The thermal insulation properties of expanded clay are well known and are largely determined by the raw materials from which it is produced. The thermal conductivity of expanded clay is one of its main characteristics, which, together with its low specific gravity and strength, determines the widespread use of this material in construction.
In this article: [Hide]
- What affects the thermal conductivity of expanded clay Expanded clay crushed stone
- Expanded clay gravel
- Expanded clay sand
- Production processes affecting the thermal conductivity of expanded clay
What is expanded clay: fractions and their properties
The term “expanded clay” implies several types of insulation, united by common raw materials for production. Three fractions of gravel, sand and crushed stone are distinguished.
Gravel appears as round or oval granules. It is produced by firing low-melting clay rocks in rotary kilns. Features of application are determined by the diameter of the fraction:
- Expanded clay gravel, fraction 20 – 40 mm. Has the lowest bulk density. It is used where a thick heat-insulating layer is needed: filling foundations and cellars, backfilling floors in attics.
- Expanded clay gravel, fraction 10 – 20 mm. Serves as insulation for roofs, floors in the house and walls with a well masonry method.
- Expanded clay gravel, fraction 5 – 10 mm. It is used for backfilling as a base for a “warm” floor. Grains of this fraction are used when insulating the facade, when a mass of a small amount of cement and expanded clay is poured between the masonry and the facing layer.
Sand is obtained by screening out fine clay and crushing large pieces of expanded clay in shaft kilns. Areas of use:
- Expanded clay sand, fraction up to 5 mm. Indispensable for laying cement floor screeds.
- Expanded clay sand fraction up to 3 mm. Allows you to obtain a unique “warm” masonry mortar. The thermal conductivity of such a solution is 0.34 W/(m*C), while that of a mixture based on quartz sand is 1.15 W/(m*C).
Crushed stone also comes from crushing large pieces of baked clay. It is used as a filler in the production of concrete structures with lower specific density and better heat and sound insulation.
Production processes affecting the thermal conductivity of expanded clay
The technology for producing expanded clay involves processes to increase porosity and obtain isolated closed contours of different sizes. The raw material is quarry clay, mined in open pits. Before use, laboratory expansion tests are carried out on samples to determine suitability for production.
Equipment includes:
- loosening machines;
- granulators;
- drying drums;
- rotating crucibles for firing;
- cooling tanks with air supply;
- conveyors.
In production, dry or wet raw materials of various grinding sizes are used. At a temperature of +1000 - +1300°C, the mass swells and the surface of the particles becomes sealed due to sintering.
Basic properties
Expanded clay, the thermal conductivity of which was mentioned above, has certain properties, including:
- high strength;
- frost resistance;
- durability;
- fire resistance;
- optimal ratio of quality and cost.
Considering this material, one cannot help but highlight its good thermal insulation qualities, acid resistance and chemical inertness. Expanded clay is considered a natural material and is an environmentally friendly heat insulator.
Manufacturers and prices
Expanded clay production facilities are available in all CIS countries. The quality of the products varies, but it depends primarily on the raw materials (the quality of the clay). The human factor is also present, but minimally.
In Russia there are similar enterprises in almost every region. The TOP 10 includes:
- "Expanded clay" (Ryazan);
- Expanded clay concrete plant ZhBI-3 (Belgorod);
- "Klinstroydetal" - a brick factory in the city of Klin;
- "Expanded clay plant" (Serpukhov);
- "PSK Shchurovsky Plant" (Kolomna);
- "KSK Rzhevsky" (Rzhev, Tver region);
- "Meliz" (Kursk region);
- “Experiment” (Kostroma);
- "Expanded clay plant Aleksinsky" (Aleksin, Tula region);
- "Belkeramzit" (Stroitel, Belgorod region).
The price depends on the type of ceramic pellets (gravel, sand, crushed stone), the size of the fraction, which is reflected in the brands of expanded clay and packaging. So, a big bag with a volume of 2.8 m 3, a fraction size of 10-20 mm, can be bought for 2040 rubles. (728 rub./m 3 ).
Small packaging costs much more, from 1800 to 3640 rubles. for 1 m 3 (the price of a bag with a volume of 0.05 m 3 of the M200-250 brand starts from 99 rubles).
Expanded clay. Types and production. Advantages and disadvantages. Application
Expanded clay is a porous building filler obtained by firing clay or shale. Due to its thermal insulation qualities and low weight, it is used in the preparation of lightweight concrete, and is also used as a heat insulator.
How is expanded clay produced?
Clay or clay slate is used as the raw material for the production of expanded clay. The further technical mode of production depends on its qualities. When using clay, the raw materials are adjusted to a moisture level of 30%. Since it is mined in an open pit, its moisture content depends on current weather conditions. In this regard, the clay is moistened or diluted with dry previously prepared material stored in a closed warehouse.
The material undergoes primary grinding and granulation to completely destroy lumps. After this, the cylindrical granules are re-crushed and pressed again, but into balls. After this, the workpieces are dried by blowing air. The resulting semi-finished product can be fired in a pipe-shaped oven. The workpieces are heated to a temperature of +1200-1350°C. At the same time, they constantly roll, which ensures uniform heating and prevents sticking.
The duration of heating depends on the required density to be obtained. Typically, heat treatment of granules does not exceed 30-60 minutes. As a result of heating, the clay swells, acquiring an internal porous structure and a dense ceramic crust. The longer the firing takes place, the more pores are formed. An increase in porosity reduces the strength characteristics of the finished product.
Scope of application
Thanks to firing, the material acquires a number of characteristics that provide it with a wide range of applications. It does not get wet in water, is not afraid of heat and frost, so it is used as:
- Filler for lightweight concrete.
- Bulk heat insulator.
- Drainage element.
- Biofilter.
- Decorative material.
Expanded clay is most widely used in the production of lightweight concrete. Adding it instead of gravel will reduce the actual mass of the solution, as well as increase its thermal insulation qualities. At the same time, the strength of such concrete does not allow it to be used for the construction of load-bearing heavily loaded structures.
Expanded clay concrete is not only poured on construction sites, but is also used to produce building blocks for laying walls. The characteristics of the blocks, in particular the level of their thermal insulation, depend on the mass fraction of cement in them. They can be used for laying load-bearing walls of low-rise buildings, as well as for fences and interior partitions. The use of expanded clay for filling lightweight concrete allows you to minimize the cost of their production.
Expanded clay gravel is an effective bulk heat insulator. It is used to fill voids in walls using frame construction technology. The material is poured between the floor joists before laying the boards. It is also used as a leveling and insulating bedding before pouring a dense concrete screed. This allows you to minimize the load on the floor during multi-story construction.
Expanded clay granules are a popular drainage material for potting ornamental plants. They are inexpensive and do not change the chemical composition of the soil. The granules are poured into the bottom of the pot in front of the soil layer. This prevents acidification of the soil and ensures air ventilation of the root system.
Expanded clay gravel is widely used as a filler for industrial biofilters. Beneficial bacteria colonize the surface of the granules, absorbing hazardous compounds from wastewater, such as nitrite, nitrate, and ammonia.
It is also used as a decorative material for landscape design. Colored granules are especially popular. They are used to mulch the soil under trees and shrubs. Mulch prevents sunlight from penetrating the soil, which prevents weeds from growing. Also, various images are laid out on flowerbeds from colored expanded clay. Colored granules under the tree trunk not only prevent the growth of weeds, but also slow down the evaporation of moisture. They prevent overheating of the root system.
Insulating a house with expanded clay: questions and answers
The modern construction market offers many ways to insulate a private home. Our portal has already talked about the most common types of insulation, such as stone and ecowool, extruded polystyrene foam, etc. We also wrote about whether it is profitable to build an energy-efficient house.
Can expanded clay as insulation in a wall compete with modern insulation materials? how and where it is better to use it as insulation; is there any economic benefit from using this material? Let’s look at the experience of FORUMHOUSE users.
What is expanded clay
Expanded clay is a porous granular material of low weight. Low-melting clay is usually used for its production. It is rapidly heated to 1000-1300°C for 25-40 minutes in a thermal chamber. During this process, the raw material “boils” and “swells.” Due to this, voids appear, when they harden, pores are formed in the granules of the material, enclosed in a shell of clay.
Expanded clay is an environmentally friendly and durable material that is widely used in construction.
The scope of application of the material directly depends on its density and the size of the crushed stone fraction. Namely:
- 0-5 – so-called expanded clay sand;
- 5-10;
- 10-20;
- 20-40.
The grade (depending on the bulk density) can vary from 200 to 800 kg/m3.
The most popular brands:
- M350
- M600
The higher the density, the stronger the material, and the worse its thermal insulation qualities as insulation. In addition to density and thermal conductivity, you need to pay attention to the water absorption of expanded clay. This indicator largely determines the durability and possible areas of application of the insulation. Simply put, is the material afraid of water or not, i.e. how much moisture will it absorb (as a percentage of its dry weight) when placed in a moisture-saturated environment. On average, the water absorption of this material (depending on the production technology at the plant) ranges from 8 to 20%.
How to choose and use expanded clay
Most often, the idea to buy expanded clay comes for its use as bulk insulation for thermal insulation of floors, interfloor excavations, external walls in the so-called. well masonry.
Three-layer well masonry is when a layer of expanded clay is poured between the internal main load-bearing wall (made of foam or aerated concrete) and the external decorative brickwork. The material is also used as a filler in the production of lightweight concrete.
Anyone who is planning to build a house from foam blocks will find it useful to read the article, which talks about the features and principles of choosing foam concrete.
Despite the fact that this insulation has been used in construction for a long time, there are many different conjectures and rumors about its properties and methods of use. Some builders scold this material, believing that it is subject to strong moisture accumulation. Others consider it ideal for a do-it-yourself developer. Here is a comment from a member of our portal:
Stupid FORUMHOUSE User
The following experiment came about naturally - expanded clay in bags stood on my street for two years. Recently I opened the bags and saw that there was nothing left of it - the balls had turned into damp dust.
Any building material, be it expanded clay, brick, foam and aerated concrete, etc. If used incorrectly, installed, stored and operated, it will lose its quality.
user343FORUMHOUSE user
I think I just got it “undercooked”. I once had to collect expanded clay that had been lying on the ground for 30-40 years. The granules were even overgrown with moss. I sifted it from the ground, after which there were more whole granules than fragments.
The properties of the material directly depend on the quality of the raw materials and on whether, when making expanded clay, the plant complies with all stages of production. Hence: from different manufacturers, expanded clay of the same fraction and density may differ from each other.
Therefore, you can buy either a “pig in a poke” or a relatively cheap but high-quality product, which, if used correctly, will show all its positive properties.
To choose this material, you first need to decide for what purpose it is needed and what it will be used to insulate.
bagdanovaFORUMHOUSE user
I need it as insulation for walls and as a filler for lightweight concrete. I was wondering which factions to choose.
According to a forum member with the nickname soniikot, it is better to take fractions of 5-10 or 10-20 as a filler for lightweight concrete, because The higher the bulk strength, the higher the grade of expanded clay concrete.
The specific brand is selected depending on the requirements for the wall material. Also, the user of our portal advises, before buying expanded clay in meshes, to study reviews on the Internet about the plant and the supplier company. It happens that careless sellers, offering expanded clay cheaply, mix dirt into the bags or weigh down buyers.
Where to buy expanded clay
FORUMHOUSE is often asked how to choose this material. To get a comprehensive answer from experienced builders, you need to clarify in which region of the Russian Federation the construction is planned, what kind of house is being built, according to what project. This will help you understand why and where the insulation will be used.
A general rule that is useful to everyone: the characteristics of the product (density, brand, frost resistance, etc.) must correspond to the declared technical parameters, which can be found on the manufacturer’s website. When delivering, they should bring “honest” cubes and kilograms, not “air”. It is worth paying attention to where you buy expanded clay - the price from intermediaries and directly from the manufacturer will vary significantly; also look at how long the manufacturer has been on the market and what equipment he has. You shouldn’t throw all your energy into buying expanded clay cheaply; listen to the opinions of those who have already built it, and look for a manufacturer that has proven itself well.
Is insulation with expanded clay beneficial?
When choosing expanded clay as wall or floor insulation, wondering whether a frame wall with expanded clay insulation will withstand Russian frosts, you need to immediately calculate the economic feasibility of this idea. It's all about its thermal conductivity coefficient.
Consider the following examples:
Oleg Lvovich FORUMHOUSE user
Depending on the density, the thermal conductivity coefficient (lambda) of expanded clay varies from 0.11 to 0.23 W/(m*°C). At a density of 400 kg/m3, its thermal conductivity coefficient will be 0.15 W/(m*°C). Insulation thickness 0.15/0.15 W/(m*°C) = heat transfer resistance R=1. Next: 1*0.05 W/(m*°C) (thermal conductivity coefficient (lambda) of PPS polystyrene foam) = 0.05 m.
Hence: according to the thermal characteristics, 15 cm of expanded clay with a density of 400 kg/m3 corresponds to 5 cm of expanded polystyrene grade PSB-25.
If you take and compare expanded clay/stone wool, then the comparisons will again not be in favor of the first. If we take average values (the average thermal conductivity coefficient of expanded clay depending on its density is 0.1-0.14 W/(m*°C), and stone wool is 0.04 W/(m*°C), then in order to obtain a comparable thermal protection effect, Expanded clay will require about 120 mm versus 50 mm of stone wool.You will have to increase the thickness of the expanded clay layer.
44alexFORUMHOUSE user
I thought about using expanded clay instead of extruded polystyrene foam in the foundation of the USP.
The forum member made calculations and found out that such a replacement is unlikely to be justified. The fact is that although the price of expanded clay is approximately three times lower than the price of EPS, its thermal conductivity is five times (or even higher) higher. Therefore, you will have to lay a layer of at least 0.5 m, and in combination with a warm floor system - 0.7-0.8 m.
Although the price for 1 cubic. m of expanded clay is less than the price of 1 cubic. m EPS, but due to the increase in the bedding layer, expanded clay will be required 4-5 times more. Those. the price of a layer of equivalent insulation of the material we are considering will be 2-2.5 times more expensive than EPS, which will negate all the benefits of its use.
This article talks about all the features of the USHP foundation.
If we are talking about a wooden house, then in order to insulate it with expanded clay, you will have to build a strong foundation (since granules weigh more than stone wool), think about how to place a scattering of granules so that they do not spill out, etc. d.
Note: because the cost of insulation in Moscow and different regions can vary significantly; the final price is calculated based on local characteristics and the availability of certain materials.
For the same expanded clay in bags, the price can be blatantly different in different regions; as if the place of sale makes two different materials out of it: “expanded clay Moscow” and “expanded clay region”.
Therefore, for each specific case of insulating a house with expanded clay, a separate calculation is necessary based on the climate zone, the degree of heat loss of the house, the duration of the heating season and the cost of expanded clay must also be taken into account. On our forum there are examples of how to competently approach insulating a house with this material and win.
Spiker99FORUMHOUSE user
I have a house 8x8 meters, built of aerated concrete with a density of D600, block sizes 625x300x200. I spent a long time choosing how to insulate the cottage. After going through several insulation materials, I settled on backfilling with expanded clay as an environmentally friendly and relatively inexpensive material.
Insulation of walls with expanded clay. Layer thickness
An interesting approach to implementing home insulation. Place of construction - Kirov region. The walls of the house are made in the form of three-layer masonry. Between the blocks of aerated concrete and the external masonry of sand-lime brick, expanded clay is poured; the layer of backfill is not thick - 15 cm. It is spilled with cement laitance. Heated area – 50 sq. m. The second floor is closed. The house is heated by three electric convectors with a total power of 4 kW. Food is cooked on an electric stove, + there are 2 water heaters in the house with a total capacity of 150 liters. Total: heating costs for December amounted to 1.5 thousand rubles. at a tariff of 2 rubles. 7 kopecks for 1 kW*hour. The cost of insulating a house, including delivery and labor, is about 77 thousand rubles.
Insulated blind area made of expanded clay
Builders who use this material are familiar with the expression “expanded clay does not work in the ground.” That is, in structures below ground level (especially in moisture-saturated soils and high groundwater levels), expanded clay insulation has nothing to do. If you neglect this rule, he will “drink” water and lose all his positive properties.
All the more interesting is the method in which the material we are considering can be used as a replacement for extruded polystyrene foam in the construction of an insulated blind area.
TraksFORUMHOUSE User
Expanded clay was used in the blind area as a remedy against frost. Expanded clay of the M450 brand, fraction 5-20, was used. The fragility of this material is very conditional. You need to buy high-quality material, follow the installation technology, and all problems will be solved.
The essence of the method, successfully tested by a forum member, is as follows. Because “burying” expanded clay in the ground is a futile task; in order for it to “work”, it must be isolated from the influence of the external environment, i.e. – waterproof. Which is what was done. The blind area pie (if we consider the layers from bottom to top) has the following structure:
- priming;
- coarse sand, mechanically compacted;
- expanded clay, “wrapped” in a 2x20 m profiled drainage membrane;
- geogrid;
- crushed stone
The backfill width is 1.2 m, the layer thickness is about 15-20 cm.
In the FORUMHOUSE topics you can learn how to insulate the walls of a house with expanded clay, and whether it is worth insulating the foundation with expanded clay.
Do-it-yourselfers will find useful topics with a detailed description of building a house using monolithic expanded clay concrete technology, as well as a detailed report on how to build a cottage from lightweight expanded clay concrete.
In our video, the owners of a house in the forest tell us why they chose expanded clay concrete as a wall material.
Advantages and disadvantages of the material
As a result of the analysis of these varieties of expanded clay, the conclusion suggests itself that it is better to choose gravel as insulation. Its advantage is confirmed by a set of properties:
- Durability. Retains its qualities for a long time.
- Fire resistance. The material is absolutely not flammable.
- Chemical inertness. Not affected by acids and other chemicals.
- Biostability. Resistant to fungus formation and does not allow rodents to enter.
- Frost resistance. Stable under temperature fluctuations. Tolerates more than twenty shifts of freezing and thawing.
- Low bulk density. From 250 to 800 kg/m3. The larger the fraction, the lower the density.
- High strength.
- Good heat and sound insulation. A consequence of low thermal conductivity, about 0.16 W/m, and porosity.
- Ecological cleanliness. Does not emit harmful substances.
It is worth separately considering the reaction of expanded clay to water . It has solid water resistance and, if the gravel is dried after wetting, all parameters will be restored.
But at the same time, expanded clay has noticeable moisture absorption. Moisture-saturated gravel gains weight and loses insulating properties . Therefore, do not forget about waterproofing.
compare the technical characteristics of different types of insulation.
Table 1 . Basic technical characteristics of some popular insulation materials
| Name of insulation | Specific gravity, bulk density, kg/m 3 | Thermal conductivity, W/(m*S) | Moisture absorption coefficient,% |
| Expanded clay (gravel) | 250 | 0,099 | 10-20 |
| Same | 300 | 0,108 | 10-20 |
| « | 350 | 0,115 | 10-20 |
| « | 400 | 0,12 | 10-20 |
| « | 450 | 0,13 | 10-20 |
| « | 500 | 0,14 | 10-20 |
| « | 600 | 0,14 | 10-20 |
| Foam glass | 200-400 | 0,07-0,11 | 0,05 |
| Fiberglass mats | 150 | 0,061 | 10-130 |
| Mineral wool slabs | 40-180 | 0,036 | 50-225 |
| Polyurethane foam | 40-80 | 0,029-0,041 | 18-50 |
| Styrofoam | 125 | 0,052 | 3-5 |
The table is based on data from SP-23-101-2004 and advertising sites.
the consumption of gravel , given its loose form. When filling large areas, you simply need to calculate the required volume. And 0.1 cubic meters are spent on insulating surfaces. m per layer of 10 cm per 1 m 2.
The positive aspect of using expanded clay for home insulation measures should be recognized:
- We guarantee that having completed all the work correctly, the house will be insulated for its entire service life.
- The material does not emit harmful substances.
- The opportunity to do everything yourself. Minimal skills required.
The thermal conductivity coefficient of expanded clay gravel is slightly higher than that of modern synthetic and mineral insulation. This leads to the main disadvantage, which manifests itself in the significant thickness of the insulating layer and an increase in the thickness of the walls. It is advisable to take this incident into account at the design stage.
Description of thermal conductivity
The low level of thermal conductivity of expanded clay is explained by its porous structure.
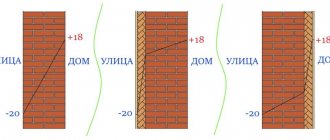
The ability of insulation to transfer energy from heated layers to parts with a lower temperature is called thermal conductivity. The process is ensured by the chaotic movement of molecular particles, its intensity depends on humidity, compaction, and pore size.
The physical process of heat conduction accelerates when there is a large temperature difference between the outside and inside of the building. Spontaneous energy transfer always occurs from a hotter environment towards a colder environment and occurs before thermodynamic equilibrium occurs.
Coefficient of thermal conductivity
To numerically express a material's ability to transfer energy, there is a thermal conductivity coefficient. The indicator indicates the amount of heat flowing through a sample of material under given conditions. The test standard always has the same dimensions in length, width and area and is tested at a standard temperature difference (1 K). Heat transfer coefficient is measured in W/mK, which corresponds to the International System of Units.
The name thermal resistance coefficient is used in the construction field. The thermal conductivity of expanded clay is 0.1 – 0.18 W/m·K. High-quality material is characterized by a numerical value of 0.12 – 0.17 W/m K; insulation with such properties retains up to 80% of internal heat.
How to insulate the floor in a steam room
Floors in a frame bathhouse are insulated with expanded clay very often, but the high hygroscopicity of the granules requires careful attention to the process. To begin, calculate the required amount of material; for this it is convenient to use an online calculator, in which you will be asked to enter the length and width of the surface and the height of the expanded clay layer filling with a choice of particle fraction. During transportation, some of the granules may break , so take extra. If the task is to make a dense backfill to prevent shrinkage, the particle size should not be the same.
Instructions for insulating floors in a frame bath with expanded clay:
- Bitumen for waterproofing is spread overlapping 10 cm over the concrete covering, extending up to 15 cm onto the walls.
- Along the perimeter of the floor, “beacons” are attached with alabaster, indicating the thickness and evenness of the insulating layer.
- Wooden logs must be treated with an antiseptic before filling with granules.
- Expanded clay insulation is poured up to a height of 20 cm.
- The surface is filled with “cement laitance” made from primer, water and cement - this is done to strengthen adhesion .
- A day later, a reinforcing mesh of metal is laid on top for greater structural rigidity.
- The cement-sand screed is poured with a thickness of 3 cm, it is necessary to wait until it hardens completely. Determine the drying of the screed using a glass jar: you need to lean the neck against the floor, if the jar does not fog up, everything is in order.
- The waterproofing is fixed, then the finished floor is installed. The flooring will be ready for use after a month .
Application area
Expanded clay, as insulation, is used for thermal insulation:
- floor - can be used as a dry screed, expanded clay concrete screed, combined screed (cement mortar is poured on top of the dry screed);
- walls - filled between the load-bearing wall and decorative brickwork. Another option for wall insulation is expanded clay concrete blocks;
- ceiling - insulation is poured onto the ceiling from the attic side;
- roofs.
Main technical characteristics of the material
Brief overview of expanded clay concrete blocks
Expanded clay concrete has currently gained high popularity among both builders and developers. This is due to high quality indicators and relatively low cost of products.
So what is this material?
As the name suggests, the main component that distinguishes expanded clay concrete blocks from similar products for construction is expanded clay. The material is light, inexpensive, and most importantly – durable and has the properties of heat and sound insulation.
In addition to expanded clay, the blocks contain cement, sand, water and organic impurities in the form of sawdust or ash. The brand of expanded clay and cement directly affects the characteristics of the future material and can vary from M100 to M500.
The production technology of expanded clay concrete blocks is quite simple, and in many ways similar to the production of blocks based on other materials. The finished mixture is placed in molds, dried and processed under high temperature.
Those who want to save money on construction can try making blocks from expanded clay concrete with their own hands. However, it is worth considering that the possibility of producing low-quality products increases significantly.
Classification of expanded clay concrete and scope of application
Depending on the proportions of the constituent materials, some differences in production processes and areas of application, expanded clay concrete is distinguished into three types:
- Thermal insulation
- Structural and thermal insulation
- Constructive
Let's take a closer look:
- The first type of expanded clay concrete is used exclusively as thermal insulation. Such a block is light in weight and low in density, but its thermal insulation or temperature exchange properties are much higher than those of most materials. As can be seen in the photo, the heat-insulating block is externally distinguished by particularly pronounced porosity.
- The second type has greater density and thermal conductivity, due to this the strength indicators increase, but the property of temperature transfer is significantly reduced. This type of block is used as a material for the construction of partitions and internal walls.
- The third type , structural, has the highest density. It can be used as a facing wall material, for the construction of partitions for the purpose of sound insulation and external walls of low-rise buildings. Such blocks are often used as one of the components of load-bearing structures in the construction of various engineering structures. For example, a bridge. Sometimes used as an alternative to curb stones. Can also serve as a support for a bench.
Note! Each of these types of expanded clay concrete blocks has its own advantages and disadvantages - and here you have to make a choice: either thermal conductivity or strength suffers. But with the right approach, this may not affect the future building. For example, thermal insulation blocks with the lowest density are perfect for building a bathhouse, for which heat retention is most important. But when building a two-story house, it is better to give preference to denser products.
Factors influencing the thermal conductivity value
Thermal conductivity depends on the method of production of the material and the size of the granules.
Expanded clay is used in construction as a porous bulk insulation or as a filler in the production of lightweight concrete. The granules are obtained by firing shale or clays and have an oval, round shape, sometimes with sharp corners. The building material is produced in the form of sand.
The bulk density of expanded clay is in the range of 150 – 800 kg/m3, the volumetric weight depends on the technological regime during production. The ability to conduct heat depends on the size of the granules, the porosity of the material and its moisture content.
Expanded clay fraction
When comparing the characteristics, it is concluded that thermal conductivity decreases with increasing granule size. Medium and coarse gravel are best used for insulating unloaded roofs and wooden floors. Fine-grained expanded clay is used for lightweight floor screed.
Expanded clay fractions are installed in accordance with GOST 9757 – 90 standards:
- From 5 to 10 millimeters a small group is determined. The material is used for the production of expanded clay concrete wall blocks. Filler made from small granules is used in concrete screed coverings or floors, since large parts increase the thickness of the layer.
- From 10 to 20 mm – average fraction. The material in bulk well insulates floors and attic floors from the cold, and is used for insulating lawn areas and draining the ground. The fraction is rarely used in screeds and concrete floors; it is added to the solution if the thickness of the layer does not matter.
- From 20 to 40 mm – large granules. They insulate heating mains, basements, floors of utility rooms, and insulate the building from noise.
Layers of bulk insulation effectively protect against cold if 2-3 fractions are used simultaneously. This fills voids, increases rigidity, and prevents convection of flows.
Porosity
During the production process, the raw material is heated and swells, forming pores.
The raw material is placed in drums, where it rotates and is simultaneously heated to high temperatures. Under such conditions, the material swells, producing porous granules that are protected on the outside by a baked clay crust. Most of the voids are closed; the partitions between them also contain voids.
The pore size is regulated by the introduction of citrogypsum and mineral impurities into the charge during production. An additive in an amount of 1 to 3% forms closed voids up to 1 mm in size. An increase in the volume of the additive to 4–9% leads to an expansion of the pores to 1.5–2 mm, while the number of closed cavities increases. The number of insulated voids increases thermal insulation properties and reduces water absorption.
Humidity
The water absorption of expanded clay ranges from 8 to 20%. When moisture gets inside the material, the surfaces of the granules are moistened, which slowly absorb the liquid. Gradually, water enters the spheres through microscopic cracks and is retained inside. Expanded clay accumulates moisture and is difficult to release it. The mass increases, the thermal conductivity characteristics of expanded clay change, and the strength decreases.
Dry expanded clay can withstand up to 25 series of freezing and thawing, while wet expanded clay is destroyed by the expansion of water at subzero temperatures. Expanded clay is protected by hydro- and vapor barrier films from moisture.
Types of expanded clay concrete materials
There are several different types of expanded clay concrete. In particular, they should be divided into the following types:
- Thermal insulating expanded clay concrete;
- Structurally – heat-insulating expanded clay concrete;
- Structural expanded clay concrete.
Each type has its own characteristics and characteristics. Thermal insulating expanded clay concrete is the least dense, due to this it has less weight and, again, has high thermal insulation properties, as its name may suggest.
From such material you can easily build a structure whose task is precisely to preserve heat, or vice versa, cold. An example of such a building is a bathhouse. Below you can see the process of building one from expanded clay concrete blocks.
Bathhouse made of expanded clay concrete
The next type that should be considered is structural and thermal insulating expanded clay concrete. The intended purpose of this material is most suitable for buildings that need to reduce the weight of the structure. Most often used in large blocks. This material is distinguished by its high strength, but, in comparison with thermal insulating expanded clay concrete, it also has greater thermal conductivity.
In the figure below you can see this type of building materials.
Structurally Thermal insulating expanded clay concrete
As for the latter type, structural expanded clay concrete has the highest strength among its analogues. It is used to build both ordinary houses and industrial buildings. The density of this material is 1800 kg per cubic meter. When it completely hardens, its strength does not need to be checked; usually, it is 100 kg per 1 square centimeter. True, the thermal conductivity of this material is much higher, much greater than that of other types and amounts to 0.55 W/(m*K).
In the figure below you can see what structural expanded clay concrete looks like.
In the figure you can see the load-bearing structural block made of expanded clay concrete “Cube”, in particular, its shell made of high-strength expanded clay concrete.
Small and useful tips on how to choose blocks
There are several nuances that will be useful to know for an inexperienced, novice builder who has decided to start building using expanded clay concrete blocks.
First of all, when selecting blocks, you should focus on such parameters as strength, density, thermal conductivity, frost resistance and hollowness.
Different types of expanded clay concrete are suitable for different construction sites. For example, hollow blocks are best used in walls. This is due to the fact that they have high thermal conductivity and are modest in weight. Sand-cement options are best preferred for foundations, support and load-bearing points. This solution will be relevant due to its high strength, and the parameter of thermal insulation or conductivity is not so important.
Expanded clay as insulation
Expanded clay is used as insulation in private and industrial construction. Due to its high strength indicators, the material is used for insulating floors that will be subject to high loads. Since expanded clay is completely natural, it is widely used for thermal insulation of private houses.
The lightness of the material allows you to insulate roofs, ceilings and walls of buildings. By laying expanded clay under the foundation, you can reduce the depth of concrete laying, increasing the thermal insulation properties of the floors. However, the insulation needs high-quality waterproofing. The material absorbs moisture and becomes compacted, which leads to loss of the air gap. This, in turn, worsens the thermal insulation properties of expanded clay. Therefore, you should choose reliable means to protect against moisture.
Advantages and disadvantages of the material
The advantages of expanded clay include:
- Possibility of performing insulation work with your own hands.
- Environmental friendliness. Does not contain chemical impurities, the composition includes only natural materials.
- Reduces noise levels.
- Resistant to frost. This allows it to be used in places with harsh climates.
- Practically not subject to chemical and biological effects.
- You can change the thermal conductivity indicators. This is achieved by changing the density of the layer, using different fractions, etc.
- Fragility. Ceramic is a fragile material, so it is important to be careful when installing it.
- Hygroscopicity. Without high-quality waterproofing, expanded clay loses its thermal insulation properties over time. Granules absorb moisture, but do not release it back well.
- Layer thickness. To create a high-quality protective layer, you need to pour at least 10 cm of insulation. When laying is done on the ground, the thickness of the layer can reach 30 cm. This makes you think about choosing insulation for the floor or ceiling if the room has low ceilings.
Like any insulation, expanded clay has its pros and cons. Whether it is worth choosing this material as thermal insulation, everyone decides for themselves.
Comparison of different types
Expanded clay today can be presented in several types, each of which has its own technical characteristics and scope of application. The presented heat insulator is classified according to the method of production and the size of the granules.
Thus, the following material options can be distinguished:
- gravel;
- crushed stone;
- sand.
But what expanded clay is best for floor screed will help you understand the information from the article.
The information from this article will help you understand what characteristics exist for expanded clay concrete wall panels.
It will also be interesting to learn about which expanded clay concrete blocks are best for building a house: https://resforbuild.ru/beton/bloki/dlya-stroitelstva-doma-kakie-luchshe.html
For those who want to know what the weight of a hollow expanded clay concrete block is, you should follow the link.
Gravel
Gravel is a material that comes in the form of rounded grains. Their size can reach 2-4 cm. They have a porous structure, and the grains are covered with a durable shell. The structure of the material contains closed cells that are filled with air.
The image shows expanded clay gravel
Thanks to this quality, expanded clay gravel can be used as insulation. To make it, the method of swelling of light grades of clay is used. The resulting material has the best thermal insulation properties. But what are the differences between gravel and crushed stone can be found in the article.
Expanded clay crushed stone
Expanded clay crushed stone is a material that is produced by crushing expanded soft clay. The result is fractions 1-2 cm in size. The formed elements have an irregular shape, most often it is angular. If the composition of the heat insulator contains grains only of this type, then the thermal conductivity of expanded clay will be higher. But what the thermal conductivity of expanded clay is is described in great detail in this article.
In the photo - expanded clay crushed stone:
Expanded clay sand
Expanded clay sand is a by-product that is formed during the production of two main fractions. This material is presented in the form of grains. Their size reaches 0.5-1 cm. They have poor thermal insulation properties when compared with gravel and crushed stone.
In the photo - expanded clay sand
The presented variety of expanded clay is actively used as a porous heat insulator, which is part of the concrete screed.
Table - Characteristics of various types of expanded clay
| Brand by bulk density | Highest quality category | First quality category | ||
| Strength grade | Ultimate compressive strength in a cylinder, MPa | Strength grade | Ultimate compressive strength in a cylinder, MPa | |
| 250 | P35 | 0,8 | P25 | 0,6 |
| 300 | P50 | 1 | P35 | 0,8 |
| 350 | P75 | 1,5 | P50 | 1 |
| 400 | P75 | 1,8 | P50 | 1,2 |
| 450 | P100 | 2,1 | P75 | 1,5 |
| 500 | P125 | 2,5 | P75 | 1,8 |
| 550 | P150 | 3,3 | P100 | 2,1 |
| 600 | P150 | 3,5 | P125 | 2,5 |
| 700 | P200 | 4,5 | P150 | 3,3 |
| 800 | P250 | 5,5 | P200 | 4,5 |
But what are the pros and cons of dry floor screed and what reviews exist about such a building material. The information in this article will help you understand.
You may also be interested to know what the weight of a gas silicate block is.
What is the cost of dry floor screed per square meter is described in great detail in this article.
Any modern construction uses foam plastic, but what are the technical characteristics of 50 mm foam plastic will help you understand the information from this article.
Alternative types of insulation
Expanded clay is not the only widespread thermal insulation material used in roofing structures. Let's look at the most common options:
Expanded polystyrene, better known as a type of polystyrene foam. The thermal protection of such material is much better than that of cotton insulation. The layer of polystyrene foam insulation will be much thinner. Polystyrene foam does not absorb water and is quite rigid and durable. The use of specialized additives allows for increased fire resistance. But, if the material does catch fire, toxic gases will be released that are dangerous to human health and life. Unlike expanded clay, mice and rats love to chew foam.
Basalt wool and mineral wool. The fibrous structure of this type of insulation ensures its high saturation with air. This allows them to be used as a thermal insulation material. When laying fiberglass, you will need additional protection: gloves and a respirator. Disadvantages include susceptibility to rotting, as well as high cost.
Polyurethane foam. Foam insulation manufactured directly on the construction site. Application is carried out with a special gun. The expansion of the material after application allows you to create a monolithic insulating structure. It is lightweight and fire resistant. The service life is about half a century. The disadvantage is the need to use specialized equipment and an experienced team for high-quality work.
Ecowool. A material containing 80% cellulose fiber and 20% fire-resistant and antiseptic additives. Has good heat and sound insulation. Ecowool forms a seamless coating that eliminates the formation of cold bridges. Service life - more than 50 years.
Preparation method
Expanded clay is obtained by firing clay in special rotary kilns shaped like drums, the diameter of which is from 2 to 5 meters, and the length is about 70 meters, installed at a certain angle. Expanded clay semi-finished granules are poured into the upper part of the stove, which rolls down to the lower part. There is a nozzle located there, the main purpose of which is to burn fuel. The process of making expanded clay takes approximately 45 minutes. Depending on what operating mode of the furnace was used during the production process, you can obtain a product with different densities - from 250 kg/m³ to 800 kg/m³. But despite this, the result will still be a lightweight porous material - expanded clay, which is completely environmentally friendly and safe.
In some cases, double-drum ovens are used. Their drums are separated by a threshold, which allows them to perform rotational movements at different speeds. Even if low-quality raw materials were used, the resulting expanded clay crushed stone or gravel is not inferior in quality, and often even exceeds the same fractions of expanded clay produced in single-drum kilns.
It is also worth noting that the raw materials used in production must contain quartz, the amount of which should be approximately a third of the total mass of the source material.
Insulation under a concrete base
Dismantling and removal of old floor screedCleaning the floor
Floor waterproofing
The joints around the perimeter of the floor must be closed, so the film is placed on the walls. The damper tape is attached last at the level of the future screed. Now you can start insulating.
Damper tape.png
Step 1. Installation of beacons
Beacons must be metal; it is best to use T-shaped aluminum slats. Mix a little cement or gypsum mortar to fix the beacons, take the first strip and lay it under the wall opposite the doorway on the mortar. Be sure to check the location of the guide with a level and, if necessary, press it into the solution or, conversely, lift it. The height of the beacons should not exceed 10 cm, and the distance between them should be from 0.5 to 1 m.
Installation of floor beaconsBeacons
Step 2. Backfilling insulation
A mixture of expanded clay of different fractions is used to fill the space between the beacons and level it with a rule or a piece of plywood. Particular care should be taken to fill corners and joints where voids may form. After this, the expanded clay is carefully compacted so as not to damage the granules.
Filling with expanded clayFilling with expanded clay
Step 3. Reinforcement
A metal mesh with large cells is laid on the insulation, leaving 4-5 cm indentations from the walls along the entire perimeter. The mesh should not have any dents or bulges or protruding sharp edges.
A mesh is laid on the expanded clay
Step 4. Making the screed
For the screed, take 3 parts of sifted sand and 1 part of cement, mix thoroughly with water to a uniform thick consistency and pour in portions onto the floor between the guides. Level the screed using a long rule, running along the beacons and removing excess mortar. Now you need to wait for the concrete to dry completely and you can lay the floor.
The screed is laid directly on the expanded clay, without additional insulation. Leveling the cement screed
Use of car sound insulation in apartments.
This misconception is similar to the previous myth about thin structures. The argument usually given is: “It works in machines!” Indeed, car soundproofing materials are quite thin (usually only a few millimeters thick) and actually work: cars become noticeably quieter! There is a great temptation to use similar materials for the apartment: soundproofing the ceiling, walls and floor.
However, what works in cars will not work in an apartment. The reason is simple: in a car, noise is created by a vibrating sheet of metal less than a millimeter thick, and in an apartment the source of noise is a massive thick wall or ceiling 15–20 cm thick (or even more).
And the mechanisms for dealing with noise from a thin sheet of metal and from a thick massive wall are fundamentally different! If in the first case it is enough to simply dampen the metal with any viscous membrane (the mass and thickness of which is several times greater than the similar parameters of the metal), then in apartments the sound insulation can only be increased with multilayer cladding, and this is a certain thickness.
Insulation technology
Insulation of various building structures is carried out using different technologies.
Insulation of walls with expanded clay is carried out with a complex, 3-element design of the latter, when the first layer is a load-bearing element, the second is a backfill of expanded clay pellets, compacted and spilled with impregnation such as “cement laitance” (water-cement mortar without fillers, diluted in a ratio of 3:1 , where 3 is water, 1 is Portland cement), the third is a cladding of decorative material or a layer for attaching the finish.
This option for constructing a wall is very complex, requires additional labor, and therefore is not suitable for all wall materials.
Aerated concrete. First, a building is erected, and then an additional wall is constructed (laid out). Expanded clay is poured into the formed well, compacted, and impregnated with binding compounds (so that it does not settle over time). Ventilation gaps must be installed to remove condensation moisture.
Frame walls. In such a building design, expanded clay is not the best insulation option - difficulties arise during compaction: the frame may be damaged. If you refuse to artificially compact ceramic granules, they cake and settle over time, despite impregnation.
Wooden house. Walls are not insulated with ceramic granules, as the wall may not be able to withstand such a load.
Ceiling
Ceiling The ceiling space is insulated only in private buildings, when expanded clay is covered with a layer of 5-10 cm for a warm roof and 30-40 cm for a cold one (poured onto the ceiling from the reverse side).
Roofs
Insulation of a pitched roof with expanded clay is rarely carried out, but the technology is simple:
- boards are packed along the bottom of the rafters, forming a plane on which the insulation will be poured;
- A vapor barrier film made of polyethylene is laid overlapping. It has several functions: vapor and waterproofing, preventing small fractions of pellets from spilling through the cracks between the boards;
- Ceramic granules are poured over the film in an even layer;
- the thermal insulation layer is covered with a vapor barrier membrane;
- a counter-lattice is filled to create a ventilation gap;
- boards are attached on top of the counter-lattice to secure the roofing material;
- the roof is being installed.
You can insulate the floor in 3 ways:
- perform a dry screed (for a wooden floor - dry insulation);
- carry out thermal insulation using the “wet method”;
- pour a layer of ceramic pellets under the cement screed.
Each method of performing work is discussed in detail in articles on our portal:
Attention: insulation of expanded clay coverings in a bathhouse is carried out using other technologies, which will be discussed in a separate material.
Features of roof insulation using expanded clay
As a result of taking into account the positive and negative aspects of expanded clay, rules for working with it have been developed:
- Expanded clay is poured exclusively onto the substrate, and it is better to use a vapor barrier, especially when treating the ceiling in bathhouses, where the insulation is likely to get wet due to a large volume of steam. Moreover, it is applied to the surface with the foil part.
- Next, a waterproofing ball is applied to the top of the insulation. And if you need to walk on expanded clay, you need to fill it with a layer of screed with cement and sand.
- The thickness of the insulating insulation should be used within 10-20 cm.
Today you can purchase three types of expanded clay, differing in type of application.
- expanded clay crushed stone, comes with clearly defined edges, its grains range from 0.2-0.4 cm, used exclusively for insulating foundations;
- Expanded clay gravel is the insulation material for the ceilings of private and interfloor buildings. Comes in the form of an oval or round shape, grains from 0.1 to 0.2 cm;
- Expanded clay sand - due to its small size, it is not used as insulation.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=W7CNaXfxy4w