FORUMHOUSE has already repeatedly talked about the basic principles of design and construction of an autonomous country house. The essence of all materials comes down to the following - each has its own “autonomy”. Before buying a plot where there is no or is not expected to be at least a centralized power supply, you need to think 100 times whether it is needed. Because material investments in the construction of a completely autonomous house, provided that these are not southern regions, may exceed all reasonable limits.
The purpose of this article is practical recommendations on how to independently install a water-heated floor as one of the engineering elements of a real, and not a mythical, autonomous house.
So we'll tell you:
- What prevents you from building a completely autonomous house in Russia.
- What are the features of calculating a heated floor?
- Can a heated floor be the only heating system for a country house?
- What nuances need to be taken into account when installing a heated floor yourself?
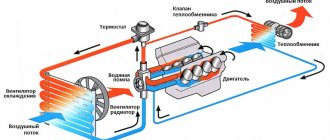
Design and principle of operation
A water heated floor is a room heating system in which the coolant circulates along a circuit located under the floor covering. Please note that the pipes are not always screeded. There are “decking systems” in which the contour is not poured with concrete.
Upon closer examination, the water heated floor cake consists of the following elements:
- Prepared base;
- Screed (5 cm);
- Thermal insulator (5 cm);
- Pipes (2 cm);
- Screed (4 cm);
- Floor covering (2 cm).
Depending on the pipes used, there may be several layers of waterproofing. The base is a subfloor in the basement or on the first floor of a private house. The first layer of screed is required precisely in the absence of a flat surface.
A 5 cm thick thermal insulator is a standard solution. But if possible, it is better to increase the thickness to 10 cm. This increases the efficiency of the entire system by 10-15%. Especially if the water-heated floor is installed on the first floor. The best material for this layer is extruded polystyrene foam.
Pipes in the vast majority of water heated floors are used with a diameter of 16 mm.
The second layer of screed covers the entire system and serves as a giant heat accumulator.
The thickness of the water heated floor cake varies from 18 to 23 cm. And the weight of 1 m2 of this system reaches a quarter of a ton! Such harsh conditions significantly limit the spread of water-heated floors.
The circuit is connected to the pump and boiler through an adjustment and control system.
Collector installation
The manifold serves to distribute liquid in the floor line. It consists of a supply and return tube; has outlets for a separate water circuit. The equipment is mounted on the wall. It is installed at an equal distance from all circuits of the heating system.
If, according to the calculation results, the length of the floor main exceeds 60 m, then 2 circuits are installed in the room. They are connected to the collector through separate outputs. If the room is small, then instead of a manifold, a two-way valve with a thermostat is provided.
Flow meters are located on the supply manifold. They control the filling of the water main in a certain room. Valves with thermal heads are installed on the return line. They allow you to set a certain thermal regime in the room.
Water heated floor collector
The supply manifold is connected to the boiler by metal pipes with a diameter of 26 mm. The outlets on the return pipe are connected to the floor piping. You can assemble a warm water floor with your own hands, but connecting the collector to the boiler and to the main requires consultation with specialists.
A circulation pump with a three-way mixing valve is installed on the bypass or hot circuit. It is equipped with a control device, thermal head or servo drive.
The control group helps maintain a certain temperature in the floor line. The manifold for a warm water floor is assembled according to the diagram with your own hands. The diagram is indicated in the technical data sheet for the equipment.
Where can I use it?
Due to the sufficient thickness and mass of the entire system, its use is limited to private housing construction. It is extremely irrational to install water-heated floors in apartments.
The main reason is difficulties with connecting the power. You can connect to the central heating system only after permission from the regulatory authorities. And it is almost impossible to get it. Even if it exists, the main leitmotif – autonomy – will disappear. We know of options for installing electric and even gas boilers in an apartment, but these are isolated cases that only confirm the rule: water heated floors are used only in private homes.
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantages of water heated floors are fully revealed only when using cheap energy sources, such as gas, coal, firewood. Heating the coolant with an electric boiler is approximately 7 times more expensive than using gas equipment.
The gigantic heat capacity of the water heated floor system is another plus. A room containing ≈ 100 kg/m2 of heated concrete cannot cool down quickly (only the top layer of screed is taken into account).
But there are also disadvantages. First of all, this is monstrous inertia. It takes time and energy to warm up such a layer of screed.
Inertia leads to the fact that temperature control of a water heated floor is very conditional. Control equipment takes temperature readings from the coolant, floor surface and air (in some thermostats). But the changes made through the thermostat appear very slowly.
The role of the collector unit
Not everyone knows that heated floors with a water circuit can function normally without a collector. But even less people know what this looks like in practice.
Manufacturers recommend using pipes with a length of no more than 70 m. If the coils are arranged with a maximum pitch gap, then this length will be enough for only 7 m2, which will ensure the arrangement of three circuits in a room with an average area
However, in most cases, a heated floor system is installed in several rooms. In this case, without a collector unit it is impossible to ensure uniform distribution of the coolant.
Installing floor heating without a collector has a number of disadvantages: the coolant can only be supplied at the same temperature as in a general heating system, automatic air outlet is not possible, the same applies to pressure regulation.
Installation of water heated floor
The task is quite difficult, but doable. You just need to level the base first. This is a very important requirement, given that leveling will still be required and it is more effective to do this with the first layer of screed. Why?
For example, the height difference in a room is 3 cm. If you immediately lay the pipe and only then level it with a screed, it will turn out that in one corner the height of the cement mixture will be minimal - 4 cm, and in the other 7. This means that during the operation of heated floors, with They will heat 4 cm of concrete on one side and 7 cm of concrete on the other. Such an uneven load has a very detrimental effect on the entire system as a whole and leads to rapid deterioration of the floor covering.
See also: Warm floor under linoleum
Therefore, the first and important step is to level the floors to the horizon level. To prepare concrete floors you will need:
- Beacon profile;
- Laser level;
- Construction square;
- 5-10 kg of gypsum;
- Primer;
- Mobile concrete mixer;
- Cement;
- PGS;
- Polypropylene fiber.
Work progress:
The floors are swept and primed. While the soil dries, beacons are set up. To do this, install a laser level in the middle of the room so that the projection of the horizontal beam is at a height of 15-20 cm from the floor. Then, using a square, measure the height from the floor to the beam in different corners of the room and, based on the results, determine the highest point. In this place, the height of the screed will be the minimum allowable - 4 cm. In other places - according to need.
To install beacons, gypsum is diluted to a thick sour cream state. Then small piles are made from the resulting mass along one wall, in increments of 60-80 cm, and a beacon profile is laid on them. By placing a square on it, level it with the horizon, placing it at the desired height. There should be 50 cm from the wall to the first beacon. Between adjacent beacons the distance varies depending on the length of the rule (guide by 1-1.3 m). Please note that the plaster sets quickly, the work is carried out “without a smoke break”.
After about 30-40 m, you can pour the screed. Cement is diluted with ASG in a ratio of 1:5. Polypropylene fiber is added at the rate of 80 g. per 100 liters of mixture. Fiber is an element of dispersed reinforcement, qualitatively increasing the strength of the coating. In addition, after hardening, the new surface will be perfectly smooth.
Pour the resulting mixture so that each subsequent portion overlaps the previous one by 10-15 cm. The screed is leveled according to the rule, with orientation along the beacons.
After filling the entire surface, time is required for the technical maturation of the cement-sand screed. Calculation is approximately the next 1 cm of thickness – 1 week.
Laying the heat insulator
Extruded polystyrene foam and cross-linked polyethylene foam, only these two materials can be used for thermal insulation in a water heated floor system.
Before laying the heat insulation sheets, a damper tape 10-12 mm thick is glued around the perimeter of the room. It serves not only to compensate for the thermal expansion of the screed, but also to prevent heat from escaping into the walls. In height, it should protrude beyond the boundaries of the top layer of the screed.
The heat insulation sheets are laid out staggered and always on top of the waterproofing layer. For waterproofing, it is best to use polyethylene film with a thickness of 0.2 mm.
If you decide to make the thermal insulation thickness 10 cm, then it will be better if you lay two layers of slabs 5 cm thick. Be sure to have a spacing between the layers.
There is an option to use special slabs designed for organizing water-heated floors as a heat insulator. Their difference is in the bosses on one of the surfaces. A pipe is laid between these bosses. But their cost is unreasonably high. In addition, not all pipes will be supported in such slabs. For example, polypropylene and polyethylene pipes are too elastic and will require additional fixation.
The pipes are not attached to the heat insulator. The fastener must pass through the foam layer and be fixed in the screed. This is a very labor-intensive process considering the amount of work involved.
Mounting tapes are a more acceptable solution, but it is very difficult to lay a pipe on them in a spiral (snail).
The best option would be to fix the pipes on the mesh. In this case, the mesh will serve specifically for fastening pipes, and not for reinforcing the screed.
There are special meshes made of biaxially oriented polypropylene, or you can use a simple masonry mesh.
See also: Infrared heated floor
Finishing
The work at this stage is no different from conventional flooring installation. Restrictions are imposed on the surface temperature, and not on the type of decorative finish.
IMPORTANT: absolutely any floor covering can be laid on water-heated floors. But some of them can reduce the energy efficiency of underfloor heating. The type of substrate is also taken into account when laying laminate flooring. For such a base, a thin, noise-absorbing, rather than heat-insulating, substrate is needed.
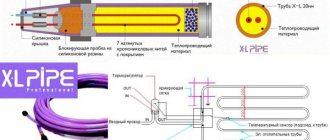
Selection of pipes and their installation
The following types of pipes are suitable for water heated floors:
- Copper;
- Polypropylene;
- Polyethylene PERT and PEX;
- Metal-plastic;
- Corrugated stainless steel.
They have their own strengths and weaknesses.
| Characteristic Material | Bend radius | Heat transfer | Elasticity | Electrical conductivity | Life time* | Price for 1 m.** | Comments |
| Polypropylene | Ø 8 | Low | High | No | 20 years | 22 RUR | They bend only with heat. Frost-resistant. |
| Polyethylene PERT/PEX | Ø 5 | Low | High | No | 20/25 years | 36/55 RUR | Can't withstand overheating. |
| Metal-plastic | Ø 8 | Below the average | No | No | 25 years | 60 RUR | Bending only with special equipment. Not frost-resistant. |
| Copper | Ø3 | High | No | Yes, requires grounding | 50 years | 240 RUR | Good electrical conductivity may cause corrosion. Grounding required. |
| Corrugated stainless steel | Ø 2.5-3 | High | No | Yes, requires grounding | 30 years | 92 RUR |
Note:
* pipe characteristics are considered when operating in water-heated floors.
** Prices are taken from Yandex.market.
The choice is very difficult if you try to save on yourself. Of course, you don’t have to consider copper ones - they’re very expensive. But corrugated stainless steel, at a higher price, has exceptionally good heat transfer. The difference in temperature in the return and supply is the largest. This means that they give off heat better than their competitors. Considering the small bending radius, ease of operation and high performance characteristics, this is the most worthy choice.
Pipe laying is possible in a spiral and snake. Each option has pros and cons:
- Snake - simple installation, almost always a “zebra effect” is observed.
- Snail – uniform heating, material consumption increases by 20%, installation is more labor-intensive and painstaking.
But these methods can be combined within one circuit. For example, along the walls “facing” the street, the pipe is laid in a snake pattern, and in the rest of the area in a snail pattern. You can also change the frequency of turns.
There are generally accepted standards that professionals are guided by:
- Step – 20 cm;
- The length of the pipe in one circuit is no more than 120 m;
- If there are several contours, then their length should be the same.
It is better not to install pipes under stationary and large-sized interior items. For example, under a gas stove.
IMPORTANT: be sure to draw the installation diagram to scale.
Laying begins from the collector. Unwinding the coil, fix the pipe according to the diagram. It is convenient to use plastic clamps for fastening.
Corrugated stainless steel is produced in coils of 50 m. To connect it, proprietary couplings are used.
The last element laid between the turns of pipes is a temperature sensor. It is pushed into a corrugated pipe, the end of which is capped and tied to a mesh. The distance from the wall is at least 0.5 m. Don’t forget: 1 circuit – 1 temperature sensor. The other end of the corrugated pipe is led out to the wall and then along the shortest path is brought to the thermostat.
Control system and circuit testing
The control system for water heated floors includes:
- Pump;
- Boiler;
- Collector;
- Thermostat.
The arrangement of all elements in compliance with technical parameters is a very complex thermal engineering task. A lot of parameters are taken into account, starting from the number of fittings and the length of pipes, and ending with the thickness of the walls and the region of the country. In general terms, you can focus on the following data:
- The pump can only be used as a circulation pump. The “wet” type of pump is more reliable than the “Dry” type and less demanding to maintain.
To calculate performance, use the following formula:
P = 0.172 x W.
Where W is the power of the heating system.
For example, with a system power of 20 kW, the pump capacity should be 20 x 0.172 = 3.44 m3/h. Round the result up.
The pressure is calculated using a more complex technique. After all, the pipes are located horizontally, and the pump characteristics show vertical pressure. Use the following formula: H = (L * K) + Z/10. Where L is the total length of the circuits, K is the pressure loss coefficient due to friction (indicated in the pipe passport, converted to MPa), Z is the pressure reduction coefficient in additional elements
Z1 – 1.7 thermostat valve;
Z2 – 1.2 mixer;
Z3 – 1.3 valves and fittings.
Using an example, it looks like this, let’s say there are 3 circuits, 120 m each. In total there are 18 fittings, 3 thermostat valves, 1 mixer. Pipe – corrugated stainless steel ø16 mm, loss coefficient 0.025 MPa.
H = (120*3*0.025) + ((1.7 * 3) + (1.3 * 1) + (1.2 * 18))/10 = 9 + (5.1 + 1.3 + 21 .6)/10 = 11.8 m. The result is rounded up - the pump head is 12 m.
- The boiler power is calculated using the formula W = S * 0.1. Where S is the area of the house. There are also a lot of correction factors, depending on the thickness and material of the walls of the house, the climate of the region, the number of floors, and the presence of adjacent rooms.
Please note that the outlet water temperature should be more than 30 – 35˚C. To withstand this temperature, a mixer is installed in front of the collector. In it, water is mixed to the desired temperature before entering the circuit.
- The collector regulates the water supply in each circuit. Without it, the water will follow the path of least resistance to flow, that is, along the shortest circuit. The adjustment is carried out by servo drives, according to data from the thermostat.
- Thermostats monitor the temperature in controlled rooms by taking readings from temperature sensors.
Before crimping the circuit, it is washed and only then connected to the manifold. Water is supplied at normal pressure, but the temperature is increased by 4˚C per hour, up to 50˚C. In this mode, the system should function for 60-72 hours. IMPORTANT: constant monitoring is required during crimping!
At home, without the use of special equipment, it is impossible to pressurize with high pressure.
If the inspection does not reveal any installation flaws, then you can proceed to further operations.
Screed
IMPORTANT: the top layer of screed is poured only when the contour is filled. But before this, the metal pipes are grounded and covered with thick plastic film. This is an important condition to prevent corrosion due to electrochemical interactions of materials.
The issue of reinforcement can be solved in two ways. The first is to place a masonry mesh on top of the pipe. But with this option, cracks may appear due to shrinkage.
Another method is dispersed fiber reinforcement. When pouring water-heated floors, steel fiber is best suited. Added in an amount of 1 kg/m3 of solution, it will be evenly distributed throughout the entire volume and will qualitatively increase the strength of hardened concrete. Polypropylene fiber is much less suitable for the top layer of screed, because the strength characteristics of steel and polypropylene do not even compete with each other.
Install the beacons and mix the solution according to the above recipe. The thickness of the screed must be at least 4 cm above the surface of the pipe. Considering that the pipe ø is 16 mm, the total thickness will reach 6 cm. The maturation time of such a layer of cement screed is 1.5 months. IMPORTANT: It is unacceptable to speed up the process including floor heating! This is a complex chemical reaction of the formation of “cement stone”, which occurs in the presence of water. And heating will cause it to evaporate.
You can speed up the maturation of the screed by including special additives in the recipe. Some of them cause complete hydration of cement within 7 days. And besides this, they significantly reduce shrinkage.
You can determine the readiness of the screed by placing a roll of toilet paper on the surface and covering it with a pan. If the ripening process is over, then in the morning the paper will be dry.
Commissioning
Full maturation of the cement screed occurs after a month, which is when balancing needs to be done using collector flow meters.
Using balancing valves, the coolant flow is regulated; it should become the same in all circuits. If you have no experience with self-balancing, it is better to invite a specialist.
After manipulating with cold water, if the system is working correctly, you can conduct tests with heated coolant. At this point, the installation of the heated floor is considered complete.