In houses where there is no gas or centralized heating, individual heating systems are used, including solid fuel and electric boilers or solar systems powered by solar energy. These systems have an important drawback - uneven heating of the coolant due to the fundamental features of operation or the influence of external factors. They can be optimized using a heat accumulator for heating, which will play the role of a buffer between the heat source and consumers.
Purpose of the heat accumulator
The heat storage tank can be connected to any type of boiler.
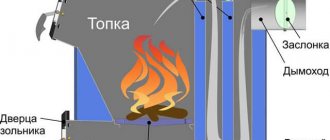
The heat storage tank for various types of heating boilers is an impressively sized water-filled tank that allows you to solve problems that arise during the operation of the heating boiler:
- excessive energy consumption;
- excess heating power;
- overheating of water in the boiler;
- periodic fluctuations in heating temperature due to the unevenness of the combustion process itself and untimely placement of firewood and coal;
- discrepancy between the peaks of production and consumption of thermal energy.
Some problems can be solved by installing a long-burning pyrolysis boiler, but in the latter case it will not help. The peculiarity of the boiler operation is that after adding fuel, the power of thermal energy output gradually increases, reaching peak values, and then also gradually decreases. If you do not add fuel to the boiler in time, it stops, the coolant begins to cool, and at the same time the temperature in the house drops. During the period of peak heat production, the system is not able to efficiently distribute all the energy, since it is equipped with thermostats, so some of the heat is wasted. If the boiler is electric, it is much more profitable to accumulate heat at night, when electricity is calculated at a preferential night tariff, in order to consume as little electricity as possible during the day.
The heat accumulator reservoir for the heating system is made of stainless or ordinary steel; the inside can be coated with a protective varnish. The walls are painted on top with heat-resistant paint, then covered with heat-insulating material and leatherette. In fact, when a heat accumulator is connected, the volume of coolant in the heating system increases, which makes it possible to compensate for the peak power of the boiler and at the same time accumulate heat to transfer it to the coolant when the boiler’s thermal energy generation capacity drops. Thanks to high-quality insulation, the water in the heat accumulator cools down for a long time. It is kept in a heated state for several hours and even days and is fed into the system through a pump. The operating principle of a heat accumulator is based on the different heat capacities of different media, in particular water and air. A decrease in the temperature of 1 liter of water by one degree leads to an increase in the temperature of air with a volume of 1 m3 by 4 degrees.
If, when using solid fuel and electric boilers, the installation of a heat accumulator is desirable, but not mandatory, then the presence of a heat accumulator in the solar system is a necessary condition for operation, since in the evening and at night solar energy cannot be obtained, and in the fall and winter on cloudy days, the use of the system is very limited.
Advantages and disadvantages
You can install a heat accumulator, which has boiler functions.
Advantages of using a heat accumulator:
- Retains thermal energy for hours and days.
- Overheating of the boiler is avoided.
- Thermal energy is not wasted, but is accumulated to be used in the future, thanks to this the efficiency of the boiler and the heating system as a whole increases.
- Allows you to save money.
- The air temperature in the rooms is easily maintained at the optimal level, sudden temperature changes are excluded.
- There is no need for frequent fuel loading.
- In addition to a solid fuel boiler, you can install a solar system, which is a free source of thermal energy.
- Some models of thermal accumulators for heating can combine the functions of a boiler.
Disadvantages of the system:
- Long heating - optimal installation in houses intended for permanent residence. In country cottages that are visited on weekends in winter, such a device will not be of any use.
- High cost - they cost about the same as the boiler, and sometimes more.
- Significant dimensions and weight - because of this, certain difficulties arise during transportation and installation. In addition, a heat accumulator intended for heating is installed in close proximity to the boiler; additional equipment must also be located there, so it is often necessary to allocate a special room for installing devices and prepare it in a special way: to equip a support platform capable of supporting the weight of the accumulator. When filled, the tank can weigh 3-4.
- A high-power boiler is required - the purchase of a storage tank is justified if the boiler’s power is not fully used; there is at least a double power reserve, otherwise the device will be inactive.
You can make a heat accumulator with your own hands from stainless steel and copper pipe.
By making a heat accumulator with your own hands, you can save a significant amount. The simplest design is made from a stainless steel barrel or even stainless steel sheet with a thickness of at least 3 mm. You will also need a copper tube with a diameter of 3 cm and a length of 14 m. It is bent into a spiral and placed inside the tank. A cold water supply is made from below, a hot water outlet is made from above, and shut-off valves are installed on the outlets. It is imperative to insulate a heat accumulator made by yourself for a solid fuel boiler, otherwise it will be ineffective. It is also necessary to install pressure and temperature sensors.
If you can’t weld a cylindrical container, you can make a heat accumulator for heating in the shape of a parallelepiped - it’s easier to make a tank of this shape with your own hands. The corners are further strengthened, and the structure is supplemented with stiffening ribs from the outside - they are welded at a distance of 30-35 cm from each other. The ratio of the diameter and height of the device is 1:3(4).
Main types of heat accumulator designs
All heat accumulators are vertical cylindrical containers. This volumetric arrangement of the device is considered optimal:
- simplifies connection to a solid fuel boiler and heating;
- facilitates differentiation of the temperature regime of the coolant by its volume;
- takes up little space.
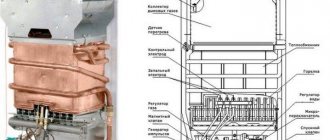
The simplest design is a tank without internal filling. It has two pipes installed - one for connecting to a solid fuel boiler, the other to the heating network. A sleeve for installing a thermometer is mounted in the upper part. This is how heat accumulators for solid fuel boilers are usually made with their own hands.
Factory models are more complex. They are provided with a thermometer and an internal filling in the form of a coil, which acts as a heat exchanger.
The coil can be located at the entire height of the heat accumulator or occupy part of it. Most often the location is lower, although there are many variations. One of them is several heat exchangers located evenly in height.
The purpose of the spiral is to provide the hot water supply system with heated water, plus connect alternative energy sources to the battery. The most common option is a solar battery.
Another type of design is a tank inside a container. The first is intended for hot water supply. Not the easiest option. It is usually used when the heat accumulator has a large volume - at least 800 liters.
The tank itself is a capacity of up to 100 liters. This design has a disadvantage - at maximum heating temperature load, the consumption of hot water in the hot water supply should be minimal. Which is not always possible at the same time.
Design features of a heat accumulator for solid fuel boilers
Selection criteria
Select a heat accumulator, taking into account the parameters of the heating system and the type of coolant.
It is necessary to select a heat accumulator in accordance with accurate calculations that take into account the parameters of the home heating system. However, in addition to the calculated values, the general characteristics of thermal storage devices are taken into account.
- Pressure in the heating system. According to this parameter, the heat accumulator must correspond to the heating system. In any case, the value can be higher, but not lower. What pressure the drive can withstand depends on the thickness of the walls, the shape of the tank, and the material of manufacture. Heat accumulators for boilers that can withstand more than 4 bar have convex bottom and top covers.
- Buffer capacity volume. This parameter is considered the most important and they try to choose a container of such a volume that the drive can accumulate all the excess heat. But at the same time, an excessively voluminous device is not needed.
- External dimensions and weight. Issues of transportation and placement of equipment will have to be resolved, so you need to carefully calculate everything: will the tank fit through the doorway, will the ceilings withstand it when the tank is completely filled with water.
- Equipped with additional heat exchangers. They allow you to further optimize the functioning of the system. Models are selected in accordance with the complexity of the entire system.
- Possibility of installing additional devices. Together with the battery clipboard, additional heating elements, sensors and temperature controllers are installed. If all elements of the system are selected correctly, fuel consumption can be reduced by half.
Tanks are made of carbon steel or stainless steel. The latter are more expensive and last longer, while the former necessarily have an anti-corrosion coating. You need to make sure of its quality.
Buffer tank - hydraulic separator in the heating system
In this heating system with a solid fuel boiler, the buffer tank serves mainly as a hydraulic separator between the boiler and heating circuits, as well as to protect against overheating (boiling) of the coolant.
The tank capacity is selected at the rate of about 10 liters/1 kW of boiler power. The buffer tank also functions as a hydraulic separator. eliminating mutual influence on the circulation mode in different circuits of the system. The coolant circulates freely from the boiler into the heating system.
For example, the circulation of coolant in the boiler circuit does not depend on the operating mode of the heating devices. And stopping the movement of water in the heating circuit with radiators will not in any way affect the circulation in heated floors.
Calculation of the volume of the boiler buffer tank
According to calculations, the heat accumulator must receive all the energy from one load of fuel into the boiler.
The volume of the buffer tank is usually calculated in such a way that during the burning of one load of fuel the heat accumulator retains all the heat generated by the boiler. You can only make approximate calculations on your own that do not take into account heat loss from heating radiators and the influence of air temperature in the room. The basic formula for calculating the volume of a heat accumulator:
W = k × m × c × Δt, where
- W – excess amount of heat;
- m – liquid mass;
- с – heat capacity of the coolant;
- Δt – the number of degrees by which the coolant needs to be heated;
- k – boiler efficiency.
From here you need to calculate the mass of the coolant: m = W / (k × c × Δt).
Since W is defined as the difference in the values of energy generated by the boiler and spent on heating the house, it is also necessary to clarify them and the burning time of the fuel load. If the boiler power is given in the device passport, the thermal energy consumption for heating must be calculated. The fuel burnout time is determined experimentally. Let’s say it’s 3 hours, and 10 kW/h is required to heat the house. This means that in 3 hours the following will be consumed: 10 × 3 = 30 kW.
The heat production of a 22 kW/h boiler is: 22 × 3 = 66 kW.
Based on the calculation results, the excess heat will be: W = 66 – 30 = 36 kW. Convert to W, we get 36000 W.
Using the formula m = W / (k × c × Δt), we determine the desired value of the mass of water. The efficiency is indicated in the passport as a percentage. This value must be converted to decimal by dividing by 100. For example, 80/100 = 0.8. The heat capacity of water is 4.19 kJ/kg×°C or 1.164 Wh/kg×°C or 1.16 kW/m³×°C.
Δt is determined by measuring the temperature of the supply and return pipes, subtracting the smaller value from the larger value. For example: Δt = 88 – 58 = 30°C. Thus m = 36000/(0.8 × 1.164 × 30) = 1,288.7 kg.
To store all the excess energy generated by the boiler, a tank with a volume of at least 1,288.7 m3 will be required. A Jaspi GTV Teknik heat accumulator with a capacity of 1500 liters is suitable. With more modest calculation values, you can limit yourself to a tank of, for example, 750 liters.
DIY connection methods and diagrams
A heat accumulator with an empty tank is installed if the pressure in the system is low.
The complexity and features of the connection depend on the type of heat accumulator. Therefore, you should figure out what they are.
- The simplest design is an empty tank inside. The boiler and consumers are connected directly. Use is optimal if the same coolant is used in all circuits, the pressure in the system does not exceed the permissible values of the storage tank and the temperature of the coolant supplied from the boiler does not exceed the permissible values for the heating circuit. If the first two requirements are not met, additional external heat exchangers must be used when connecting to the system. In the latter case, mixing units with three-way valves should be installed.
- Buffer tank with an internal heat exchanger - one or more. The heat exchanger is a spiral pipe made of copper or stainless steel. In such a storage tank, the coolant is mixed. The coil, located in the lower part, heats the coolant, hot water rushes upward as it is less dense. At the top there is another coil, which takes energy and outputs it to the heating circuits. A device of this type is optimal when using different types of coolants, at high pressure and temperature of the coolant, and connecting several heat generators.
- A tank with a flow-through hot water supply circuit. The heat exchanger is mostly located at the top of the tank. It must be made of metal that meets food water consumption standards. The circuits are connected directly. This system is preferable for uniform flow of hot water.
- Heat accumulator with internal boiler. The storage tank stores heated water for domestic consumption. This type of heat storage battery can be easily integrated into open and closed heating systems equipped with solid fuel, electric boilers and solar collectors. Buffer tanks of this type are especially relevant when using electric boilers, when the coolant is heated at night and water is consumed during the day. A 150 liter boiler is quite enough for the daily water consumption of an average family.
Flow heat accumulator
With boiler
With heat exchanger
The heat accumulator intended for the heating system has several outlet pipes, and they are located vertically along the tank, since there is a temperature gradient along the height. This is done so that it is possible to connect circuits with different requirements for coolant temperature and reduce the load on temperature controllers. As a result, thermal energy is used as efficiently as possible.
In a system with three-way valves, more precise temperature control is possible.
Other types of systems:
- The simplest strapping scheme, limiting the possibilities of adjustment. Hot water rises up and is taken from the top point, after cooling it falls and enters the boiler again. Used if the pressure and temperature in the heat generator and heating circuits are the same. The temperature is regulated only by increasing/decreasing the coolant flow.
- The system contains mixing units and bypasses, so more precise adjustment of the coolant temperature is possible. Equipment efficiency is achieved through the installation of, for example, three-way valves.
- The system includes an additional tank, so that a small volume of hot water is available immediately after starting the boiler. The consumer does not have to wait for the system to warm up completely, but the water supply is not large, and the system heats up more slowly than a classic one.
- There is one coil inside the buffer tank; thermal energy from the source passes through it, and the coolant in the heat storage tank is heated from the coil. This type of system uses different coolants. You can choose those that cannot be mixed due to incompatible chemical characteristics. Heating or DHW can be powered through the coil, or coolant from the source will circulate through this circle.
- The system has an additional external heat exchanger. It allows you to maintain the desired temperature in the battery.
- System with a flow-through hot water supply circuit. It is optimal if hot water is used evenly. Otherwise, it is recommended to purchase an energy accumulator with a built-in boiler.
- A system with one coil and connection to an alternative energy source, for example, a solar collector. It's called bivalent. The connection is made in such a way that the collector plays a leading role in heating the system, and the boiler is connected when there is not enough thermal energy.
- A multivalent system where the main heating is carried out by low-temperature sources, such as a solar collector and a geothermal heat pump. They are connected at the bottom of the heat accumulator. A high-temperature boiler is used as an auxiliary source of thermal energy.
In the presence of various heating circuits and thermal energy sources, a complex branched system is formed with a lot of additional control equipment, sensors, and safety groups. It is recommended to entrust its design to professionals, as highly accurate calculations will be required.
TOP 10: heat accumulators for heating with solid fuel boilers, features
Heat accumulators are represented quite widely on the market. There are different models from a large number of manufacturers. Not only experts, but also consumers who have experience using devices of this type took part in compiling the rating.
Tenth place - Nibe BU
It is occupied by a Nibe BU – 500.8 brand unit from the company “NIBE Industrier AB” from Sweden. Floor-standing battery with an internal volume of 500 liters. Can withstand hot water pressure up to 6 bar and temperatures up to +95°C.
This is a standard modification, simple, inexpensive, and has proven itself in operation. But quite heavy - 107 kg. Expanded polystyrene with a thickness of 140 mm is used as insulation.
Can connect to multiple consumers. The model line includes heat accumulators with a coil and a storage tank.
Ninth place - ETS 200
This is the ETS 200 seat. The manufacturer is the German company Stiebel Eltron. The device should be classified as an electric heat accumulator. They are almost never used with solid fuel boilers. But it is very popular among consumers.
Eighth place - HAJDU AQ PT 500
This is a Hungarian unit, a classic one. Brand – HAJDU AQ PT 500. The model range includes combined varieties with a coil and a tank. Compatible with various types of boilers, including solid fuel ones. Additionally equipped with a heating element.
Flaws:
- The package does not include a thermal insulation layer; it will have to be purchased and installed separately;
- the pressure inside the container is no more than 3 bar.
Seventh place - HAJDU AQ PT 1000
It is occupied by the HAJDU AQ PT 1000 C model from a Hungarian company. The manufacturer initially manufactured the device with full compatibility with a solid fuel boiler with a power of 25-35 kW. Plus - two additional pipes for connecting to the solar collector.
The design includes two coils with a total area of contact with water of 4.2 m² and a hole for installing a heating element. It will have to be purchased separately.
This heat accumulator model can work with a solid fuel boiler and a heating system in which a circulation pump must be installed. Without it, the efficiency of the unit decreases sharply.
Sixth place - S-TANK HFWT SERIES
It was given to a Belarusian battery - S-TANK SERIES HFWT - 300. The classic version with a heat exchanger. The tank volume is 300 l, hence the small overall dimensions. Withstands pressure up to 6 bar and temperature up to +110°C.
Thermal accumulator from Belarus
Fifth place - S-Tank AT 300
It is from the same manufacturer, but the S-Tank AT 300 model. The difference from the previous version is compatibility with various types of heating boilers: gas, electric, solid fuel, fuel pumps, fireplace jackets, etc.
Fourth place - S-TANK AT AT-1000
This is the simplest model without heat exchangers and other functional devices. Therefore, it is compatible with solid fuel boilers with a power of up to 10 kW. Characteristics:
- volume 1000 l;
- pressure 6 bar;
- temperature +95°C.
Third place - HAJDU AQ PT 750
HAJDU AQ PT 750 differs from previous models of this manufacturer only by the presence of an additional tank inside, which is used as a heat exchanger.
Characteristics:
- pressure 3 bar;
- temperature +95C;
- presence of a heating element in the kit;
- floor version;
- volume 750 l;
- insulation thickness 10 cm.
Second place - HAJDU PT 300
It is for HAJDU PT 300, the tank volume of which is 300 liters. This is a standard container, not coated on the inside with an anti-corrosion coating, and without a coil. There is a hole for installing a heating element. A simple, reliable and inexpensive heat accumulator, hence its high popularity, especially among consumers. Compatible not only with solid fuel boilers.
Heat accumulators from a Hungarian manufacturer
First place - S-TANK AT PRESTIGE
It was given to the Belarusian model S-TANK AT PRESTIGE - 500. It is made of stainless steel, hence the almost unlimited service life. A coil is installed inside.
The manufacturer has provided the device with an overheating protection unit, which increases the safety of the unit. The model has double thermal insulation. The volume is 500 l.
Battery connection for heat
The container must be well insulated. If this is a purchased heat accumulator, you need to evaluate the thickness and quality of the external insulation. The better and thicker the heat insulator, the longer the heat will remain. Thanks to the special structure of the heat insulator, the heat accumulator works like a thermos. The thickness of the thermal insulation in high-quality models is about 10 cm. It covers the body painted with heat-resistant paint. There is a layer of leatherette on top of the thermal insulation. Independent insulation is carried out according to the same scheme. First, the tank is painted with paint that is resistant to high temperatures, then it is insulated with basalt wool at least 150 mm thick, and the top is covered with foil.