Using this calculator, you can calculate heating radiators and find out the number of sections for comfortable heating of the specified area. To perform the calculation, enter the cubic capacity of the room, the heat transfer of one radiator section according to the passport (or see the table below), indicate the type of connection and the heating rate per 1 m3 of room (approximately for brick houses - 37 W/m3, for panel houses - 41 W/m3 ). When calculating through the heat losses of the room, you must use a heat loss calculator in advance. It is recommended to leave the power reserve in the region of 10-15%, since SNiP does not contain a detailed description of the calculation methodology.
Related regulatory documents:
- SP 50.13330.2010 “Thermal protection of buildings”
- SP 60.13330.2012 “Heating, ventilation and air conditioning”
- SNiP 2.04.07-86* “Heat networks”
- GOST 30494-2011 “Residential and public buildings. Indoor microclimate parameters"
- GOST 22270-76 “Equipment for air conditioning, ventilation and heating”
- GOST 31311-2005 “Heating devices”
The influence of connection methods and installation location on the heat transfer of radiators
When calculating the actual power of radiators, you should know that the heat transfer of devices also depends on the method of placement.
The actual power obtained as a result of calculations shows how much heat the radiator will give off with the calculated parameters of the coolant, a competent connection diagram, a balanced heating system, and also when installed openly on a wall or under a window without the use of decorative screens. As a rule, window openings are building elements with maximum heat loss, regardless of the number of chambers and other energy-efficient indicators. Therefore, it is customary to place heating radiators in the space under the window. In this case, the radiator, heating the air in the installation area, creates a kind of choking curtain along the window, directed upwards into the room and allowing the flow of cold air to be cut off. When cold air is mixed with warm currents from the radiator, convective currents arise in the room, which allow the heating rate to increase.
It is recommended to install radiators with a width of at least half the width of the window opening.
Another requirement to increase the efficiency of heating a room is to select the size of the radiator relative to the width of the window opening. It is recommended to select the length of the radiator at least half the width of the window opening. Otherwise, there will be a high probability of cold zones forming in close proximity to the window and the convective component of heating the room will be noticeably reduced.
If the building has a large number of corner rooms, then a number of heating devices should be placed equal to the number of external enclosing structures.
For example, for a room on the 1st floor of a residential building with an area of 8.12 m2, considered as an example, 2 radiators should be provided. One is located under the window structures, the second either at the opposite window or against a blank wall, but as close as possible to the corner of the room. Thus, the most uniform heating of all rooms will be observed.
If the heating system of the house is designed according to a vertical scheme, then the installation of risers for supplying radiators to corner rooms should be done directly at the corner joints of the walls. This will allow additional heating of external building structures and prevent dampness and damage to finishing materials in the corners.
If radiators are installed under windows using additional decorative elements (screens, wide window sills) or installed in niches, the following correction factors must be used to calculate the actual power of heating devices:
- The narrow window sill does not block the radiator in depth, but the front panel of the heating device is covered with a decorative screen (the distance between the wall and the screen is at least 250 mm) - Kcorr = 0.9.
- A wide window sill completely covers the depth of the radiator, a decorative screen covers the front panel (the distance between the wall and the screen is at least 250 mm), but in the upper part there is a gap equal to 100 mm vertically - Kcorr = 1.12.
- The wide window sill completely covers the radiator in depth, there are no additional decorative structures - Kcorr = 1.05.
From the options for installing heating devices discussed above, it is clear that in order to prevent the level of convection from being reduced, air gaps should be left on all sides of the heating devices. The minimum distances from the finishing level of the floor covering and from the window sill to the heating device must be at least 100 mm, and the gap between the wall and the rear surface of the radiator must be at least 30 mm.
There are one-sided connections of radiators to heating systems and multi-sided ones, when pipelines are connected to the device from opposite sides. The one-way method is the most economical and convenient from the point of view of further operation of heating devices. Connecting radiators from different sides slightly increases their heat transfer, but in practice this method is used when installing heating devices of more than 15 sections or when connecting several radiators in a bundle.
Heat removal from radiators also depends on the point of entry of the supply pipeline. When connecting according to the “top-down” scheme, when hot water is supplied to the upper pipe and the return pipe to the lower one, the heat transfer from the radiator increases. When connecting from bottom to top, the heat flow is reduced, while the radiators are heated unevenly, and the standard size of the devices must be significantly increased to achieve the design power.
Another calculation example
A room with an area of 15 m2 and a ceiling height of 3 m is taken as an example. The volume of the room is calculated: 15 x 3 = 45 m3. It is known that to heat a room in an area with an average climate you need 41 W/1 m3.
45 x 41 = 1845 W.
The principle is the same as in the previous example, but heat transfer losses due to windows and doors are not taken into account, which creates a certain percentage of error. To make a correct calculation, you need to know how much heat each section produces. Steel panel batteries can have fins in different numbers: from 1 to 3. The number of fins a battery has, the greater the heat transfer.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=ZkvOaJlQetM
The greater the heat transfer from the heating system, the better.
Classification
Steel batteries are available in three types:
- tubular - welded structure made of pipes with a working pressure of up to 15 atmospheres;
- sectional - durable sections are connected by spot welding, operating pressure up to 16 atmospheres;
- panel ones are the most popular, they are made of two welded rectangular sheets with stamped recesses.
In panel pipes, the operating pressure reaches 13 atmospheres at a coolant temperature of no more than 110 degrees.
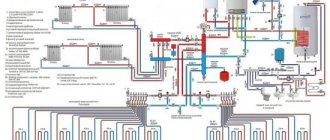
Closed heating system - what is it?
As you know, any heating system in a private home has an expansion tank. This is a container that contains some coolant removal. This tank is necessary to compensate for thermal expansion under various operating conditions. By design, expansion tanks are of open and closed type, respectively, and heating systems are called open and closed.
Closed two-pipe heating system
In recent years, a closed heating scheme has become increasingly popular. Firstly, it is automated and works without human intervention for a long time. Secondly, it can use any type of coolant, including antifreeze (it evaporates from open tanks). Thirdly, the pressure is maintained constant, which allows the use of any household appliances in a private home. There are several more advantages that relate to wiring and operation:
- There is no direct contact of the coolant with air, therefore, there is no (or almost no) unbound oxygen, which is a powerful oxidizing agent. This means that the heating elements will not oxidize, which will increase their service life.
- A closed-type expansion tank is placed anywhere, usually close to the boiler (wall-mounted gas boilers come immediately with expansion tanks). An open-type tank should be located in the attic, and this means additional pipes, as well as insulation measures so that heat does not “leak” through the roof.
- The closed type system has automatic air vents, so there is no airing.
In general, a closed heating system is considered more convenient. Its main drawback is its energy dependence. The movement of the coolant is ensured by a circulation pump (forced circulation), and it does not work without electricity. It is possible to organize natural circulation in closed systems, but it is difficult - it requires regulating the flow using the thickness of the pipes. This is a rather complicated calculation, which is why it is often believed that a closed heating system only works with a pump.
To reduce energy dependence and increase heating reliability, install uninterruptible power supplies with batteries and/or small generators that will provide emergency power supply.
Peculiarities
Heating radiators are calculated in accordance with the heat loss of a particular room, as well as depending on the area of this room. It would seem that there is nothing complicated in creating a proven heating circuit with pipe contours and a medium circulating through them, however, correct thermal engineering calculations are based on the requirements of SNiP. Such calculations are performed by specialists, and the procedure itself is considered extremely complex. However, with acceptable simplification, you can perform the procedures yourself. In addition to the area of the heated room, some nuances are taken into account in the calculations.
It is not for nothing that specialists use various techniques to calculate radiators. Their main feature is taking into account the maximum heat loss of the room. Then the required number of heating devices is calculated to compensate for these losses.
It is clear that the simpler the method used, the more accurate the final results will be. In addition, for non-standard premises, experts use special coefficients.
Specialists often use special devices in their projects. For example, a thermal imager can accurately determine actual heat loss. Based on the data obtained from the device, the number of radiators is calculated that accurately compensate for losses.
This calculation method will show the coldest points of the apartment, the places where heat will be lost most actively. Such points often arise due to construction defects, for example, made by workers, or due to low-quality building materials.
The results of the calculations are closely related to existing types of heating radiators. To obtain the best result in calculations, it is necessary to know the parameters of the devices planned for use.
The modern range includes the following types of radiators:
- steel;
- cast iron;
- aluminum;
- bimetallic.
To carry out calculations, you need such device parameters as the power and shape of the radiator, and the material of manufacture. The simplest scheme involves placing radiators under each window in the room. Therefore, the calculated number of radiators is usually equal to the number of window openings.
Design
A steel panel radiator can become not only a source of heat, but also a stylish piece of furniture. In addition to the traditional white color, there are radiators on the market in a variety of colors, even with patterns.
Steel panel radiators can be “packed” into decorative boxes - screen and sidewalls, which... Decor for heating devices can be made to order according to an individual design or purchased ready-made from the manufacturer.
New items
Tubular heating radiators, due to the shape of the pipes, can be of a wide variety of designs: both classic options and bold interior experiments are available for them.
For example, a new popular design made of heating pipes has entered the market - bench radiators covered with varnished boards. This bench can be installed in the hallway, kitchen, children's room or winter garden. Its compliance with hygienic standards allows it to be placed in medical institutions.
Formula and calculation example
2215 sections
In a private house with its own water heater, the coolant power is calculated to the maximum. Then we divide 1800 by 150 and get 12 sections. We will need this much to heat a room of 18 m2. There is a very complex formula that can be used to calculate the exact number of sections in a radiator.
The formula looks like this:
- q 1
is the type of glazing: triple glazing 0.85; double glazing 1; regular glass 1.27; - q 2
- thermal insulation of walls: modern thermal insulation 0.85; wall of 2 bricks 1; poor insulation 1.27; - q 3
- ratio of window area to floor area: 10% 0.8; 20% 0.9; 30% 1.1; 40% 1.2; - q 4
- minimum outside temperature: -10C 0.7; -15C 0.9; -20С 1.1; -25C 1.3; -35C 1.5; - q 5
- number of external walls: one 1.1; two (corner) 1.2; three 1.3; four 1.4; - q 6
- type of room above the design one: heated room 0.8; heated attic 0.9; cold attic 1; - q 7
- ceiling height: 2.5 m - 1; 3 m - 1.05; 3.5m - 1.1; 4m - 1.15; 4.5m - 1.2;
Let's carry out the calculation for a corner room of 20 m2 with a ceiling height of 3 m, two double-hung windows with triple glazing, walls of 2 bricks, located under a cold attic in a house in a village near Moscow, where in winter the temperature drops to 20C.
The result is 1844.9 W. Divide by 150 W and get 12.3 or 12 sections.
Radiators are made from three types of metal: cast iron, aluminum and bimetallic.
Cast iron and aluminum radiators have the same heat output, but heated cast iron cools down more slowly than aluminum. Bimetallic batteries have greater heat transfer than cast iron ones, but they cool down faster. Steel radiators have high heat transfer, but they are susceptible to corrosion.
The most comfortable indoor temperature for the human body is considered to be 21C. However, for a good sound sleep, a temperature no higher than 18C is more suitable, so the purpose of the heated room also plays a significant role. And if in a room with an area of 20 m2 it is necessary to install 12 battery sections, then in a similar sleeping room it is preferable to install 10 batteries, and a person will sleep comfortably in such a room. In a corner room of the same area, feel free to place 16 radiators, and you won’t be too hot. That is, the calculation of radiators in a room is very individual, and only rough recommendations can be given on how many sections need to be installed in a particular room. The main thing is to install it correctly, and there will always be warmth in your home.
Example Method
A simplified version of the calculations is based on taking several indicators as a standard:
In a room with ordinary ceilings, 1 section of the battery will heat 1.8 m2. For example, if the room is 14 m2. 14: 1.8 = 7.7. Round up = 8 sections.
Or like this:
In a room with 1 window and 1 external wall, 1 kW of radiator power can heat 10 m2. Example: room 14 m2. 14:10 = 1.4. That is, for such a room you need a heater with a power of 1.4 kW.
Such methods can be used for approximate calculations, but they are fraught with serious errors.
If the results of the calculations are a long radiator of more than 10 sections, then it makes sense to divide it into two separate radiators.
Calculation of thermal power
We will look at several calculation methods that take into account different numbers of variables.
By area
The calculation of the area is based on sanitary standards and rules, which tell the Russians in plain English: one kilowatt of thermal power must be per 10 m2 of room area (100 watts per m2).
The lower the outside temperature, the greater the heat loss.
It is clear that the method gives a very significant error:
- Single-strand panoramic glazing will clearly result in greater heat loss compared to a solid wall.
- The location of the apartment inside the house is not taken into account, although it is clear that if there are warm walls of neighboring apartments nearby, with the same number of radiators it will be much warmer than in a corner room that has a common wall with the street.
- Finally, the main thing: the calculation is correct for the standard ceiling height in a Soviet-built house, equal to 2.5 - 2.7 meters. However, back in the early 20th century, houses with ceiling heights of 4 - 4.5 meters were built, and Stalin buildings with three-meter ceilings will also require more precise calculations.
Let's still use the method to calculate the number of cast iron sections of heating radiators in a room measuring 3x4 meters located in the Krasnodar region.
The area is 3x4=12 m2.
The required thermal heating power is 12 m2 x 100 W x 0.7 district coefficient = 840 watts.
With a power of one section of 180 watts, we need 840/180 = 4.66 sections. We will, of course, round the number up to five.
A reserve of thermal power never hurts. If necessary, you can simply close the valves in front of the radiator.
Simple calculation by volume
Not our choice.
Calculation based on the total volume of air in the room will obviously be more accurate because it takes into account the variation in ceiling heights. It is also very simple: for 1 m3 of volume you need 40 watts of heating system power.
Let's calculate the required power for our room near Krasnodar with a small clarification: it is located in a Stalin building built in 1960 with a ceiling height of 3.1 meters.
The volume of the room is 3x4x3.1 = 37.2 cubic meters.
Accordingly, the radiators must have a power of 37.2x40 = 1488 watts. Let's take into account the regional coefficient of 0.7: 1488 x 0.7 = 1041 watts, or six sections of cast-iron fierce horror under the window. Why horror? The appearance and constant leaks between sections after several years of operation do not cause delight.
If we remember that the price of a cast iron section is higher than that of an aluminum or bimetallic imported heating radiator, the idea of buying such a heating device really begins to cause a slight panic.
Refined calculation by volume
A more accurate calculation of heating systems is carried out taking into account a larger number of variables:
- Number of doors and windows. The average heat loss through a standard size window is 100 watts, through a door - 200.
- The location of the room at the end or corner of the house will force us to use a coefficient of 1.1 - 1.3, depending on the material and thickness of the walls of the building.
- For private houses, a coefficient of 1.5 is used, since heat loss through the floor and roof is much higher. Above and below are not warm apartments, but the street...
The basic value is the same 40 watts per cubic meter and the same regional coefficients as when calculating by room area.
Let's calculate the thermal power of heating radiators for a room with the same dimensions as in the previous example, but mentally transfer it to the corner of a private house in Oymyakon (the average temperature in January is -54 C, the minimum during the observation period is 82). The situation is aggravated by the door to the street and the window from which cheerful reindeer herders are visible.
We have already achieved the basic power, taking into account only the volume of the room: 1488 watts.
The window and door will add 300 watts. 1488+300=1788.
A private house. Cold floor and heat leakage through the roof. 1788x1.5=2682.
The angle of the house will force us to apply a factor of 1.3. 2682x1.3=3486.6 watts.
By the way, in corner rooms, heating devices should be mounted on both external walls.
Finally, the warm and gentle climate of the Oymyakon ulus of Yakutia leads us to the idea that the result obtained can be multiplied by a regional coefficient of 2.0. 6973.2 watts required to heat a small room!
https://youtube.com/watch?v=mVNWfHKN-Pw
We are already familiar with the calculation of the number of heating radiators. The total number of cast iron or aluminum sections will be 6973.2/180=39 sections, rounded up. With a section length of 93 millimeters, the accordion under the window will have a length of 3.6 meters, that is, it will barely fit along the longer of the walls...
“- Ten sections? A good start!" — with this phrase a resident of Yakutia will comment on this photo.
pros
A steel panel radiator of any type has the following advantages:
- high heat transfer at low cost;
- the ability to create an interesting design due to a wide selection of colors, shapes and sizes;
- the ability to independently regulate the air temperature and calculate the heating area;
- small volume and weight;
- radiators are resistant to chemical solutions, including alkaline ones;
- optimal combination of radiator and convector properties.