Taps on radiators vary in purpose and principle of operation. When choosing suitable shut-off and control valves, knowledge of what types of taps are produced and what design is best to purchase for installation on batteries in a house or apartment will be useful.
Purpose and scope
Today's installation technologies require that each heating device be equipped with a locking element. This allows in emergency situations to cut off the flow of coolant into the battery, dismantle it and carry out repairs without draining water from the system.
Along with shut-off valves, heating devices are equipped with temperature control devices. A Mayevsky bleed valve is mounted in the upper radiator plug.
These types of fittings have become a mandatory attribute of a “smart home”; they are used both in residential premises and in administrative buildings, institutions, shopping centers, and everywhere where people live and work.
Why are balancing valves needed?
Let us immediately make a reservation that not every system requires balancing as such. For example, 2-3 short dead-end branches with 2 batteries on each can immediately switch to normal operating mode, provided that the pipe diameters are selected correctly and the distances between the devices are small. Now let's look at 2 situations:
- 2-4 heating branches of unequal length with a number of radiators from 4 to 10 are connected to the boiler.
- The same layout, but with batteries equipped with thermostatic valves (described in another publication).
An example of a dead-end circuit with arms of unequal length and load.
The last radiator of the short branch also needs a balance valve. Since the bulk of the water always flows along the path of least hydraulic resistance, in situation No. 1 the first heating devices located close to the boiler will receive more heat. If the flow of coolant to these radiators is not limited, then the last batteries in the chain will heat up much less, the temperature difference between them can be 10 ° C or more.
To direct the required amount of coolant to distant batteries, radiator balancing valves, shown in the photo, are installed on the connections to nearby devices. They restrict the flow of water, partially blocking the flow area of the pipes and increasing the hydraulic resistance of the area.
In the same way, the coolant supply is regulated in systems with five or more dead-end branches. Manual balancing valves intended for pipelines are installed on the tie-ins close to the heat generator. Partially blocking the passage of water, they direct the main flow further along the highway.
Situation #2 is more complicated. Installing radiator thermostats with heads allows you to change the coolant flow automatically as needed. But imagine that in the room closest to the boiler the window opened, the air temperature dropped, and the thermostat opened completely. Then the last room will also become colder, because it will not have enough heat taken away by the first battery.
The purpose of the valves is to limit the coolant flow to the risers (or horizontal branches)
On long branches with a large number of heating devices equipped with thermal heads, balancing valves are combined with automatic differential pressure regulators, as is done above in the diagram.
Regulators connected by capillary tubes to balance valves respond to a decrease/increase in water flow and maintain the return pressure at the same level. Then all consumers have enough coolant, despite the activation of the thermal valves. The benefits of such control taps are described in detail in the video:
Advantages and disadvantages
This type of fittings has its pros and cons.
The advantages of a radiator shut-off, as well as a shut-off and control device include:
- cutting off the flow into this battery, which allows it to be dismantled, repaired and reinstalled without draining the contents from the pipeline;
- turning off the radiator and directing the coolant flow around it through the bypass, which makes it possible to remove the battery without stopping the operation of the entire heating system in the house;
- draining water from a specific heater, bleeding air from it;
- adjusting the amount of heat supplied to the heater.
If the single-pipe system is not equipped with a bypass, closing the valve in the battery will lead to the blocking of the entire pipeline, for example, in the entrance.
The need to disconnect
Before moving on to the diagram for disconnecting the battery from the riser in an apartment building, we suggest considering the basic reasons that can cause a malfunction of the heating system.
Here is a list of the most likely reasons for a battery disconnection:
- an emergency situation that threatens to flood your and your neighbor’s apartment with hot coolant;
- painting radiators in the cold season, when the heating is already on;
- if there is a need to change the radiator or flush it;
- In winter, the radiators are too hot and you want to lower the room temperature.
In some apartments, residents practice shutting off radiators in the summer without draining the coolant in order to protect radiators from blockages when the heating system is turned on in the fall. At this time, water often flows through the pipes with rust fragments. We will tell you how to do this correctly in one of the sections of this article.
Differences between a faucet and a valve
Radiator shut-off devices differ from valves in their compactness and ease of use. In them, just turn the handle and the valve will be closed.
In addition, valves break quickly and constantly require maintenance and replacement of seals.
It is difficult to imagine their use in a home heating network. Due to their low cost, they are used in central heating pipelines where the pipe cross-section is greater than 100 mm.
Features of the ball product
integrity violations
If the water pressure is insufficient, then the reason should be sought in the valve, which is most likely clogged. To prevent similar situations in the future, you should take care to install a hard filter.
Most often, control ball valves for heating radiators are used in heating, ventilation and cooling systems. This element acts as a regulator of the water flow circulating in the heating and cooling system.
The advantages of ball valves include increased operational reliability. Thanks to them, it is possible to protect a certain section of the heating network, which reduces consumers’ costs for servicing these systems.
Types and designs
Varieties of modern radiator fittings include:
- regulators in the form of valve devices with thermal heads that control the temperature of heating devices;
- ball valve;
- balancing valves, manually operated in most individual homes and capable of creating uniform heating in all areas of the house;
- air bleed valves, including, in addition to manual Mayevsky valves, more advanced automatic air vents;
- flushing tap used to flush the battery;
- a check valve that prevents flow in the opposite direction, for example, in networks with forced circulation.
Heating radiator maintenance
Elementary ball valves installed on the supply and return pipelines will help eliminate a leak or replace a heating device without draining the coolant from the system. The operating position of the device is open or closed, the flow of hot water in the open position is maximum, in the closed position there is no flow.
Manual control of coolant flow
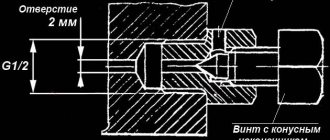
A cone valve helps to smoothly regulate the amount of liquid in the radiator. The cone-shaped stem in its design gives the user the opportunity to approximately adjust a comfortable microclimate. In extreme positions, the valve completely shuts off or opens the flow of water.
Removing air from the system
An air lock that forms in the upper part of the radiators when starting water does not allow full use of the working surface of the heating device.
A specialized Mayevsky faucet helps remove this air.
In operating condition, its valve is always closed; it opens only when setting up the system.
Automatic flow control
Precise adjustment of the microclimate makes it possible to perform a control valve with a thermostatic head. The liquid or gas bellows in its composition reacts to changes in ambient temperature and automatically controls the coolant flow.
Tips for choosing
For home wiring without adjustment, it is enough to install ball valves on the devices. If used correctly, they will last a long time and be effective.
In apartments with central heating, it is recommended to install control valves with thermal heads. They do not clog so quickly and are capable of performing both shut-off and regulating functions.
The technical characteristics of the fittings can be determined by the markings stamped on the body of each product.
Flow regulator
Having installed energy metering devices, the question naturally arises of how you can regulate and control the supply of coolant, limit or add its flow. For this purpose, there are all kinds of automatic regulators, the use of which allows you to save money; they operate from outside air temperature sensors and return pipeline sensors. Another advantage of temperature controllers is that they control the temperature directly at the radiator installation site, unlike other devices. This advantage gives priority in obtaining a uniform temperature background for a comfortable stay in the room. The regulator will prevent overheating of the air in the room, which sensors on centralized automation cannot always track. It is possible to adjust the temperature for each room separately. Sometimes, when solving the adjustment issue, ordinary taps are installed. Of course, this solution reduces financial costs, but deprives a number of useful advantages. The faucet has limited functionality to open and close. There is a danger of stopping or airing the riser. By adjusting the heating using taps it is impossible to achieve the required temperature. Using automatic regulators, you can adjust the system accurately and efficiently.
Theme Options
Search by topic
Rules for installation and operation of the crane
It is important to choose the right installation scheme for reinforcement accessories.
The procedure for installing the fittings in all schemes is the same - an ordinary ball valve is mounted on the supply line, and a control valve is mounted on the return outlet. A Mayevsky valve or automatic air vent is mounted on the upper corner.
Before installation, check the arrow on the device body with the coolant flow.
Before the start and at the end of the season, it is necessary to turn the handles to avoid sticking of the shutter and to clean the mechanism from accumulated particles.
Required tools and materials
The tools you will need are:
- pliers;
- adjustable or universal wrenches;
- a set of Phillips and slotted screwdrivers;
- ratchet wrench.
You will need the fittings itself, tow, fum tape, and plumbing paste.
Work progress
The installation process is straightforward.
- Drain all the water from the heating pipes.
- First, screw the device onto the pipe.
- They disassemble the American coupling and screw it into the radiator lining.
- Connect the pipe with the tap to the battery and screw on the nut.
The connection is ready.
Thermostatic valve
In modern realities, a thermostatic valve is a prerequisite for modern and reliable equipment in a heating system. The valve temperature is automatically adjusted. The operation of a heating system mixing valve for radiators is to limit the supply level to an individual heating radiator. The valve stem makes movements to open and close the hole. Through this hole, coolant enters the radiator. When the valve with a thermostatic head heats up, the inlet opening is closed, as a result of which the coolant flow rate decreases. The thermostatic valve constantly changes its position. And an important factor is the quality of the materials on which this product is made. The product may fail due to sticking of the rod, as well as significant corrosion and breakthrough of sealing materials. But even if the thermostatic valve fails, you can extend its service life by replacing the thermostatic element.
Heating system valves with thermal heads differ depending on the shape and type of supply to the heating system. They can be angular when connected to radiators from the floor, or they can be straight, which connect the pipes to the battery relative to the wall surface. Axial, mainly when connecting pipes from the wall to the battery. When connecting batteries sideways, a special kit is required. It uses thermostatic heads and valves. Batteries that come with a bottom connection are obviously equipped with valve-type inserts.
Frequent errors and problems during installation
The fittings are placed in a limited space, there is poor access to it, and the crane handle cannot be fully deployed.
The tap is installed incorrectly in relation to the direction of coolant flow.
Before installation, you must follow the direction of the arrow on the device body.
A protective screen is installed next to the thermostatic valve. In this case, the readings of the thermal valve relative to the air temperature in the room will always be inaccurate, since it is located in the warmer part of it.
Elevator unit
In apartment buildings, valves are usually installed at the entrance and exit of the elevator unit of the heating system. Their body has two rings made of corrosion-resistant steel, which encircle the passage for the coolant (mirrors). Another pair of mirrors is located on the surface of the valve - its moving part.
When the damper is in the lower position and lowers, it blocks the movement of water, but if it moves to the upper position, it goes beyond the circulating flow.
To close the valve, the consumer needs to rotate the handwheel, which drives the screw-threaded rod. A seal packed around the stem will help ensure tightness. For heating and hot water, the product must be graphite. There is no alternative to this device for pipe diameters of 50 millimeters or more. It is necessary to determine which taps are best for heating radiators.
If this parameter is lower, it is recommended to use modern plug valves, such as in the photo, since valves have serious disadvantages:
- it is necessary to periodically fill the oil seal, even when the valve is not in use, since the packing, in contact with water, is gradually destroyed;
- After a short period of time, the cheeks begin to become overgrown with deposits. If the valve sits for several years without being used, it will not be possible to close it completely;
- In the event of an emergency, every second can be decisive. If it takes literally a moment to close the plug valve, then it will take a long time to rotate the valve’s steering wheel, even when it is fully operational.
It should be noted that plug valves, which are a ball with a channel for water surrounded by a plastic shell, differ in:
- practicality;
- durability;
- reliable fluid retention;
- no need for maintenance.
Plumbing specialists do not recommend purchasing and installing a screw valve on a heating radiator or the same products of any other type. They have significant design disadvantages:
- The seal will need to be filled periodically if there is no desire to put up with constant leakage along the rod. When it is difficult to replace the valve or fill the oil seal, then to eliminate the leak, the valve must be opened all the way with a little force. The leak will stop due to the fact that the thread on the rod will press the oil seal:
- Rubber gaskets for elements of heating structures have a limited shelf life. Heating radiator valves with flat brass valves do not hold water after a certain time due to the appearance of deposits on the valve and seat. These same locking elements with wedge-shaped valves made of brass, after closing them with force, often jam in the seat (about
Expert advice
The diagonal connection scheme for radiators has already proven its best efficiency. The greatest heat loss is allowed when installing the bottom connection.
The thermoregulatory valve head should be placed perpendicular to the radiator screen so that the flow of warm air does not have a corrective effect on its readings.
Do not install the tap on the pipe connecting the expansion tank to the boiler. Unexpected overlap can lead to an explosion.