For the effective functioning of ventilation and chimney systems, stable natural draft is required. Only under this condition will normal air circulation and effective removal of combustion products occur. To prevent foreign objects and precipitation from entering ventilation and smoke ducts, as well as to protect the internal surface from soot and fat deposits, deflectors are widely used.
A modification of the TsAGI type deflector is one of the most common among such devices. This article will discuss the design features, operating principle, pros and cons of this device.
What is a TsAGI deflector and why is it needed?
The TsAGI deflector is a development of the Central Aerohydrodynamic Institute, designed to enhance natural draft, prevent reverse draft and protect against moisture and foreign objects getting into ventilation shafts and chimneys.
The use of these types of deflectors allows you to improve the microclimate in the room due to intensive air circulation and promotes more complete combustion of fuel.
Design and principle of operation
The TsAGI deflector has become widespread due to its efficiency and affordable cost. The deflector design includes the following elements:
- the lower shell, with the help of which the product is attached to the upper part of the air duct or chimney;
- diffuser, which is an expanded cone located between the pipe and the cap;
- a hollow metal cylinder, which is the outer part of the deflector;
- an upper conical hood designed to protect the air duct from clogging with foreign objects and adverse atmospheric influences;
- upper cone mounting brackets;
- mounting brackets.
Typically, TsAGI deflectors are made of galvanized or stainless steel.
The principle of operation of the device is based on the cutting of the air flow by a deflector, as a result of which an area of low pressure (rarefaction) is formed above the head of the air duct. Thanks to this, the natural draft in the ventilation system increases by 15-20%.
By enhancing natural draft, the efficiency of ventilation and heating devices increases by 20-25%. Fuel combustion occurs with greater heat transfer, which reduces fuel consumption and reduces the emission of toxic compounds into the atmosphere. As for ventilation systems, when using a TsAGI deflector, the intensity of air circulation increases.
Can it be installed on a chimney?
By installing a deflector, unlucky homeowners are trying to solve the problem of lack of draft. This happens when the chimney pipe is made incorrectly - the head falls into the zone of wind support of the roof, is raised to a low height, or a neighbor has built a tall building nearby.
The best solution for insufficient draft is to raise the chimney to the required height. Why is it undesirable to jam various attachments onto the head:
- It is prohibited to place umbrellas and other exhaust devices on pipes that discharge combustion products from gas boilers. These are safety requirements.
- When burning, stoves and solid fuel boilers emit soot that settles on the internal surfaces of chimneys and caps. The deflector will have to be cleaned, especially the rotating one.
- At the bottom of a properly constructed smoke channel there is a pocket for collecting condensation and excess moisture. There is no point in covering the pipe from precipitation; it is enough to attach a nozzle at the end that protects the insulation of the sandwich.
The heads of stove flues can be equipped with umbrellas, but a turbo deflector is definitely not needed there. The topic of installing hoods on smoke exhaust ducts is covered in detail in a separate material.
Advantages and disadvantages
Like any other product, the TsAGI deflector has its pros and cons. The feasibility of using the product is determined by their ratio. The advantages of the device include:
- reliable protection against foreign objects, birds and atmospheric influences getting inside ventilation ducts and chimneys;
- a significant increase in the service life of the head of ventilation ducts or chimneys. This is due to the fact that the presence of a deflector slows down the process of destruction of the upper part of the air duct caused by adverse atmospheric influences;
- prevention of reverse draft even with a large cross-section of ventilation lines and ventilation ducts;
- possibility of self-production. Thanks to its simple design and the use of available materials, a TsAGI type deflector can be made with your own hands. This does not require special tools or experience as a tinsmith.
A significant drawback is that in completely calm or weak wind conditions, such deflectors can create resistance to natural draft. In addition, if the ambient temperature drops significantly, the outer cylinder may freeze, which can lead to partial or complete blockage of the air ducts.
Area of use
Where exactly can turbo deflectors be used? The products have proven themselves excellent in rooms and facilities where air exchange is extremely necessary. Scope of use:
- For private and apartment buildings. In addition, it should be noted that increased demands are placed on the operation of ventilation ducts in a high-rise building. Often in such houses the quality of ventilation is not the best, since they were made in the Soviet Union. But thanks to the use of a deflector, this problem is solved.
- Turbo deflectors are good for livestock farms and agricultural buildings such as stables, poultry houses, granaries and haylofts. They help ventilation more effectively remove odors, fumes and gases generated when keeping livestock. In addition, the humidity in the room is controlled, it is optimal.
- For processing enterprises. Since the turbo deflector does not require electricity to operate, the savings on the device are corresponding. The exception is enterprises that produce or process substances hazardous to humans.
- Public buildings such as sports complexes, swimming pools, shopping centers and cinemas.
Important! The turbo deflector is also used to ventilate the under-roof space.
But how to make turbo ventilation deflectors with your own hands? Let's find out.
Calculation and drawings
Before purchasing a factory deflector or starting to manufacture the device yourself, you need to carry out an aerodynamic calculation and familiarize yourself with the drawings of existing devices.
The main criterion when creating a deflector drawing is the internal diameter of the duct (D). The figure shows the dimensions of the structural elements.
TsAGI deflector dimensions
- diameter of the upper base of the diffuser – 1.18-1.26D;
- outer char diameter – 1.8-2D;
- outer ring height – 1-1.2D;
- distance from the ring to the base of the diffuser – 0.4-0.5D;
- height – 1.4-1.7D;
- diameter of the cap is 1.3-1.5D.
When making a deflector yourself, it is advisable to follow the SNiP recommendations given in the table.
| Deflector No. | Diameter of the lower base of the diffuser, mm | Diameter of the upper base of the diffuser, mm | Outer cylinder diameter, mm | Diameter of the lower base of the cone, mm | total height of the deflector, mm | Diffuser height, mm | Cone height, mm | Cylinder height, mm |
| 3 | 265 | 380 | 600 | 510 | 510 | 295 | 90 | 360 |
| 4 | 375 | 504 | 800 | 680 | 680 | 400 | 120 | 480 |
| 5 | 495 | 630 | 1000 | 850 | 850 | 500 | 150 | 600 |
| 6 | 595 | 736 | 1200 | 1020 | 1020 | 600 | 180 | 720 |
| 7 | 660 | 882 | 1400 | 1190 | 1190 | 700 | 210 | 840 |
| 8 | 775 | 1008 | 1600 | 1360 | 1360 | 800 | 240 | 960 |
| 9 | 885 | 1134 | 1800 | 1530 | 1530 | 900 | 270 | 1080 |
| 10 | 1025 | 1260 | 2000 | 1700 | 1700 | 1000 | 300 | 1200 |
Features of device installation and useful tips for proper installation
To correctly calculate the deflector, you need to measure the diameter of the exhaust shaft. If there is a rectangular exhaust shaft, you should select a device with a round cross-section, the value of which is equivalent to the size of the channel. That is, you need to calculate the cross section of the rectangle and take a circle with a similar area. It is also necessary to remember that in this case, an additional adapter will be required for installation.
As for the installation of the deflector, they are guided by SNIP standards governing installation rules
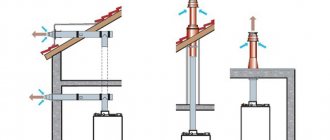
So, first of all, you need to pay attention to the height of the ventilation pipe and hood, which is determined depending on the location on the roof:
- The height is 50 cm, if the air duct is located closer than 1.5 meters from the edge of the roof.
- At the same level as the ridge or slightly higher, when the distance from the parapet to the ventilation shaft varies from 1.5 to 3 meters.
- If the pipe is more than 3 meters away, the height is selected so that the top of the deflector is not below the deviation line drawn from the ridge down to the edge of the roof at an angle of 10°.
It is optimal when the deflector is installed at the stage of roof installation.
Additional points to consider during installation:
- The deflector cannot be mounted in an area covered by the aerodynamic shadow of other buildings.
- The device must be mounted where there is free airflow. It is best when the cap is the highest point of the roof.
When organizing a ventilation system, you should also not forget how to install the ventilation grill correctly - up or down
Most craftsmen focus on the fact that if there is forced ventilation, air will somehow get into the shaft, so when installing it is better to focus on how the wall will look after installation and whether the grate gaps will be noticeable
Making a TsAGI deflector with your own hands
Considering the relative simplicity of the product design and the availability of galvanized steel sheets, many owners of private houses have a desire to make a TsAGI deflector themselves. This task is quite within the capabilities of any home craftsman; it is enough to have a set of the most common tools and minimal practical skills in sheet metal processing.
What you need
To make a full-fledged deflector at home you will need:
- sheet metal 0.5-0.7 mm;
- Whatman paper or thick cardboard for making templates;
- marker;
- ruler;
- compass;
- scriber;
- pliers;
- two types of scissors: regular and for metal;
- electric drill or screwdriver;
- drills with a diameter of 2 to 2.5 mm;
- special tool for installing rivets.
Design work
First of all, you should measure the diameter of the air duct and obtain the value D necessary for further development of the design. Next, based on the above relationships, draw up drawings of the TsAGI deflector corresponding to the existing diameter of the air duct.
Since the dimensions of the main structural elements remain unchanged for a specific diameter of the chimney or ventilation pipe, for ease of calculation these values are given in the table.
| Diameter Air duct, mm | Diameter Outer ring, mm | Height of outer ring with cap, mm | Diffuser outlet diameter, mm | Umbrella diameter, mm | Mounting height of outer ring, mm |
| 110 | 210 | 130 | 135 | 170-190 | 50 |
| 125 | 250 | 150 | 157 | 215-240 | 65 |
| 160 | 320 | 195 | 200 | 270-305 | 80 |
| 200 | 400 | 240 | 250 | 345-385 | 100 |
| 260 | 510 | 310 | 315 | 425-475 | 125 |
| 315 | 630 | 380 | 395 | 535-600 | 160 |
The drawing up of drawings must be approached with all responsibility, since the efficiency of the deflector will depend on their accuracy.
Preparing templates
When making templates, you will have to remember a short course in geometry. The most difficult thing to make is a diffuser pattern, which is a development of a straight truncated cone. Below is the methodology for its construction.
The cap pattern is nothing more than a development of a cone with an upper base with a diameter of 1.18-1.26D and a lower base corresponding to the diameter of the air duct D.
The length of the generatrix can be determined using the Pythagorean theorem. Here the hypotenuse is the desired length of the generatrix, and the legs are the radius of the base, equal to 0.65-0.75D, and the height of the cap, which is equal to 0.24D.
Developments of cylindrical parts are rectangles, the length of which is equal to the circumference, and the width is determined from the above ratios.
Important! When constructing templates, it is necessary to take into account the amount of margin required for fastening the reamers. Usually it is 15-20 mm.
Assembly sequence
From ready-made cardboard templates, using paper clips or another method, a layout is assembled on a scale of 1:1 and the coincidence of its geometric parameters with the specified values is checked. Making a mock-up of the TsAGI deflector completely eliminates the occurrence of inconsistencies during the assembly process.
Product assembly consists of several successive stages.
- The patterns are placed on a metal sheet and traced along the contour with a marker or felt-tip pen.
- Using metal scissors, individual pieces are cut.
- Using pliers, the outer edges are bent to a width of 3-5 mm and tapped tightly with a hammer. This will provide the structural elements with additional rigidity.
- The cut blanks of the outer shell and the input cylinder are given the appropriate shape, so that the overlap is 20-25 mm. After this, holes with a diameter of 2-2.5 mm are drilled in the center of the lining, into which rivets are installed. The distance between the rivets depends on the overall dimensions of the product and can range from 20 to 50 mm. If the necessary tools are not available, the rivets can be replaced with screws of the appropriate diameter. The top hood and diffuser are made using the same technology.
- The next step is the manufacture of connecting brackets. The design provides for the presence of 3 fasteners, but to increase rigidity you can increase their number to four. The bracket blank is a strip, the width of which is 30-35 mm, and the length is 200-300 mm. A 5mm hem is made along the entire length of the workpiece on both sides and tapped tightly with a hammer.
- The brackets are attached to the cone using rivets or screws at a distance of 45-50 mm from its outer edge.
- After this, the strips are folded back and the conical cap is connected to the diffuser.
- Bracket blanks are attached to the conical cap and bent at the desired angle.
- The umbrella with attached brackets is connected to the diffuser using rivets or screws.
- The resulting structure is fixed in the outer shell taking into account the dimensions shown in the drawing. After this, the deflector assembly can be considered complete.
Varieties
Many users constantly wonder: which deflector is best for a chimney? To answer this question, you need to study existing models and, based on their characteristics, select the most optimal option.
Today, there are several types of deflectors that have gained popularity due to their practicality and reliability.
Disc Astato. This deflector is open, but at the same time it is very effective. Its main distinguishing feature is that it is able to provide good traction, regardless of which direction the wind blows. Material of manufacture: galvanized/stainless steel.
Disc chimney deflector Astato
TsAGI deflector. This model is recognized as one of the most popular and in demand. It is made in the shape of a cylinder. The manufacturing material is stainless or galvanized steel. Connection type: flange.
Round Volper. In terms of design features, this model resembles the previous one. The main distinguishing feature is the top of the device. Typically, such deflectors are made of stainless steel or copper. Most often they are purchased for installation on the chimney of a bathhouse.
Grigorovich deflector. This type is a more modern and improved version of TsAGI. It is installed in places where the winds are generally not very strong.
H-shaped. This model is highly durable and reliable, regardless of the direction of wind movement - it is effective. The H-shaped deflector is made of stainless steel. The connection is made through a tap on the device pipe.
Deflector-weathervane. It is a rotating body with a weather vane on top. Made from stainless steel or carbon steel.
Types of chimney deflectors
Basically, chimney deflectors differ in shape and component elements. As can be seen from the examples, products are usually made from stainless steel and galvanized steel. Models are round, square, in the form of an open and closed cylinder. The “top” of the device also varies. In some it has the shape of an umbrella, in others the lid can be gable or hipped, and in others it is completely flat or with decorative figured elements.
The diameter of the deflector on the chimney pipe can be 100-500 mm, the width of the diffuser varies from 240 to 1000 mm, and the height of the device is 140-600 mm.
The deflector is connected to the chimney using brackets, bolts and sealing tape. It is made of steel, the thickness of which is 0.5-1 mm. You can also install a spark arrester. Typically, the equipment is equipped with such parts in case of risk of a possible roof fire.
Which is better, a TsAGI deflector or a turbo deflector?
Compared to TsAGI, rotary deflectors provide greater thrust even with the same dimensions. Another advantage of the turbo deflector is its high efficiency.
With the same dimensions of the outlet pipe, the dimensions of the TsAGI deflector are significantly larger than the dimensions of the rotating devices. With an air duct diameter of 100 to 150 mm, the operating efficiency of both devices is approximately the same, however, when the passage increases to 200 mm or more, the size ratio changes sharply in favor of turbo deflectors. They have less mass and are several times more compact.
The large weight and dimensions of the deflectors significantly complicate installation work with an air duct diameter starting from 600 mm. In comparison, a rotating device for a 600 mm diameter ventilation duct is between 12 and 15 kg and can easily be installed by one person. A deflector for the same duct will weigh about 40 kg, and two people will be required to install it.
Despite the above advantages of rotary devices, TsAGI deflectors have become more widespread. This is due to the affordable cost of the products and simplicity of design. In addition, such devices are often manufactured independently, which saves significant money.
TsAGI deflectors are widely used in both industrial and civil construction. The design developed at the Central Aerohydrodynamic Institute has proven itself over many years as an effective and easy-to-use device. In addition, many owners of private houses make such deflectors themselves. With correct calculations and careful execution of work, the quality of homemade ventilation devices is not inferior to factory-made analogues.
Area of use
Where exactly can turbo deflectors be used? The products have proven themselves excellent in rooms and facilities where air exchange is extremely necessary. Scope of use:
- For private and apartment buildings. In addition, it should be noted that increased demands are placed on the operation of ventilation ducts in a high-rise building. Often in such houses the quality of ventilation is not the best, since they were made in the Soviet Union. But thanks to the use of a deflector, this problem is solved.
- Turbo deflectors are good for livestock farms and agricultural buildings such as stables, poultry houses, granaries and haylofts. They help ventilation more effectively remove odors, fumes and gases generated when keeping livestock. In addition, the humidity in the room is controlled, it is optimal.
- For processing enterprises. Since the turbo deflector does not require electricity to operate, the savings on the device are corresponding. The exception is enterprises that produce or process substances hazardous to humans.
- Public buildings such as sports complexes, swimming pools, shopping centers and cinemas.
Important! The turbo deflector is also used to ventilate the under-roof space. Number of blocks: 18 | Total number of characters: 23820 Number of donors used: 6 Information on each donor:
Number of blocks: 18 | Total number of characters: 23820 Number of donors used: 6 Information on each donor:
Number of blocks: 18 | Total number of characters: 23820 Number of donors used: 6 Information on each donor:
- https://ventkam.ru/ventilyatsiya/rotatsionnyj-deflektor: 3 blocks out of 7 were used, number of characters 2861 (12%)
- https://trubanet.ru/sistemy-ventilyacii/deflektor-na-vytyazhnuyu-trubu-princip-raboty.html: 3 blocks out of 6 used, number of characters 2191 (9%)
- https://oventilyacii.ru/ventilyaciya/deflektor.html: 4 blocks out of 6 were used, number of characters 6964 (29%)
- https://www.stroy-podskazka.ru/ventilyaciya/montazh-turbodeflektora/: 3 blocks out of 5 were used, number of characters 6282 (26%)
- https://proventilation.ru/ventilyatsiya/turbodeflektor-svoimi-rukami: 1 blocks out of 5 used, number of characters 2510 (11%)
- https://ProRoofer.ru/aksessuary/turbodeflektor-dlya-ventilyacii-svoimi-rukami.html: 3 blocks out of 8 were used, number of characters 3012 (13%)