A pressure gauge is a device for monitoring gas or water pressure in a closed system. This device is mandatory if you are installing independent heating. Together with the safety valve, it protects the system from critical pressure deviations. To measure fluctuations in this value, you need to find a reliable and simple pressure gauge. You can install it yourself. The article will help you with the choice, as well as with installing the device yourself.
Pressure measuring instruments
Often there is an urgent need for a device for measuring the pressure of liquids and gases. Operating pressure limits require continuous monitoring in each piping system or container, and for this purpose gas pressure measuring devices or measuring installations are used. A good gas pressure meter will guarantee constant operation of the equipment, regardless of the system used where pressure is present, be it a gas pipeline, a heating circuit or a closed circuit. Factors to consider when choosing a gas measuring device:
- What is the working principle
- Type of pressure measured
- Type of accuracy class
- Application and its purpose
Pressure gauges
A pressure gauge is a measuring device or installation for measuring differential (for example, dp05 differential pressure sensor for liquid gases), absolute or gauge pressure. The most common ones are designed to measure only excess pressure. “Zero” in such a device is in accordance with the level of air pressure. There are pressure gauges that are designed for universal measurement, for example, FD 09 - a gas pressure meter.
How is gas pressure measured?
1 Newton per square meter is equal to 1 Pascal, and 1 atmosphere is equal to 101325 Pascal. A unit such as “bar” is equal to 105 Pa.
According to their intended purpose, the following types of pressure gauges for measuring gas pressure are distinguished:
- General technical
- Reference
- Special
What devices to measure gas pressure
At the moment, advanced technologies allow the use of different types of devices, which show the pressure value in certain intervals:
- Electronic pressure gauges are high-precision devices. Such devices can operate from 0 to maximum temperature values. One such device is an electronic pressure gauge for measuring gas pressure ht.
- Pressure-vacuum meters are used for excessive characteristics from - to +.
- Vacuum gauges (divided into draft gauges and less common draft gauges) are designed for low atmospheric pressure in the range from -1 to 0.
- Pressure gauges that are designed for extremely low values up to +40 kPa.
Pressure gauge installation
The device must be located in an open place no higher than 3 meters from the site level so that control services can recognize its readings. The pressure gauge is installed on the pipeline between the shut-off valve and the container.
According to the rules, the diameter of the device body must be greater than or equal to 10 cm. In order to distinguish the type of pressure gauge used, they are painted in different tones.
- Blue – used in oxygen devices
- Yellow – for ammonia devices
- Red – for flammable gases
- Black – for non-flammable gases
- White – used for devices with acetylene.
The pressure gauge can be installed in several ways:
- Directly
- On a three-way valve
- Using an impulse tube
How much more accuracy do we need?
In general, everyone decides for themselves. For many applications, it is also important that the needle has moved from zero. The accuracy of a pressure gauge may be needed to inflate the battery diaphragm tank. Particular precision can be useful if the battery tank needs to be pumped up without releasing the water pressure. But here we also care about the error of the pressure gauge, which will measure our air pressure. One way or another, it is better to have an accurate pressure gauge than an inaccurate one. Moreover, a pressure gauge is a relatively cheap thing and it’s not a sin to pay a little more for better quality. Let me remind you that this, as always, is my personal opinion.
Selecting and installing a pressure gauge
The device for measuring excess pressure must be selected according to the maximum atmosphere indicated in the documents for the boiler. To select a suitable pressure gauge, the following aspects must be considered:
Pressure gauge installation diagram
Installation of a pressure gauge and a safety group in a heating system is accessible to a person without specific skills who has a regular plumbing kit.
There are such ways:
Calculate the place for tapping into the system so that there is the minimum possible distance from the pressure gauge to the boiler. Ideally, right next to the boiler. In this case, there should be no additional fittings or other devices connected via a tee (taps, valves, etc.).
Advice. Mount the pressure gauge so that you can easily take its readings. To do this, you may have to install the device on a vertical piece of pipe or bracket attached to the wall.
Selecting a pressure gauge is an important component of installing a heating system. If the device and its “assistants” are installed incorrectly, you may even be denied warranty service for the boiler. Take care of monitoring the pressure in your heating pipes, because prevention is always cheaper than repairs and eliminating negative consequences.
Why is it important to control the pressure in the system?
Individual heating is a closed system with water as the coolant. The liquid is in a static state when the boiler and pump are turned off. As soon as you light the burner, the water becomes mobile and hydrodynamic pressure appears in the system. It can be of 3 types:
- Natural circulation. When the boiler is turned on and the pump is turned off, water still moves in the pipes, because it has different temperatures in different places in the system.
- Forced circulation. The pump “drives” water in a circle.
- Expansion of a liquid due to heat, which in the process displaces air and occupies the vacated space.
All these types of pressure, which add up to one indicator, are what the pressure gauge is designed to measure. Together with the automatic air vent and emergency safety valve, it is the key to the safety of your system, since going out of range means your heating is not working properly. This could even cause the equipment to explode.
Closed heating system
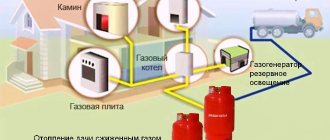
The installation of these 3 elements (they are also called the safety group) is required only for solid fuel boilers (wood, coal). If the device is purchased complete with a boiler, then it is compatible with it, but you can assemble the group separately. Installation of a pressure gauge, emergency valve and air vent is not necessary for a closed system with a gas or electric boiler, because they can stop heating themselves if an extremely high pressure or temperature develops. However, in this case, the pressure gauge and its “assistants” are recommended for convenience and additional protection. Moreover, the devices and their components are inexpensive.
Decrease and increase in pressure
There can be many reasons for a decrease in pressure in the water supply, and first you need to find out them, and then begin to eliminate them.
Regardless of whether we are talking about city apartments or a private house, a common cause of low pressure is clogged with limescale, rusted pipes. This happens from old age, when plaque accumulates over decades, and due to too hard water. In this case, the water supply needs to be changed; there is no other way to solve the problem of low pressure.
It would be a good idea to invite a plumber who will check the condition of the filter, shut-off valves, and will also be able to correctly measure water pressure indicators.
If the pipes are relatively new, but in the apartment of a multi-storey building on the top floors the pressure is weak, then you need to contact a service company. It may be necessary to install a pump in the house after inspection.
In a private house or country house, the solution to the problem largely depends on the owner. When installing water supply, he will try to ensure that the pressure meets the requirements of regulatory documents and at the same time provides a sufficient level of comfort for residents.
To create the required pressure, two options for organizing water supply can be used. The first is to use a water tank, and the second is to install a pumping station or pump that increases water pressure.
A reducer installed at the entrance of the water supply to the apartment (in apartment buildings) or a relay located on the hydraulic accumulator helps reduce the pressure. The adjustment is carried out in accordance with the instructions. You cannot reduce the water pressure to 1.5 bar; a value of 3-4 bar is considered optimal.
How is pressure in pipes measured?
This indicator is measured in pascals and atmospheres. The second scale is most often used. Individual approaches are used to heat objects of various purposes and heights.
So, the norm is:
- autonomous boiler - 1.5-2 atmospheres;
- houses 3-5 floors - 2-4 atmospheres;
- nine-story buildings - 5-7 atmospheres;
- high-rise buildings - 10 atmospheres;
- underground supply lines - 12 atmospheres.
Pressure adjustment is carried out using automatic and manual valves, expansion tanks, regulators and safety membranes. The condition of the heating system is monitored by pressure gauges installed on the pipes at certain intervals.
As a rule, control devices are mounted at the entrance to the building and at its highest point.
What are the selection criteria?
The device should be selected in such a way that it is suitable for each specific case. This is affected by:
- Measuring range. For domestic needs, a range from 0 to 4 bar is sufficient. But even in industrial conditions, high rates are rarely used. Even in boiler houses that heat multi-storey buildings, the pressure usually does not exceed 10 bar.
- Connection diameter. Previously, the standard size was ¼ inch, so adapters had to be used to connect.
Manufacturers now produce devices with different thread diameters, but most often use ½ inch.
Location of the fitting. It can be located on the case or behind the dial. You should choose so that after installation you can conveniently view the readings.
Size. Sometimes the pressure gauge simply does not fit in the place where you planned to install it. But there are quite a lot of sizes, so you can easily choose the right one.
Working temperature. Operating conditions are not always comfortable. In some cases, models that can withstand low or, conversely, high temperatures may be required.
Intervalidation interval. Each manufacturer sets its own terms for verification of metering devices. The longer the interval, the less often you will have to service or change pressure gauges.
If the fitting is located on the opposite side of the dial, the pressure gauge is called axial. If the fitting is on the side of the dial, the pressure gauge is radial.
Causes of pressure drop
The operating pressure level of the system is not always at the required level and may fall or increase.
The main reasons for its decline:
Coolant leaks. Leaks can appear in all elements of the heating circuit - in pipes, radiators, and are usually associated with defects in their manufacture.
Leaks at joints are often caused by loose fasteners or damage to the joint during assembly.
- Wear of the structure. Usually caused by improper installation of the circuit or violations of operating standards - too high pressure or significant changes in it, increased water temperature or high “hardness”. Individual elements of the system, including the circulation pump, have a warranty period, and after its expiration they may reduce performance, requiring their adjustment or replacement.
- Scale. It appears when water heats up to too high temperatures. Scale is solid deposits of salts that form on the heating surfaces of a heat exchanger. Accumulating in the heat exchanger, scale blocks the flow of water and lowers the operating pressure.
Important! Too “hard” water contains an increased amount of oxygen, chemical impurities and salts that form rust deposits. Hard water may be present in the system due to frequent replenishment of it with fresh water, including due to coolant leaks
Purpose
Thermometers used in heating systems measure the coolant at the outlet of the boiler: they display the temperature of the coolant in real time. The device visualizes the received data on the screen or a standard digital scale, and the temperature range is 0-120 degrees. If necessary, the operating parameters of the heating system do not correspond to the required ones, you can adjust them.
Pressure gauges measure fluid pressure in heating circuits. They can take readings between 4-6 bar. If the pressure level is outside the recommended range, the user needs to add water to the system or drain it. To make it easier to control the process, pressure gauges for heating systems are equipped with a scale with color division into zones.
How to choose a pressure gauge?
A pressure gauge is a device for determining pressure. It is used in a variety of areas, including in everyday life. Thus, there are pressure gauges for measuring blood pressure and for car tires. Meteorologists also use this device. In industry, pressure gauges are simply irreplaceable because they help prevent industrial accidents. Its operation and safety in the enterprise as a whole depend on how correctly a measuring device is selected for a particular area. Remember two main rules: the pressure gauge must be of high quality, and its parameters must correspond to its purpose.
How to select the required pressure gauge parameters?
We determine the type of pressure that needs to be controlled. For pressure above atmospheric you need a pressure gauge, below - a vacuum gauge. A universal option that is suitable for measuring both types of pressure is a pressure and vacuum gauge. If you need to control low overpressure, buy a pressure gauge, and if you need to control low vacuum pressure, buy a draft gauge. The pressure gauge is suitable for both excess and vacuum pressure. Also consider pressure limits. Add 25% to these numbers and you get the range in which the pressure gauge should work.
We determine the medium with which the pressure gauge will come into contact. For non-aggressive substances such as water, steam, oil and air, the heating temperature of which will not exceed +150°C, a general technical pressure gauge is suitable. For example, DM05100 or DM 05063. But to measure pressure in propane, ammonia, acetylene or other specific media, you need a special device designed for such purposes. For example, to measure oxygen pressure, a pressure gauge without oil lubrication is required. If you use a regular one, an explosion may occur from the interaction of oil and oxygen! As a rule, all such devices also come with corrosion protection. Environmental influences also include vibration. This point should not be overlooked - for such areas you need a special vibration-resistant pressure meter. Based on the purpose of the pressure gauge, select its accuracy class, which is measured in numbers from 0.15 to 4. This indicator indicates how large the error can be in the device’s performance. The number that defines the class means the maximum error, so the smaller it is, the better. For general technical pressure gauges, a relatively high accuracy class is allowed.
We determine the distance to the controlled object. To monitor remote areas (for example, at a height), you need a pressure gauge with the largest dial - 250 mm. Medium-sized pressure gauges, 100 mm, are most often used - they are placed where you can get close to the device and take readings. There are also miniature instruments, with a dial up to 50 mm. As a rule, they are used on mobile devices (for example, on gas cylinders).
When purchasing a pressure gauge, pay attention to the following points:
Availability of a certificate of inclusion of the pressure gauge in the register of measuring instruments.
Availability of a state inspection stamp.
There should be no mechanical damage or signs of repair on the pressure gauge.
It is better to choose a pressure gauge with a glass rather than a plastic dial, since the plastic will quickly become cloudy and crack.
Ideally, the device should be disassembled, the build quality and fixation checked. Also take care of additional tools for installing and operating the pressure gauge. For example, you may need a thread adapter, mounting tap, and Perkens tube.
Open and closed heating system
If an open type expansion tank is installed, then the system is called open. In its simplest form, it is some kind of container (saucepan, small plastic barrel, etc.) to which the following elements are connected:
- small diameter connecting pipe;
- a level control device (float), which opens/closes the make-up valve when the amount of coolant drops below a critical level (in the figure below it works on the principle of a toilet flush cistern);
- air release device (if the tank without a lid is not necessary);
- drain hose or circuit for removing excess coolant if its level exceeds the maximum.
One of the open type expansion tanks
Today, open systems are made less and less often, and all because a large amount of oxygen is constantly present in it, which is an active oxidizer and accelerates corrosion processes. When using this type, heat exchangers fail much faster, pipes, pumps and other elements are destroyed. In addition, due to evaporation, you have to constantly monitor the coolant level and periodically add it. Another drawback is that it is not recommended to use antifreeze in open systems due to the fact that they evaporate, that is, they harm the environment, and also change their composition (the concentration increases). That’s why closed systems are becoming more and more popular - they exclude the supply of oxygen, and the oxidation of elements occurs much slower because they are considered better.
A membrane-type tank is installed in closed heating systems
In closed systems, membrane-type tanks are installed. In them, the sealed container is divided into two parts by an elastic membrane. At the bottom there is a coolant, and the upper part is filled with gas - ordinary air or nitrogen. When the pressure is low, the tank is either empty or contains a small amount of liquid. As the pressure increases, an increasing amount of coolant is forced into it, which compresses the gas contained in the upper part. To prevent the device from bursting if the threshold value is exceeded, an air valve is installed in the upper part of the tank, which is activated at a certain pressure, releasing part of the gas and equalizing the pressure.
Main characteristics and principles of operation of the pressure gauge
There are devices for different pressure levels. For convenience, buy a device with an intuitive scale that will not require additional calculations. Usually there are two arrows on it: red and black. Red controls the permissible level. For home boilers, manufacturers recommend 2 atmospheres (the exact value is indicated in the passport). If the black one “runs” behind the red one, something is broken. A decrease in value by 0.02 MPa (0.2 atm) means that you need to look for a coolant leak or check for a sufficient pressure level in the expansion tank.
The pressure gauge usually has two scales: pressure in atmospheres and bars. Sometimes the device is combined with a thermometer, so it also has a temperature scale. The operating principle of pressure gauges is based on balancing the desired pressure with another force. According to this characteristic, devices are divided into:
- liquid;
- spring;
- membrane;
- electrical contact (ECM);
- differential.
Advice. Since the pressure in a conventional closed heating system fluctuates between 2-3 atm, choose a pressure gauge with a scale of up to 4 atm. If the upper value of the pressure gauge is, for example, 50 atm, the divisions will be small. You will not record a small pressure drop, which can become critical for the system.
It is not advisable to install the device when:
- there is no seal or other verification mark on it;
- the pressure gauge verification period has expired;
- it has visual damage, such as a crack in the glass;
- after disconnecting, the arrow does not return to “0”.
Pressure gauge
Installation and removal rules
To ensure stable operation of the pressure gauge and reduce the risk of its breakdown, follow certain rules:
- The installation of pressure gauges must be carried out in such a way that it would be quite easy to take measurement results and carry out routine maintenance and repairs.
- The rules define a number of conditions that determine the maximum dimensions of the distances between the measuring device and the walls of the room in which the device is installed.
- If the pressure gauge is mounted at a height of 2 to 3 meters, the diameter of the housing must be no less than 160 mm. It is unacceptable to install pressure gauges at a height of more than three meters. This is defined in the requirements of regulatory documentation.
- To carry out the checks of measuring instruments and equipment prescribed in the regulatory documentation when using the instruments, a three-way valve must be installed in the installation structure. Its installation location should be between the pressure gauge and the pipe (vessel).
- When installed in conditions where it may be influenced by external external factors, for example, precipitation or high temperature, it is necessary to provide additional protection. For this purpose, so-called buffer elements, siphons and other products are used. The efficiency of the installed measuring equipment depends on how well it is protected from external influences.
- To prevent freezing of the measuring instrument, they are provided with thermal insulation.
- When connecting, it is necessary to vent any gas that has entered the system. To do this, slightly tighten the fixing nut on the fitting.
- Pressure gauges that have not been verified and do not have a seal or appropriate seal on the body should not be allowed to be used for operation in networks. If the verification period has expired, or during operation it turns out that the operation differs from the standard one, then it must be removed and sent for diagnostics and repair. If damage appears on the meter body, or a crack appears on the glass, then such a device cannot be used and must be disposed of.
- Damaged sensors are dismantled and transferred to a certified laboratory for repair work. If such a pressure gauge cannot be restored, then it is disposed of.
Types of pressure gauges
The vast majority of modern pressure gauges are digital. Analogue devices, in which the pointer on the dial moves under the influence of pressure, are less popular. Digital instruments provide more accurate results and can also be connected to process control systems.
In addition, pressure gauges for heating systems are divided into stationary and portable.
Submersible water temperature sensors
These measuring instruments are designed to take temperature readings inside pipes. They are installed at specific locations in the pipeline system. The direct choice of one modification or another depends on the preferred method of recording readings.
Bimetallic sensors
The operation of this device is based on the principle of metal deformation when heated, which causes pressure on the indicator needle. This gives high accuracy of the readings obtained, but is characterized by a high degree of inertia.
Alcohol sensors
The operating principle is similar to that of a conventional thermometer. Alcohol placed in a sealed flask is used as an indicator. When heated, it expands and the arrow points to the corresponding division of the flask scale. The advantage of the design is low inertia, the disadvantage is the inconvenience of recording readings.
Installation of immersion sensors requires careful selection of the sleeve length depending on the pipe diameter; it is also very important to take into account the installation dimensions and the range of measured temperatures
How to properly install a pressure gauge
The measuring device must be installed in a visible and easily accessible place to ensure easy monitoring of its readings.
The diameter of the body must be at least 10 cm. When installing the meter at a height of 2-3 meters, the diameter of its body must be at least 16 cm. The maximum height of the meter above the platform should not exceed 3 m. As a rule, pressure gauges are installed with a vertical dial position, which allows personnel to conveniently measure and control the pressure value in the system.
It is recommended to place the pressure sampling point (impulse) on straight sections of the pipeline, which will avoid distortions in the readings. The pressure gauge is connected to the pressure sampling point using an impulse line - a route made of copper, steel or PVC pipes, the diameter of which is selected taking into account the total length of the line and the value of the operating pressure. It is recommended to install a special shut-off device between the pulse and the measuring device, which can be a tap or a three-way valve. This will allow you to purge, replace the device, and control the “zero” without disconnecting the entire pipeline.
To protect the device from water hammer, as well as to smooth out pressure surges in the system, it is recommended to connect it through a throttling device or a special valve that closes when the pressure increases excessively. The so-called internal protection - installation of a pressure gauge with increased resistance to excess pressure.
The device is usually connected using a threaded connection.
In this case, it is not allowed to screw it into the body: it is necessary to use special surfaces for a wrench on the fitting of the device. To install the pressure gauge in the correct position for easy reading, use a union nut. The joint is sealed using sealing elements made of soft copper, lead, fiber, and leather. The use of seals made of red lead or tow is prohibited. Some models of pressure gauges can be installed using a flange connection. In this case, it is necessary to use seals of the appropriate diameter recommended by the manufacturer.
If the pipe connection to the device is not rigid enough and does not ensure its stable position, the pressure gauge must be additionally secured. For this purpose, special mounts are used on the wall or on the pipe.
Source
Step-by-step instructions for connection
There are usually no difficulties during installation, so it’s quite possible to do all the work yourself . So that the pressure gauge can be changed at any time without shutting down the system, a tap is installed in front of it.
The location does not play a special role, but usually a place is chosen close to the boiler. The main thing is convenience. The pressure gauge must have direct access so that pressure readings can always be viewed.
If there is no tap, the device should be installed only on a disconnected system. To do this you will need:
- choose a place;
- take the wrench;
- if there is no gasket on the pressure gauge, you need to rewind the thread;
- tighten the device using the key.
It is worth noting that you cannot tighten the pressure gauge while holding the housing. This way it can be damaged. It is better to use a special nut on the fitting.
The pressure gauge is part of the heating safety group. This also includes an automatic air bleeder and a safety valve. If the group has not yet been installed, you can buy it assembled . You just have to connect it to the highest point of the pipe, since the air bleeder should be located there.
Water pressure in the water supply
Low pressure level
With a fairly low pressure, which is manifested by a fairly weak water supply directly from the tap and indicates a completely low level. A fairly pressing and common problem is for residents of upper floors, as well as owners of country houses. Low pressure in the water supply will prevent many necessary household appliances from working, which will become a significant problem, and there will also be a desire to correct this situation.
Carrying out installation work to install equipment that can increase this indicator is a fundamental technique for ensuring a solution to this issue. Naturally, before using modern units designed for these purposes, it is necessary to determine whether the system is clogged, which may also be one of the reasons for this phenomenon.
In a certain way, this problem can be completely eliminated with the help of a specialized pumping unit, which will help increase the pressure, or by modernizing the system itself by integrating the pumping station with the storage tank.
Naturally, a more rational and suitable method should be determined directly by the owner himself, which is determined by the goals being pursued, as well as the necessary volumes of liquid that will be required to fully provide the home.
Installation features
The pressure meter must only be mounted in a vertical position. This should ensure normal reading of the received data. The meter scale can be tilted at an angle of no more than 30°. The sensor must be illuminated and protected from exposure to sunlight and low temperatures.
After the device is installed and the system is ready for operation in normal mode, then to ensure the safety of the device, it is not advisable to immediately load the installed measuring equipment. It is advisable to increase the pressure gradually, without any jumps and without crossing the established boundaries.
When installing the meter in place, it is necessary to ensure that the connection between the meter and the fitting in which it is mounted is tight. For this, various sealing materials are used, for example, FUM tape or thread. To increase reliability, sealing materials can be treated with a sealant. All materials used must comply with operating conditions, that is, if superheated steam is used in the pipeline system (minimum temperature 130 °C), then installing FUM tape designed for an operating temperature of 95 °C is unacceptable. By the way, some installation organizations, in the old fashioned way, use tow as an insulating material; it should be noted that this is not encouraged.
Source
Connecting diameters of pressure gauges
A pressure gauge for plumbing or heating must be liquid, that is, designed to work with water. Over time, the range of parts offered by retailers changes. The same applies to pressure gauges. When I was doing my own heating, I purchased a pressure gauge for a very small connection diameter. The thread is only 1/8 inch. Now such pressure gauges are no longer available in stores. There are pressure gauges for 1/4 and 1/2. Maybe there are 3/8 inches, but this is not a very common size in our country and I have not seen such ones. Adapters from 1/8 inch are also not widely available in retail. Thus, to connect a pressure gauge, you can safely make a separate tee with a diameter of 1/2 in the line. To such a tee you can connect either a 1/2-inch or 1/4-inch pressure gauge, but through an adapter. There are no problems here.
Types of pressure gauges: what to choose
- In a liquid pressure gauge, the pressure difference is calculated using a column of liquid, which is used as a balancing force (communicating vessel principle). They are used either in laboratory research or in industrial settings.
- In a membrane pressure gauge, the measured pressure is recorded by a pair of welded membranes (membrane box), which change the volume and thereby move the needle along the scale.
- An electric contact pressure gauge is used in automatic control, alarm or regulation systems. The pressure difference causes a short circuit in the electrical circuit.
- Differential devices combine the properties of different types of pressure gauges.
- The most popular devices are those with a spring mechanism. Among other things, they are most often used in heating systems, as they have a number of advantages:
- simplest in design;
- can have a wide measurement range;
- the most reliable.
A curved tube reacts to changes in pressure in a spring pressure gauge. It receives fluid from the system. Under pressure, the tube bends or straightens, moving the needle along the scale.
Types of devices
Since the scope of application and operating conditions are different, the pressure gauges are also different. For heating there are 5 types:
- Spring. The most popular models that are used in domestic and industrial environments. There is a spring inside. Under pressure, it transmits force to the dial hand.
Membrane. These pressure gauges are also in good demand. The principle of operation is similar to spring ones, only an elastic plate or membrane box is used as a sensing element.- Liquid. There is a tube running inside them that operates on the basis of communicating vessels.
When a load is applied to one vessel, the liquid in the other rises to a certain height. Such devices are very accurate, but are more suitable for laboratory research. - Electric contacts are used not only for measuring pressure. They can be connected, for example, to a circulation pump to control it. When the arrow reaches the desired value, the circuit will close or open. This is especially useful in industrial settings.
- Differential. They consist of several chambers that are separated from each other by a sensitive element. Usually these are portable devices with the help of which the pressure difference is calculated.
If we talk about working conditions, pressure gauges are also divided into:
- general technical;
- exemplary;
- self-writing;
- railway;
- ship's
Only general technical ones are suitable for heating. The rest are either too accurate or contain additional functions that are not needed in everyday life.