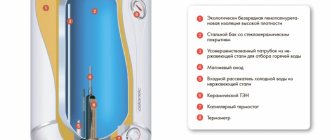
What is an electrolyzer
An electrolyzer is a special installation used to separate its components from a solution or melt.
The main characteristics of the electrolyzer are:
- The operating voltage for one electrode ranges from 1.8 to 2.0 V;
- Current strength - for the normal course of the electrolysis process, a current with a value of this characteristic from 5 to 10 A is supplied to the electrodes;
- Number of electrodes – the minimum number of electrodes is 2, the maximum is limited by the size of the installation itself and its purpose;
- Dimensions of electrodes - not carbon rods are used as electrodes, but metal plates, the size of which is determined by the purpose of the installation, the current-voltage characteristic of the current supplied to the plates;
- Distance between differently charged electrode surfaces – the minimum distance between electrode plates must be at least 1.5 mm;
- Electrode material - in modern electrolysers, stainless steel sheets with the addition of nickel are used as the material for the anode and cathode.
Also another important characteristic of an electrolysis plant is the use of catalysts.
Such settings are used for the following purposes:
- Production of detonating gas consisting of a mixture of hydrogen and oxygen (Brown's gas);
- Isolation of pure aluminum, magnesium, zinc from molten salts;
- Purification of water from dissolved salts and impurities;
- Applying a thin corrosion-preventing layer of nickel and zinc to the surface of metal parts;
- Disinfection of food products;
- Purification of wastewater from heavy metal salts and other harmful substances dissolved in them.
Important! Platinum electrode made from ordinary iron is used in electrolysis installations less often than from stainless steel, since it oxidizes faster and becomes unusable.
In progress
The device looks impressive in operation. When disgusting dark flakes form in clean water in seconds, the first thought is “I’m drinking this!” And the hand itself reaches for the wallet. How many people remember electrochemistry?
TB
It was dark before the first turn on. Firstly, I assembled the entire circuit on a stool and turned it on with dry hands from a distance of several meters. Secondly, I plugged into a socket protected by a 10 mA RCD, characteristics A, that is, also responsive to pulsating current. Thirdly, I did everything at night, when the children had calmed down and could not run and grab the electrode. And still I didn’t take something into account. It turned out that the water gets very hot when the device is operating. And my glass of thick glass could easily burst due to temperature changes. A stream of boiling water under voltage is a bad prospect. It worked out, however. But I won’t repeat it myself and I don’t recommend it to others.
Testing
For tests, I bought a liter of distilled water from auto parts and a bottle of low mineralization drinking water. I took a pinch of salt from the kitchen.
Distilled water is a good insulator; a yellow substance appears in drinking water
Now add a pinch of salt to distilled water. Wow! I didn’t expect such a strong response!
It’s clear that a pinch of salt in a glass of water couldn’t produce so much black rubbish. It is a product of electrochemical corrosion of the iron electrode. Basically, iron hydroxides with a small admixture of salts, ferric chloride in this case.
In principle, the experience in terms of entertainment is good. And I was thinking about showing it to the children. But he didn’t, and now we’ll see why - the inner world is very poor and dangerous.
Brief theoretical part
Hydrogen, also known as hydrogen, the first element of the periodic table, is the lightest gaseous substance with high chemical activity. During oxidation (that is, combustion), it releases a huge amount of heat, forming ordinary water. Let us characterize the properties of the element, formatting them in the form of theses:
- The combustion of hydrogen is an environmentally friendly process; no harmful substances are released.
- Due to chemical activity, the gas does not occur in free form on Earth. But its reserves in water are inexhaustible.
- The element is extracted in industrial production by a chemical method, for example, in the process of gasification (pyrolysis) of coal. Often a by-product.
- Another way to produce hydrogen gas is by electrolysis of water in the presence of catalysts - platinum and other expensive alloys.
- A simple mixture of hydrogen + oxygen gases explodes from the slightest spark, instantly releasing a large amount of energy.
For reference. Scientists who first separated the water molecule into hydrogen and oxygen called the mixture an explosive gas due to its tendency to explode. Subsequently, it received the name Brown's gas (after the name of the inventor) and began to be designated by the hypothetical formula NHO.
Previously, airship cylinders were filled with hydrogen, which often exploded
From the above, the following conclusion suggests itself: 2 hydrogen atoms easily combine with 1 oxygen atom, but they part very reluctantly. The chemical oxidation reaction proceeds with the direct release of thermal energy in accordance with the formula:
2H2 + O2 → 2H2O + Q (energy)
Here lies an important point that will be useful to us in further debriefing: hydrogen reacts spontaneously from combustion, and heat is released directly. To split a water molecule, energy will have to be expended:
2H2O → 2H2 + O2 – Q
This is the formula for an electrolytic reaction that characterizes the process of splitting water by supplying electricity. How to implement this in practice and make a hydrogen generator with your own hands, we will consider further.
We create the device with our own hands
The device for this process can be made by hand.
For this you will need:
- Stainless steel sheet;
- Bolts M6 x 150;
- Washers;
- Nuts;
- Transparent tube;
- Connecting elements with threads on both sides;
- One and a half liter plastic container;
- Water filter;
- Check valve for water.
An excellent option for stainless steel is AISI 316L from a foreign manufacturer or 03Х16Н15М3 from a manufacturer from our country. There is absolutely no need to purchase stainless steel, you can use old one. 50 by 50 centimeters will be enough for you.
“Why use stainless steel itself?” - you ask. Since corrosion will occur on even ordinary metal. Stainless steel withstands alkalis better. You should mark the sheet in such a way as to divide it into 16 similar squares . You can cut it with an angle grinder. Cut off one of the corners of each square.
On the other side and opposite corner from the cut corner, drill a hole for a bolt that will help hold the plates together. The electrolyzer does not stop working like this: electricity flows from plate to plate - and water breaks down into oxygen and hydrogen. Thanks to this, we will need a good and negative plate.
The plates must be connected alternately: plus-minus-plus-minus , with this method there will be a strong current. To isolate the plates one from another, a tube is used. The ring is cut from the level. By cutting it, we get a strip a millimeter thick. This distance is more correct for gas production.
The plates are connected to each other using washers: we put a washer on the bolt, then a plate and three washers, then another plate and so on. Eight plates must be placed on the plus and minus. If everything is done correctly, the cuts of the plates will not touch the electrodes.
Afterwards you will need to tighten the nuts and insulate the plates. Then we place the structure in a plastic container.
Application of electrolyzers
The constant rise in energy prices has made it possible to take a new approach to electrolytic processes. Various types of installations have been developed to obtain:
- aluminum;
- chlorine;
- hydrogen for plasma cutting and welding machines.
The devices also work as part of units that purify and disinfect drinking water and swimming pool water, as an additive to fuel for cars, allowing the full potential of hydrocarbons to be used. Hydrogen burns much earlier than gasoline. Gasoline is no longer ignited by a spark, but by a flame, which increases the force pressing on the piston of the car’s engine.
Some craftsmen use electrolysis of water at home to heat rooms. But here it is worth noting that the cost of the resulting combustible hydrogen is significantly higher in price than the same natural gas. In addition, the combustion temperature of hydrogen is quite high and not every metal can withstand prolonged exposure without destruction. But the use of heat-resistant materials is not economically justified.
Purpose
According to the seller
Using this device will help you check all types of impurities in water by showing different colors. There are 6 colors (yellow, green, blue, red, white, black) to represent different objects in water and only yellow color shows that water is good for health.
It’s funny what is said a little lower about yellow
Yellow: dissolved acids, fluoride and other organic matter
The real purpose is to give scam victims a scary look at how horribly dirty the water is that they are drinking. Steam filters, etc.
Models of industrial electrolyzers
Carbon anodes (and graphite is an allotope of carbon) have a significant drawback - during the reaction, they emit carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, thereby polluting it. Currently, inert anode technology is especially relevant; a well-known aluminum manufacturer is currently testing this technology. Its essence is that a non-reactive carbon-free anode is used, and not carbon dioxide, but pure oxygen is released into the atmosphere as a by-product.
This technology significantly increases the environmental friendliness of production, but it is still at the testing stage.
Despite the wide variety of electrolytes, electrodes, and electrolyzers, there are common problems in technical electrolysis. These include the transfer of charges, heat, mass, and the distribution of electric fields. To speed up the transfer process, it is advisable to increase the speed of all flows and use forced convection. Electrode processes can be controlled by measuring limiting currents.
Origin
This rubbish was given to me by friends following the post about the Fuel Shark. Since I got it for free, I put 18 points. My friends themselves seem to (but I’m not sure) politely asked the distributor for clean water as a gift (and where the handsome man emerged from, they won back this crap a long time ago... Well, after all, the new is the well-forgotten old The seller with such a product I googled it. Although it’s unlikely that the scammer took it from him, but IMHO any seller of such a product deserves to be rewarded with a boot in the face. Repeatedly.
Since I got it for free, I put 18 points. My friends themselves seem to (but I’m not sure) politely asked the distributor for clean water as a gift (and where the handsome man emerged from, they won back this crap a long time ago... Well, after all, the new is the well-forgotten old The seller with such a product I googled it. Although it’s unlikely that the scammer took it from him, but IMHO any seller of such a product deserves to be rewarded with a boot in the face. Repeatedly.
There are, of course, similarities with the fuel shark - both products are intended to deceive and scam money. But there is also a significant difference: During the analysis, we will see that the electrolyzer under review poses a mortal danger when used, both for the fraudster using this equipment and for his victim.
Main types of electrolysis plants:
- Installations for the production and refining of aluminum;
- Electrolysis installations for ferrous production;
- Electrolyzers for nickel-cobalt production;
- Installations for magnesium electrolysis;
- Copper electrolysis (refining) installations;
- Installations for applying galvanic coatings;
- Electrolysis plants for chlorine production;
- Electrolyzers for water disinfection.
- Electrolyzers producing hydrogen for nuclear power plants...etc.
Oxygen is a byproduct of many redox reactions.
During electrolysis, the current strength, its frequency and voltage, even polarity are regulated; these parameters control the speed and direction of the processes. The electrolysis reaction is always carried out at constant current, since the constancy of the poles is very important here. In very rare cases, when polarity is not significant, alternating current is used (for example, during electrolysis of gases).
Modern aluminum electrolysers, based on the design of the cathode device, are divided into
- Electrolyzers with and without bottom,
- With stuffed and block hearth;
- according to the current supply method: with one-sided and two-sided busbar circuit;
- according to the method of gas capture: open type electrolyzers, with bell gas suction and covered type.
The unsatisfactory properties of all existing designs of aluminum electrolyzers include an insufficiently high energy utilization factor, a short service life and insufficient efficiency of exhaust gas collection. Further improvement of the design of electrolyzers should follow the path of increasing its unit capacity, mechanization and automation of all maintenance operations, complete capture of all waste gases with subsequent regeneration of their valuable components.
Industrial electrolysis plants have many types of design, the main ones being membrane and diaphragm. There are also dry, wet and flow electrolysis plants. In general, the installation is a closed system containing electrodes placed in an electrolyte, to which an electric current with certain characteristics is supplied. Electrolysis cells can be combined into a battery. There are also bipolar electrolyzers - where each electrode, with the exception of the outer ones, works on one side as an anode, on the other side as a cathode.
This equipment operates at different pressures, depending on the type of reaction. To obtain some substances, for example, when obtaining gases, pressure adjustment or special conditions are required. You also need to monitor the pressure of gases that are a byproduct of electrolytic reactions. Electrolysis plants, which are used to produce hydrogen and oxygen at power plants, operate under excess pressure of up to 10 kgf/cm2 (1 MPa). The installations also differ in their productivity.
Some of them use linear electric mechanisms. For example, they are used to move electrodes, regulate electrolyte levels, move reservoirs, electrolyte baths, etc. One example of such a design is shown in the drawing.
All electrolysis installations must be grounded. To operate a large industrial electrolyzer, a rectifier unit or a converter substation is needed to convert alternating current into direct current. Stationary local lighting in electrolysis workshops (buildings, halls) is usually not required. The exception is the main production premises of electrolysis plants for the production of chlorine.
Model with two filters
The electrodes are small square sheets cut from galvanized steel or, better, from stainless steel grade 03Х16Н15М3 (AISI 316L). Ordinary steel will be very quickly “eaten up” by electrochemical corrosion.
Having cut a hole in the wall of the container with a knife, you need to install two coarse filters on it - “mud filters” (the second name is an oblique filter) or filters from washing machines will do.
Next, the container is fixed to a metal base using bolts, after which a check valve is attached to it.
Next, a 2.3 mm thick board and a bubble tube are installed.
The creation of the electrolyzer is completed by installing a nozzle with a shutter located on the board side.
Device with two valves
The manufacturing process of a 2-valve electrolyzer model is not particularly complicated. As in the previous version, assembly should begin by preparing the base. It is made from steel sheets, which need to be cut in accordance with the dimensions of the container.
The board is firmly attached to the base (we use M6 screws), after which you can install a bubbling tube with a diameter of at least 33 mm. Having selected the valve for the device, you can begin installing the valves.
Plastic container
The first one is installed on the base of the pipe, for which it is necessary to secure a fitting in this place. The connection is sealed with a clamping ring, after which another plate is installed - it will be needed to fix the shutter.
The second valve should be mounted on the pipe with a distance of 20 mm from the edge.
Three valve models
This modification differs not only in the number of valves, but also in the fact that the base for it must be especially strong. The same stainless steel is used, but of greater thickness.
The location for installing valve No. 1 must be selected on the inlet pipe (it is connected directly to the container). After this, the top plate and the second bubble-type tube should be secured. Valve No. 2 is installed at the end of this tube.
When installing the second valve, the fitting must be secured with sufficient rigidity. You will also need a clamp ring.
Ready-made hydrogen burner
The next stage is the manufacture and installation of the valve, after which valve No. 3 is screwed to the pipe. It must be connected to the nozzle using studs, while insulation must be ensured using rubber gaskets.
Water in its pure form (distilled) is a dielectric and in order for the electrolyzer to work with sufficient productivity, it must be turned into a solution.
The best performance is demonstrated not by saline, but by alkaline solutions. To prepare them, you can add baking soda or caustic soda to the water. Some household chemicals are also suitable, for example, “Mr. Muscle” or “Mole”.
Model with plexiglass
Assembling an electrolyzer using organic glass blanks cannot be called a simple task - this material is quite difficult to process.
Difficulties may also arise at the stage of finding a container of a suitable size.
One hole is drilled in the corners of the board, after which the installation of the plates begins. The step between them should be 15 mm.
The next step is to install the shutter. As with other modifications, rubber gaskets should be used. You just need to take into account that in this design their thickness should be no more than 2 mm.
Top container device
The electrodes are made from a stainless steel sheet measuring 50x50 cm, which must be cut into 16 equal squares with a grinder. One corner of each plate is trimmed, and in the opposite corner a hole is made for an M6 bolt.
One by one, the electrodes are put on the bolt, and the insulators for them are cut from a rubber or silicone tube. Alternatively, you can use a tube from the water level.
The container is fixed using fittings and only after that the bubble tube and electrodes with terminals are installed.
Bottom container model
In this version, the assembly of the device begins with a stainless base, the dimensions of which must correspond to the dimensions of the container. Next, install the board and tube. Installation of filters is not required in this modification.
Then you need to attach the shutter to the bottom board with 6mm screws.
The nozzle is installed using a fitting. If you nevertheless decide to install filters, then plastic clips with rubber gaskets should be used to secure them.
Finished device
The thickness of the insulators between the electrode plates should be 1 mm. With such a gap, the current strength will be sufficient for high-quality electrolysis, at the same time, gas bubbles can easily break away from the electrodes.
The plates are connected to the poles of the power source alternately, for example, the first plate to the “plus”, the second to the “minus”, etc.
Dry
Such electrolysers consist of plate electrodes separated from each other by sealed rubber gaskets. Often the “cells” of the installation are additionally placed in a sealed housing.
The hydrogen and oxygen produced as a result of electrolysis are discharged through special pipes located at the end of the housing or the outer plates of the installation.
Flow-through
A simplified design of devices of this type can be found in the figure. As you can see, the design includes a bath with electrodes “A”, completely filled with solution and a tank “D”.
Design of a flow electrolyzer
The operating principle of the device is as follows:
- at the entrance of the electrochemical process, the gas together with the electrolyte is squeezed into container “D” through pipe “B”;
- in tank “D” gas is separated from the electrolyte solution, which is discharged through the outlet valve “C”;
- the electrolyte returns to the hydrolysis bath through pipe “E”.
Membrane
The main feature of devices of this type is the use of a solid electrolyte (membrane) on a polymer basis. The design of devices of this type can be seen in the figure.
Membrane type electrolyzer
The main feature of such devices is the dual purpose of the membrane: it not only transfers protons and ions, but also physically separates both the electrodes and the products of the electrochemical process.
Diaphragm
In cases where diffusion of electrolysis products between the electrode chambers is not permissible, a porous diaphragm is used (which gives such devices their name). The material for it can be ceramics, asbestos or glass. In some cases, polymer fibers or glass wool can be used to create such a diaphragm. The figure shows the simplest version of a diaphragm device for electrochemical processes.
Design of a diaphragm electrolyser
Explanation:
- Oxygen outlet.
- U-shaped flask.
- Hydrogen outlet.
- Anode.
- Cathode.
- Diaphragm.
Alkaline
Unlike other models of electrolyzers, these use an alkali solution as an electrolyte - caustic soda (sodium hydroxide), which is not only an additional source of hydrogen and oxygen, but also a catalyst for electrolysis.
Alkaline electrolyzer circuit
Such installations, unlike analogues of other types, allow the use of cheaper electrodes made of ordinary iron.
PREPARATION OF IONIZED WATER
The positive result of electrolysis depends primarily on the quality of the liquid. It should have a minimum amount of impurities. For this purpose, ordinary tap water is allowed to settle for at least two to three hours and passed through a filter.
At the beginning of the process, a current consumption of 1 A or more indicates an increased content of metal salts in the solution. The optimal current consumption value is 0.2 A, which at the final stage does not exceed 1 A. Temperature is also a determining indicator of electrolysis. It should not exceed 35 degrees.
The procedure for preparing activated water does not significantly depend on the version of the device, but has some features.
Sequence of actions in the first option:
- Place the tarpaulin bag in an empty container.
- Pour liquid 1 cm below the top edge.
- Place the electrodes in a jar and the anode in a bag.
- Connect the device to the mains.
- After 5-12 minutes, turn off the mains voltage and remove the electrodes.
- Immediately remove the canvas bag with the acidic liquid and pour it into a separate container.
Sequence of actions in the second option:
- Pour the liquid into a jar and into a clay glass.
- Place the glass in a glass jar.
- In both containers, the water levels should be the same, but so that the liquid does not overflow into the glass from the jar.
- Place the plate with the positive electrode in the clay glass.
- Place a negative electrode in a glass jar so that its plates are parallel to the anode plates.
- Check that there is no contact between the cathode and the anode.
- Connect the device to the network for 5-12 minutes.
- Turn off the device and remove the ionized water.
DIY electrolyzer for a car
On the Internet you can find many diagrams of HHO systems, which, according to the authors, allow you to save from 30% to 50% of fuel. Such statements are too optimistic and, as a rule, are not supported by any evidence. A simplified diagram of such a system is shown in the figure.
Simplified diagram of an electrolyzer for a car
In theory, such a device should reduce fuel consumption due to its complete burnout. To do this, Brown's mixture is supplied to the fuel system air filter. This is hydrogen and oxygen obtained from an electrolyzer powered from the car’s internal network, which increases fuel consumption. Vicious circle.
Of course, a PWM current regulator circuit can be used, a more efficient switching power supply can be used, or other tricks can be used to reduce energy consumption. Sometimes on the Internet you come across offers to purchase a low-ampere power supply for an electrolyzer, which is generally nonsense, since the performance of the process directly depends on the current strength.
This is like the Kuznetsov system, the water activator of which is lost, and the patent is missing, etc. In the above videos, where they talk about the undeniable advantages of such systems, there are practically no reasoned arguments. This does not mean that the idea has no right to exist, but the declared savings are “slightly” exaggerated.
Electrolyzer for hydrogen production: drawings, diagram
Let's look at how you can make a powerful gas burner powered by a mixture of hydrogen and oxygen. A diagram of such a device can be seen in Figure 8.
Rice. 8. Hydrogen burner design
Explanation:
- Burner nozzle.
- Rubber tubes.
- Second water seal.
- The first water seal.
- Anode.
- Cathode.
- Electrodes.
- Electrolyzer bath.
Figure 9 shows a schematic diagram of the power supply for the electrolyzer of our burner.
Rice. 9. Electrolysis torch power supply
For a powerful rectifier we will need the following parts:
- Transistors: VT1 – MP26B; VT2 – P308.
- Thyristors: VS1 – KU202N.
- Diodes: VD1-VD4 – D232; VD5 – D226B; VD6, VD7 – D814B.
- Capacitors: 0.5 µF.
- Variable resistors: R3 -22 kOhm.
- Resistors: R1 – 30 kOhm; R2 – 15 kOhm; R4 – 800 Ohm; R5 – 2.7 kOhm; R6 – 3 kOhm; R7 – 10 kOhm.
- PA1 is an ammeter with a measurement scale of at least 20 A.
Brief instructions on parts for the electrolyzer.
A bathtub can be made from an old battery. The plates should be cut 150x150 mm from roofing iron (sheet thickness 0.5 mm). To work with the power supply described above, you will need to assemble an 81-cell electrolyzer. The drawing for installation is shown in Figure 10.
Rice. 10. Drawing of an electrolyzer for a hydrogen burner
Note that servicing and managing such a device is not difficult.