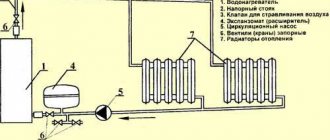
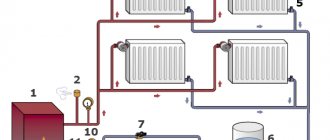
The problem of insulating communications in the basement, as a rule, is not familiar to ordinary city residents. But it is very often encountered by all those who live outside the city or have a dacha (or private house) for seasonal residence. Insulation of pipelines is not only useful, but also often a necessary measure, protecting the entire building from many potential problems.
How to insulate pipes in the basement with your own hands
Insulating a pipe with mineral wool with your own hands
Insulating a pipe with mineral wool
Stage 1
For plastic heating pipes, it is best to use mineral wool or glass wool. Take a roll of cotton wool, unwind it and cut off small pieces. Wrap it around the water pipe and secure it with a nylon rope. To do this, wrap and tie a rope on one side of the pipe, and in a spiral, wrap it all the way around the pipe and tie the rope securely - this is the initial insulation.
Stage 2
Waterproof the water pipe. To do this, take a roll of roofing felt and cut small pieces of 2-3 m each. Wrap the heating pipe around the top of the insulation. Try to make overlaps of at least 10 cm. Take the nylon rope again, tie it at one end and also wrap it around the heating or water pipe in a spiral. Additionally, the insulation can be wrapped with tape.
Pipe insulation with polystyrene foam
Pipe insulation with polyurethane foam
Take a polyurethane foam “shell” and connect the two halves around the pipe, wrap the edge with tape. Place the following parts “overlapping” by about 10-20 cm. Wrap the shell with tape at the junction. The insulation may have a layer of foil, which makes it similar to a thermos. This insulation can be used in the basement and outdoors.
Pipe insulation with polystyrene foam
Insulation with polystyrene foam is the most affordable material. Expanded polystyrene “shells” are produced for different pipe diameters; installation is easy and at the lowest cost. Take the insulation halves, connect it around the pipe and wrap it with tape. Carry out this operation until the entire pipe is covered with insulation.
How to properly insulate
Thermal insulation of heating pipelines in a private home is not very difficult; it can be done with your own hands. It is enough just to follow simple conditions. All the details of the pipe insulation process can be seen in the video.
On the street
When installing thermal insulation in an open space, it is important to ensure that the pipeline is reliably sealed from precipitation and to isolate the insulation from sunlight. Previously, mineral wool was often used for thermal insulation and wrapped in roofing felt; now shells made of PPS or polyurethane foam with an outer layer of galvanized steel, reinforced foil, fiberglass or fiberglass are usually used. The heating main on the street experiences constant wind loads, so it is necessary to select a durable material for thermal insulation - polyurethane foam, extruded polystyrene foam. For large-diameter heating mains, galvanized steel shells are used.
Underground
When installing thermal insulation underground, it is necessary to especially carefully seal the insulation of steel heating pipes. It is necessary to carefully glue the joints of the shells and seal difficult areas with polyurethane foam foam. The quality of installation of the heating pipeline and thermal insulation depends on the preparation of the trench - the slope must be maintained, the pipeline with thermal insulation must be covered with sand. Underground, it is best to use ready-made shells with an outer shell made of fiberglass, fiberglass, or kraft paper for thermal insulation.
Indoors
Inside dry rooms, attics, and basements, mineral wool is often used for thermal insulation of heating pipes - rolled or in the form of shells. On top it is wrapped in penofol, fiberglass, roofing felt, and fixed with wire or tape. You can also use foam shells or penofol.
Insulation materials and requirements for heating systems
List of materials used for thermal insulation of pipelines:
- mineral wool;
- expanded polystyrene;
- penoizol;
- foamed polyethylene;
- polyurethane foam;
- penofol.
Not only the main main pipelines are subject to insulation, but also the heating pipes of private and apartment buildings located in the basement, cellar, roof, street. Modern insulation materials are developed from inexpensive materials, with an ergonomic design that helps process pipes without the help of professionals and special tools.
Insulation for heating and hot water supply pipes - material requirements:
- Low thermal conductivity.
- Safety for humans and the environment.
- Inert to acids, alkalis and other biological substances.
- Non-flammable material.
- High melting point.
- Low hygroscopicity.
- High corrosion resistance.
- Durability.
- Economical.
- Easy installation.
What to consider when performing thermal insulation
Before you begin insulating a structure located in the basement of an apartment building, you should understand the basic requirements in order to get the expected result and avoid numerous problems.
- Maximum service life.
- Self-extinguishing ability.
- Availability of water-repellent properties.
- Easy to install.
- Low cost.
- Environmentally friendly.
- Low thermal conductivity.
Thermal insulation in an apartment building
Which materials are preferable?
Today, the variety of materials with which you can easily and quickly insulate the water supply in the basement is impressive.
Among the effective and most popular are the following:
Mineral wool
Elements made on the basis of mineral wool will cope with temperature changes. With its help, you can insulate not only pipes in the basement of an apartment building, but also those located outside or in the ground. You can see what mineral wool looks like in the photo below.
Polyurethane foam
Ideal for insulating basement water pipes and attics. In essence, it is the outer shell of the water supply system. This design minimizes heat loss and adds strength. This heat insulator is not afraid of chemical influences and does not rot. But it has one drawback - high cost.
Expanded polystyrene
This material is characterized by a high level of rigidity. Expanded polystyrene insulation is sold in the form of a part of a pipe that has protrusions for fastening.
Foamed polyethylene
This heat insulator is best suited for internal insulation of a heating system.
Styrofoam
Polystyrene foam is good for insulating heating and water supply systems on ground and basement floors. Has a low level of moisture absorption. Foam plastic is also very durable and can be used for more than two decades.
Foam rubber
The heat insulator has a number of advantages. It is elastic, temperature resistant and not afraid of fire. Due to the fact that it is fire resistant, it is suitable for insulating external pipelines.
Liquid heat insulator
High-quality material that can compete with others on equal terms. For example, one layer of paint can replace a 5-centimeter layer of polyurethane. In addition to its insulating properties, liquid thermal insulation can protect metal from corrosion and give pipes a good appearance. But it is not used for thermal insulation of plastic pipes.
Regardless of the material you choose, the main thing is that the insulation is effective and there are no problems with tearing or other damage on cold days. More detailed instructions for installing a particular heat insulator can be viewed in the video on the Internet. It is worth noting that working with insulation is not difficult; you can easily do it yourself.
Why do you need insulation for attic ventilation?
The ventilation system is designed to maintain a certain level of humidity and temperature in the room. It also needs insulation. This is especially true for the attic in winter, when the pipes are very hot from the inside and are blown with cold air from the outside.
Then condensation appears on the surface, which can damage the material. Proper insulation will reliably protect the structure and prevent negative consequences. This applies not only to pipes, but to the entire ventilation system as a whole. In addition, it will help save energy, which is also an important factor in favor of insulation.
PPU insulated pipes
Alternative thermal insulation options
There are alternative methods of thermal insulation that prevent adverse consequences. They do not apply in all cases. First, you can remove all the water from the system - no water, no problem. This method is applicable for houses not used in winter. It will help protect the system from damage if water pipes freeze.
Secondly, you can ensure constant movement of water in the pipeline by opening the tap a little. This is not difficult to do if you live permanently. But the option is dangerous - suddenly you will have to leave home for a couple of days, and upon return you will be surprised in the form of a damaged water supply.
The insulation helps get rid of condensation, which has a positive effect on extending the service life of metal pipes
In addition to holding the tap slightly open, there are other ways to ensure constant pressure in the pipeline. For example, use a special pump to increase the water pressure in the system or add another element - a receiver. It should be cut into the pipe immediately near the pump. The operation of the receiver will maintain constant pressure, which will protect the system from freezing.
Laying pipes below freezing depth
This method is advisable to use if in winter the soil freezes no deeper than 170 cm. A trench is dug from a well or borehole, the bottom of which is 10-20 cm below this value. Sand (10-15 cm) is added to the bottom; the pipes are laid in a protective casing (corrugated sleeve), then covered with earth.
To avoid having to insulate the outdoor water supply in cold weather, it is better to do this in advance
This is the easiest way to make winter water supply at the dacha, but it is not the best, although it is the cheapest. Its main drawback is that if repairs are necessary, you will have to dig again, and to the full depth. And since it is difficult to determine the location of a leak with this method of laying a water pipeline, there will be a lot of work.
To ensure that there are as few repairs as possible, there should be as few pipe connections as possible. Ideally, there should be none at all. If the distance from the water source to the dacha is greater, make connections carefully, achieving perfect tightness. It is the joints that leak most often.
Choosing a material for pipes in this case is not the easiest task. On one side, a solid mass presses from above, so a strong material is needed, and this is steel. But steel laid in the ground will actively corrode, especially if the groundwater is high. The problem can be solved by properly priming and painting the entire surface of the pipes. Moreover, it is advisable to use thick-walled ones - they will last longer.
Even if the ditch was dug below the freezing level, it is still better to insulate the pipes
One more thing. The depth of soil freezing in the region is determined over the past 10 years - its average indicators are calculated. But firstly, very cold winters with little snow occur periodically, and the ground freezes deeper. Secondly, this value is the average for the region and does not take into account the conditions of the site.
You might be interested in reading “How to make automatic watering“.
Methods for insulating water pipes
To prevent frost from damaging water pipes in a private house/dacha/cottage, you need to worry about their thermal insulation in advance.
It is important, even at the stage of laying communications, to consider options for insulating pipes, and not only water pipes. If this is done in a timely manner, the costs will be minimal.
There are quite a lot of options for insulation for pipes - it is important to choose high-quality material among the mass of proposals, without focusing too much on price. The cheapest option is wasted money. Among the methods of insulating a pipeline for supplying water to a house, the most popular among homeowners are:
Among the methods of insulating a pipeline for supplying water to a house, the most popular among homeowners are:
- extend the pipeline 0.5 m below the freezing level;
- use a heating cable;
- insulate with heat-insulating material;
- provide an air gap;
- buy a ready-made factory pipe;
- apply several methods at once.
Most often, more than one method is used. So, if the water pipes are deep, then the area responsible for the entrance to the house still needs insulation. Therefore, the most optimal option is selected for it in order to protect the local water supply system.
The depth of the pipeline depends on the region. To find out, you can use special lookup tables by finding your region or check it empirically
The heating cable has become widespread due to its ease of installation and high-quality performance of its functions.
Depending on the type of installation, there are 2 types of cable:
- outer;
- interior.
The first is mounted on top of the water pipe, and the second - inside. It is reliably insulated and made of safe materials. It is connected via a heat-shrinkable sleeve to a regular cable with a plug or to a machine. Read more about heating cable for water supply below.
The heating cable comes in different capacities. Most often found from 10 to 20 W
There are a great variety of thermal insulation materials on the market. They all differ in their properties, quality, price, installation difficulties and service life.
Which one to choose depends on the specific situation.
Among insulation materials, polyethylene and polyurethane foam half-cylinders - shells - are particularly easy to install.
The method of providing an air gap is also often used. It consists of a water pipe placed inside a cheap, smooth plastic or larger diameter corrugated pipe.
Inside there is free space for the circulation of warm air coming from an insulated basement or heated in another way.
Warm air perfectly protects the water pipe from freezing. Although it is often additionally insulated with polypropylene or other material
Another option is to purchase ready-made insulated pipes of factory origin. They are sold completely ready for installation.
They consist of 2 pipes of different diameters placed inside each other. Between them there is a layer of insulation. This insulation method is often called pre-insulation.
The option with ready-made pipes does not always satisfy the needs of a particular user - diameter, type of material and cost can become a real problem for purchasing them
The use of several methods of thermal insulation of pipes is due to the fact that all methods are imperfect and it will not be possible to apply them in all cases. Conditions of use in various households located in all regions of the country are radically different from each other. Therefore, you have to choose the option that suits your specific requirements.
Recommendations from experts
When choosing a suitable material for thermal insulation of a ventilation system, consider:
- The thermal conductivity coefficient should be as low as possible.
- Moisture resistance. The loss of insulating properties due to moisture absorption can nullify all the advantages of the material, including the low price.
- Difficult to install. The cost of specialist services depends on the danger of the material and the characteristics of its fastening. Insulating with cheap insulation can end up costing more than the highest quality insulation. If the work is supposed to be done independently, then the investment of time and effort is important.
- Fire safety class. This indicator can be decisive when choosing between two insulation materials with similar characteristics, if we are talking about a room with a high risk of fire.
According to experts, the best option for insulating vent pipes is foamed polyethylene. Foam rubber surpasses it in all characteristics and has no disadvantages.
Insulation of ventilation ducts.
Selection of material for thermal insulation
Mineral wool materials
Today, a variety of materials are used to reduce heat loss when moving hot water through pipelines. The choice of material depends on the pipe diameter, operating conditions, efficiency requirements, etc.
Below we will look at the most common insulation options.
The most popular materials used to protect coolant in heating systems are mineral wool. It is used in a wide variety of conditions, and at the same time provides fairly effective thermal insulation. Materials based on mineral wool can withstand temperatures up to 650 0 C, which makes it possible to use them directly in boiler rooms.
The advantages include:
- High resistance to various chemical influences - alkalis, acids, oils, organic solvents, etc.
- Non-toxic and safe to use.
- Low water absorption. This parameter is very important, since when moistened, any heat insulator loses a significant share of its effectiveness.
- Low price.
It will be most effective to use mineral wool for insulating external pipelines, heating systems in the basements of multi-story buildings, as well as for thermal insulation of chimneys, the surface of which is very hot.
Mineral wool derivatives are often used as more effective materials:
- Basalt wool
is made from natural raw materials, the main component of which is basalt-containing rocks. It has all the advantages of mineral wool, in addition, 0 has a lower thermal conductivity coefficient. Very durable. - Glass wool (glass fiber)
- made from quartz sand and cullet. It is characterized by low density and vulnerability to high temperatures, therefore it is used exclusively for external thermal insulation.
Polyurethane foam insulation
For domestic use, polyurethane foam insulation is most often used. These materials are produced in the form of special tubes assembled according to the “pipe-in-pipe” principle (pictured). This design, in addition to reducing thermal energy losses, additionally gives the pipeline mechanical strength.
The positive qualities of polyurethane foam thermal insulation include:
- No toxic compounds in the material.
- Weather resistance.
- High mechanical strength.
- Electroneutrality.
Such insulating materials do not rot or break down when exposed to most chemicals.
True, there is also a very obvious drawback - the rather high cost of the material. It is this feature of polyurethane foam thermal insulation that limits its use.
Insulation with polyurethane foam
Recently, more and more people have begun to pay attention to modern heat insulators. And one of the most popular and effective is polyurethane foam (PPU). This type of material is excellent for pipes and is, in fact, the outer shell for a water pipe (“pipe within a pipe”).
Polyurethane foam significantly reduces heat loss.
This type of design not only minimizes thermal energy loss, but also gives the pipes a high level of strength.
Positive characteristics of polyurethane foam:
- the material does not contain any compounds hazardous to humans;
- high level of resistance to climate impacts;
- increased mechanical strength;
- neutral to electricity and biological influences.
Polyurethane foam insulation materials will not rot or be destroyed by chemical exposure. The only obvious drawback of the material is its high cost. In fact, only this can be considered a reason to refuse thermal insulation from polyurethane foam in the basement of a private house.
Ready-made polyurethane foam shells.
It should be noted that insulating pipes with polyurethane foam is not so easy to do with your own hands, so it is better to hire specialists for this work. In the basement of a private house, the use of polyurethane foam often does not look like a very profitable option: the cost of a single installation (for example, for one or two pipes) will be quite high, so there is no urgent need for it.
Types of ventilation systems
Ventilation systems are divided according to the principle of operation into exhaust, supply, and supply and exhaust. There are no differences in the installation of thermal insulation for them. Depending on the location of installation, ventilation systems can be domestic or industrial. The area, air exchange of pipelines, and the volume of harmful fumes in production are many times higher than in residential, office or commercial premises - more powerful equipment is required. Another difference is that household ventilation systems often use plastic pipes, while industrial ones use galvanized metal pipes.
Metal ventilation pipes especially need protection from condensation. In the process of cutting into pieces of the required length, the galvanization layer is broken. Contact with moisture causes the metal to quickly rust, and the pipe becomes unusable within 2 to 3 years.
Fig.3 Industrial ventilation system
The need for insulation
Now look: you invest in paying for resources, but the heat is released not only into the house, but also outside, into the basement, into the attic, etc. Do you need these expenses? Hardly. Agree, spending money on heating your yard during the cold winter is perhaps the most useless investment of all.
This is why it is so important to insulate pipes. This prevents heat from escaping to places where it is not needed.
Non-residential premises and the street are areas where the pipeline must be protected. Inside the house - in its residential parts - this does not need to be done for obvious reasons, heat transfer should occur there anyway.
In addition, there are other advantages that insulation of heating pipeline segments provides:
protection against condensation and freezing
As long as the heated coolant circulates through the pipes, even if not insulated, critical situations do not arise - if you do not pay attention to heat loss, then everything is in order. But there are times when a heating system malfunctions for some reason.
For example, an accident occurs and the house is left without light - as a result, both the electric heating boiler and the circulation pump stop. That is, heating of the coolant and its forced circulation through the pipes stops. What happens in this case? That's right, the liquid inside the pipeline is cooling. If it happens in the summer, there is no problem. If in winter, then first condensation forms on the pipe, which in itself is not a very useful phenomenon, and then the cooled liquid begins to freeze. It also depends on what kind of coolant you use. Antifreeze, for example, will obediently turn into a gel and wait until the system is restored to functionality. But the water will turn into ice, expand and can do a lot of damage to the pipeline, especially at the junction of the segments. Thus, breakthroughs may subsequently occur, and the restoration of the heating system will take a long time. Agree, in winter a house without heat is terrible. Of course, insulation on the pipes will not completely solve the problem, but it will prolong the cooling of the coolant for a long time, thereby giving you a considerable amount of time to troubleshoot problems in the system;
Possibility of underground pipe laying. Not everyone wants to look at the pipeline located in the yard. It is much more aesthetically pleasing to hide it underground. But, as you know, the temperature there is usually lower than on the surface. Therefore, insulation in this case is an absolutely necessary protection of the pipeline from freezing.
As you can see, pipe insulation is necessary both to save your money and to extend the life of the heating system. A nice bonus is that you can easily perform the procedure yourself, even without special skills. You just need to figure out what material to use for the job. But let's talk about this in more detail.
The process of insulating the water supply in the basement
- Measure the outer diameter and length of the pipeline. Cut the material according to the parameters. Sometimes it is necessary to wrap sewer pipes several times. This should be taken into account when “cutting” the insulator.
- Wrap the heating structure and immediately secure the insulation. Wrap the tape or rope tightly. It is easier to work if the materials are cut into small pieces lengthwise.
For those of us who have an individual heating system installed in our apartment, such a question as insulating heating pipes may seem far-fetched. And really, why insulate something that already has a fairly high temperature?
However, the owners of country houses, as well as those who use communal heating, know very well that thermal insulation of pipelines is not only useful, but also necessary. In our article we will tell you why you need to insulate yourself and what material is best suited for this.
Materials
It is also important to consider the method in which the insulation will be installed. On the modern market, materials are presented in three varieties, depending on this factor:
- roll Used for wrapping pipes. Their advantage is that they can be used on elements of any diameter;
- cylindrical. In accordance with the name, they are a cylinder. It can be either solid or with a cut. In the first case, the pipe is inserted inside the element; in the second, the insulation can be put on after the pipeline has been assembled. It is clear that in this case the diameter of the segments is very important, since the cylinders have certain dimensions. They must cover the pipe without any gaps, otherwise heat will escape through the latter;
- semi-cylindrical. In principle, this is the same cylinder, but divided lengthwise into two halves. One is installed on the top of the pipe, the second on the bottom. The disadvantage here is the same as that of the previous version - it is tied to the diameter of the pipeline. In addition, it should be noted that half-cylinders, also called “shells,” can be hard or soft. The former can only be used on straight sections of the pipeline, since the material does not bend. If you need to insulate a bend in a highway, then you need to use a softer option.
Fiber wool
These are the well-known mineral wool and glass wool. They are rolled varieties of materials, which makes them quite convenient for installation. The thermal insulation characteristics of both wools are simply excellent - both retain heat perfectly.
But there is a drawback that can cover all the advantages - it is unstable to moisture. With glass wool this is even more or less the case, but mineral wool not only instantly absorbs water, but also almost completely loses its insulating properties when wet. In addition, over time it is compressed, as a result of which it also begins to insulate worse than initially.
Glass wool does not have such problems, but there are others. Over time, it begins to disintegrate, releasing tiny particles of glass into the air. Naturally, if inhaled, this can seriously harm health, so such material is usually not used in a residential building.
If you decide to use cotton insulation, then the best option would be to combine them. Sections of the pipeline located on the street can be wrapped with glass wool - there it will not harm anyone, and moisture will not interfere with it. And insulate those segments that are located in the attic or basement using mineral wool. It is safe for people, and its location indoors will protect it from exposure to precipitation. However, it is better to make an additional protective layer of steel tape on top - this way you will definitely protect the material from getting wet.
Foamed polymers
This variety includes foamed polyethylene, polystyrene foam, polyurethane foam and rubber. The first is a roll material, the rest are semi-cylindrical. The main advantage of all foamed polymers is excellent resistance to moisture. They can be safely placed outdoors.
In addition, they all have a long service life, ranging from 30 to 50 years. The only drawback of the materials is their high level of flammability. Moreover, they not only ignite, but also emit very acrid smoke.
Therefore, when deciding to use these particular insulation materials, it is necessary to pay increased attention to fire safety issues.
Painted and sprayed insulation
With this approach, the insulation layer turns out to be monolithic; it, as it were, becomes another shell of the pipe, and therefore reliably protects the pipeline. However, it is worth considering that it is almost impossible to remove it.
In addition, polyurethane foam is damaged by the sun's rays, so when placing it outdoors it is necessary to provide protection. Paint does not have this problem, but it insulates worse. It is better to use it in regions that do not experience cold winters.
Dear readers, based on today’s article you will be able to decide exactly what and how to properly insulate the heating pipeline in your home. Do not neglect this procedure, because in the end you will receive significant cost savings and also protect the system from possible breakdowns. Good luck!
Where is pipe insulation required?
Insulation of heating pipes and hot and cold water supply is necessary if the lines run underground, in an open space, in the basement or attic of apartment buildings or private houses. Insulation for outdoor heating pipes allows you to cope with many of the disadvantages of the physical and chemical properties of the pipeline material and the disadvantages of installing the system.
Polymer heating pipes are more resistant to corrosion, but they also require protection from freezing, physical damage, abrasion, etc. Metal pipes, despite their rigidity and strength, can quickly rust and become unusable. In addition, metal is a conductor of current and has good thermal conductivity, which is a big disadvantage for heating and hot water pipes. Insulation eliminates these disadvantages and preserves the temperature of the coolant. What to use for pipe insulation, everyone decides according to their own capabilities.
Materials that reduce the heat transfer of heating pipes are used everywhere in construction. Today, manufacturers offer a huge range of thermal insulation materials that can be used without special tools and skills.
How much insulation do you provide for the heating system in your own home? What materials do you recommend using when insulating pipes in a private home?
Insulating water pipes in the basement means creating a comfortable microclimate and reducing the cost of the heating system. Such work is important for both private houses and multi-apartment buildings. Certain requirements apply to the pipeline insulation process. This applies to any systems: plumbing, heating and sewer.
In recent years, polypropylene structures in basements have become popular. Do they need to be insulated? If the strip foundation was not insulated during the construction process, then it is necessary. If a private building is used only in summer and is not heated in winter, pipe insulation will prevent the system from freezing and failing.
How to calculate the thickness of insulation
The thickness of the thermal insulation of heating pipes is calculated in accordance with SP 61.13330.2012 Thermal insulation of equipment and pipelines. Updated version of SNiP 41-03-2003. Below is a calculation for above-ground installation of heating pipelines - in this case it is important not to make a mistake with the thickness of the thermal insulation so that the pipes do not freeze in frosty weather. When laying underground, even if the pipeline is buried 500 mm, the earth will serve as additional insulation and a small error with its thickness does not play a special role. In most climatic zones, a thickness of 50 mm thick PPU or PPS shells is sufficient.
The calculation is carried out with some approximations - the heat transfer of the heating pipe itself is not taken into account, but this parameter can be neglected. They also neglect the outer insulating layer - galvanization, roofing felt, fiberglass, since it is too thin to really influence the thermal insulation parameters. Calculations are given for single-layer thermal insulation of a heating pipe.
Basic formula (for pipes with a diameter of less than 1400 mm):
ln B = 2πλ [K*(tT - to)/qL - RH], where
- λ — thermal conductivity coefficient of thermal insulation (reference data);
- K is the coefficient of additional heat loss through the supports, we take K = 1.2;
- tT— coolant temperature (see table 1);
- to— outside air temperature (average annual during the heating season, selected for your area according to SP 131.13330.2012 Construction Climatology, Appendix 3);
- qL—heat flow value (see table 2);
- RH—heat transfer resistance on the outer surface of the insulation (tabular value, for temperatures up to 100 °C with a diameter of 32 mm – 0.5; 40 mm – 0.45; 0.50 – 0.4 m °C/W).
Table 1. Average annual coolant temperatures in water heating networks, °C
| Type of pipeline | Design coolant temperatures, °C | ||
| Innings | 65 | 90 | 110 |
| Return | 50 | 50 | 50 |
Table 2. Heat flux density standards for pipelines in the open air and
duration of operation less than 5000 hours per year
| Conditional diameter of the pipeline, mm | Coolant temperature, °C | ||
| 20 | 50 | 100 | |
| Heat flux density, W/m | |||
| 15 | 4 | 10 | 18 |
| 20 | 5 | 11 | 21 |
| 25 | 5 | 12 | 23 |
| 40 | 6 | 14 | 26 |
| 50 | 7 | 16 | 29 |
Calculate ln B, determine the value of coefficient B using an online calculator, and substitute the value of B into the following formula.
Where
- δiz is the thickness of the insulating structure;
- dizn—outer diameter of the heating pipeline with thermal insulation;
- dstn—outer diameter of the insulated pipe.
Calculate the thickness of the insulating layer:
The thickness of the pipe for insulating heating pipes in a private house can be calculated using an online calculator. SP 61.13330.2012 provides calculation methods and reference information for other pipe laying conditions, but in difficult cases it is necessary to contact specialists.
Which material is better for pipe insulation: polyurethane foam or mineral wool?
Polyurethane foam insulation (or shell) is specially designed for metal and polymer heating pipes of various diameters. It is a drop-down casing with a layer of dense polyurethane foam several centimeters thick and an outer covering of metal foil. A pipe is placed into the finished product and the edges of the insulation are tightly closed. At the junction there is a self-adhesive tape that tightly closes the seam and prevents the edges from diverging. Insulated pipes look aesthetically pleasing.
Polyurethane foam insulation provides reliable protection of polymer and metal pipes from external influences. Today it is the most popular material for insulating heating mains in modern construction.
You can compare polyurethane foam and mineral wool by studying the characteristics given in Table 2.
Foamed polymer materials
These include:
- Foamed rubber
. It has a number of advantages: elastic, temperature-resistant, fire-resistant. Good resistance to high temperatures and open fire allows this material to be used in cases where the insulation is constantly exposed to open fire or sparks. - Foamed polyethylene
. This material is well suited for internal insulation of premises. Foamed polyethylene is produced in the form of tubes with special cuts that facilitate the installation of insulation. A large assortment allows you to choose a heat insulator of the required shape and size. Polyethylene reacts quite calmly to cement and other building materials, which makes it possible to use it in any construction work. - Styrofoam
. Its characteristics are similar to polyethylene foam, but it has greater rigidity. It is manufactured in the form of pipe elements equipped with grooves for fastening. Polystyrene foam is very durable: its service life can be several decades. - Foam glass
. It is far from the most common material, despite its good performance. It is moisture resistant, has low thermal conductivity, and is very dense. It retains its shape during prolonged physical exposure. Well protects against a variety of rodents.
Characteristics of insulation
The choice of material for thermal insulation of ventilation pipes is carried out according to the following criteria:
- thermal conductivity;
- vapor permeability;
- resistance to various reagents;
- temperature limit;
- compliance with sanitary and hygienic standards
Each insulation for ventilation pipes has both its advantages and disadvantages, which are determined by its structure and technical parameters.
Mineral wool
It belongs to the traditional type of insulation and has good thermal insulation properties. In addition, mineral wool and other fibers are among the most affordable materials. However, when using it for internal insulation, a seal will be required, and for external insulation, reliable protection from moisture will be required.
Mineral wool with foil outer layer
Foamed polyethylene
Available in the form of shells that tightly fit the surface of the pipes, or in rolls. It is durable, long-lasting, affordable, resistant to moisture and chemicals. In addition, foamed polyethylene is not only a good insulator, but also helps to significantly reduce vibration of air ducts.
Expanded polystyrene
It is characterized by resistance to moisture, prevents the appearance of microorganisms and corrosion. This provides reliable protection of the metal from destruction, so polystyrene foam is used not only to insulate air ducts, but also to insulate the gas pipe.
Using shell-shaped insulation, you can provide access to the ventilation pipe for repair work.
Features of using mineral wool as insulation
Mineral wool is perhaps the most famous, oldest and reliable material of all types of insulation. Along with high-quality thermal insulation, it ensures the safety and durability of pipelines. The material does not burn, is inert to acids, alkalis, and other chemical compounds. The cost of mineral wool is significantly lower than most modern insulators, which plays an important role for large volumes of construction.
Types of mineral wool for insulation:
- glass - obtained from molten glass;
- stone - obtained from the melt of volcanic rocks;
- slag - a product of processing slag from a blast furnace.
Like most porous materials, mineral wool is hygroscopic and readily absorbs moisture from the environment. A material saturated with water sharply loses its thermal insulation properties and contributes to metal corrosion. Therefore, when insulating pipelines, external waterproofing must be provided. Usually these are sheets of roofing felt or aluminum foil of increased strength.
The need to use waterproofing dramatically increases the overall cost of installing a heating system. Therefore, today mineral wool is used for insulation of heating pipes in rare cases when it is not possible to use cheaper analogues.
Recommended materials for insulation
The most effective materials for thermal insulation of pipes, among all existing ones, are:
Foamed synthetic insulation for pipes
- Minvata;
- Polyurethane foam;
- Foamed materials;
- Liquid materials;
- Thermal insulation paint;
- Coating thermal insulation;
Minvata
Insulation of heating pipes with mineral wool + foil
This insulation is a combination of a mineral wool shell, polystyrene foam and a foil shell. This insulation is considered the most popular among all presented. It has many advantages, including: resistance to chemicals, cost-effectiveness, ease of installation. This material is perfect for insulating external pipelines and for basement communications. The service life of mineral wool is up to 15 years, it all depends on the operating conditions. Installation is not complicated and will take little time; installation can be done by yourself. It is enough to wrap the pipe with material and secure it securely. There are two types of this material:
The latter is used more often, since its production is simpler, and a more affordable price allows you to fully purchase the material for complete insulation of the pipeline system.
Polyurethane foam (PPU)
PPU shell for pipe insulation
This is a material that provides reliable insulation of pipes, even in the most severe frosts. It is less popular than mineral wool, but is just as often used. Polyurethane foam ensures minimal heat loss in communications. The main advantages of polyurethane foam can be noted: environmental safety for others, reliability, resistance to any harsh climatic influences, resistance to mechanical stress, as well as electrical neutrality.
Another excellent addition to all the advantages is the high resistance to corrosion on steel pipes. The only significant drawback is the high cost. But it is completely justified by the presence of a large number of advantages.
Polymer foam materials
This group of insulation materials includes materials that best play the role of an insulator in the basement of a residential building. The best foam materials are:
Insulation of heating pipes with polystyrene foam
- foam rubber - has unique elasticity and has increased resistance to temperature changes, it does not burn and therefore is most often used in rooms with a high level of fire hazard;
- foamed polyethylene (Penofol, Izolon) is a substance that is used for internal insulation of communications in the basement; it also has excellent heat-resistant qualities and is completely safe for human health. It is a material in the form of a hollow tube with a cut.
- expanded polystyrene is one of the insulating foam materials that has a long service life. Expanded polystyrene for pipe insulation consists of cylindrical parts with reliable protrusions for fastening.
- Foam glass is a material that is rarely used, but has a number of advantages: it is highly resistant to mechanical stress and is difficult to deform.
Liquid materials
Applying polyurethane foam to heating pipes
This type of pipe insulation is quite common and inexpensive. In some cases, liquid insulation can be more effective than polyurethane or foam insulation. In addition to the fact that such a material retains heat well, it also plays the role of an inhibitor, that is, it stops the occurrence of corrosion. At high temperatures, liquid insulation does not undergo any deformation. In addition to all of the above, it is worth noting that this material also gives the pipe a pleasant, aesthetic appearance.
Thermal insulation paint
Ultra-thin insulation in the form of paint for heating pipes
This paint makes it possible to achieve even higher efficiency than mineral wool wrapping. One layer of heat-insulating paint can be equal to five centimeters of polyurethane. It is worth noting the cost-effectiveness and high environmental friendliness of the material.
Coating liquid thermal insulation
When using coating-type liquid thermal insulation, external factors such as weather and climate must be strictly taken into account. When applying thermal insulation, you need to make sure that the ambient temperature does not drop below +7 degrees Celsius. The operating temperature, after the material has completely dried, reaches up to +200 degrees, and the minimum temperature should not be less than -60 degrees Celsius.
Coating insulation for pipes
With proper operation and compliance with all rules, you can achieve a working life of up to 15 years, which is considered an excellent indicator. I would like to note two important factors: environmental friendliness and efficiency.
The process of applying insulation is simply simple. First you need to arm yourself with the necessary material in certain quantities. Next comes the surface preparation stage, followed by material preparation, and finally application.
Stages of applying thermal insulation:
- Surface preparation. This stage is considered one of the most important, because preparing the pipe involves completely cleaning the surface from mechanical particles and moisture. In simple words, we clean all dust, dirt from the pipe, and also remove moisture;
- Preparation of material. At this stage, the liquid substance is mixed. Remember that this is not paint, that is, diluting the material is under no circumstances recommended;
- Application. The mixed liquid must be applied to a previously cleaned pipeline. To do this, take a brush and apply the material to the entire surface area. This should be done in at least two layers, or even three. Before applying each subsequent layer of thermal insulation, allow the previous one to dry.
Although this liquid material is environmentally friendly, it is still recommended to wear protective gloves and goggles when working with it. Provide good lighting in the work area to ensure that the insulation is evenly applied over the entire area. Valves and other moving parts should not be treated, because after drying a dense crust forms, which in the future will become a problem when unscrewing or tightening the valves.
Purpose of insulation of heating pipes
heating system
In private and country houses, the situation looks somewhat different: often boiler or heating elements are located in a heated room, so heat loss is almost zero. However, very often a situation arises when even in such a house it is necessary to insulate the pipelines, for example, if the boiler is located in the basement or remote room of the building. Thus, installing insulation allows you to solve two problems at once: firstly, the room temperature rises, and secondly, the amount of fuel consumed will be significantly reduced - and this is a direct cost saving.
What do angiography indicators mean?
The amount of radiation that will penetrate the veins and other brain tissue is determined by their density. It is expressed in various color shades. The bone in the image will be white, and the cerebrospinal fluid will practically not appear on the resulting images. Other brain substances have different colors and densities. Using them, doctors evaluate the internal structure. The doctor will provide a detailed transcript of the received images.
How to insulate a pipeline in the basement
What is the best way to insulate water pipes in the basement, because the choice of materials is wide
First of all, it is important to choose insulation that meets the above requirements.
Mineral wool and glass wool
These insulators are best used for metal-plastic structures. Fiberglass has low thermal conductivity and resistance to elevated temperatures. But it does not tolerate moisture. Therefore, you will have to spend extra money on insulation from humidity. This insulation is used only for buildings that are heated all year round.
Mineral wool is dangerous for human skin and mucous membranes. It is recommended to work with it wearing gloves and a respirator. The material must be wound around the pipeline and secured with a strong rope. Wrap along the entire length of the pipe and secure at its end. It is recommended to apply foil or roofing felt on top of the mineral wool.
PPU and expanded polystyrene
Such insulators are resistant to moisture and mechanical stress. They can be used several times if repairs and disassembly of the structure are required. To insulate heating pipes in the basement with polystyrene foam, you need to wrap it around the pipe and secure it with tape around the entire circumference. This insulation has the properties of a thermos. It is very resistant to environmental influences and perfectly retains heat around the pipe.
Foamed polyethylene
The insulator is easy to install. Quickly attaches to pipes. Using clamps or foil tape. Perfectly protects heating structures in private homes. Can be used many times.
Liquid thermal insulation
Liquid thermal insulation is a special composition that has increased heat transfer resistance. The composition must be applied to the pipes in a thin layer. The manufacturer notes that one layer of liquid thermal insulation can replace a layer of polyethylene or polyurethane foam thermal insulation up to 50 mm thick.
Liquid thermal insulation in the basement.
In addition, one cannot fail to note other advantages of using this heat-insulating material: ease of installation, aesthetic appearance, protection of metal parts from corrosion. In addition, the layer of liquid thermal insulation is not exposed to temperature, so the applied composition will not lose its integrity even after 10-15 years of active use.
You can insulate heating pipes in the basement of a private house using liquid thermal insulation with your own hands. The composition is applied with a regular brush or roller, after which you need to wait some time for the insulation to harden, and you can start moving water through the pipes.
Technical characteristics of polystyrene foam
Two half-cylinders of polystyrene foam are placed on the pipe from above and below. There is a groove at the cut points, which ensures the absence of gaps and reliable joining of the parts to each other. The insulated pipe is wrapped with metal wire, tape or secured with clamps. The casing reliably protects the line from cooling and physical damage. Despite the water-repellent properties of the material, it must be protected from moisture. For this purpose, waterproofing is provided.
Compared to mineral wool, expanded polystyrene is a cheaper and easier to use insulator. It is preferably used when installing heating systems in private homes and basements, since the material is easy to install even for a non-professional
It is quite easy to insulate risers with your own hands - it is important to choose the correct diameter of the casing, secure it to the main line, and treat it with waterproofing. If the area is damaged, the coating is removed and replaced with a new one.
The disadvantage of using polystyrene foam as pipe insulation is the inability to handle bends and turns of the heating system with a casing made of this material.
The main characteristics of expanded polystyrene are given in Table 1.
| The name of indicators | PSB-S-15U | PSB-S-15 | PSB-S-25 | PSB-S-35 | PSB-S-50 |
| Density, kg/m3 | to 10 | up to 15 | 15,1-25 | 25,1-35 | 35,1-50 |
| Compressive strength at 10% linear deformation MPa, not less | 0,05 | 0,06 | 0,08 | 0,16 | 0,20 |
| Bending strength, not less | 0,08 | 0,12 | 0,17 | 0,36 | 0,35 |
| Thermal conductivity in dry condition at 25 °C, W (m K) | 0,043 | 0,042 | 0,039 | 0,037 | 0,036 |
| Water absorption in 24 hours, % by volume, no more | 3,0 | 2,0 | 2,0 | 2,0 | 2,0 |
| Humidity, % no more | 2,4 | 2,4 | 2,4 | 2,4 | 2,4 |
Why is thermal insulation needed?
As we noted above, many people do not understand the very purpose of insulating pipes through which hot water passes. The situation at first glance looks somewhat absurd: it warms up the pipe itself, and even in the most severe frost it cannot freeze, which means a breakthrough is practically excluded.
But the whole point is that the task of thermal insulation of heating systems is not to protect them from freezing.
- If the house is heated by a separate boiler room, then all lines through which the coolant flows must be effectively insulated. This is done to reduce heat loss during the passage of hot water from the boiler room to the consumer.
- The same applies to pipes in the basement of an apartment building: the more effective the thermal insulation of the pipes, the higher the temperature of the radiators in the premises will be.
- In private houses with individual heating, the situation is somewhat different, but even in them there is sometimes a need to protect pipelines from heat loss. For example, if the boiler is located in a remote wing of the building, then the pipes passing through the basements and storerooms can be covered with thermal insulation.
Naturally, in such a situation, insulated heating pipes provide us with a double benefit: on the one hand, the temperature in the room increases, and on the other, we reduce the cost of purchasing energy.
We insulate heating pipes in the attic and basement
House heating costs are increasing every year. Each owner is looking for ways to save: the boiler turns on periodically, or constantly works only at a minimum, and so on. The use of such methods leads to a significant decrease in the temperature in the house. But few people think about how efficiently the living area is heated, because most of the heat is lost on the way to it. If heat loss can be minimized, then the rooms will warm up better and faster; therefore, continuous operation of the boiler will not be required, and it will be possible to resort to savings without compromising the temperature. Since boilers are often located in basements and other utility rooms, we will consider how to insulate heating pipes in the basement and other possible places where the system passes.
Foam plastic for pipes in the basement
The insulation technology depends on the choice of a specific material, which is selected depending on the conditions under which it will be used in the future. The most basic difference between basements and other possible places for pipes to pass is the high level of humidity. Therefore, it is necessary to choose a material taking into account this important feature.
It is best to insulate heating pipes on the ground and basement floors using polystyrene foam, foam glass, penoizol or expanded polystyrene. This group of insulation materials has the lowest moisture absorption rates. Among the materials mentioned there are both budget and more expensive options.
Before starting insulation, the surface of the products must be thoroughly cleaned of rust and dried from moisture. It is advisable to cover the elements with protective agents - a special paint that can withstand high temperatures. After this, you can begin to attach the insulation to them. You should start either from the beginning of the element coming out of the wall, or from the junction of two elements at a right angle. The insulation segments have a basic connection system with each other - a tongue and groove.
The first half of the insulation is applied to the pipe, and then the second half is applied and secured. The material is easy to cut, but does not bend. It will not be difficult to adjust the dimensions of an excessively long segment to the required ones, but to insulate the corners you will have to cut out rings with different side widths.
Glass wool for pipes in the attic
Unlike the previous location of the pipes, high humidity is rarely observed here, which is explained by strong ventilation. Complete insulation of attic spaces is not yet common. That is why the distinctive feature is high levels of sub-zero temperatures.
The choice of material should be determined by its thermal conductivity, as well as the ability to connect segments without the risk of forming cold bridges. Based on this, it turns out that insulation of heating pipes in the attic is best done using glass wool, slag wool, stone wool and basalt wool.
The products are sold in rolls, which is convenient for working with pipes. In addition, joining the edges of the sheets overlapping allows you to avoid the formation of weak points in the insulation. Cheaper options are used if the region of residence has mild winters. Otherwise, you should turn your attention to higher quality and more expensive materials.
Before starting work, you should clean the elements from dust, debris and dirt. It is advisable to coat them with radiator paint to protect them from rust. When working with this material, you must use gloves, a respirator, safety glasses and a robe that covers the entire body. The material is cut into sheets, the dimensions of which depend on the diameter of the pipes, as well as the number of layers of wrapping. It is advisable to wrap each section of the system at least twice. The edge of each subsequent canvas overlaps the edge of the previous one. Next, clamps are put on the insulated heating pipes. They are tightened at the joints of the canvases, securely fixing them in place.
Foiled foam foil for outdoor pipes
The passage of heating pipes on the street greatly affects the decrease in temperature in the house. In addition, areas of the system located in the open air quickly deteriorate due to constant exposure to adverse weather conditions. Therefore, insulation of heating pipes on the street should be carried out using materials with the lowest thermal conductivity and moisture absorption.
In order for insulation to last as long as possible, they must be closed. For these purposes, a waterproofing membrane is most often used. Insulation in this case is carried out mainly using foamed polyethylene or polyurethane, as well as foil foam. The highest quality insulation with the longest service life will be done using heat-insulating paint. This material is several times superior to other options in its properties.
The surface of pipes located outside must be thoroughly cleaned before insulation; this step is especially important for elements that have been installed a long time ago. Next comes the process of painting this section of the system, and it is necessary to apply paint for radiators in two or three layers. After it dries, insulation segments are installed. Its inner diameter must exactly match the outer diameter of the pipes. This material is laid in exactly the same way as the foam plastic considered. The final step will be to wrap several layers of waterproofing membrane around the insulated element. Its canvases, just like when wrapping glass wool, are overlapped. Then clamps are installed in these places.
Insulating heating pipes with your own hands is quite simple. You don't need a power tool. It will only be expensive to purchase materials that will pay for themselves in the first heating season. And changes in the quality of heating of residential premises will be noticeable immediately, since the heat will not be wasted.
Conclusion
As you can see, independent insulation of ventilation pipes, both in the attic and in any other room, is not something exorbitant. And if desired, a good owner will be able to cope with this task. The photos and videos in this article show options for installing such insulation. If you have anything to add or have any questions, write in the comments, I will try to help.
In a private house, the attic can be very warm and used as an additional room. But most often it is used as a storage room. The pipelines that run across its area make it difficult to change its purpose. If you decorate them correctly and sew them up with boxes, you will be able to make this room more cozy and comfortable.
Classification
Cardiomyopathies are divided into primary (idiopathic) without an established cause and secondary with a known etiology.
Primary cardiomyopathies
- genetic: hypertrophic cardiomyopathy;
- arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy;
- non-compact myocardium of the left ventricle;
- Lenegre's disease;
- ion channelopathies.
- mixed: dilated cardiomyopathy;
- primary restrictive cardiomyopathy;
- acquired: inflammatory cardiomyopathy;
- stress-induced cardiomyopathy (tako-tsubo syndrome);
- postpartum cardiomyopathy.
Secondary cardiomyopathies
The group of secondary cardiomyopathies is extensive and includes myocardial lesions in various diseases and pathological conditions. Among secondary cardiomyopathies, the most common are alcoholic cardiomyopathy, thyrotoxic cardiomyopathy, diabetic cardiomyopathy, autoimmune cardiomyopathy, etc.