Home » Insulation
Reading time 12 min Published 08/17/2019
Every year before the heating season, utility services notify citizens living in high-rise apartments that it is necessary to bleed air from the heating system. The reasons for the formation of air in the heating system are factors such as the release of hydrogen during chemical reactions, as well as repair work, as a result of which water is drained from the system. To remove air, special devices are used - air vents.
Air vents for heating systems are also called air release valves, without which it is impossible to ensure the normal functioning of the heating system.
Air in the heating system: causes
Air enters the heating system for a number of reasons:
- filling the line with water, resulting in the formation of air accumulation areas;
- violation of the quality of sealing devices;
- corrosion processes occurring inside pipelines;
- improper execution of installation work.
The main reason why it is necessary to remove air from the heating system is that oxygen contributes to the creation of air pockets. These plugs help reduce pressure and also reduce the rate of coolant circulation. If you do not bleed the air mixture in the heating radiators, you may experience a process such as a lack of heating of the battery sections.
Causes of air
The logical question is: how does air get into the heating system if it is completely sealed?
There can be many reasons for this phenomenon:
- High blood pressure. Water contains not only magnesium and calcium, but also oxygen. The volume of oxygen depends on the pressure level in the system. As pressure increases, the concentration of oxygen in water increases.
- Violation of requirements for pipe slopes during installation work.
- Incorrect filling of the pipeline, leading to air congestion. Water should be supplied slowly while air is pumped out of the batteries, right? otherwise, the formation of bubbles is inevitable, which causes airing of the heating system. The general rule is: the more branches a system has, the slower its filling should occur.
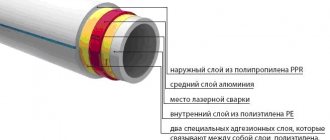
- Diffusion. This phenomenon is a process during which the ability of molecules of one substance to penetrate between the molecules of another is realized. In the described case, we mean the penetration of oxygen molecules between the molecules of polypropylene or polyethylene. To prevent diffusion, special coatings are applied to the pipe material.
- Insufficient connection density between system elements.
- Faulty or missing air vents.
- Carrying out repair work during which depressurization occurred.
- Corrosive processes leading to violation of the tightness of equipment.
The above factors do not exhaust the reasons that cause air in the heating system, but they are the most common.
What types of air vents are there?
Air vents are divided into two types:
Manual products are designed to deflate air through human intervention. To do this, utility workers either independently go around all the apartments to carry out such manipulations, or inform the residents of the house. Automatic air vents for heating systems do not require human intervention, so they release oxygen on their own. The cost of such devices is several times higher than manual ones, so utility services are not able to provide all high-rise apartments with automatic air vents.
Automatic air vents are installed in places where there is a high probability of air lock formation. The locations for such devices are heating radiators.
What is an air valve?
The air valve for heating is a sealed cone-shaped or cylindrical body made of brass. Inside it is a hollow float made of Teflon or polypropylene. This float is connected by a lever to the drain valve, which is equipped with a locking plug. This plug prevents coolant leakage if the device breaks down.
Now, once and for all, without any registrations or SMS, you can download 1xBet for Android for free by clicking on the active link and continue to enjoy the game and place bets on your favorite team in a convenient mobile application.
Air vents for heating systems come in three types:
- Direct devices of traditional type. They are mounted only vertically.
- Corner type devices that are installed at right angles. They are mounted on radiators instead of Mayevsky taps or in the event that a direct type of air vent cannot be installed.
- Special models for installation on radiators.
According to the principle of operation, the air vent can be manual (Maevsky tap) or automatic. The last variety is the float-type devices described above.
Operating principle of manual valve
Let's figure out how a manual air bleeder for a heating system works. To understand the structure of this type, you need to look at the drawing of the Mayevsky crane. At the end of the brass body with external thread there is a hole with a diameter of 2 mm. It is covered by a screw with a cone tip. On the side of the same body there is a hole of a smaller diameter, which is used to bleed air.
The operating principle of a manual air vent is as follows:
- In operating mode of the heating circuit, the shut-off screw is tightly tightened. The outlet is hermetically sealed with a cone.
- To release the air lock, the screw is unscrewed a couple of turns. As a result of coolant pressure, air begins to escape through a small hole, then enters the outlet channel and is discharged outside.
- Moreover, at first only air comes out of the hole, then an admixture of water appears. The tap must be closed when only a stream of water flows from the hole.
Because there are no moving parts to clog, rust, or wear out, a manual air vent is a reliable, trouble-free device. This valve is installed only on radiators.
What are the dangers of not having air vents?
Air vents are used not only in heating networks of multi-storey buildings, but also in private ones. Each radiator is equipped with an air vent, which is often presented as a manual type.
The air inside the heating system impedes the circulation of the coolant, which negatively affects the heating of the premises. If you do not bleed air from the system in a timely manner, vibration is created when the coolant heats up. This phenomenon can ultimately lead to physical damage to the heating network circuits. The main places of damage are the connection points of heating radiators, as well as welding or soldering seams.
If there is no air in the metal pipe circuit, then the internal walls of the pipelines do not corrode, unlike in cases where there is oxygen in the system. When the internal walls of pipelines rust, not only does the service life decrease, but also the coolant becomes clogged. Draining or bleeding air is a prerequisite, since residents of houses and apartments who ignore to carry out such a procedure themselves may be left without heat.
The influence of air on the heating system
The functioning of the heating system is based on the circulation of heated water with the release of part of the heat into the radiators to heat the room. If air enters the internal part of the system (the process is called airing), a disruption in the circulation of the coolant occurs. The system responds to airing as follows:
- When the coolant circulates, noises are clearly audible, which not only creates discomfort for residents, but is also a symptom of pipeline vibration, as well as backlash in connections. In some cases, vibrations result in the destruction of welded joints with obvious unpleasant consequences.
- Air pockets form in the circuits. This happens especially often in non-residential premises where there is no regular temperature control. The result of traffic jams is defrosting the system.
- Deterioration of circulation or its complete cessation. Under conditions of slow circulation, the efficiency of the system decreases and fuel consumption increases.
- The development of corrosion processes as a consequence of air penetration into internal metal parts. The result of corrosion is a reduction in the operating life of equipment.
Features of the functioning of manual descenders
The design of the simplest manual air vent is shown in the diagram below.
This air vent is called the Mayevsky crane, the operating principle of which is very simple. The device has two holes that are covered by a threaded element. When unscrewing the threaded element, air is released, which is pushed through the 2 mm hole in the diagram above, and exits the system through the second hole.
To bleed air from the system, it is enough to make 2-4 turns of the screw, after which, under the pressure of the coolant, the air will tend to escape through the holes. You can know that all the air has been drained from the system by the appearance of water flowing out of the hole. As soon as a dense stream of water flows from the hole, you need to screw the screw in until it stops. Modern Mayevsky cranes are presented in various types: turnkey, with handles and even with a screwdriver. The photo below shows a list of such types.
A manual air valve in a heating system is an ideal device that functions flawlessly over a long period of time. The reliability of this device is due to the absence of moving parts, which over time are subject to clogging, corrosion and failure. This is typical for automatic air exhaust products.
Often, instead of Mayevsky’s manual taps, apartment owners install drainage taps. They can be installed temporarily, but not permanently, since they are not intended for installation on radiators. If such products fail, it will be very difficult to replace them during the heating season.
Another option for a manual air vent
This valve is produced by the same companies that make automatic valves. There is also a cone here, but the design of the device is somewhat different. In addition there is a handle. It is, of course, more convenient to use than a key. The principle of operation is similar: turn in one direction, the cone moves away from the hole, the air comes out. Turned it in the opposite direction and closed the hole.
This is another manual air vent. There is also a shut-off cone here, but of a slightly different shape
A little about prices. The price of the Mayevsky faucet is $1.2-1.5, manual valves of other types start from $2. It’s hard to say how much the most expensive one might cost, but there are “antique” models that offer to buy for $20.
How does an automatic air vent work?
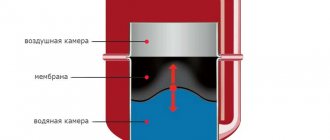
Let's figure out how an automatic air vent works, the cost of which is 2-3 times higher than manual devices. Such products are equipped with air release valves that function without outside intervention. The design of the product is a vertical barrel with a ½-inch threaded connection method. The body of the product is made of brass, and inside the device there is a plastic float. This float is connected to the spring-loaded air release valve and the cap.
Automatic air vents have ½ and 3/8 inch threads. The last option comes up rarely.
The operating principle of the automatic air valve is to perform the following tasks:
- If there is no air in the system, the chamber of the device is filled with water, which presses the float to the top. In this case, the spring-loaded valve is in the closed position.
- When air enters the system, the pressure decreases, so the float drops.
- When the pressure decreases to a certain value, the mass of the float device will overcome the spring, which will lead to the opening of the valve.
- The excess pressure will force air out of the circuit, after which the valve will close again.
The diagram shows in detail how the automatic air vent functions. The advantage of such a product is the complete absence of water leakage, since the device leaves some of the air mixture inside, which does not negatively affect the operation of the heating network.
Depending on the type of connection, automatic air vents can be straight or angular. The photo above shows a corner air vent with a jet in the upper part. On direct devices, such a jet is located on the side. The products differ from each other not only structurally, but also technologically. A valve with a side outlet is more reliable, but it does not retain air as well as a device with a vertical outlet.
Automatic air vent valves from the heating system are constantly being modernized, as manufacturers strive to make them more advanced. At the same time, they are complemented by various functions:
- Elimination of water hammer, which is facilitated by a special plate inside the product.
Air vents
The purpose of all air vents is to eliminate air locks from the heating system. They are divided into manual and automatic.
Manual air vent - used for manual air release. This procedure is carried out with human participation. Another name for a manual air vent is the Mayevsky tap.
- Mayevsky crane;
- Faucet key.
To find out whether you need to bleed air from the heating system using a Mayevsky tap, you need to check the radiator fins. If the temperature of the fins is different in different places of the radiator, this means that an air plug has formed inside. To remove air from the system, take a screwdriver and carefully turn the screw on the faucet cap; after the air has been bled, screw the screw back.
Automatic air vent - designed to automatically bleed air from the radiator. The release of excess air occurs automatically, without human intervention.
Automatic air vent design
- Frame;
- Float;
- Case cover;
- Jet;
- Valve O-ring;
- Cork;
- Spool;
- Spring;
- Holder;
- Housing O-ring.
Operating principle of automatic air vent
After air enters the air vent from the system, a valve inside it opens and releases excess air. When all the air is released, water will begin to flow into the recess under the float. Under the influence of water, the float will begin to float, acting on the rod and the valve will then close.
The catalog contains various models of automatic air vents, but they all operate on the same principle.
Types of automatic air vents
Automatic air vents are divided into:
- Straight;
- Angular - used as a replacement for the Mayevsky crane;
- Radiator plugs - their threaded connection has the same diameter as that of radiator plugs, so they can easily be interchanged with each other.
It doesn’t matter what kind of air vent you have, you need to install it so that the drain hole is directed to the top. It can be screwed directly into the system, or the shut-off valve can be screwed in first, and then the air vent can be screwed into it. The shut-off valve allows you to remove the air vents from a working system, which is very convenient when it needs to be repaired or replaced with a new one.
Rice. Shut-off valve
To remove air from the heating system, it is enough to install a manual air vent. However, if air jams regularly form in your system, the best solution for you would be to install an automatic air vent. This way, you won't have to constantly check to see if your batteries are heating up or if there is a build-up of air there.
Features of choosing air vents
Not everyone knows where to start choosing an automatic air vent. In order for the product to serve for a long time and without failure, it is recommended to buy products of European or domestic production, but not cheap Chinese counterfeits. Buying a cheap automatic graduate can cause the following adverse consequences:
- Passing not only air, but also coolant through the valve. In this case, a puddle of water will be detected under the radiators or in the places where the air vents are installed.
- The product is jammed, so it will not work.
- Rapid deterioration.
Although automatic type safety valves have a shorter service life than manual ones, they must serve without fail for at least 10 years. Manual products have a service life of over 15 years, so instead of buying a cheap machine, it is better to give preference to a manual device. This will allow you to win not only in terms of savings, but there will also be no problems with air bleeding.
To choose good quality Mayevsky uranium, you need to pay attention to the following criteria:
- The presence of a handle allows you to conveniently open the valve for bleeding air. The disadvantage of faucets with handles is that they can be accessed by children, who are quite capable of opening them. Installation of such outlets with handles is appropriate only in hard-to-reach places; in other cases, it is recommended to install conventional products with a key or a screwdriver.
- To avoid losing the special bleeder key, it should be placed on the wall next to the radiator. This will prevent you from losing the key, and will also allow you to quickly bleed the air.
- Buy products with anodized coating. This spraying allows you to protect the metal from the occurrence of oxidative processes.
- If your budget allows, you can purchase a product that can trap air bubbles. However, such manual air vents do not differ much in cost from automatic air vents.
In order not to make a mistake with your choice, you need to pay attention to the manufacturer. Depending on the brand of plumbing and heating equipment, not only the quality, but also the cost will differ. In addition, if a closed heating system is used, then you need to pay attention to the technical parameters of the devices, in particular, operating pressure.
The air in the heating system is one of its main enemies. Therefore, automatic air vents must be provided in the heating system. Since not all heating systems operate on the same principle, the process of air circulation in the circuit also differs. Before you bleed air from the heating system, you should figure out how to do this, or you don’t need to do anything and it will come out on its own, for example, like in an open system.
Mayevsky crane
If air accumulates in the heating radiators, it is necessary to use a special key or a screwdriver to turn the slot on the gas vent disk one or two turns counterclockwise. After this you can hear hissing. The coolant will begin to come out with the air in a small stream. But when the coolant begins to flow out in a continuous stream, you need to close the tap and turn the key or screwdriver in the opposite direction.
When turning on the heating system, it is necessary to carry out such a procedure, but during the year it will not be superfluous to check the presence of air a couple of times. After the heating season has ended, it is recommended to check the presence of air. But for this you cannot drain the coolant. After turning off the radiators, you can turn the tap a little. This will create a small hole through which the coolant will not be able to flow, and the resulting air will escape.
How does air enter the circuit?
There are two types of contours:
Peculiar automatic air vents in an open-type heating system allow coolant to pass through them, which circulates by gravity. The direction of circulation is determined by the design of the circuit. It always maintains a slope from the highest point, on the supply flow, to the lowest, on the return. There should be no air pockets. Air enters the heating system together with the coolant, which is in contact with it in the expansion tank. Then it is drawn into the flow in the form of small particles, since it is impossible to bleed air from the heating system from a coolant with a temperature of 20 degrees. The hotter the water, the more intense the process of separation of bubbles from the coolant occurs. The liquid pushes the bubbles upward. Accordingly, they reach a peak point where they find a way out.
Since expelling air from heating is one of the key tasks for safe and efficient heating of premises, equipment specially designed for this purpose is installed in the circuit.
Closed systems are sealed and circulation in them occurs thanks to a pump. In such circuits the flow rate is higher. They are designed in such a way that air pockets are formed in them. In this case, the installation of special equipment is required, since it is necessary to bleed air from the heating system while maintaining its tightness. It's called an automatic heating system air bleeder. Since the system is not in contact with the environment and is sealed, oxygen can only enter it with the coolant.
In addition to the transit of oxygen by the coolant into the circuit, airing can occur:
- due to mechanical damage;
- due to repair work;
- in case of leakage;
- after verification work.
Since it is not possible to prevent oxygen from entering the system, it is necessary to ensure that it finds a way out. For this purpose, several types of equipment are used to perform the task. They can work autonomously or in manual mode.
How to remove a plug from a circuit
Before removing air from the system, it must be detected. Options:
- before you bleed the air from the heating system yourself, would it be better to call a technician and get it over with?;
- try to find it yourself by knocking on the pipes. The sound in the area where the traffic jam is located will be different;
- check the uniform heating of the radiators. The top should be warm, there may be a slight difference from the bottom. The main thing is that the temperature at the top is higher. If this is not the case, then there is a problem in the batteries.
To remove air from the radiators in a private heating system, it is enough to use a Mayevsky tap. In other cases, you must first check the condition of the equipment responsible for this process. If it is in working condition, you can increase the pressure so that the plug comes out on its own, or refuel the system. If the circuit is filled from scratch, then you need to fill in water in several stages, without rushing. In this case, all taps, except the drain, must be open. We need to provide more options for oxygen to escape. Some craftsmen remove the cork by tapping along the contour. The method works, but this does not mean that you need to take a hammer and hit the pipe harder. No, you need to know how and where to hit, otherwise there will be no use, only harm.
Types of equipment and principle of its operation
- open type expansion tank.
How to remove air from a closed heating system with a simple tank? It can perform the function of an air vent only in open circuits. Since it is not possible to ventilate a closed circuit heating system using a tank. Only sealed tanks are installed in them. The open tank is at the peak of the circuit, where oxygen bubbles tend to flow. The problem is that the water is enriched with it in the same tank, so there is a high level of air in the coolant, which is there until the liquid is heated;
Installed at the highest point or in a place where oxygen accumulates. The threaded part of the heating system air bleeder comes in two diameters: ½ or ¾ inch. In shape they can be flat or bent at a right angle, like the letter “g”. The air outlet hole is located either at the end or on the side of the housing. Works offline. Air is released from the heating system when the pressure in the system rises to a critical level. Consists of a valve and a float. The working principle is that when oxygen rises, the float moves down and opens the valve. As soon as a release occurs, the float rises, returning to its original position, and closes the valve;
- air separator for heating.
How to pour antifreeze into a closed heating system?
A closed heating system is filled with glycol antifreeze using a pump that is connected to the charging connection. If there is no pump, you will have to fill the liquid through the highest point. To do this, you need to unscrew the automatic air vent. This is a long and labor-intensive process that is difficult to cope with alone. The role of the assistant is to monitor the timely removal of air from the batteries at the moment the coolant is poured into the system.
Before starting work, it is important to check:
- whether the shut-off and control valves are open;
- are the valves shutting off the boiler closed?
- Is the antifreeze concentrate properly diluted?
- whether the Mayevsky relief valves are closed;
- Is the valve that shuts off the membrane expansion tank open?
- Antifreeze is pumped into the system until the pressure gauge readings reach 1.5 Bar (average value).
After this, you need to bleed the air from the heating radiators and at the same time monitor the pressure drop in the system using pressure gauges (the minimum acceptable value is 1 Bar). After this, you need to regulate the pressure level by periodically pumping the coolant. Important! In closed-type heating systems, a spring-type check valve must be located on the make-up connection. Otherwise, it is almost impossible to pump antifreeze into the system. - After removing air from the heating radiators, the working fluid is added to the system until the pressure reaches 1.5 Bar.
- Next, you need to open the boiler shut-off valves: on the return and supply lines. Open the second tap as carefully as possible so that atmospheric air has time to escape through the automatic air vent.
- When test running the boiler and warming up the working fluid, monitor the pressure in the system. The maximum permissible value is 1.8 Bar (average value).
- The last stage of filling antifreeze is re-venting the air and adjusting the pressure.
After completing the work, carefully inspect the pipelines and connections for antifreeze leaks. If a leak is detected, you can not drain the entire volume of coolant from the system, but cut off a separate branch or radiator of the fittings. After eliminating the design defects, adjust the pressure by releasing air and adding the required volume of working fluid.
What can lead to traffic jams in the circuit?
The importance of air vents cannot be overstated. Traffic jams in the circuit can lead to different processes:
- circulation disturbance;
- pressure surges;
- reduction in the efficiency of heating equipment;
- corrosion of metal.
Autonomous air vent
Installing an air vent in the heating system prevents the formation of plugs and pockets. When bumping into them, the coolant stops. Sometimes plugs cut off entire sections with radiators from the circuit. At the same time, the pressure in the system increases. When it reaches a critical level, an emergency release of coolant occurs. This, in turn, leads to a drop in pressure. At the same time, there are many cases when air collected in the batteries, the circuit continued to work, only half of the radiator became cold. This significantly reduces the heating efficiency and slightly increases the cost of its operation.
For open systems, one of the most serious threats is rust. At the same time, the question of how to remove air from the heating system arises only at the design stage. Such circuits are assembled at an angle from pipes with a large diameter, so there is a lot of water in the system. Considering the fact that the coolant is in contact with air and draws it into circulation, the oxygen level in the pipes is more than sufficient. Since it takes a long time to remove air from the heating system, oxygen reacts intensively with the metal. The result of the interaction is the formation of corrosion on the inner walls of the pipes. Rust sometimes eats up the tank so much that you have to replace it.
The direct consequences of traffic jams in the circuit entail indirect ones, which are no less dangerous:
Occurs if the valve for bleeding air from the heating system and all sensors are in good working order and working correctly. Due to the increase in pressure, an emergency release of the coolant occurs, which leads to a decrease in its quantity in the circuit. After cooling, there will not be enough fluid in the system, and the pressure will drop sharply. If it does not correspond to the minimum required to turn on the boiler, the heater will not turn on. And from this moment in winter, the countdown begins when the pipes defrost. Depends on how insulated the house is. Sometimes this happens in just three hours. In this case, unpleasant news awaits you at home from work;
This occurs if there is a malfunction of the valve for bleeding air from the heating system, or the temperature-controlling equipment. An unlikely situation, although possible. The results of this are very disastrous. At best, repair or replacement of the boiler; at worst, injury;
- rupture of the circuit and release of the hot water fountain.
A very likely situation is that the joints may not be tightened enough. As the pressure increases, they cannot withstand and crack. At the same time, hot coolant flows from the pipe like a fountain. Not only does the circuit need to be repaired, but the neighbors also need to repair the ceiling, since you flooded it thoroughly. This is the kind of chain that can be caused by simply airing the system.
A plug in the circuit can lead to serious consequences, such as system defrosting or an accident.
Water comes out of the air vent
Automatic air vent - how it works, why it leaks
Automatic air vents have not yet appeared that would not leak periodically. Which, in general, is not difficult to eliminate temporarily. Why do they leak, how to deal with it, and also why such devices are needed in heating, and how to use them correctly...
Why do you need an air vent?
Any closed pressure coolant system must have one or more air vents. At least one of them is automatic, releasing air on its own, without human intervention, as accumulation occurs.
This ensures the operability of the system and prevents airing. In an air-filled system, the coolant does not move normally, the equipment does not operate stably, noises and pops are heard - small water hammers. Equipment and pumps wear out faster.
Or the air lock will stop the movement of the coolant completely. Without a small device - an automatic air vent - the system will not work normally - airing will occur.
Where does the air in heating come from and how is it removed?
Air is dissolved in water (in the coolant) and is released when there are changes in pressure and temperature, forming bubbles that accumulate in the upper part of any system.
To remove air, it is necessary to install air vents in many characteristic places of the system, and automatic ones at the most important points where air accumulation is likely. To quickly, constantly bleed off the gas.
They also make separators - sections of pipe with a significant difference in diameter. In the area where the pressure decreases (the movement of the liquid accelerates), air bubbles are released, then they accumulate at the expansion - where they are removed by the described device.
Automatic air vent design
The device is based on a body with a float. The float is connected to a needle release valve, which is located at the very top. If the body is filled with water, the float closes the valve, and the outlet is closed. When air appears, water is displaced, the float sags, the hole opens, and air, accordingly, comes out.
The design of the automatic air vent may be different, the body is steel or bronze, the lever mechanism from the float to the needle may vary. But there is one peculiarity - always strictly vertical installation, only in this position the device works.
A corner design is also possible - the so-called. radiator automatic air bleeder, which is screwed into the end of the structure, usually instead of a radiator plug.
In what places are they located?
The safety group for non-automated heating systems (solid fuel boiler) is equipped with an automatic air vent. In automatic boilers, such a device is always provided inside.
As a rule, for a small home system, one such air valve is sufficient, which is complemented by Mayevsky taps - manual devices for bleeding air. They are installed at the end of each radiator.
Where to locate - automatic air bleed points
In branched systems, automatic air vents are installed in several places. In addition to the boiler device, the following are also installed:
On each collector, including underfloor heating.
- On high, U-shaped non-standard bends, for example, on the edge of a door.
- At the top point of the highway of each floor in a multi-story building.
Where do gases come from?
Air and gas may appear in the heating system for several reasons, namely:
- Poor water quality;
- Water is highly acidic and reacts with the radiator material;
- The coolant began to disintegrate due to long-term use;
- Incorrectly selected or low-quality coolant.
The central heating system may receive water in which a lot of air or other gas is dissolved. When passing through the radiators, it begins to release and an air lock appears. Airiness can form both in the heating radiator and at the top point of the system.
Causes and consequences of air locks in an open heating system with natural circulation
If the pipe slopes in the system are correctly designed, then all the air will be released through the open expansion tank, which is located at the top point of the heating circuit. There can be several reasons for an air lock:
- After repairs, air remained in the heating radiators;
- Incorrect (too fast) filling of the system at startup;
- The circuit is filled with water through an expansion tank;
- When heated, air begins to be released from the water, which was previously in a dissolved state;
- When filling the circuit, water was supplied from above.
The consequences are not difficult to predict - stopping circulation, cold batteries, rapid corrosion of the internal surface of system elements. To avoid this, it is enough to install manual air vents on all radiators - Mayevsky taps.
The automatic air vent is divided into the following main types:
1. Permanent air vent. Fig. 1. This means that the automatic air vent removes air and gases constantly in a filled system. It is characterized by high reliability, relatively low throughput and, as a rule, works both for air intake and exhaust. These are models for both domestic and industrial use, for example on risers of residential buildings.
2. Starting air vent. Fig. 2. Used to quickly remove air when filling systems, then it closes and does not remove air. An automatic air vent of this type can operate only to release air, or to release and start while the system is draining. As a rule, these air vents are used only on water systems with temperatures up to 60C.
3. Combined action air vent. Fig. 3. This automatic air vent in its design has 2 floats - a large one for starting or emptying the system and allowing a large amount of air to pass through, and a small one for operating the valve when the system is already filled. Such valves are mainly used in water supply and sewerage systems, much less often in heating systems.