Machine power calculation
The circuit breaker must be selected in such a way that it best matches the power of the connected electrical appliance. In simple words, if you are installing a 6 kW electric boiler, then you need to choose the machine with the appropriate power.
To do this, you first need to find out how much this or that machine can withstand, for example, 16 or 32 Amperes. To do this, you can use one simple formula and multiply the voltage in the network by the rating of the machine. If the network is 220 Volts and the circuit breaker is 16 Amperes, then we multiply 220 * 16 and get the power that the circuit breaker can withstand. In this case it is approximately 3.5 kW.
As you can see, much of the selection of circuit breaker power is related to the network voltage. That is, 220 or 380 Volts are very important, since the load is distributed evenly over each phase, and not into two. For clarity, below is a table from which you can easily calculate the power of the circuit breaker.
What wire cross-section is needed for 3 kW and others - we study the issue from different angles
Wiring
31.03.2017
18.8 thousand
12.6 thousand
5 minutes.
When installing electrical wiring in a new house or replacing an old one during renovation, every home craftsman asks the question: what cross-section of wire is needed? And this question is of great importance, since not only the reliable operation of electrical appliances, but also the safety of all family members largely depends on the correct choice of cable cross-section, as well as the material for its manufacture.
The most common types of wiring in our homes are aluminum and copper. Which one is better is a question that still haunts users of numerous forums. For some, copper is a priority, while others say that there is no need to overpay and aluminum will do for a home network. In order not to be unfounded, let's do a little analysis of these options and then everyone can choose an option for themselves.
Aluminum wiring is very popular because it is lightweight
Aluminum wiring is lightweight, due to which it is widely used in the electrical power industry. It is used for laying power lines, since in this way the load on the supports can be minimized. In addition, it has gained popularity due to its low cost. Aluminum cable costs several times less than its copper counterpart. During the Soviet Union, aluminum wiring was very common; it can still be found in houses built some 15-20 years ago.
However, aluminum cable also has its downsides. One of these points that is definitely worth mentioning is the short service life. After two decades, aluminum wiring becomes highly susceptible to oxidation and overheating, which often leads to fires. Therefore, if you still have such cables in your home, think about replacing them. In addition, the oxidation to which aluminum is susceptible reduces the useful cross-section of the cable with a simultaneous increase in resistance, and this leads to overheating. Another significant disadvantage of aluminum is its fragility. It breaks quickly if the cable is bent several times.
Important! PUE prohibits the use of aluminum cable for installation in electrical networks if its cross-section is less than 16 mm.
Copper cable bends well and does not break
As for copper wire, its advantages include a long service life - more than half a century, excellent conductivity and mechanical strength. It is much easier to work with copper cable, because it bends without breaking and can withstand repeated twisting. The disadvantage of copper cable wiring is the cost. To replace the power cable in the entire apartment you will need a significant amount of money. To save money, some craftsmen combine the laying of aluminum wires with copper ones. The entire lighting part is mounted from aluminum, and the socket part is made from copper, since the lighting does not require such a large load as electrical appliances powered into the network.
If previously the equipment in an apartment was limited to a refrigerator and a TV, then nowadays you won’t find anything in an apartment: vacuum cleaners, computers, hair dryers, microwave ovens, etc. All this requires power, and depending on the time of day, the load from devices connected to the network can vary greatly. And in order to choose the right cable for each point to which the device is powered, you need to know:
- current strength;
- voltage;
- power consumption of the device in watts or kilowatts.
For single-phase networks that are present in our apartments, there is a certain formula that allows you to determine the current strength of the devices:
I = (P × Ki) / (U × cos(φ) ), where
I – current strength;
P – power consumption of all electrical appliances (it is necessary to add their nominal value):
| Single-phase boiler | 5–7 kW |
| Fan | up to 900 W |
| Oven | from 5 kW |
| Computer | 600-800 W |
| Microwave | 1.2–2 kW |
| Mixer | 300 W |
| Freezer | 150–300 W |
| Lighting | 100–1000 W |
| Grill oven | 1 kW |
| Dishwasher | 1.8–2.5 kW |
| Vacuum cleaner | 1200 W |
| Juicer | 250 W |
| Washing machine | 600–2500 W |
| TV | 100–200 W |
| Warm floor | 0.7–1.5 kW |
| Toaster | 750–1000 W |
| Iron | 1000–2000 W |
| Hairdryer | 500–1000 W |
| Fridge | 150–300 W |
| Electric hob | from 5 kW |
| Electric coffee maker | 700–1000 W |
| Electric meat grinder | 1000 W |
| Electric stove | 9–12 kW |
| Electric fireplace | 9–24 kW |
| Electric boiler | 9–18 kW |
| Electric kettle | 2 kW |
Ki – simultaneity coefficient (often, for simplicity, a value of 0.75 is used);
U – phase voltage, it is 220 (V), but can range from 210 to 240 (V);
Cos (φ) – for household appliances the value is unchanged and equals 1.
For simplicity, you can use the formula: I = P / U.
When the current is determined, the wire cross-section can be determined using the following table:
Table of power, current and cross-section of cable and conductor materials
| Conductor cross-section, mm | ALUMINUM | |||
| Voltage, 220 V | Voltage, 380 V | |||
| current, A | power, kWt | current, D | power, kWt | |
| 2,5 | 20 | 4,4 | 19 | 12,5 |
| 4 | 28 | 6,1 | 23 | 15,1 |
| 6 | 36 | 7,9 | 30 | 19,8 |
| 10 | 50 | 11,0 | 39 | 25,7 |
| 16 | 60 | 13,2 | 55 | 36,3 |
| 25 | 85 | 18,7 | 70 | 46,2 |
| 35 | 100 | 22,0 | 85 | 56,1 |
| 50 | 135 | 29,7 | 110 | 72,6 |
| 70 | 165 | 36,3 | 140 | 92,4 |
| 95 | 200 | 44,0 | 170 | 112,2 |
| 120 | 230 | 50,6 | 200 | 132,0 |
| Conductor cross-section, mm | COPPER | |||
| Voltage, 220 V | Voltage, 380 V | |||
| current, A | power, kWt | current, A | power, kWt | |
| 1,5 | 19 | 4,1 | 16 | 10,5 |
| 2,5 | 27 | 5,9 | 25 | 16,5 |
| 4 | 38 | 8,3 | 30 | 19,8 |
| 6 | 46 | 10,1 | 40 | 26,4 |
| 10 | 70 | 15,4 | 50 | 33,0 |
| 16 | 85 | 18,7 | 75 | 49,5 |
| 25 | 115 | 25,3 | 90 | 59,4 |
| 35 | 135 | 29,7 | 115 | 75,9 |
| 50 | 175 | 38,5 | 145 | 95,7 |
| 70 | 215 | 47,3 | 180 | 118,8 |
| 95 | 260 | 57,2 | 220 | 145,2 |
| 120 | 300 | 66,0 | 260 | 171,6 |
If during the calculations it turns out that the value does not coincide with any one given in the table, then the next larger number should be taken as a basis. For example, if your value is 30 A, then when using aluminum wiring you should choose a wire cross-section of 6 mm2, and 4 mm2 will be enough for copper.
To choose the right cable for each point at which the device is powered, you need to know the current, voltage, and power consumption of the device
Typically a modern apartment consumes approximately 10 kW.
When buying a wire, it would be useful to check its cross-section, since many manufacturers work according to specifications. Because of this, not all products meet the declared characteristics. Therefore, it is necessary to stock up on calipers and measure the diameter of the core, which will help us determine the real value of the wire cross-section. To simplify the work, we present the simplest formula, so you will not need to make additional calculations: S = 0.785d2, where S is the desired section; d – core diameter. The final value must be rounded to 0.5. So, if you get a value of 2.4, then you should choose a cable with a cross-section of 2.5 mm2.
In most of our houses, the cable is laid in the walls. This is called closed wiring. Wires can run through cable ducts, pipes, or simply be walled into the wall. In some houses, and this applies to wooden buildings and old housing stock, you can find exposed wiring. It is noteworthy that for open installation you can use a cable of a smaller cross-section, since such a wire heats up less than the one that is walled into the wall. For this reason, when laying wires in grooves, it is recommended to choose a cable with a larger cross-section. This way the cable will heat up less, which means it will wear out more slowly. In the table below you can find out how many squares of cable you need to take for devices of different power, be it 1 or 6 kW:
| Cable cross-section, mm2 | Open wiring | Gasket in channels | ||||||||||
| Copper | Aluminum | Copper | Aluminum | |||||||||
| Current | power, kWt | Current | power, kWt | Current | power, kWt | Current | power, kWt | |||||
| A | 220V | 380V | A | 220V | 380V | A | 220V | 380V | A | 220V | 380V | |
| 0,5 | 11 | 2,4 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | |
| 0,75 | 15 | 3,3 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | |
| 1,0 | 17 | 3,7 | 6,4 | – | – | 14 | 3,0 | 5,3 | – | – | – | |
| 1,5 | 23 | 5,0 | 8,7 | – | – | 15 | 3,3 | 5,7 | – | – | – | |
| 2,0 | 26 | 5,7 | 9,8 | 21 | 4,6 | 7,9 | 19 | 4,1 | 7,2 | 14,0 | 3,0 | 5,3 |
| 2,5 | 30 | 6,6 | 11,0 | 24 | 5,2 | 9,1 | 21 | 4,6 | 7,9 | 16,0 | 3,5 | 6,0 |
| 4,0 | 41 | 9,0 | 15,0 | 32 | 7,0 | 12,0 | 27 | 5,9 | 10,0 | 21,0 | 4,6 | 7,9 |
| 6,0 | 50 | 11,0 | 19,0 | 39 | 8,5 | 14,0 | 34 | 7,4 | 12,0 | 26,0 | 5,7 | 9,8 |
| 10,0 | 80 | 17,0 | 30,0 | 60 | 13,0 | 22,0 | 50 | 11,0 | 19,0 | 38,0 | 8,3 | 14,0 |
| 16,0 | 100 | 22,0 | 38,0 | 75 | 16,0 | 28,0 | 80 | 17,0 | 30,0 | 55,0 | 12,0 | 20,0 |
| 25,0 | 140 | 30,0 | 53,0 | 105 | 23,0 | 39,0 | 100 | 22,0 | 38,0 | 65,0 | 14,0 | 24,0 |
| 35,0 | 170 | 37,0 | 64,0 | 130 | 28,0 | 49,0 | 135 | 29,0 | 51,0 | 75,0 | 16,0 | 28,0 |
It should be understood that incorrect determination of the cross-section of the power cable will, at best, damage the electrical appliance, and at worst, it may result in a fire. This, in particular, applies to laying electrical wiring of a smaller cross-section. When laying a deliberately larger cross-section, you are wasting money, since there is no point in deliberately increasing the cross-section of the cable unnecessarily. Following all of the above methods, you can easily determine what wire cross-section is needed for 3 kW, both for aluminum and copper cable.
obustroen.ru
What is important to know when connecting electrical appliances
So, having calculated the approximate rating of the required machine, you need to give an explanation regarding the power. Many people wonder whether it is possible to plug in very powerful electrical appliances into a regular outlet, such as an electric boiler, for example.
According to the rules of the PUE, connecting an electric boiler with a power of more than 3 kW to a regular outlet is unacceptable. And each outlet has its own specific characteristics. Most often, home sockets are rated at 16 amperes, and, therefore, electrical appliances with a power of no more than 3.5 kW can be connected to them.
Therefore, any more or less powerful electrical appliance must be connected only through a separate circuit breaker. Moreover, it is the phase wire that is supplied to the circuit breaker, and not the working zero. Thus, knowing the approximate power of the equipment, you can easily calculate the rating of the circuit breaker.
Is it worth taking a machine with a reserve?
This is a moot point. On the one hand, the circuit breaker must correspond to the power of the electrical appliance; on the other hand, it must have a small margin so as not to turn off during operation.
As an example, we can cite the same electric boiler with a capacity of 6 kW. Divide 6 kW by 220 volts (mains voltage) and get a value of 27. These are amperes. That is, to connect a 6 kW boiler, you need a 27 Ampere circuit breaker. However, such machines do not exist in nature.
Therefore, here you have to choose between a 25 and 32 Ampere machine. Ideally, of course, so that the boiler does not turn off, you need to install a 32 Ampere machine. But this does not mean that a 25 Ampere machine will not work as expected. It’s just that, given the somewhat reduced power, it may turn off from time to time when the boiler operates at full capacity for a long time.
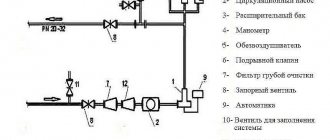
Automation design
All internal equipment of automation for gas boilers, which is used when installing a heating system, can be divided into categories, there are only two of them:
- the first category is those devices that ensure the safe and proper operation of all boiler equipment;
- the second category is those devices that can significantly increase the comfort when using the boiler.
Safety automation for gas boilers consists of the following elements:
- the module that provides flame control. It consists of a thermocouple and a gas valve that works like an electromagnetic valve and shuts off the fuel supply;
- there is also a device that protects the system from overheating and maintains the required temperature; this task is performed by the thermostat. It independently, if necessary, turns on or off the boiler at those moments when the temperature approaches the specified peak levels;
- the sensor that controls traction. This device works based on vibrations depending on how the position of the bimetallic plate changes. It, in turn, is connected to a gas valve, which stops the gas supply to the burner;
- there is also a safety valve, which can be responsible for discharging excess coolant (for example, air or water) in the circuit. Some manufacturers immediately provide an element that helps dump excess.
The devices included in the security system are divided into the following types:
- mechanical;
- and operating from a power source.
They operate either under the influence of a drive and a controller that controls them, or are coordinated electronically.
Automation provides the user with more comfortable functionality, which is additional:
- automatic ignition of the burner;
- flame intensity modulation;
- self-diagnostic functions.
But such functionality is not limited to the internal design of the models.
Some design features of the models include additions such as sending data and processing it by an electronic system on equipment equipped with controllers and microprocessors. Then the following situation occurs: based on the received data, the controller itself begins to adjust the commands that activate the machine’s system drives.
Mechanical automation of a gas boiler also requires detailed consideration.
- The gas valve is completely closed and the heating installation is inoperative.
- In order to start a mechanical gas boiler, the washer is squeezed out, allowing the fuel to start and opening the valve.
- The valve opened under the influence of the washer and gas flowed to the igniter.
- Ignition is in progress.
- After this, gradual heating of the thermocouple begins.
- The electric shut-off magnet is supplied with a voltage that ensures its open position so that fuel access is not blocked.
- Mechanical rotation of the washer regulates the required power of the gas heating device, and the fuel in the required volume and with the required pressure is supplied to the burner itself. The fuel ignites and the boiler unit begins to operate.
- And after that, this process is controlled by a thermostat.
You might be interested >> Gas double-circuit boiler Buderus