In modern society, people think about the environmental friendliness of technologies used in everyday life, especially if they help save money. One such solution is solar collectors. A primitive solar collector is a black metal barrel with water, which is installed for arranging a summer shower in the country. However, there are now advanced modern technologies for harnessing solar energy. What you need to know about a solar collector if you are planning to purchase one...
Solar collectors on the roof of a private house Source retinapost.com
We will consider only the domestic use of the collector in a private residential building. Often what keeps people from purchasing is the lack of reliable information about the product. It is not clear what to trust, so we have collected the characteristics of solar collectors verified by experts and users.
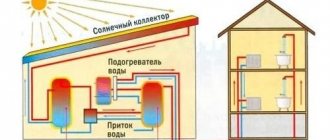
The solar collector accumulates the energy of the sun, which is then used to heat water or space heating. In manufacturing, it is also used to generate electricity.
How solar collectors work
A solar collector is a functional structure used to generate energy. Its photosensitive elements absorb light to heat the liquid or air inside the tubes.
The principle of operation of a solar collector (SC): the rays of the sun heat the black plates, and the energy is accumulated for domestic needs. The method of obtaining it is environmentally friendly and economical.
The following types of household collectors are distinguished:
- flat;
- vacuum;
- air.
Let's talk more about each of these types below.
Flat
Popular and budget-priced devices. They consist of a flat photosensitive plate connected to heat-conducting pipes, a glass coating, thermal insulation and a metal frame. The plate absorbs sunlight and accumulates thermal energy, which heats the coolant fluid. Unlike other types, they lose a lot of absorbed heat. Ineffective in cloudy weather. High humidity has a bad effect on structural parts.
Flat-plate collectors
Vacuum
There are 2 types of vacuum collectors: direct-flow and with indirect heat transfer. The former are used in the warm season, the latter - all seasons. The design is based on a vacuum tube system with a metal rod inside, which contains a coolant fluid. This installation works on the principle of a thermos. Characterized by optimal efficiency.
Vacuum manifold
Air
The principle of operation is similar to flat ones. But air collectors use air as a coolant. Installed for heating houses. Heated air fills the room using air ducts and a fan.
Air manifold
The type of device is chosen based on the purpose of use. The designs are suitable for summer cottages, cottages, village houses and duplexes.
Flat appliances
Their design is simpler than that of vacuum devices, and at the same time they are less efficient. The water is heated as it circulates through tubes attached to a thermally conductive substrate of copper or aluminum sheet called an absorber.
The substrate is thermally insulated from below, and from above it is protected by a transparent material that allows radiation to pass through - polycarbonate or tempered glass with a slight addition of metal.
The most effective device is a flat device with copper tubes that are soldered to a molded copper substrate. A manifold equipped with tubes made from cross-linked polyethylene absorbs less heat because they have lower thermal conductivity.
Flat devices have the following characteristics:
- Their working environment heats up to a maximum of 200 - 210 degrees.
- Solar energy absorption is up to 70%.
- Minimal reduction in heating efficiency in winter at the solar collector in snowy weather. The transparent sheet, which serves as protection for the substrate with the tubes, heats up during operation, as a result of which the snow cover quickly melts.
- Heat loss occurs. They arise as a result of contact of air heated in the device with the protective glass, but they do not exceed 30%. As the temperature outside decreases, the heat loss from the device begins to increase. It stops functioning at -20 °C and below.
- High windage. This property can become an obstacle to installing a flat-plate collector in regions where strong winds blow in winter.
- They are installed at an angle to the horizon so that the location provides them with maximum illumination throughout the day.
Principles and subtleties of the work process
Before you start making a solar coolant yourself, you need to carefully study the basic rules of its operation and the components of the entire structure. As paradoxical as it may seem, the design of a solar collector is quite simple - the principle of its operation is based on ordinary physical laws, according to which a liquid with a higher density displaces a liquid with a lower density.
In principle, the same operating scheme is incorporated into the functioning of the heating system with the natural movement of the coolant: warmer water rises upward at the expense of cooler water. The main difference between natural heating and solar heating is only the method of heating water - with a collector, the water is heated by the sun.
- Why do solar systems need an inverter and how to choose one
Solar panels built into the roof of a house
Based on this principle, we can conclude that the design of the solar coolant is very simple: a vertically located coil, in which the water gradually rises upward as it heats up, and then enters a storage tank, from which the already heated liquid is collected. In order for homemade solar collectors to work more efficiently, it is necessary to establish natural fluid movement.
Based on the above subtleties and nuances of the operation of collectors, the principle of installing numerous units of alternative solar heaters is formed. In order for the vital circulation of liquid to be properly ensured without the use of a pump, the solar collector for heating must be located on the highest part of the building (often on the roof), and the storage tank should be located just below the coolant (for example, in the attic).
Solar collector connection diagrams
When installing a solar water heater or heating system, a storage tank must be connected to the device. It is needed due to the disproportionate energy consumption and distribution of generated heat. Over time, the tank fills with water, which the system owners use at their discretion.
It is recommended to install a standard boiler or buffer tank. A rationally constructed design is a connection of a collector with a heat conductor, which communicates with the boiler.
For home heating
In the northeastern regions of Russia, there is no maximum solar activity in autumn and winter. Solar power plants are used as an auxiliary energy source for heating. The connection diagram is shown in the figure below.
The solar collector is connected to the water supply and a circulation pump. The energy is used to indirectly heat the room.
For hot water supply
There are 2 options for use: for summer and winter.
The first one is suitable for summer residents. They heat water only in summer. Therefore, such an installation has minimal inertia. It is necessary to install the solar collector below the level of the storage tank so that the water circulates naturally.
- How to connect solar panels: diagrams and explanations
In winter, antifreeze is used as a coolant fluid, which is poured into a storage tank with a coil. Due to its continuous circulation, the water is constantly heated to the optimal temperature.
Heating + hot water
The essence of the connection diagram is the combination of heating and domestic hot water processes. A double-circuit heat-storing tank with an internal reservoir is used. This helps separate process water from drinking water. For automation, an SC controller is included in the circuit to prevent overconsumption.
For heating the pool
To warm up a portable or stationary pool, use a submersible pump. It can be replaced with an automated pumping station, which will circulate cold water from the pool, and heated water from the SC.
Necessary tools and materials for installing a solar collector
Installation of solar collectors is carried out outdoors. Consequently, the structure itself, the pipeline system and all auxiliary fastenings are subject to environmental damage over time. They may experience corrosion and deformation. Therefore, only stainless materials are used for installation.
To install the solar collector, use the following auxiliary tools:
- crane or lift;
- scaffolding;
- roof ladder;
- safety equipment - vest, rope, etc.;
- building level;
- vacuum grip;
- insulating material for pipes.
The reliability, efficiency and durability of the equipment depend on the quality of installation.
How to calculate collector area
The working surface area of the system is calculated taking into account its type and location features. It should be remembered that the efficiency of the collector depends on the temperature conditions and the amount of solar energy.
Approximate values for summer in Russia per 1 m²: up to 160 kWh per month, the rest of the time - from 20 to 80 kWh.
- How does a solar collector work?
For hot water supply you will need approximately 100 * 1.16 * 30 = 3.48 kWh. At the same time, 1.16 Wh is the energy that will be needed to heat 1 kg of water by 1 °C.
Heat pumps are used to regulate energy production in hot weather. Also in summer, structures are covered with a thick awning if they generate a lot of energy. The installation plan and area of photosensitive elements are determined individually.
Classification by temperature regime
Solar equipment for the home is often classified by type of coolant. Today, liquid and air systems can be found on the world market. In addition, collectors are divided according to operating temperature conditions, that is, classification is applied according to the maximum heating temperature of the working elements. The following types of systems are distinguished:
- low-temperature - the coolant for solar collectors heats up to 50℃;
- medium temperature - the temperature of the circulating liquid does not exceed 80℃;
- high-temperature - the maximum temperature of the coolant material can rise to 300 degrees.
The first two options are most suitable for home use, while collector models with high-temperature operating conditions are more often used in the manufacturing and industrial sectors of the economy. This is due to the fact that in high-temperature water heating systems the process of transforming solar energy into heat is quite complex. Moreover, such solar installations occupy large areas. Not every owner of a “dacha” property can afford such luxury.
Where to install solar collectors
The main condition for the operation of the collector is an open space where direct sunlight freely reaches at any time of the year. The device is installed in the territories of private houses, where there is no shadow from other buildings and trees. More often, photosensitive plates are mounted on the roof of a building.
A common method is to install several plates, so-called “geofields”. Both pitched and flat roofs are suitable for installation. Due to the large weight of the collector, it is fixed to supporting structures - beams, rafters, etc.
The devices are installed on balconies or horizontal surfaces of the facade. To make it work more efficiently, photosensitive elements in Russia are located strictly on the south side. If they deviate to the west or east, the absorption coefficient of solar rays will decrease.
Thermal insulation
To reduce the overall weight of the solar collector, its back wall is cut from a single slab of rigid foam. Due to the excellent thermal insulation properties of polystyrene foam, this makes it possible to reduce heat loss and at the same time reduce the weight of the solar collector. The dimensions of the rear wall are adjusted exactly to the dimensions of the case so that it fits tightly, with virtually no gaps, between its side walls. To reduce heat loss, the joints between the rear wall and the side panels of the case are additionally sealed with elastic silicone sealant. An additional layer of thermal insulation made of mineral wool mats is laid on top of the hard foam back wall.
What should be the angle of inclination of the collector?
The installation angle of the flat solar collector depends on the following factors:
- Region of residence. For the southern regions - 30-35°, for the middle zone - from 40°.
- The time of year when the installation is planned to be used (summer or winter season, year-round). For all-season use, choose an angle that is approximately equal to the geographic latitude of the region. In summer this value is reduced by 15°. In winter, on the contrary, they increase.
- Climatic conditions and precipitation. If the solar system is used in winter, the angle of inclination is made steep so that snow does not accumulate on its surface.
In the accompanying instructions, the manufacturer indicates the optimal angle of inclination for each solar heater. Compliance with all conditions for determining angular inclination values contributes to the most efficient operation of the equipment.
Solar collector: types and subtypes of coolants
Depending on the temperature the collector plates can reach, they can be divided into the following types:
- Low temperature manifold;
- Medium temperature collector;
- High temperature collector.
solar collector will not be able to provide high-power energy. It will be able to heat water no warmer than 500 C.
Medium-temperature collectors can heat water up to 850-900 C. Such solar collectors are most optimal for heating a home and premises.
And high-temperature collectors are in great demand in industrial enterprises and large plants, so it is simply not possible to make them on your own.
External view of the solar collector
All integrated solar energy carriers are divided into:
- Flat solar collectors;
- Air manifolds;
- Liquid energy carriers;
- Storage integrated solar collectors.
Thermosyphon solar coolant
Storage integrated solar collectors are also called thermosyphon collectors. Its main purpose is not only to heat water, but also to maintain the desired temperature for a certain time. These collectors do not have pumps, so they are much cheaper than other varieties.
The thermosyphon solar collector is manufactured in the form of a structure with one tank, which is filled with water and placed in a heat-insulating box. On top of the tank there is a glass cover, through which solar radiation passes through the glass and heats the water.
The purchase of such a solar collector will not require large expenses, moreover, it is not difficult to operate and is easy to maintain. The only drawback of the solar collector is that it is unlikely to be used to its full potential in winter.
Flat coolant
Scheme of heating water in a boiler using a solar collector
A flat-plate solar collector looks like a regular flat metal box, inside of which there is a black plate through which solar energy passes.
The glass cover of the box accumulates solar radiation. Since glass has a low iron content, all the accumulated energy is transferred to the plate.
The flat-plate collector box is thermally insulated, and the black plate is thermally sensing, so heat is released from this design. And since the efficiency of the plate is no more than 10-15%, it is additionally coated with an amorphous semiconductor.
Flat energy carriers are designed for heating water in saunas, swimming pools, as well as for heating living rooms and other domestic needs.
Liquid solar collector
A liquid solar collector can be either glazed or unglazed. And also with a closed or open heat exchange system. But they are all united by the principle of operation of the coolant, which is based on liquid.
Air coolant
Scheme of drying grain using a solar collector
An air solar collector vaguely resembles the operation of a liquid collector. But it takes much less money to install and purchase it. In addition, air coolants do not freeze at negative air temperatures and do not leak.
Airborne solar collectors are good for drying agricultural products.
Concentrate
In addition to all the above types and subtypes of solar collectors, concentrators are also distinguished. The main distinguishing feature of concentrates from collectors is the concentration of solar radiation. This seems possible due to the mirror surface of the structure, thanks to which the sun's rays are directed to the absorbers.
The most significant disadvantage of this type of collector is the inability to function normally on bad weather days.
That is, concentrates are only suitable for work in countries where the climate is constantly hot.
Solar oven and distiller
And the last type of solar collectors can be considered furnaces powered by solar radiation and distillers. The operating principle of distillers is to evaporate water. Thus, they not only provide heat energy, but also purify water. Solar ovens also work using the same algorithm.
The operating principle of modern solar systems
The concept of “solar collectors” combines several design options for home use, but the operating scheme is not fundamentally different. All collectors “powered” by the Sun are equipped with a system of tubes, which, depending on the design of the equipment, can be mounted in the form of a coil or connected in series to the output and input lines. The coolant fluid for solar systems—water, oil or antifreeze—circulates in the tubes themselves. The absorption and subsequent accumulation of thermal energy from the Sun is carried out by absorbers. In technical terms, the design is quite simple. The high cost of such installations is due to the use of expensive materials.
For the outer surface of the structure, wear-resistant materials with excellent light transmission characteristics are used - organic glass, polymer compounds and others. But since polymer “synthetics” cannot withstand prolonged exposure to UV rays (they have a high coefficient of thermal expansion, which leads to depressurization of the solar system), manufacturers use tempered or organic glass as an alternative. And the tubes themselves are most often made of borosilicate glass, which is characterized by a minimal coefficient of thermal expansion (8 times less than quartz glass). That is why the material does not crack during sudden temperature fluctuations.