Home / Solid fuel boilers
Back
Published: 06/14/2019
Reading time: 4 min
2
2626
Air heating is the oldest heating system for houses in Rus'. The Russian stove is the real ancestor of air-heating boilers (VK) and is still used in rural areas.
The next “historical” modification of the VK is the potbelly stove, which became widely known during the terrible years of the October Revolution and has a more modern version in the form of wood-burning fireplace heaters. In all these examples, the heat from fuel combustion was not used efficiently, and most of it was simply wasted.
Photo source: zaognstrok.ru
Modern long-burning air-heating boilers have given new life to the technology of air heating of buildings. Today, the devices modernized by Russian specialists have become competitive in the boiler industry.
A new generation air-heating boiler appeared in 2002 in the Novosibirsk region. It was invented by heating engineer E.Yu. Zubkevich named Professor Butakov in honor of his relative. Today, this design belongs to the class of energy-efficient devices that reduce the cost of heating a home and emissions into the environment.
- 1 Pros and cons of hot air boilers
- 2 Furnace structure
- 3 Model range of boilers by Professor Butakov
- 4 Operating principle of an air-heating boiler
- 5 Installation standards
Description and features of the air heating system
Autonomous water heating of a private house is impractical. Its widespread use is in most cases explained by thoughtless copying of centralized heating systems. They are characterized by large heat losses, since the boiler room is located at a distance from consumers. Therefore, a liquid with high energy intensity is required as a working medium.
In an autonomous system, the boiler is located directly inside the heated object, so there are no losses. Air with a heat capacity 800 times less than that of water can be used as a working medium. Instead of pipes, boxes with adjustable outlet grilles are laid; radiators are not used.
The movement of air in the system, like liquid, can be carried out in 2 ways:
- natural;
- forced.
The first option is based on convection - the property of a heated medium to rush upward. It is acted upon by an Archimedean force caused by a decrease in density.
A system with natural circulation has 2 disadvantages:
- length limitation;
- large cross-section of air ducts.
They are deprived of the alternative option, in which the work environment moves forcibly. To do this, install a fan in the box before the branching.
Air heating combined with ventilation
As a rule, air heating and ventilation systems operate autonomously, without interacting with each other. Combining two separate circuits into a single system can sometimes improve heating efficiency and reduce heat loss.
It is worth noting that this approach is suitable for heating small spaces, such as garages or workshops, which are used only from time to time. In this case, compact devices with a fan for air heating are used, which run on electricity or diesel fuel. The fan blows warm air into the room.
In large residential buildings, such installations are not used because they are uneconomical and ineffective.
Installation of air-heating solid fuel boilers
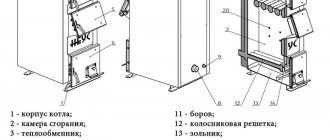
The heat generator housing contains the following elements:
- Firebox. It is a chamber for burning fuel. There is a door in the front.
- Ash pit. Ash collection box. Some models do not have it.
- Convection pipes around the firebox. Located vertically, open at the bottom and top.
- Analogue (non-volatile) or electronic automation.
The condition for operating a solid fuel installation is the presence of a chimney in the house.
The device is connected to it via a pipe in the upper part of the combustion chamber.
Principle of operation
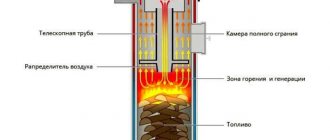
When fuel burns, heat is released, which heats the air in the convection pipes. It rushes up, falls into the box and is then distributed among the rooms. At the same time, the convective flow draws cold air into the pipe through the lower hole. It heats up, under the influence of Archimedean force it begins to move upward, and the cycle repeats.
According to the method of fuel combustion, air-heating boilers are divided into the following types:
- Direct burning.
- Pyrolysis.
- With forced air supply.
- Top burning.
- Pellet.
- Designed for smoldering mode.
The first option is a classic “potbelly stove” with minor improvements.
Its advantages are:
- simple design;
- possibility of non-volatile execution.
The device is considered unpractical due to significant disadvantages:
- low efficiency;
- the need to frequently add firewood.
The firebox of a pyrolysis boiler consists of 2 parts. In one, firewood or coal, under conditions of heating and lack of air, decompose into flammable gases, in the other, this mixture is burned.
Advantages:
- long-term operation on 1 load of fuel;
- high efficiency;
- minimum amount of ash;
- clean exhaust.
Flaws:
- the impossibility of a non-volatile design (a strictly adjusted air supply controlled by an electronic controller is required);
- use only dry fuel.
It is necessary to note the high cost of such devices.
Boilers with forced air supply are structurally similar to direct combustion heaters. The difference is that oxygen is forced into the firebox by a fan, so at the right time its access can be blocked. Thus, the boiler operates in a “start-stop” mode: thanks to this scheme, firewood needs to be added less often.
Advantages:
- simple design;
- low inertia.
Disadvantage: dependence on electricity.
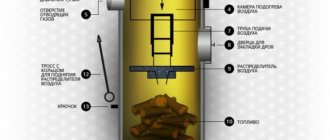
In top-burning boilers, the firebox is oriented vertically. There is no door at the front. Fuel is loaded from above, and it is set on fire from the same side. Air is supplied through a telescopic pipeline to the combustion zone.
Advantages of the scheme:
- long-term operation on 1 load of fuel;
- Possibility of energy-independent design (for wood-burning version).
Flaws:
- Ash sticks to the walls.
- A new portion is loaded only after the previous one has completely burned out.
It is necessary to note the large sizes.
This heat generator, as well as pyrolysis and forced air, due to its ability to work for a long time on 1 load of fuel, is called “long-burning boilers.” The download frequency for some is 3 days.
Pellet boilers use granules of uniform size as fuel, made by pressing sawdust, cake and other organic waste. The material is fed into the furnace by a screw feeder from the hopper.
Advantages:
- relatively infrequent service;
- power adjustment within a wide range (depending on the pellet feeding speed);
- low inertia.
Flaws:
- energy dependence;
- inability to produce fuel at home.
Boilers designed for smoldering mode include devices from the brands “Professor Butakov”, “Buleryan”, etc.
Heaters combine 3 advantages:
- ability to work for a long time on 1 load of fuel;
- energy independence;
- simple design.
This is an option for field conditions when there is no power supply and, due to busyness, there is no opportunity to frequently add firewood. Using a damper, the flow of air to the fuel is limited, and instead of burning, it smolders, slowly releasing heat.
In some models, for example, the Buleryan brand, the chimney begins with the so-called. "economizer". Its task is to block traction when the fuel ignites (a gas plug is formed). This ensures the stability of the smoldering regime.
Areas of application: country house, garage, temporary sheds and industrial premises in areas with undeveloped infrastructure.
It is not practical to heat a comfortable home with such a heat generator due to significant disadvantages:
- low efficiency;
- a lot of smoke;
- abundant formation of condensation, which is a caustic acid cocktail.
Devices of this type are designed for low temperatures. Therefore, when burning fuel in them in the traditional way, they quickly burn out.
Advantages of air heating
There are many advantages to heating your home with air:
- The efficiency of the air heating system reaches 90%.
- When using filters, oxygen can be purified or filled with silver ions. This feature will be indispensable for people with allergic reactions.
- Excellent drying of the house from air humidity.
- If desired, the heating structure can operate in a gentle mode. Useful for maintaining optimal temperature during periods of long absence of owners.
- In case of hot weather outside, air heaters can be used to supply cool air.
- The long-burning system will provide the owner with the opportunity to save on fuel and not have to constantly visit the boiler room.
- There is no need to install batteries and pipelines in the home interior.
- The ventilation system can be used with a solid fuel boiler for heating other rooms.
We invite you to watch a video about the Energy pyrolysis air-heating boiler and its operating principle.
Advantages and disadvantages
The air heating system has a number of advantages:
- Low cost. Instead of expensive pipes and radiators, air ducts are used, which you can make yourself from plywood.
- Simple design. No pump, expansion tank, pressure gauge, safety valve, or air vent are needed. Cheap dampers are used instead of expensive fittings.
- Security. The coolant does not freeze, does not boil, does not cause corrosion of metal elements, and air pockets do not form in it.
The disadvantage is that, due to their large size, the boxes cannot be laid in a finished house without compromising the aesthetics of the interior design. The air system is designed together with the house, laying channels in the walls, between the floor joists and behind the suspended ceiling.
Safety precautions
Compliance with fire safety rules is one of the main requirements for designed systems with air heating boilers and ventilation. The full text of the requirements can be read in manual 13.91 SNiPa 2.04.05-91. Only part of the standards are used for equipping residential buildings.
In particular, if the air ducts are made of flammable materials, then they are laid in non-flammable sleeves or shafts. It is advisable to use materials with a flammability level of at least group G1, that is, low-flammability. In this case, the temperature of combustion products should not exceed 135 ℃.
The optimal material for air ducts is galvanization. But fans and their casings may consist of flammable materials. In any case, it is worth making sure that the temperature of the air entering the room does not exceed 60 ℃.
Rating of the best equipment models from Professor Butakov
This brand produces energy-independent air-heating boilers that operate in smoldering mode. There are 6 models in the line, 3 of which are most in demand:
- "Student".
- "Engineer".
- "Professor".
The heat with a mass of 70 kg is 9 kW. Room volume – up to 150 cubic meters. m. The firebox holds 20 liters of fuel. There is a hob on top; there are modifications with a glass insert. Door material – steel or cast iron (customer’s choice).
The power of the “Engineer” is 15 kW, weight is 110 kg. Allows you to heat an area of up to 150 square meters. m. Firebox volume – 40 l. At the buyer's request, the door can be equipped with a translucent screen.
“Professor” emits 40 kW of heat in nominal mode, which makes it suitable for heating a room of 400 square meters. m (with a ceiling height of up to 2.5 m) or a volume of up to 1000 cubic meters. m. Weight is 230 kg. The firebox holds 200 liters of fuel. The coal version comes in 2 versions: the smoke outlet is directed upwards or backwards.
Types of fuel for boilers
Depending on the fuel used, heat generators are divided into two types:
- wood;
- coal.
The first ones are designed for temperatures up to 185°C.
They can be heated:
- firewood;
- briquettes;
- pellets;
- peat;
- straw;
- pressed paper or cardboard.
Coal ones are made from thicker and heat-resistant steel. They can withstand temperatures up to 230°C. Any type of fuel is suitable for long-burning boilers, but coal or coke is required to reach nominal operating conditions.
Installation Features
The air-heating boiler is placed on a concrete floor or fireproof stand. The latter protrudes beyond the contours of the device by 300 mm in each direction.
For a massive product with a power of over 50 kW, a foundation is constructed that is not connected to the building structures, incl. floor.
The minimum distance to the wall is 1 m. If it is covered with fire-resistant plaster (vermiculite, etc.) with a layer thickness of 25 mm, the distance can be reduced to 0.8 m.
The wooden floor in front of the combustion door within a radius of 1.2 m is covered with fireproof flooring - a steel sheet with a thickness of 1.5 mm on a basalt cardboard lining.
For boilers of the “Professor Butakov”, “Buleryan” and other brands, oriented towards smoldering mode, an external chimney is preferable. In this case, harmful condensate fumes formed in large quantities will not enter the room.
Air circulation standards
According to SNiP 2.04.05-91, the general air circulation rate is 35% per hour, that is, complete replacement of exhaust air must occur within 3 hours. In this case, at least 30 m3/hour of air per person must enter the room. For the kitchen, this figure is increased to 60 m3/hour in the presence of electric stoves, and up to 90 m3/hour if a 4-burner stove is used.
Additionally, the room must be equipped with vents or folding transoms on the windows to ventilate the room and let in at least 180 m3/hour of fresh air. Sometimes a hood is used for these purposes.
In bathrooms and toilets, air circulation rates are 25 m3/hour for each room. In combined bathrooms, the norm doubles.
Is it possible to make an air-heating boiler yourself at home?
When making a heat generator with your own hands, the blank for the firebox is a large diameter pipe or an old gas cylinder. The latter needs to be washed several times before cutting. Otherwise, the remaining gas may detonate.
The firebox is placed horizontally and sealed on the back side with a plug with a smoke exhaust pipe. Holes are drilled from below so that the wall turns into a grate.
The minimum diameter of convection pipes is 60 mm. This value is taken taking into account the viscosity and thermal conductivity of air. The pipes are installed vertically on both sides along the firebox in a checkerboard pattern. They should go around it and converge at the top in a pointed arch.
The front of the firebox is sealed with a plug with an opening and hinges for the door. The latter is made of steel sheet.
A short pipe with a damper made in the form of a disk is welded into the door. With its help, the air supply is regulated. The disk is welded onto a rod threaded through the holes in the middle of the pipe. One end of it is made longer and bent so that it looks like a handle.
A similar damper is installed in the initial section of the chimney. Here a quarter of the disk is cut out so that under no circumstances is the channel completely blocked. Otherwise, there is a risk of carbon monoxide entering the room.
An ash box assembled from steel sheets is welded to the firebox below. It is also equipped with a door in front.
The legs from the corner are welded to the ash box.
The installation is enclosed in a housing with fireproof thermal insulation made of mineral wool. This makes the boiler safe: if accidentally touched, the user will not receive a severe burn.
Purpose of the ventilation system
Whatever the purpose of the room, ventilation ducts are its integral attribute. This especially applies to residential buildings and apartments, since during human activity dust, excess moisture and unpleasant odors, as well as carbon dioxide, accumulate. All this is removed outside through ventilation, and in return fresh, oxygen-rich air enters the room. In addition, thanks to the hood, condensation does not accumulate on the walls and fungus does not grow.
Thus, ventilation systems are designed to circulate oxygen in the room. There are exhaust and supply and exhaust ventilation systems. When using a supply and exhaust ventilation system, a recuperator is installed. This means that the warm air leaving the room will transfer some of the heat to the incoming flow. As a result, heat loss will be noticeably lower.