Here you will learn:
- Distinctive features of an indirect heating boiler
- Types of gas boilers
- What is a single-circuit boiler
- Schemes for connecting a boiler to a single-circuit boiler
- What is a double-circuit boiler
Modern models of gas boilers with one circuit for heating the heating fluid could be called primitive water heating devices if they were not equipped with high-precision control and monitoring equipment to ensure the reliability and safety of all operating cycles. To solve the problems of regulation and safety of boilers, an automatic boiler protection system with gas flow and pressure regulators, fittings that regulate the flow, temperature and pressure of heated water, all kinds of sensors, instruments and safety devices is aimed. This is the main advantage of gas boilers.
Other important benefits:
- simplicity of design and installation of the boiler, which includes a combustion chamber with a gas burner, a loop heat exchanger in the firebox, a system of manifolds and pipelines, and pumping equipment;
- efficiency achieved by automation and adjustment work for optimal and efficient combustion of fuel, mixing processes and regulation of coolant parameters in accordance with standards;
- the ability to connect boilers to cascade heating systems within cities and large towns, which allows not only to centrally control the system, but also to ensure reliable and high-quality heat supply to consumers in residential areas, neighborhoods, microdistricts, as well as enterprises whose boiler houses are included in the cascade;
- more environmentally friendly emissions of gas combustion products into the atmosphere compared to similar boiler houses using liquid and solid fuels.
Distinctive features of an indirect heating boiler
A boiler is a large barrel whose main function is storage. It comes in different volumes and shapes, but its purpose does not change. Without a boiler, a problem may arise when using, for example, two showers or a shower and a kitchen tap at once.
If a household 2-circuit boiler with a power of 24-28 kW produces only 12-13 l/min per flow, and one shower requires 15-17 l/min, then when any additional tap is turned on, there will be a shortage of water supply. The boiler simply does not have enough working capacity to provide hot water to several points.
If a large storage tank is installed in the house, even with several water points turned on at the same time, everyone will be provided with hot water
All storage boilers can be divided into 2 large categories:
- direct heating, creating a supply of hot water using a heating element - for example, an electric heating element;
- indirect heating, heating water with already hot coolant.
There are other types of boilers - for example, conventional storage water heaters. But only volumetric storage devices can indirectly receive energy and heat water.
BKN, unlike energy-dependent equipment running on electric, gas or solid fuel, uses the heat generated by the boiler. Simply put, it does not require additional energy to function.
BKN design. Inside the tank there is a coil - a steel, brass or copper tubular heat exchanger that acts as a heating element. Heat inside the tank is retained according to the principle of a thermos
The storage device fits easily into the DHW system and does not cause problems during operation.
Users see many advantages in using BKN:
- the unit does not require electrical power and benefits from the economic side;
- hot water is always “ready”, there is no need to let cold water pass through and wait for it to heat up;
- Several water distribution points can operate freely;
- stable water temperature that does not drop during consumption.
There are also disadvantages: the high cost of the unit and additional space in the boiler room.
The volume of the storage tank is chosen based on the number of people permanently residing in the house. The smallest boilers are designed for 2 consumers, so when choosing, you can start from a volume of 50 liters
According to all characteristics, the BKN is suitable for use in conjunction with a gas boiler. Moreover, this is one of the best solutions for equipping a hot water preparation system for a private house with a large number of residents.
But boilers are different, so we will consider both acceptable options and those where problems may arise.
Nuances of the strapping device
It is easier to do the wiring and piping if the KN boiler is installed together with a boiler, pumps and other equipment involved in the assembly of the hot water supply system. It is much more difficult to insert an additional device into an existing network.
In any case, for normal operation of the devices you will have to follow a number of rules:
- choose the right installation location - as close to the boiler as possible;
- provide a flat surface for mounting the boiler;
- to protect against thermal expansion, install a membrane hydraulic accumulator (at the heated water outlet), the volume of which is at least 1/10 of the volume of the BKN;
- equip each circuit with a ball valve - for convenient and safe maintenance of devices (for example, a three-way valve, pump or the boiler itself);
- to protect against backflow, install check valves on the water supply pipes;
- improve water quality by installing filters;
- correctly position the pump (or several pumps) - the motor axis must be in a horizontal position.
For safety reasons, do not attempt to secure heavy devices to plasterboard or thin wood partitions. Walls made of concrete and brick are suitable. Brackets or other types of holders are secured with brackets, anchors, and dowels.
When installing, the pipes are directed towards the boiler (even if they are masked in the back or behind a false wall). Do not use unreliable equipment, such as corrugated hoses that cannot withstand pressure and water pressure.
For normal operation of an indirect heating storage water heater, the following functional devices must be included in the piping:
Types of gas boilers
Gas devices with an indirect heating boiler may differ in the type of placement and shape of the tank.
According to the principle of placement: wall and floor
Can be:
- wall;
- floor
Units of the first category are devices of small volume - up to two hundred liters.
A floor-standing gas boiler in a package, with an indirect heating boiler, is installed in a special room.
They are installed using special brackets on a stable wall that can support the weight of the water tank without loss. It is clear that flimsy plasterboard partitions are not suitable for this purpose. Typically, such devices are purchased by one small family for their private home.
The second ones are capacious water heaters designed for a large number of people. Such devices will require the installation of a special boiler room.
They are usually purchased by enterprises and owners of large cottages and estates.
According to the shape of the tank
- Horizontal: very bulky, but they do not require pumps; they themselves maintain the water in the required volume.
- Vertical: have a small capacity.
When choosing, you should take into account the number of people in the family, as well as the layout features and the availability of free space in the country house or in the house.
Gas floor-standing boiler installed in the boiler room and a small vertical expansion tank.
Wood-fired hot water supply
For organizing hot water supply in a small country house with seasonal residence, a titanium wood-burning hot water heater may be suitable. It consists of a stove, a vertical water tank, a tap and a shower device.
Advantages of titanium:
- energy independence – the ability to use any type of solid fuel (with the exception of coal);
- maintaining a certain water temperature (for models with heating elements);
- heating the room in which it is located.
To remove combustion products, you will need to install a chimney and connect a column to it.
What is a single-circuit boiler
Single-circuit gas boilers are used to heat the coolant that fills the heating system. A single-circuit boiler does not prepare water for hot water supply. In rooms where the heated area sometimes exceeds three hundred square meters, floor-standing boilers are used. These heating devices are much more powerful than wall-mounted ones.
Wall-mounted single-circuit heating devices are most often used in high-rise apartments and can heat an area of up to three hundred square meters. These boilers are much more compact than floor-standing ones, and weigh just over 40 kilograms. The wall-mounted single-circuit boiler fits organically into the interior. Also, these wall-mounted devices are more functional than their floor-standing counterparts. The power of the most advanced models of wall-mounted single-circuit boilers is no more than 35 kilowatts.
A single-circuit gas boiler does not have any complex elements or mechanisms in its design. This boiler consists of:
- burners;
- heat exchanger;
- control unit;
- water pump;
- turbine electric motor (if the boiler has a closed combustion chamber);
- pressure gauge;
- sensors;
- shut-off valves.
Wall-mounted single-circuit boilers can be equipped with an expansion tank, which is hidden under the boiler casing. Also, the expansion tank can be part of a floor heating device, which has low power.
Operating principle of single-circuit boilers
Gas single-circuit boilers with an indirect boiler operate according to two main connection schemes. The principle of operation of the first is as follows:
- The three-way valve dominates here. A pump is installed directly into the outlet of the gas boiler, which provides circulation and creates pressure. The next step is to install a three-way valve, which is connected to the boiler thermostat. When heating tap water or other coolant, its flow is directed to the heating system, with priority for the hot fluid entering the boiler coil. This happens with the help of an additional, second pump. And it turns out that in this case the hot water supply and the heating system are connected in parallel, and they can form two circuits, precisely in this closed chain. And after the boiler, an additional pump is installed, which helps regulate the operation of the thermostat. The principle of starting and stopping the process is also regulated by a thermostat, namely, when the heating is strong, the fuel supply is forced to shut off, when the coolant cools down, the fuel is passed through again, and the burner is automatically ignited.
- If there is no double circuit and priority is not given to heating hot water, the boiler is mounted in a common system, installed in a convenient location, and water is heated along with all radiators.
Methods of heating water - flow-through from a small tank
More and more combined gas boilers are appearing on the market, i.e. instantaneous water heaters, but at the same time equipped with a storage tank for hot water with a capacity of several tens of liters. This combination makes sense because it allows:
- reduce the frequency of boiler starts, since with low water consumption from the tank there is enough water;
- provide a stable flow of water even when drawing from several points;
- use the hot water circuit for domestic needs;
- provide any amount of water for increased consumption (i.e. prepared tap water).
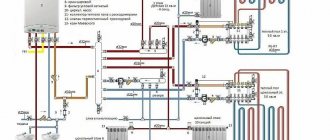
Schemes for connecting a boiler to a single-circuit boiler
There are three ways to connect the boiler to the boiler.
Direct connection of the water heater to the heating system
In this embodiment, the BKN is included in the heating system, in series or in parallel with other radiators. The simplest and most ineffective scheme is not recommended for use and is given for reference.
Scheme of direct connection of a water-heating gas single-circuit boiler to the heating system.
If the boiler temperature is set below 60 °C, this scheme becomes even less economical, and the water takes a very long time to heat up.
Temperature increase
A three-way valve is added to the connection diagram - a special device that switches the movement of the coolant when the temperature in the water heater tank drops to DHW and vice versa.
Thus, if the DHW water cools down, the heating is temporarily turned off. All boiler power is redirected to DHW. The temperature on the device in this scheme is set higher (usually 80–90 °C). And the heating temperature is regulated by a three-way valve.
Reference! The boiler temperature must be set 5 °C above the required DHW water.
Using a thermostat in a water heater and automation
If a thermostat is installed in the BKN (a device that gives a signal when a set temperature is reached), and the boiler controller has contacts for connecting the boiler thermostat, then this circuit is the most preferable.
In this case, the boiler electronics know about the temperature of the water in the DHW system, and it decides where to direct its power: to heat water in the BKN or for heating.
Thermostat for a water heater in a heating system, with it you can find out data on the water temperature.
Electric water heaters
One of the options for organizing hot water supply (DHW) in a country house is an electric water heater that heats water using electricity. They are divided into flow and storage.
Flow-through models heat water as soon as the user opens the tap. A storage type water heater allows you to use hot water only after some time has passed (the duration of heating depends on the power and capacity of the water heater, as well as on the set temperature).
Water heaters spend the same amount of energy to heat a certain volume of water to the desired temperature. But since the “flow tank” must heat the water quickly, it consumes a lot of energy at a time and in many country houses the power may not be enough for its operation. Powerful (from 10 kW) instantaneous water heaters require connection to a three-phase network with a voltage of 380 V. Storage water heaters are simpler - to put them into operation, you just need to connect them to a water supply system and connect them to a regular single-phase electrical network.
What is a double-circuit boiler
This heating device not only heats the coolant, but is also intended for preparing hot water. A double-circuit boiler has a more complex structure than its single-circuit counterpart. The most complex device has a dual-circuit heating device, which is equipped with a three-way valve.
There are dual-circuit heating devices that are equipped with a pair of heat exchangers. One heat exchanger is responsible for heating water in the heating system, and the second heats water for water supply. The most rational design has dual-circuit heating devices that are equipped with a bithermic heat exchanger. Such a heat exchanger is two in one. Inside the bithermic heat exchanger there is another heat exchanger, which is designed to heat water for domestic purposes. But boilers with separate heat exchangers are considered more popular models.
Double-circuit gas boilers are good because they solve all the problems associated with preparing hot water for heating a room. Such heating devices are quite compact and fit organically into any interior. The design of a double-circuit heating device resembles the design of its single-circuit counterpart, which is also supplemented:
- a second heat exchanger (if the boiler design provides for this);
- 3-way valve (if the heat exchanger is not bithermic);
- inlet and outlet for the DHW pipeline.
Advantages and disadvantages
The absolute advantages of boilers with indirect heating heaters include savings on electricity.
No atmospheric burner or power source is required, as with direct heating devices. The heating system will do everything itself, which significantly reduces waste of money.
- Productivity: a tank with a capacity of one hundred liters produces approximately 400 liters of hot water per hour.
- Virtually instant hot water supply.
- Possibility of using multiple energy sources, for example, a geothermal system.
- Democratic price.
- Simplicity in the device.
- The warm-up speed, even in new models, will not be instantaneous.
- Massiveness.
Attention! If the family is very tall, then one room will need to be given over to the boiler room, displacing itself. Small models will not solve the problem of washing.
Placement of a double-circuit boiler
The main purpose of double-circuit boilers is in small houses and apartments, where the equipment is located near the kitchen, but not far from the bathroom. Short distances are a necessity for this type of boiler; the shorter the path of hot water to the consumer, the better, so that you don’t have to wait too long for hot water to flow.
Experts believe that the maximum distance from the heating circuit to the tap is 7 meters. Anything more and it all just becomes wasteful. The usual distances are from 1.5 to 3 meters. But the priority placement is the kitchen, where the hot tap opens frequently.
Introduction of a boiler into the DHW circuit
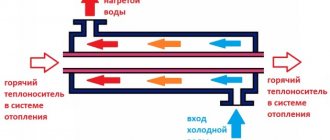
First, let's consider the option when the boiler is integrated into the DHW circuit. From a hydraulic point of view everything looks correct. A three-contact mechanical thermostat, placed in the boiler body, closes the power supply circuit to the pump when the temperature drops.
That, in turn, begins to pump water, which circulates along the circuit between two heat exchangers: it is heated by a gas burner, and then moves to the BKN coil.
Simply put, both devices perform their functions: the boiler stops heating and begins to heat water for hot water supply, and the boiler tries to heat the contents of its “storage” due to the increased temperature of the hot water.
The problem arises precisely because of the mismatch of temperature parameters. Let's assume that the initial filling temperature of the boiler is +15˚С, and the recommended temperature for heating water in the boiler is +60˚С - the automatic limiter no longer allows.
The difference between the two set parameters of 45˚ is significant, so the heat exchange in the boiler occurs quite intensively. But the temperature begins to rise, and when it reaches +40˚С, the difference is much smaller - only 20˚. Accordingly, heat transfer slows down.
Don't forget that water continues to circulate between the two devices. The gas burner of the boiler begins to receive not a 15-degree coolant from the cold water system, as recommended by the manufacturer, but a 40- and then 50-degree heated liquid from the boiler.
As a result, the temperature of the liquid instantly soars to +60˚С, the sensor is triggered, the burner turns off, as it is programmed for parameters that are safe for consumers
The water in the boiler begins to cool - the sensor turns on again and the circulation process resumes. And so on all the time. This leads to the fact that the water in the boiler does not reach the required temperature, but remains insufficiently hot, which is not suitable for domestic hot water use.
The process of interaction between the two units could take place if the boiler burner heated the coolant to +80˚C, but this is prohibited by the instructions to protect users from burns.
Another reason not to use the BKN and DHW circuit of a gas boiler in steam lies in the inability to heat the water in the boiler to a temperature exceeding +60˚C. This is due to sanitary standards.
About once a week, the device is filled with hot water at about 70-75˚C, so that the legionella bacterium, whose colonies resemble mucus, does not multiply in the tank. A large number of bacteria in water leads to the development of allergies and other diseases
It can be concluded that due to only two, but significant reasons, the scheme of combining a gas boiler and BKN through a hot water supply circuit was recognized as ineffective and unsafe. If you already have a double-circuit boiler, just use it for its intended purpose: use one circuit for the heating system, the second for DHW.
Interaction of BKN with the heating circuit
The second option is the interaction of the BKN with the heating circuit. The technical solution works great if the performance of the gas boiler is not enough, and this is the only effective way to connect the BKN to a 2-circuit boiler.
We do not touch the hot water circuit, but use only the branch responsible for heating - that is, going to the radiators and the “warm floor” system. The pipe leading to the boiler must be connected immediately under the boiler, after the tap
With electronic control, you need to set the boiler to heat water at +70°C - this is the coolant that will flow into the boiler, where further temperature adjustment will take place. The thermostat located in the boiler will turn on the pump when the temperature drops, and turn it off when the required value is reached.
With mechanical control of a gas boiler, everything happens differently. A second thermostat, the boiler, is connected to the boiler thermostat, and then the first device can be controlled using the second. For example, if you set the temperature on the second one to +80°C, then the first one, the worker, will require heating the water to +80°C, regardless of what temperature it is set to.
When the water in the boiler heats up to the required temperature, the second thermostat breaks the circuit, and the first one, located on the boiler, again becomes the “main” thermostat. If at this moment the temperature is set to +40°C, then it will drop to 40.
Solar water heaters
Currently, in the areas of heating and hot water supply, there is a tendency to increase the use of systems that operate using alternative energy sources. The hot water supply system for a private home can be built on the basis of a solar water heater.
A solar water heater is a whole system, the main elements of which are a solar collector, which is installed on the roof of the house and a boiler located on the roof or inside the house.
There are three types of solar water heaters:
- direct heating;
- indirect heating;
- split systems.
In the first case, water heated in the collector by the sun's rays enters the boiler, and from it to the water collection points. In an indirect heating scheme, a liquid is heated in the collector, which transfers its heat to the water in the boiler through condensers. Both of these systems are energy independent, but can only work during warm periods of the year (the boiler is located on the roof, since it is a single structure with the collector).
The split system is designed for year-round operation. Its collector, installed on the roof, contains a coolant that transfers heat to water through a heat exchanger in a boiler located inside the house. Such a system is energy-dependent because it includes a pump that circulates the coolant.
Operation and Maintenance
Every 2–3 years, the boiler requires a set of maintenance similar to electric water heaters: flushing the tank, removing scale, replacing the sacrificial anode when it is thinned by more than 50%, replacing gaskets. It is reasonable to carry out an inspection involving the removal of the technical flange of the tank in the summer in conjunction with maintenance of the heating system. Flushing the heating circuit and the boiler heat exchanger with chemicals must be carried out separately using appropriate cleaning agents. Otherwise, these devices are very unpretentious.
Advantages
Modern models of gas boilers with one circuit for heating the heating fluid could be called primitive water heating devices if they were not equipped with high-precision control and monitoring equipment to ensure the reliability and safety of all operating cycles. To solve the problems of regulation and safety of boilers, an automatic boiler protection system with gas flow and pressure regulators, fittings that regulate the flow, temperature and pressure of heated water, all kinds of sensors, instruments and safety devices is aimed. This is the main advantage of gas boilers.
Other important benefits:
- simplicity of design and installation of the boiler, which includes a combustion chamber with a gas burner, a loop heat exchanger in the firebox, a system of manifolds and pipelines, and pumping equipment;
- efficiency achieved by automation and adjustment work for optimal and efficient combustion of fuel, mixing processes and regulation of coolant parameters in accordance with standards;
- the ability to connect boilers to cascade heating systems within cities and large towns, which allows not only to centrally control the system, but also to ensure reliable and high-quality heat supply to consumers in residential areas, neighborhoods, microdistricts, as well as enterprises whose boiler houses are included in the cascade;
- more environmentally friendly emissions of gas combustion products into the atmosphere compared to similar boiler houses using liquid and solid fuels.