Automation in the heating system allows you to more accurately control the temperature in heated rooms and save on fuel. By installing a thermostat for the heating boiler, the owner of the cottage increases the efficiency of the boiler equipment by 20–30% and greatly simplifies its maintenance.
We will talk about the types of thermostats used in practice, the rules for their location and connection features. The article we have proposed describes in detail the options and diagrams for connecting devices. Taking into account our advice, you can choose the device wisely and install it if desired.
How does a heating thermostat work?
A conventional heating system with water as a coolant consists of heating equipment or a connection point to a centralized network, internal wiring pipes and radiators.
To regulate the volume of heat coming from it into the rooms, you have to either constantly monitor the boiler or regularly close/open the valves on the radiators.
At the same time, the inertia of such a system does not allow maintaining the desired temperature throughout the day at the set level. If you put more firewood into the stove or supply gas to the boiler, the coolant in the pipes will heat up more, and it will also release more heat through the radiators.
This is good at low temperatures outside. But with sudden warming outside, the heat in the house becomes unbearable. The fuel is already in the firebox, and the water has already heated up, there is no way to get rid of the heat. Plus the boiler continues to work.
Without a thermostat in the system, you have to turn it off manually. You can, of course, open the windows for ventilation and let out the heat, but then the fuel bills for your home boiler room will definitely ruin you. The conclusion suggests itself: a heating thermostat simplifies living and makes it as comfortable as possible.
A thermostat (temperature regulator) is a device for monitoring the temperature in a heated room and increasing/decreasing the heat supply to it
The thermostat for the heating system consists of:
- temperature-sensitive sensor (element);
- tuning unit;
- control module;
- electromagnetic relay or mechanical valve.
In the simplest models there is no control unit. Everything happens due to pure mechanics and changes in the physical properties of the temperature-sensitive element.
These thermostats do not require power supply. In terms of efficiency and accuracy of system adjustment, they are inferior to electronic devices, but they are non-volatile. If there are problems with the voltage in the network, they will definitely not stop working.
The operating principle of the thermostat is as follows:
- Using the control unit, the desired temperature is set.
- When the required parameters are reached, the sensor is triggered, which leads to the boiler turning off or the shut-off valve in the heating pipes closing.
- After the air temperature in the room drops, the boiler equipment or heaters turn back on.
The electronic control module allows you to set not just one temperature indicator, but several for each time of day separately. Plus, if such a unit is available, it is possible to install an additional temperature sensor outside and link the functioning of the thermostat to the data from it.
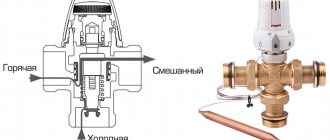
Depending on the type of device, the thermostat is connected directly to the boiler to regulate its operation or at the inlet to the radiator to control the volume of coolant supply
The simplest thermostat is a shut-off valve with a temperature sensor, located on a pipe near the battery. When the desired temperature is reached, the thermostatic valve closes and reduces the coolant flow. And when the room air cools, it opens again, resulting in an increase in the volume of incoming heat.
More complex and advanced models require wireless sensors and control units. All communication between individual elements occurs through a radio channel. In this case, wires are not laid, which has a positive effect on the aesthetic side of placing such thermostats in the room.
Why do you need a remote thermostat for a gas boiler?
It is not easy to adapt to regulating the air temperature through regulating the water temperature in the heating system. Many people are familiar with the method in which “pictures” are applied to the regulator, corresponding to the “normal” values of room temperatures at different times of the year.
The temperature in the room changes depending on the time of day, location (north-south) and the number of people in it. As a result, the boiler either heats too much or does not heat enough. You have to run to it, which is annoying, and most importantly, there is a clear overconsumption of energy resources.
This method of adjustment is called indirect. They talk about automatic thermoregulation when the connection between the temperature in the room and the operating mode of the gas boiler is direct. This opportunity is provided by a room thermostat.
Types of thermostats for boilers
The main difference between thermostats is different types of temperature-sensitive sensors. Some are installed on the heating pipe, others inside it, and others are mounted on the wall. Some are designed to measure air temperature, and the second - coolant.
The choice of thermostat model depends on:
- boiler type;
- heating system wiring diagrams;
- availability of free space;
- required functionality.
Many modern boilers are pre-designed to connect thermostats to them. Moreover, the manufacturer of boiler equipment immediately writes down all the nuances of this installation in the technical data sheet.
If an electronic thermostat model is selected, then it is best to give preference to the most efficient one - the one recommended by the boiler developer
Ideally, the thermostat should regulate the operation of the heating device itself, that is, the supply of fuel to it. This is the most efficient connection scheme in terms of fuel economy. In this case, the energy carrier will be burned exactly as much as the heat required.
But such a thermostat can only be installed on a gas or electric heating unit. If the boiler is solid fuel, then a thermostat with a mechanical valve, which is mounted on the pipe, will help regulate the room temperature.
Regulators installed on batteries are designed to shut off the water supply if the temperature in the room or coolant is too high. In this case, the boiler stops working a little later, when its own temperature sensor inside is activated, preventing overheating of the equipment.
Group #1: mechanical
The operation of a mechanical temperature sensor is based on a change in the characteristics of a material when its temperature changes. This is an easy-to-use, budget-friendly, fairly effective and completely power-independent option. It is designed for installation on pipes of a water heating system to regulate the flow of coolant.
A classic example of a mechanical thermostat is a device with a needle valve (constipation) and a thermal bellows head
The following substances are used in mechanical thermostats as a substance that responds to temperature changes:
- gas;
- liquid.
When the liquid is heated, the gases expand, which leads to their pressure on the shut-off valve stem. When the temperature drops, they compress, the constipation is returned by a spring, and the heated water again flows through the pipes into the heating radiators.
Battery thermostats are characterized by low sensitivity and large adjustment errors. They only work when the temperature rises by 2 degrees or more. Plus, over time, the bellows filler loses its characteristics, the numbers on the knob for setting the required temperature parameters and the actual degrees begin to diverge.
These thermostats are quite large in size. The vast majority of them are designed to measure the temperature of the water in the batteries, and not the air in the room. It is often difficult to precisely adjust them the way the home owner wants.
Group #2: electromechanical
These thermostats operate on principles similar to their purely mechanical counterparts. Only a metal plate is used here as a heat-sensitive element.
When heated, it bends and closes the contact, and when cooled, it returns to its original position and opens the circuit. And through this circuit a signal is sent to the burner control unit.
The electromechanical thermostat requires power supply; it controls the valves or burners in the boiler that regulate the flow of coolant using electrical signals.
Another option for an electromechanical thermostat is a device with a sensor in the form of two plates made of different metals. In this case, the heat-sensitive element is installed directly into the firebox of the solid fuel boiler.
At high temperatures, a potential difference occurs between the plates, affecting the electromagnetic relay. The contacts in the latter alternately open and close. As a result, air injection into the combustion chamber is turned on/off.
Group #3: electronic
This type of thermostats for hot water boilers belongs to the energy-dependent category. Such devices have a remote temperature sensor that monitors the room temperature and a full-fledged control unit with a display.
For electric boilers, such thermostats are a mandatory addition. Without them, electric heaters will work without stopping, heating the air or coolant too much.
In the vast majority of cases, boilers and boilers operating on electricity are equipped with thermostats at the factory.
An electronic thermostat has two main elements:
- Temperature sensor.
- Microcontroller.
The first measures the temperature, and the second controls it and issues signals to increase/decrease the supply of thermal energy to the room. The sensor can send an analog or digital signal to the controller. In the first case, the thermostat’s capabilities are similar to its mechanical counterpart, only it greatly exceeds it in the accuracy of temperature measurements.
Digital thermostats are the pinnacle of development of these devices. They allow you to regulate heat supply according to a preset algorithm. Plus, you can connect many more sensors to them, located both in rooms and outside.
Many electronic thermostats have remote control capabilities via infrared or cellular. This allows you to regulate the room temperature not only using the remote control in the room, but also from any point outside it.
For example, while still leaving work, you can send a signal to heat the room air to comfortable parameters, and when you arrive the house will delight you with comfort and warmth.
Electronic devices designed to automatically adjust the qualitative and quantitative characteristics of the coolant are a mandatory component of heating systems in smart homes. We recommend that you familiarize yourself with their device.
Types of room thermostats
Remote thermostat for gas boilers of two main types:
- Wired. These are connected to the boiler directly using wires. They are inexpensive and highly reliable. Equipped with a mechanical rotary regulator (knob with scale). The temperature setting accuracy is low and only one value can be set.
- Wireless. The kit includes two blocks. One is connected to the boiler terminals and installed directly next to it. The other is mounted in the desired location (no further than 35 meters). Communication between the receiving and control units using radio signals of a dedicated frequency. The control unit is equipped with an electronic display, a temperature sensor and a setting system to effectively control the operation of the boiler. It is sometimes called a programmer due to its long-term programming capabilities.
There are versions with a built-in hydrostat function. They control the level of humidity in rooms.
Room thermostat connection diagram
The gas boiler thermostat receives power in the following ways:
- Connecting to a public network via an adapter.
- From the built-in battery.
- Connection to the boiler electronic board. For this purpose, it has specially marked terminals (TA).
It is worth noting that the wireless thermostat (control unit) only operates on batteries. It should be taken into account that when operation stops, the boiler is controlled by signals from the internal regulator. Modern models are equipped with a low battery warning function with audio and visual alarm.
Connection diagrams
All methods of connecting a thermostat to a heating system are divided into three connection options:
- Directly to the boiler.
- To the circulation pump.
- On the pipe supplying coolant to the radiator.
The first two schemes eliminate the deterioration in the throughput of the heating pipeline. No additional locks are placed in it, and the hydraulic resistance of the entire system does not change. The thermostat here only controls the operation of the pump or boiler; it “does not come into contact” with water.
When installing a thermostat on a battery or a common pipe with several radiators, the hydraulic resistance, on the contrary, increases. Even when fully open, the thermostat valve slightly slows down the flow of coolant.
Ideally, the boiler piping project should be carried out immediately, taking into account all thermostatic and other devices.
Thermostats should only be installed into existing heating pipelines as a last resort; maximum efficiency from their use can only be achieved if they are included in the system at the design stage
If the water heating system in the house is made according to a single-pipe scheme, then it is better to immediately abandon the third option. When the temperature sensor is triggered, the valve will immediately shut off the entire radiator line in several rooms, and then you can immediately forget about comfort in rooms far from the boiler.
The thermostat should be connected to the radiator input via a bypass. So, when triggered, it will redirect the coolant flow bypassing the battery. In this case, the water will return uncooled back to the boiler. The latter will stop heating it, thereby reducing the consumption of gas fuel or electricity.
When installing a thermostat air temperature sensor, you must adhere to certain rules, otherwise, under the influence of neighboring devices or objects, it will trigger falsely.
The temperature sensor must be mounted:
- in a place where there is no direct sunlight;
- away from cold bridges, drafts and rising heat flows from radiators;
- so that it is not covered by decorative screens or curtains;
- at a height from the floor within 1.2–1.5 meters.
If the sensor is installed incorrectly, the thermostat will produce false signals. This can lead to overheating not only of the air in the room, but also of the coolant in the system. And in the second case, it won’t be long before there are problems with the boiler.
Advantages of wireless thermostats
The room thermostat in the gas boiler circuit accurately regulates the temperature and reduces energy consumption. In addition, it works in automatic mode - there is no need for manual settings.
Using a programmer relieves the user of problems with maintaining the microclimate in a house or apartment, opening up the following opportunities:
- Accurate and fast temperature control. The exhibition accuracy is 0.3 degrees.
- Day-night modes, functions for setting temperatures by time intervals several days in advance.
- Connecting a GSM module or control system via Wi-Fi further reduces the need for human participation in controlling the boiler.
- Regulation of air temperature in different rooms.
- Economical operation of gas equipment. The thermostat costs money, but pays for itself by reducing overall heating costs, including electricity, by 20-25%. The fact is that when the boiler is turned off, the automation turns off the pump, which is its consumer.
Remote thermostat control
Payback is achieved within just two seasons of operation. Reducing the number of starts/shutdowns leads to saving the life of the gas boiler, the cost of which exceeds the price of additional equipment. Programmable devices regulate the response threshold of the temperature sensor. And the use changes the delay time for turning on/off the gas boiler, which minimizes the likelihood of the automation triggering during short-term temperature fluctuations, for example due to a draft.
A modern wireless thermostat with an ergonomic design, it easily fits into any interior design. Installation does not require wiring, which is convenient when designing a system in old houses.
The only drawback is that the thermostat and boiler work together efficiently, often if they are made by the same manufacturer. Differences in electronics sometimes make devices from different manufacturers incompatible.