Calculating the heating of a private house is one of the important tasks during its construction or major repairs. It is better to do this at the planning stage. A special online calculator can provide some assistance in calculations. There are many calculators for calculating fuel consumption, furnace power, ventilation system, chimney cross-section, productivity of the “warm floor” pumping and mixing unit and others. However, it should be taken into account that all of them show only an approximate result, because can only calculate the simplest configurations. In fact, when calculating heating, it is necessary to take into account a lot of additional nuances. This must be done in order to correctly calculate the costs of the entire heating system and in the future not to suffer from cold in the house or, conversely, its excess, and therefore unnecessary fuel costs.
For help in calculating heating systems, we turned to Akvahit, a company that specializes in installing heating systems in private homes.
When choosing a boiler for heating a house, you need to take into account all the parameters: both the heating equipment and the residential building Source baraholka.com.ru
Calculation of heating in a private house - what needs to be calculated
To calculate the heating of a private home, you need to calculate the power of the heating boiler, decide on the number and placement of radiators, and take into account a number of factors from the weather to thermal insulation and the material used to make the pipes and boiler.
Keep in mind that the comfort of living in the house will depend on this process, since your calculations will directly affect the quality of heating. In addition, these calculations are the basis of the budget for the installation and further operation of the entire heating system. It is at this stage that you will have to decide how much money you will spend on heating your home in the future. When starting calculations, it is important to remember the climatic conditions in which your region is located and the conditions in which the house will be used.
Video description
In our video we’ll talk about heating in a private country house.
Our guest is the author and presenter of the Teplo-Voda channel Vladimir Sukhorukov: The heating system is not only a stove and radiators. It includes:
- Boiler;
- Pumping station;
- Pipes;
- Radiators;
- Control devices;
- Sometimes an expansion tank is needed.
This is roughly what the diagram of a house heating system looks like Source lucheeotoplenie.ru
Calculation of the power of heating devices
Before calculating the power of a heating boiler, you should determine what type of boiler will be used. Heating boilers have different efficiencies and not only the level of heat transfer will depend on this choice, but also the financial component of subsequent operation when choosing fuel:
- Electric boilers,
- Gas boilers,
- Solid fuel boilers,
- Liquid fuel boilers,
- Combined electric/solid fuel boiler.
When the choice of boiler type is made, it is necessary to determine its throughput. The functioning of the entire system will depend on this. The power of a water heating boiler is calculated taking into account the amount of heat energy required per m3. The calculator can help calculate the volume of heated rooms:
- bedroom: 9 m2 3 m = 27 m3,
- bedroom: 12 m2 3 m = 36 m3,
- bedroom: 15 m2 3 m = 45 m3,
- living room: 25 m2 3 m = 75 m3,
- corridor: 6 m2 3 m = 18 m3,
- kitchen: 12 m2 3 m = 36 m3,
- bathroom: 8 m2 3 m = 24 m3.
When calculating, all rooms of the house are taken into account, even if it is not planned to install radiators in them Source stroikairemont.com
See also: Catalog of companies that specialize in insulating houses.
Next, the results are summed up, and the total volume of the house is obtained - 261 m3. When calculating, be sure to take into account rooms and passages in which it is not planned to install heating devices, for example, a corridor, pantry, or hallway. This is done so that the heat from the radiators installed in the house is enough to heat the entire house.
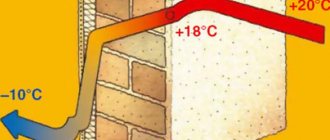
When calculating the heating system, be sure to take into account the climate zone and the outside temperature in winter.
Let's take an arbitrary indicator for the region of 50 W/m3 and a house area of 261 m3, which is planned to be heated. Power calculation formula: 50 W 261 m3 = 13050 W. The result is multiplied by a factor of 1.2 and the boiler power is calculated - 15.6 kW. The coefficient allows you to add 20% of reserve power to the boiler. It will enable the boiler to operate in a saving mode, avoiding special overloads.
Additional temperature sensors will help control the process Source dopebi.ru.net
The correction of the coefficient for the climatic conditions of the regions varies from 0.7 in the southern regions of Russia to 2.0 in the northern regions. A coefficient of 1.2 is used in the central part of Russia.
Here is another formula that online calculators use:
To get a preliminary result of the required boiler power, you can multiply the area of the room by the climate coefficient and divide the resulting result by 10.
An example of a formula for calculating the power of a heating boiler for a house with an area of 120 m2 in the northern region of Russia:
Nk=120*2.0/10=24 kW
How much heat should the pipeline supply?
Let's take a closer look at the example of how much heat is usually supplied through pipes, and select the optimal pipeline diameters.
There is a house with an area of 250 sq. m., which is well insulated (as required by the SNiP standard), so it loses heat in the winter by 1 kW per 10 sq. m. To heat the entire house, 25 kW of energy is required (maximum power). For the first floor - 15 kW. For the second floor - 10 kW.
Our heating scheme is two-pipe. One pipe supplies hot coolant, and the other pipe cools it to the boiler. Radiators are connected in parallel between the pipes.
On each floor, the pipes branch into two wings with the same thermal power, for the first floor - 7.5 kW, for the second floor - 5 kW.
So, 25 kW comes from the boiler to the interfloor branch. Therefore, we will need main pipes with an internal diameter of at least 26.6 mm so that the speed does not exceed 0.6 m/s. A 40mm polypropylene pipe is suitable.
From the interfloor branching - along the first floor to the branching on the wings - 15 kW is supplied. Here, according to the table, for a speed of less than 0.6 m/s, a diameter of 21.2 mm is suitable, therefore, we use a pipe with an outer diameter of 32 mm.
7.5 kW goes to the wing of the 1st floor - an internal diameter of 16.6 mm is suitable, - polypropylene with an outer diameter of 25 mm.
Accordingly, we use a 32mm pipe on the second floor before branching, a 25mm pipe on the wing, and we also connect the radiators on the second floor with a 20mm pipe.
As you can see, it all comes down to a simple choice among the standard diameters of commercially available pipes. In small home systems, up to a dozen radiators, in dead-end distribution circuits, 25 mm polypropylene pipes are mainly used - “per wing”, 20 mm - “per device”. and 32 mm “to the main line from the boiler”.
Which pipes are better for the heating main?
It’s not enough to know how to calculate the boiler’s power; you also need to choose the right pipes. Now the market offers several types of heating pipes made of different materials:
- polyethylene,
- polypropylene (with and without reinforcement),
- steel,
- copper,
- stainless steel
You can take different pipes for heating in a house, but it is important to check the features of the chosen type Source ms.decorexpro.com
Each of these types has its own nuances that should be taken into account when developing and calculating the heating of a private house:
- Steel pipes are universal in use and can withstand pressures of up to 25 atmospheres, but they have a significant drawback - they rust and have a certain service life. In addition, they have difficulties during installation.
- Pipes made of polypropylene, composite metal-plastic and cross-linked polyethylene are easy to install and, due to their weight, can be used on thin walls. The advantage of such pipes is that they are not susceptible to rust, rot and do not react to bacteria. An important indicator is that they do not expand from heat and do not deform in the cold. Withstands constant temperatures up to 90 degrees and short-term increases up to 110 degrees Celsius.
- Copper pipes are distinguished by their high price and increased complexity during installation, but in terms of strength they compete with plastic pipes, are not susceptible to rust and are considered the best option. In addition, copper is ductile, conducts heat well and keeps the temperature of water in pipes ranging from –200 to 250 degrees Celsius. This ability of copper will protect the system from possible defrosting, which is very important in the conditions of Siberia and the northern regions.
If the house is located in the north of the country, then copper pipes for the heating system are best suited Source svizzeraenergia.ch
Who sets the standard for thermal energy consumption for heating?
The standard for thermal energy consumption for apartment buildings is established by a special institution that monitors organizations. Most often, this is a regional energy commission, which is an executive body of government and regulates tariffs for the services of organizations that operate in the city. All changes are made on the official website of the commission, which can be viewed by anyone. Management companies must promptly monitor new tariffs and set payment standards.
Any utility service has a consumption standard, which is presented for payment in the absence of metering devices. If the apartment has an individual water meter, then payment is made based on actual consumption.
Standards are established not only for separate services for residential premises, but also for general household needs.
ORDER A SERVICE FROM ACCREDITED COMPANIES
How to calculate the optimal number and volumes of heat exchangers
When calculating the number of radiators required, you should take into account what material they are made from. The market now offers three types of metal radiators:
- Cast iron,
- Aluminum,
- Bimetallic alloy,
They all have their own characteristics. Cast iron and aluminum have the same heat transfer rate, but aluminum cools quickly, while cast iron heats up slowly but retains heat for a long time. Bimetallic radiators heat up quickly, but cool down much more slowly than aluminum ones.
When calculating the number of radiators, other nuances should also be taken into account:
- thermal insulation of floors and walls helps retain up to 35% of heat,
- the corner room is cooler than others and requires more radiators,
- the use of double-glazed windows on windows saves 15% of heat energy,
- Up to 25% of the heat energy “escapes” through the roof.
The number of heating radiators and sections in them depends on many factors Source amikta.ru
In accordance with SNiP standards, heating 1 m³ requires 100 W of heat. Therefore, 50 m³ will require 5000 W. On average, one section of a bimetallic radiator emits 150 W at a coolant temperature of 50 °C, and a device for 8 sections emits 150 * 8 = 1200 W. Using a simple calculator we calculate: 5000: 1200 = 4.16. That is, to heat this area you need about 4-5 radiators.
However, in a private house the temperature is regulated independently and it is usually believed that one battery emits 1500-1800 W of heat. We recalculate the average value and get 5000: 1650 = 3.03. That is, three radiators should be enough. Of course, this is a general principle, and more accurate calculations are made based on the expected temperature of the coolant and the heat release of the radiators that will be installed.
You can use the approximate formula for calculating radiator sections:
N*= S/P *100
The symbol (*) indicates that the fractional part is rounded according to general mathematical rules, N is the number of sections, S is the area of the room in m2, and P is the heat transfer of 1 section in W.
Radiator calculations
In our case, we will use standard aluminum radiators with a height of 0.6 m. The power of each fin of such a radiator at a temperature of 70 ° C is 150 W. Next, we will calculate the power of each radiator and the number of conventional fins:
- room 1: 28 m3 · 40 W · 1.2 = 1344 W. We round up to 1500 and get 10 conventional fins, but since we have two radiators, both under the windows, we will take one with 6 fins, the second with 4.
- room 2: 28 m3 · 40 W · 1.2 = 1344 W. We round up to 1500 and get one radiator with 10 fins.
- room 3: 56 m3 · 40 W · 1.2 = 2688 W We round up to 2700 and get three radiators: 1st and 2nd with 5 fins each, 3rd (side) with 8 fins.
- hallway: 22.4 m3 · 40 W · 1.2 = 1075.2 W. We round up to 1200 and get two radiators with 4 fins each.
- bathroom: 11.2 m3 · 45 W · 1.2 = 600 W. Here the temperature should be a little higher, you get 1 radiator with 4 fins.
- toilet: 8.4 m3 · 40 W · 1.2 = 403.2 W. Round up to 450 and get three edges.
- kitchen: 43.4 m3 · 40 W · 1.2 = 2083.2 W. We round up to 2100 and get two radiators with 7 fins each.
As a final result, we see that we need 12 radiators with a total capacity:
900 + 600 + 1500 + 750 + 750 + 1200 + 600 + 600 + 600 + 450 + 1050 + 1050 = 10.05 kW
Based on the latest calculations, it is clear that our individual heating system can cope with the load placed on it without any problems.