Pipes made of cross-linked polyethylene are a good alternative to steel communications in private housing construction. Cross-linked polyethylene is a product of high-tech production, when, through the efforts of scientists and production workers, materials with unique properties are created. Polymer communications can withstand the loads of a water heating system, they are safe for water supply, and have a long service life.
What it is
Crosslinked is polyethylene with a modified mesh structure. Its molecules are connected to each other by additional lateral bonds. Cross-linking provides the material with maximum density and reduces its thermoplasticity.
Scope of application
Cross-linked polyethylene products are used in the production of:
- pressure water pipes;
- parts of hot water supply pipelines;
- gas pipelines for underground installation;
- elements of heating systems;
- protective sleeves for high voltage cable networks;
- various parts and elements in instrument making;
- special building materials.
Technical characteristics of cross-linked polyethylene
- Density 0.94 g/m³.
- Tensile strength 22–27 MPa.
- Elongation at break 350–550%.
- Elastic modulus more than 550 MPa.
- Impact resistance 441 kJ/cm².
- Shore hardness 64.
- Vicat hardness 124.5 ºС.
- Operating temperature range -100…+100 ºС.
- Temperature:
- softening - 150 ºС;
- melting - 200 ºС;
- combustion - 400 ºС.
- Linear expansion coefficient 1.4*10⁻⁴ (ºС⁻¹).
- Thermal conductivity coefficient is 0.35–0.41 W/mºС.
- Flammability class - G4.
- Flammability class - B3.
- The toxicity class of combustion products is T3.
Kinds
The material is divided into types depending on the method of stitching:
- Peroxide. Cross-linked with hydrogen peroxide. The process takes place under pressure and covers up to 85% of the molecules.
- Silane. Chemically cross-linked, when the raw material is saturated with organic silanides and hydrated. The resulting polymer has up to 70% cross-linked structure.
- Radiation. During cross-linking, the polymer is exposed to the energy of ionizing radiation. The proportion of linked molecules is up to 60%.
- Nitric. Nitrogen compounds are used for crosslinking. The structure of polyethylene with this method is 70% cross-linked.
Leak test
After completing the work, it is necessary to check the connections for strength. It is assumed that water is supplied to the system at a pressure exceeding the operating pressure by one and a half times. Testing is carried out for at least half an hour, during which time no leaks or decrease in pressure should be recorded.
It is possible to carry out the test using inert gases and compressed air. Such pressure testing is carried out at unheated facilities, in systems that are not actually filled with drinking water, in pipelines where there is no provision for draining water. This method can be considered more industrial.
Each installation method has its supporters, but a preventive inspection is necessary for any of them. The recommended period and frequency of inspections is at least once a year. Some experts advise doing this as often as possible, especially in cases where there is suspicion of a leak.
Advantages and disadvantages
Products made from cross-linked polyethylene have the following advantages:
- high tensile and tensile strength;
- wear resistance;
- crack resistance;
- frost resistance;
- dielectric properties;
- corrosion resistance;
- easily withstands high temperatures;
- high resistance to chemicals;
- biological resistance.
The disadvantages include:
- Instability to ultraviolet radiation.
- The ability to oxidize when oxygen penetrates into the structure of the material. To mitigate this disadvantage, the material is coated with a film of ethylene vinyl alcohol: it reduces the diffusion of the outer layer.
Which is better - cross-linked polyethylene or metal-plastic?
Products made from cross-linked polyethylene, polypropylene and metal-plastic have many of the same characteristics:
- corrosion resistance;
- elasticity;
- strength;
- durability;
- convenient installation.
But metal-plastic pipes heat up faster and have greater thermal conductivity. This is an advantage for using them in heating systems. However, the metal plastic has a different coefficient of linear expansion of the layers, which can lead to wall delamination. It won’t even withstand several cycles of freezing and thawing; it will simply burst.
Products made from cross-linked polyethylene do not have all these disadvantages. But they must be installed with care so as not to damage the anti-diffusion protection layer on the outside.
Conclusion
Now you know what PE-X is, what products it is used for, and what qualities they have. Additionally, watch the video in this article. And if you have any questions that you haven’t found an answer to, ask them in the comments, and I will explain all the points you don’t understand.
Did you like the article? Subscribe to our Yandex.Zen channel
September 4, 2022
Types of pipes, Pipes
If you want to express gratitude, add a clarification or objection, or ask the author something, add a comment or say thank you!
PEX pipe joining method
PEX pipe products are produced from different types of cross-linked polyethylene and differ in their characteristics. Types of markings:
- RE-Ha. Cross-linked using the peroxide method. Uniform structure with the largest number of cross-linked molecules, durable and safe for human health.
- PE-Xb. Crosslinked using the silane method. No less durable products than peroxide polyethylene pipes, but more rigid and less able to restore their original shape. Some varieties contain chemicals and are intended only for the manufacture of cable sheaths. Therefore, when choosing water pipes, you need to be guided by the data in the hygiene certificate;
- PE-Xs made from radiation cross-linked polyethylene are more rigid, prone to creases and are inferior in structure uniformity to peroxide materials.
Application area
This option is universal and is used for different purposes. But most often cross-linked polyethylene is used in the following areas:
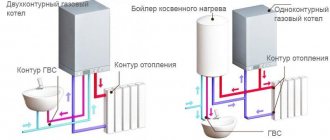
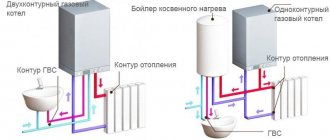
- Hot and cold water supply systems.
- Heating communications of various types.
- Water pipelines for drinking needs.
- Water heated floor systems.
- Main lines for supplying various gaseous substances.
- Technical communications supplying water or compressed air.
- Pipelines for supplying various chemicals.
- The use of cross-linked polyethylene in gutters will protect them from the formation of ice.
- Watering and irrigation systems.
If it is necessary to supply water to various objects on a personal plot (a fountain, a small pond, etc.), then cross-linked polyethylene will be an excellent solution. Essentially, this is a universal type of pipe that is well suited for a variety of purposes.
Tips on how to choose
The selection of pipes should begin with a visual inspection. They must have a smooth surface. Slight waviness and the presence of longitudinal stripes are acceptable provided that they do not thicken the wall beyond the permitted values. In addition, the pipes must have a uniform color, and the surfaces must be free of cracks, bubbles, foreign inclusions, and cavities.
Information on the main characteristics of pipes is included in the marking. From it you can find out what type of stitching was used in manufacturing, as well as the geometric parameters of the product.
Popular manufacturers
Pipe products from the following brands have proven well:
- TECEflex (Germany). The company produces pipes of the PE-Xs brand. Crosslinking is carried out by the electron beam method. Ethylene vinyl alcohol is used for anti-diffusion protection. It forms an oxygen-blocking layer that is resistant to mechanical damage.
- UNIDELTA (Italy). Manufactures pipes with an internal protective layer of EVOH, cross-linked using the silane method.
- REHAU (Germany). The company produces products from peroxide polyethylene with an external anti-diffusion coating, painted red.
approximate price
Materials made from cross-linked polyethylene are cheaper than polypropylene products, which are also used for assembling plumbing and heating systems. The cost of PEX pipes depends on the method of cross-linking polyethylene.
Connection methods
Polyethylene pipes are connected in three ways:
- Compression fittings. Compression-type fittings are easier to install and can be used to assemble cold and hot water supply pipelines.
- Press fittings. With the help of press fittings, permanent joints of parts are obtained. Due to the property of the material to restore its shape after deformation, the polymer molecules in the joint area straighten after crimping and fill all the gaps between the pipe and the connecting elements. The result is a pipeline with very reliable connections that do not require additional maintenance.
- Electric welded couplings. The electric welding method promotes the formation of monolithic joints that are not inferior in strength to the product itself.
Features of installation and operation
Polyethylene pipelines are installed according to standard schemes, with the exception of small nuances:
- The pipes are brought into the room for 2–3 hours so that they warm up to room temperature.
- It is advisable to cover pipe lines made of cross-linked polyethylene with protective boxes or place them in niches to avoid accidental mechanical damage.
- Niches and boxes must have a margin in size, since pipes made of cross-linked polyethylene expand when heated.
- Detachable fittings cannot be embedded in walls or concrete floor screed; they must be easily accessible for maintenance.
- The bending area is first heated with a hair dryer, then the workpiece is placed in a mandrel made of boards, plywood or other available materials until it cools completely.
- Burrs must be removed from the ends of the cut parts, as they can clog the pipeline.
- To fix the wiring to the walls, special fasteners are used - clips held by dowels.
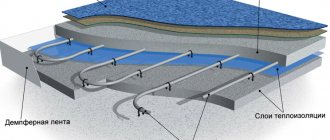
Screed rules
If the hydraulic tests are completed successfully, no depressurization of the pipes has occurred, and the system is completely filled with coolant, then the pipe installation stage is completed. Now you can begin installing the screed and finishing.
To install the screed, you must use a purchased or self-prepared mortar based on M300 cement. The minimum screed height to protect polyethylene pipes is 3 cm above the laid pipe. This thickness will be optimal for uniform heat distribution.
In most cases, the screed is made continuous without expansion joints. Thermal seams are necessary when:
- the room has an area of more than 33 m2;
- room length more than 10 m;
- the room has a complex configuration.
Damper tape is used to create seams. Thermal joints are treated with sealant.
Is it necessary to do reinforcement before pouring the screed? There is no clear answer to this question. Experience shows that the system functions perfectly without reinforcement, but at the same time, the reinforcing layer gives the screed additional strength. For reinforcement, you can use a 100x100 mm mesh made of metal or plastic.
Also, reinforcement will be useful only if the reinforcing mesh does not just lie on top of the pipe system, but “sinks” into the solution, being inside the screed when it hardens.
The correct reinforcement device complicates the laying of the screed, therefore, when there is no experience or confidence that everything can be done correctly, this stage can be skipped. After pouring the screed, the system can be started no earlier than 25-30 days later.
Any floor covering can be used as a finishing finish – the top layer of the “pie”.