type of fuel resource, operates in steps, periodically turning on and off when the optimal temperature of the heating element is reached.
When work stops, the coolant enters the reservoir, and in the system it is replaced by hot liquid that has not cooled due to the presence of a heat accumulator. As a result, even after the boiler is turned off and goes into passive mode until the next fuel supply, the batteries remain hot for some time, and warm water comes out of the tap.
Examples of homemade heat storage tanks for heating
TA for cheap heating with electricity
This heat storage tank was made for an electric boiler. With its help, heat is stored during the night tariff. The capacity turned out to be large, in order to speed up the process and have a certain power reserve in case the validity period of the night tariff was reduced, three more heating elements of 2 kW each were installed. They are connected as a star to a three-phase network.
This heat accumulator is made of ordinary sheet steel 4 mm thick
Based on materials:
- tank size - 1.5 * 1.5 * 0.75 m (capacity about 1.7 m³), sheet thickness - 4 mm (part of the sheet 1.5 * 6 m went);
- cast iron radiator - 7 sections;
- metal corner - welded around the perimeter of the upper part to fix the lid;
- rubber seal on a self-adhesive base - to seal the same lid;
- metal fittings - fittings with external threads, shut-off valves;
- electrodes for welding.
The process of assembling the container itself is simple - you need to:
- Boil all seams, clean, coat with primer.
- Make holes for the pipes, install and weld the fittings.
- Weld the “ties” inside the tank.” You can fix the radiator/heat exchanger by welding spacers (or corners) at the required level. This is how the lid is attached. This is the finished heat storage tank. View from above. Heating elements are installed at the bottom - to warm up the coldest layer. Embedded and welded fittings To prevent the walls from “blowing up”
- Drill the corners in increments of 15-20 cm. These are holes for the tie screws. then - a harness from the corner.
- Clean weld areas (all), prime, paint.
- Prime and paint all surfaces inside and out.
- Clean, coat with primer twice and paint the cast iron battery/heat exchanger.
- Connect the battery to the terminals made for the heat exchanger and secure it in the tank.
- Glue a rubber seal around the perimeter of the tank lid. It is better to glue it as a whole piece - it will be more airtight.
Installed on 10 cm foam.
After filling, no subsidence was noticed. The finished tank was installed on a layer of high-density polystyrene foam (10 cm), covered on the sides and top with a mineral wool mat 10 cm thick. The insulation was glued to the walls. During operation, the tank and components began to rust heavily. A magnesium anode installed inside helped slow down the process.
Homemade sealed stainless steel tank
Into a heating system with a coal boiler with a capacity of 56 kW (heated area 190 m
²), assembled a heat accumulator with a volume of 4 cubic meters. Both the power of the boiler and the dimensions of the tank are taken with a very large margin - the owner wants to heat in cold weather no more than once a day, with a slight minus - once every two or three days. With such parameters he succeeds. It is planned to supply coolant to the system with a temperature of no higher than 50°C, so the radiators in the rooms are installed with a double reserve (calculation was based on area). Each radiator has thermostats so that it is possible to regulate the temperature in each room separately. For a homemade heat accumulator, stainless steel sheet 2 mm thick was used.
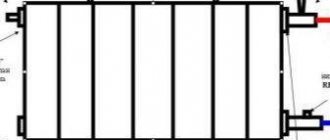
Design features: homemade heat exchanger. It is also made of sheet metal. It consists of two plates, between which strips of metal are welded. These strips are guides for the flow of coolant. They do not reach one of the edges a little, they are located so that the flow goes like a “snake”.
This is how “guides” are welded for the flow of coolant from the boiler
The size of the heat exchanger turned out to be large. To prevent the structure from moving, the lid, in addition to being scalded, was tightened over the area with pins, and the installation sites were scalded with plates made of the same stainless steel. To check the tightness, a pressure test of 3.5 atm was carried out. Everything is intact, there are no leaks.
This is a ready-made heat exchanger. It must be installed at an angle in the heat storage tank.
There are unlikely to be any questions regarding the welding of the body itself. The only thing that might be interesting is that we welded with a regular welding inverter, but with a TIG torch (purchased at a specialized store). An argon tank was also purchased, so the stainless steel was cooked in an argon environment.
This is what the TA body looks like
A corner was welded along the upper edge, and studs were welded to the corner. A cover with a rubber seal will be installed on them.
Top edge with pins to secure the lid
Since the container is large, even dense foam plastic will not support it. Therefore, a stand from a steel corner was welded under it.
Stand for an almost finished heat accumulator
All this is installed in the boiler room. The tank was covered on all sides with 15 cm thick mineral wool, OSB was sheathed on top of the insulation and painted. Everything looks good when finished.
This is a do-it-yourself heat accumulator
Based on the results of operation. In frosts of -25°C, you have to heat it once a day. At a temperature of -7°C or -10°C - once every two days. When it’s even warmer, it’s even less common.
Types of heat storage models
All buffer tanks perform almost the same function, but have some design features.
Manufacturers produce three types of storage units:
- hollow (without internal heat exchangers);
- with one or two coils , ensuring more efficient operation of the equipment;
- with built-in boiler tanks of small diameter, designed for the correct operation of an individual hot water supply complex for a private home.
The heat accumulator is connected to the heating boiler and the communication wiring of the home heating system through threaded holes located in the outer casing of the unit.
How does a hollow unit work?
The device, which has neither a coil nor a built-in boiler inside, is one of the simplest types of equipment and costs less than its more “sophisticated” counterparts.
It is connected to one or more (depending on the needs of the owners) energy sources through central communications, and then through 1 ½ pipes it is routed to points of consumption.
It is planned to install an additional heating element operating on electrical energy. The unit provides high-quality heating of residential property, minimizes the risk of coolant overheating and makes operation of the system completely safe for the consumer.
When a residential building already has a separate hot water supply system and the owners do not plan to use solar thermal heat sources to heat the room, it is advisable to save money and install a hollow buffer tank in which the entire usable area of the tank is given over to the coolant and is not occupied by coils
Thermal accumulator with one or two coils
A heat accumulator equipped with one or two heat exchangers (coils) is a progressive option for equipment with a wide range of applications. The upper coil in the design is responsible for the selection of thermal energy, and the lower one carries out intensive heating of the buffer tank itself.
A device equipped with heat exchangers has a higher price than a hollow unit, but the costs here are completely justified. The device significantly expands the functionality of the system and makes its operation much more efficient.
The presence of heat exchange units in the unit allows you to receive hot water for domestic needs around the clock, heat the tank from the solar collector, warm up house paths and make the most efficient use of useful heat for any other convenient purposes.
Module with internal boiler
A heat accumulator with a built-in boiler is a progressive unit that not only accumulates excess heat generated by the boiler, but also ensures the supply of hot water to the tap for domestic purposes.
The internal boiler tank is made of stainless alloy steel and equipped with a magnesium anode. It reduces the level of water hardness and prevents the formation of scale on the walls.
Owners choose the appropriate volume of the buffer tank on their own, but experts say that there is no practical point in purchasing a tank less than 150 liters
A unit of this type connects to various energy sources and works correctly with both open and closed systems. Controls the temperature level of the operating coolant and protects the heating complex from overheating of the boiler.
Optimizes fuel consumption and reduces the number and frequency of loading. Compatible with solar collectors of any model and can function as a substitute for a hydraulic boom.
Using a heat accumulator in different heating systems
DHW circuit
Thermal accumulators show themselves effectively when used in a wide variety of heating systems. Moreover, in each case, such a storage device allows you to significantly save on heating.
Most often, solid fuel heating systems are equipped with heat accumulators. The installation will contribute to more economical fuel consumption and efficient heating, and will also prevent premature wear of heating radiators.
A heat accumulator would also be useful in an electric heating system, especially in regions with double tariffs for electricity. At night, when electricity is sold to consumers at a more affordable cost, the battery will accumulate heat. During the day, it will be possible to turn off the boiler for a while and heat it using the heat accumulator.
Storage tanks are also used in multi-circuit heating systems. Thanks to them, the distribution of coolant between the circuits is ensured. Installation of pipes can be done at different heights, which will allow receiving water heated to different temperatures.
Scope of application of the heat accumulator
The heat accumulator collects and stores the energy generated by the heating system, and then helps to use it as rationally as possible for efficient heating and providing residential premises with hot water.
You need to purchase a device for accumulating excess heating resources only in specialized stores. The seller must provide the buyer with a product quality certificate and complete instructions for use
It works with different types of equipment, but is most often used in conjunction with solar collectors, solid fuel and electric boilers.
Thermal accumulator in a solar system
A solar collector is a modern type of equipment that allows you to use free solar energy for everyday household needs. But without a heat accumulator, the equipment is not able to fully function, since solar energy is supplied unevenly. This is due to changes in time of day, weather conditions and seasonality.
A solar collector equipped with a heat accumulator is placed on the south side of the site. There the device absorbs maximum energy and gives effective output
If the heating and water supply system is powered only by a single energy source (the sun), at some points residents may have serious problems with the supply of resources and obtaining the usual elements of comfort.
A heat accumulator will help you avoid these unpleasant moments and make the most efficient use of clear, sunny days to accumulate energy. To operate in a solar system, it uses the high heat capacity of water, 1 liter of which, cooling by just one degree, releases thermal potential to heat 1 cubic meter of air by 4 degrees.
The solar collector and heat accumulator form a single system, making it possible to use solar energy as the only source for heating a residential building
During the period of peak solar activity, when the solar collector collects the maximum amount of light and energy production significantly exceeds consumption, the heat accumulator accumulates the excess and supplies it to the heating system when the supply of resource from the outside decreases or even stops, for example, at night.
The following article will introduce you to options and schemes for alternative heating for country property, which we recommend reading.
Buffer tank for solid fuel boiler
Cyclicity is a characteristic feature of the operation of a solid fuel boiler. At the first stage, firewood is loaded into the firebox and heating occurs for some time. Maximum power and the highest temperatures are observed at the peak of the bookmark combustion.
Then the heat transfer gradually decreases, and when the wood finally burns out, the process of generating useful heating energy stops. All boilers operate on this principle, including long-burning appliances.
It is not possible to precisely configure the unit to generate thermal energy in relation to the level of consumption required at any given moment. This function is only available in more advanced equipment, for example, in modern gas or electric heating boilers.
Therefore, immediately at the moment of ignition and when reaching actual power, and then during the process of cooling and the forced passive state of the equipment, there may simply not be enough thermal energy for full heating and heating of hot water.
But during peak operation and the active phase of fuel combustion, the amount of energy released will be excessive and most of it will literally “fly down the drain.” As a result, the resource will be spent irrationally, and the owners will have to constantly load new portions of fuel into the boiler.
In order for the house to be heated for a long time after the solid fuel boiler is turned off, you need to purchase a large buffer tank. It will not be possible to accumulate a significant amount of resource in a small reservoir and its purchase will be a pointless waste of money
This problem is solved by installing a heat accumulator, which will accumulate heat in the tank at times of increased activity. Then, when the wood burns out and the boiler goes into passive standby mode, the buffer will transfer the collected energy to the coolant, which will warm up and begin to circulate through the system, heating the room bypassing the cooled appliance.
Reservoir for electrical system
Electric heating equipment is a rather expensive option, but it is sometimes installed, and, as a rule, in conjunction with a solid fuel boiler.
Typically, the electric type of heating is installed where other sources of heat are not available due to objective reasons. Of course, with this heating method, electricity bills increase significantly and home comfort costs owners a lot of money.
The buffer tank must be installed directly next to the heating boiler. The equipment has substantial dimensions and in a private house you will have to allocate a special room for it. The system will fully pay for itself within 2-5 years
In order to reduce electricity costs, it is advisable to use the equipment to the maximum during the preferential tariff period, that is, at night and on weekends.
But such an operating mode is possible only if there is a capacious buffer tank, where the energy generated during the grace period will accumulate, which can then be spent on heating and supplying hot water to residential premises.
Connecting TA to consumers
On the other hand, the heat storage tank must be connected to the heating system. If we connect only radiators, everything is simple - a pipe goes from one of the upper outlets to the supply pipeline, and we connect the return line to the lower one. But, in this case, the radiators may overheat. When the water in the tank is heated to a temperature above 60°C, it can be dangerous, and the temperature can be 90°C or even higher. If you touch such hot radiators, there is a high probability of getting a serious burn. In addition, the room will obviously be hot.
Connecting radiators
To avoid supplying too hot coolant, install another three-way mixing valve. The scheme works the same as described above. We set the required temperature on the regulator, for example, 50°C. As soon as the coolant in the supply is hotter, the valve will open the addition of water from the return.
One of the benefits of installing a heat accumulator is the ability to prepare hot water in the same container (middle picture in the figure below). To do this, a heat exchanger or container is built into the tank. Its output is connected to the hot water supply comb.
Buffer tank piping diagrams from the heating system side
Since overheating is also possible in this case, a mixing unit is also needed here. You just need to add cold tap water. This unit is implemented using another three-way mixing valve. We connect the outlet from the cold water supply to the three-way DHW mixing valve. To prevent hot water from flowing into the cold water comb in the absence of hot water supply, we install a check valve on the supply line from the hot water supply.
This heat accumulator piping scheme has a significant drawback: when hot water is not used, the water in the pipes cools down. To “get” warm water, you have to simply pour the cooled water down the drain. This is inconvenient because you have to wait, and it is not economical. To solve the problem, a return line is drawn from the last analysis point, in which a circulation pump is installed. This circuit is called recirculation. While the tap is not opened anywhere, the water runs in a circle. Thus, warm water constantly flows from all taps
Pay attention to the installation of check valves - they are required for the operation of the circuit
Connection of a heat accumulator for individual heating with all functional elements and fittings
To finalize the diagram, it is also necessary to determine the installation location of the fittings. These are automatic air vents that are installed at the highest points of the system. Shut-off valves are also needed. They are installed near each large functional unit so that, if necessary, it is possible to turn off the taps and remove equipment for repair or maintenance.
How to power a warm water floor
A heated floor can also be connected to a heat accumulator very well. The piping in this case is no different from the case with radiators. The same mixing unit with a three-way mixing valve is needed, but it should be set to a lower temperature - no higher than +40°C. In this case, you can connect a heated floor without a mixing unit - the temperature must be controlled when leaving the boiler. But you can play it safe - install a second mixing unit on the distribution manifold of the heated floor.
Connecting a heat accumulator with a warm water floor (in the green outline)
There is a second option for connecting a heat accumulator with a heated floor - supplying coolant at the same temperature that goes to the radiators. The mixing unit will lower it. There is less hassle and cost (you only need tees to drain from the main line), but the reliability of such a solution is also lower. Although, this equipment copes with the coolant supplied by a conventional boiler.
Do-it-yourself energy storage device
The simplest possible model of a heat accumulator can be made with your own hands from a ready-made steel barrel. If you don’t have one at your disposal, you will have to purchase several sheets of stainless steel with a thickness of at least 2 mm and weld them into a container of a suitable size in the form of a vertical cylindrical tank.
It is not recommended to use a Eurocube to make a heat accumulator. It is designed for contact with coolant having an operating temperature of up to + 70 ºС and simply will not withstand hotter liquids
DIY Guide
To heat the water in the buffer, you will need to take a copper tube with a diameter of 2-3 centimeters and a length of 8 to 15 m (depending on the size of the tank). It will have to be bent into a spiral and placed inside the tank.
The battery in this model will be the top of the barrel. From there you need to remove the outlet pipe for the hot water outlet, and make the same one from below for the cold water inlet. Each outlet should be equipped with a tap to control the flow of liquid into the accumulation zone.
In an open heating system, a rectangular steel tank can be used as a buffer tank. In a closed system this is excluded due to possible surges in internal pressure
The next step is to check the container for leaks by filling it with water or lubricating the welds with kerosene. If there is no leak, you can proceed to creating an insulating layer that will allow the liquid inside the tank to remain hot for as long as possible.
How to insulate a homemade unit?
To begin with, the outer surface of the container must be thoroughly cleaned and degreased, and then primed and painted with heat-resistant powder paint, thus protecting it from corrosion.
Then wrap the tank with glass wool insulation or rolled basalt wool 6-8 mm thick and secure it with cords or regular tape. If desired, cover the surface with sheet metal or “wrap” the tank in foil film.
You should not use extruded polystyrene foam or polystyrene foam for insulation. With the onset of cold weather, these materials may harbor mice looking for a warm place to live during the winter.
Holes for outlet pipes should be cut in the outer layer and the container should be connected to the boiler and heating system.
The buffer tank must be equipped with a thermometer, internal pressure sensors and an explosion valve. These elements allow you to control potential overheating of the barrel and relieve excess pressure from time to time.
To summarize: What are the advantages and disadvantages of using buffer tanks?
The obvious “advantages” of autonomous solid fuel heating systems with a heat accumulator include the following:
- The energy potential of solid fuel is used to the maximum extent possible. Accordingly, the efficiency of boiler equipment increases sharply.
- The operation of the system will require much less human intervention - from reducing the number of boiler loadings with fuel to expanding the ability to automate the control of operating modes of various heating circuits.
- The solid fuel boiler itself receives reliable protection against overheating.
- The operation of the system becomes smoother and more predictable, providing a differentiated approach to heating different rooms.
- There are ample opportunities to modernize the system, including the launch of additional sources of thermal energy, without dismantling the old ones.
- In most cases, the problem of hot water supply at home is also solved.
The disadvantages are very peculiar, and you also need to have an idea about them:
- A heating system equipped with a buffer tank is characterized by very high inertia. This means that from the moment of initial ignition of the boiler until reaching the nominal operating mode it will take quite a lot of time. This is unlikely to be justified in a country house, which in winter the owners visit only on weekends - in such situations, rapid heating is required.
- Heat accumulators are bulky and heavy (especially when filled with water) structures. They require enough space and a well-prepared, reliable foundation. Moreover, it is close to the heating boiler. This is not possible in every boiler room. Plus, there are difficulties with delivery and unloading, and often also with bringing the container into the room (it may not fit through the door). All this should be taken into account in advance.
- The disadvantages include the very high price of such devices, which sometimes even exceeds the cost of the boiler. This “minus”, however, brightens up the expected saving effect from more rational use of fuel.
- The heat accumulator will fully reveal its positive qualities only if the rated power of the solid fuel boiler (or the total power of other heat sources) is at least twice as high as the calculated value required for effective heating of the house. Otherwise, purchasing a buffer capacity seems unprofitable.
Date: September 25, 2022
Accumulated resource consumption rate
It is impossible to accurately answer the question of how quickly the heat accumulated in the battery is consumed.
How long the heating system will operate using the resource collected in the buffer tank directly depends on such items as:
- actual volume of storage capacity;
- level of heat loss in the heated room;
- outside air temperature and current time of year;
- set values of temperature sensors;
- useful area of the house that needs to be heated and supplied with hot water.
Heating of a private house in a passive state of the heating system can be carried out from several hours to several days. At this time, the boiler will “rest” from the load and its working resource will last for a longer period of time.
Rules for safe operation
Heat batteries made at home with your own hands are subject to special safety requirements:
- Hot tank elements must not come into contact with or otherwise come into contact with flammable or explosive materials or substances. Ignoring this point may cause a fire in individual objects and a fire in the boiler room.
- A closed heating system involves constant high pressure of coolant circulating inside. To ensure this point, the tank structure must be completely sealed. Additionally, its body can be reinforced with stiffening ribs, and the lid on the tank can be equipped with durable rubber gaskets that are resistant to intense operating loads and elevated temperatures.
- If the design contains an additional heating element, its contacts must be very carefully insulated, and the tank must be grounded. In this way, it will be possible to avoid electric shock and short circuit, which can damage the system.
If these rules are followed, the operation of a self-made heat accumulator will be completely safe and will not cause any problems or hassle for the owners.