Heating is the most important engineering section, without which comfortable living in a cottage is impossible.
Heating a private home must be done correctly, and this is a great art. It is necessary to have knowledge of many subtleties and nuances in order not to make mistakes. Such knowledge can only be provided by a combination of theory and practical experience. If you have questions about organizing the proper heating of a private home and require advice from an engineer, call or write to us. Subject matter experts will be happy to answer questions and explain any nuances that interest you.
Selecting a heating system
Choosing a heating system for a cottage is not an easy task. There are many pros and cons to consider. In this case, it is necessary to consider and analyze the following parameters:
- Fuel availability
- Reliability – the technologies used must be time-tested
- The cost of both the heating system itself and its operation and maintenance
- The prevalence of technologies used to heat a home and the availability of specialists to carry out regular maintenance
- Maintainability
- Appearance and design compatibility
- Individual wishes and their feasibility without loss of overall quality of the heating system
Next, we tried to reveal the main nuances, knowledge of which will help you make an informed choice. If you have any questions, you can always contact us for advice.
Types of heating in a private house
All heating systems can be classified according to the following parameters:
By fuel type
Depending on the fuel consumed, heating systems installed in private country houses can be of the following types:
- Gas (mainline or liquefied gas)
- Electrical
- Solid fuel (firewood, sawdust, pellets, coal, etc.)
- Liquid fuel (diesel fuel, waste oil, etc.)
- Geothermal – systems based on renewable (alternative) energy sources
They all have their own advantages and disadvantages. Natural gas is the optimal fuel for Moscow and the Moscow region. If a country house has the ability to connect to a gas main, then you can choose this option without hesitation.
By type of coolant
Based on the type of coolant used in the heating circuit, home heating can be of the following classes:
- Vodyanoye
- Air
- Steam
- Combined - combining several types of coolant
In Moscow and the Moscow region, the most common type of heating is the use of water heating systems. It is on them that we will dwell in more detail.
Liquid fuel boilers
In terms of the cost of heating equipment and its installation, heating with waste oil or diesel fuel will cost approximately the same as with natural gas. Their efficiency indicators are also similar, although the processing, for obvious reasons, is somewhat inferior. Another thing is that this type of heating can easily be called the dirtiest. Any visit to the boiler room will end with at least the smell of diesel fuel or dirty hands. And the annual cleaning of the unit is a whole event, after which you will be smeared with soot up to your waist.
Using diesel fuel for heating is not the most profitable solution; the price of fuel can hit your pocket hard. Used oil has also risen in price, unless you have some cheap source. This means that it makes sense to install a diesel boiler when there are no other energy sources or, in the future, a main gas supply. The unit easily switches from diesel fuel to gas, but the exhaust furnace will not be able to burn methane.
Calculation of the home heating system
In order to be absolutely sure that the heating system of your cottage will function correctly, it is necessary to carry out design. But if the cottage is small, then designing may not be necessary. In this case, it is necessary to carry out an engineering calculation of heat loss.
The essence of the calculation comes down to determining the required thermal power. It characterizes the amount of heat that needs to be transferred to each heated room of the cottage. The required heat output corresponds to the heat losses. Heat loss is the amount of heat that leaves a country house through its enclosing structures (thermal circuit).
Calculation of heat losses is performed for each individual room and the cottage as a whole. Based on this, a heating boiler is selected, and radiators or other heating devices are selected.
There is a simplified method that allows you to calculate the approximate thermal power required for each room in a country private house. To do this, the area of the room is multiplied by 100-130 W (depending on how many external walls there are). However, this method gives approximate results that do not take into account a number of factors.
There are special formulas for accurate calculations. First, the thermal resistance R is determined (in m2*C/W). It is equal to the ratio of the thickness of the enclosing structures (in meters) to their thermal conductivity. This is a table value.
| Material | Thickness | R |
| Brick | 0.8 m | 0,6 |
| 0.7 m | 0,5 | |
| 0.6 m | 0,4 | |
| 0.3 m | 0,2 | |
| Log | 0.3 m | 0,6 |
| 0.2 m | 0,5 | |
| timber | 0.2 m | 0,8 |
| 0.1 m | 0,4 | |
| Insulated frame | 0.2 m | 0,7 |
| Foam concrete | 0.3 m | 0,7 |
| 0.2 m | 0,5 | |
| Plaster | 0,03 | 0,04 |
| Ceiling or attic floor | 1,4 | |
| Wooden floor | 1,9 | |
| Wooden double door | 0,2 | |
After this, a formula is applied to calculate the amount of heat loss (in Watts) that occurs through the thermal circuit:
Q = S*(Tin-Tout) /R
S – area of the heated room,
Tin - required room temperature,
Tnar is the minimum outdoor temperature during the coldest period of the year.
Thermal energy is also consumed through ventilation (both natural and forced). Its quantity is calculated using the following formula:
Q=c*m*(Tvn-Tnar)
m is the mass of air in the premises (the product of the total volume of the premises and the density of the air, c is its heat capacity, which is equal to 0.28 W/kg*C).
To calculate the required total thermal power, you need to add up the amount of heat loss through the walls, floor, roof and through ventilation. Multiply the resulting amount by a factor of 1.3.
In addition to thermal calculations, hydraulic calculations can also be performed. It serves as the basis for choosing pipeline diameters and parameters of pumping groups. This calculation is part of the heating project.
Selection by power and methods of connecting radiators
The number of sections or the size of a panel radiator is selected based on the amount of heat required to heat the room. We have already determined this value at the very beginning; it remains to reveal a couple of nuances. The fact is that the manufacturer indicates the heat transfer of the section for a temperature difference between the coolant and the air in the room equal to 70 °C. To do this, the water in the battery must warm up to at least 90 ° C, which happens very rarely.
It turns out that the real thermal power of the device will be significantly lower than that indicated in the passport, because usually the temperature in the boiler is maintained at 60-70 ° C on the coldest days. Accordingly, for proper heating of the premises, the installation of radiators with at least one and a half heat transfer margin is required. For example, when a room needs 2 kW of heat, you must take heating devices with a capacity of at least 2 x 1.5 = 3 kW.
Indoors, batteries are placed in places of greatest heat loss - under windows or near blank external walls. In this case, connection to highways can be done in several ways:
- lateral one-sided;
- diagonal scalene;
- lower - if the radiator has appropriate pipes.
The lateral connection of the device on one side is most often used when connecting it to risers, and the diagonal connection to horizontally laid highways. These 2 methods allow you to effectively use the entire surface of the battery, which will heat evenly.
When a single-pipe heating system is installed, the lower versatile connection is also used. But then the efficiency of the device decreases, and hence the heat transfer. The difference in surface heating is illustrated in the figure:
There are models of radiators where the design provides for connection of pipes from below. Such devices have internal wiring and, in fact, they have a one-sided side circuit. This can be clearly seen in the figure, where the battery is shown in section.
A lot of useful information on the issue of choosing heating devices can be found by watching the video:
Coolant circulation
Depending on the method of moving the coolant through the pipes, home heating can be designed in two ways:
Option with forced coolant circulation
For a heating scheme for a private house with forced circulation, it is necessary to install a circulation pump in the heating system. It ensures the movement of heated liquid through pipes to the radiators. In this case, no tilting of the highways is required. When radiators are installed in the system, it is necessary to install Mayevsky taps on them to displace air pockets. The cooled coolant is supplied through the return circuit back to the boiler room.
The advantages of the option with forced movement of the coolant are:
- High speed of coolant movement. As a result, the liquid in the return circuit practically does not cool down. This allows you to optimize the use of fuel or electricity (depending on the type of boiler)
- Possibility of adjusting the temperature regime of each heating device
- Minimizing the internal cross-section of pipes without reducing the resistance of the medium in the mains
Option with natural coolant circulation
Other names used for this system built on the basis of this option are gravitational, convective. Heating a private house with natural coolant circulation is an economical option
The operating principle is as follows. When heated, the density of water decreases. Therefore, the hot water in the supply circuit is forced upward by the heavier cooled water in the return circuit.
To prevent water hammer due to an increase in volume (and, as a consequence, coolant pressure in the system), an expansion tank is installed in the upper part of the system. As a result, the hotter layers enter the radiators, and the cooled coolant enters the boiler through the return circuit.
In addition to the convection principle, the gravitational principle also works in this heating scheme for a private cottage. To do this, a slight slope is made in the incoming circuit from the riser to the heating devices, increasing the movement of the coolant by gravity. Accordingly, the return circuit provides for a slope in the direction of the boiler.
This method has few advantages:
- Low price
- There is no need for a circulation pump, which requires power supply. This allows for a heating system independent of electricity (provided that an appropriate boiler is used)
The main disadvantages of such a heating system are that a scheme with natural coolant circulation has a low level of comfort and reliability.
Boiler connection
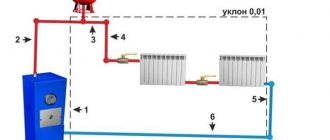
It should be noted that the wiring of gas, diesel and electric heat generators is almost the same. Here we must take into account that the vast majority of wall-mounted boilers are equipped with a built-in circulation pump, and many models are equipped with an expansion tank. First, let's look at the connection diagram for a simple gas or diesel unit:
The figure shows a diagram of a closed system with a membrane expansion tank and forced circulation. This tying method is the most common. The pump with a bypass line and a sump tank is located on the return line, and there is also an expansion tank there. The pressure is controlled using pressure gauges, and air is removed from the boiler circuit through an automatic air vent.
Note. Piping an electric boiler that is not equipped with a pump is carried out according to the same principle.
When the heat generator is equipped with its own pump, as well as a circuit for heating water for domestic hot water needs, the pipe layout and installation of elements is as follows:
Shown here is a wall-mounted boiler with forced air injection into a closed combustion chamber. To remove flue gases, a double-walled coaxial flue is used, which is led out horizontally through the wall. If the firebox of the unit is open, then you need a traditional chimney with good natural draft. How to properly install a chimney pipe made of sandwich modules is shown in the figure:
In country houses with a large area, it is often necessary to connect a boiler with several heating circuits - a radiator, heated floors and an indirect heating boiler for DHW needs. In such a situation, the optimal solution would be to use a hydraulic separator. It will allow you to organize independent circulation of coolant in the boiler circuit and at the same time serve as a distribution comb for the remaining branches. Then the basic heating diagram for a two-story house will look like this:
According to this scheme, each heating circuit has its own pump, thanks to which it operates independently of the others. Since coolant with a temperature of no more than 45 ° C should be supplied to heated floors, three-way valves are used on these branches. They add hot water from the main line when the temperature of the coolant in the heated floor circuits drops.
With solid fuel heat generators the situation is more complicated. Their strapping should take into account 2 points:
- possible overheating due to the inertia of the unit; the firewood cannot be extinguished quickly;
- formation of condensation when cold water enters the boiler tank from the network.
To avoid overheating and possible boiling, the circulation pump is always placed on the return side, and on the supply side there should be a safety group located immediately behind the heat generator. It consists of three elements: a pressure gauge, an automatic air vent and a safety valve. The presence of the latter is crucial; it is the valve that will relieve excess pressure when the coolant overheats. If you decide to heat your house with wood, then the following wiring diagram is required:
Here, a bypass and a three-way valve protect the furnace of the unit from condensation. The valve will not allow water from the system into the small circuit until the temperature in it reaches 55 °C. Detailed information on this issue can be obtained by watching the video:
Advice. Due to the nature of their operation, solid fuel boilers are recommended to be used in conjunction with a buffer tank - a heat accumulator, as shown in the diagram:
Many homeowners install two different heat sources in the furnace room. They must be properly tied and connected to the system. For this case, we offer 2 schemes, one of them is for a solid fuel and an electric boiler working together with radiator heating.
The second scheme combines a gas and wood heat generator, supplying heat to heat the house and prepare water for hot water supply:
Methods for laying heating pipelines
In the heating system of a cottage, pipes can be laid in two ways:
Open laying method
In this case, they are laid along the walls, parallel to the baseboards. Throughout their entire length they are within visibility range.
Advantages of this method:
- Access to pipes without dismantling structures
- Low heat loss
- Easy heating installation
Main disadvantages:
- The pipeline often spoils the appearance of the premises and does not fit into the design
- To avoid sagging and deformation, not all types of pipes can be used
Hidden laying method
The pipe is walled up in the wall, in the floor or decorated with external material.
The main advantages of hidden pipeline installation:
- Possibility to hide highways so they don’t spoil the interior
- Possibility to use pipes made from modern materials
The disadvantages include:
- Access to pipes is difficult in case of need for possible repairs, replacement of individual sections, or elimination of emergency situations
- Due to large heat losses, the lines must be thermally insulated
When performing hidden routing, you must use only reliable and proven pipes. The best option is pipes made of cross-linked polyethylene.
Filling the coolant with this method must be performed only after a hydraulic test of the heating system.
Basic rules for installing heating pipelines
It must be remembered that pipeline routing is performed after all heating devices are installed in the selected locations. The optimal sequence of installation operations is as follows:
Marking the passage of heating pipes
It is better to do this in advance, before installation. During the marking process, as a rule, installation difficulties are revealed that are caused by the architectural and construction features of the cottage. Knowing them, you can prepare in advance to solve them or change routes.
Most often, highway marks are applied to the walls. In some cases, they can be performed on the floor, but in this case they can be rubbed down by people passing through the premises.
Making the necessary technological holes and grooves
It is also better to complete this stage in advance throughout the entire work area. The locations of the required holes and the passage of the grooves are determined during the marking.
The grooves can be cut with a wall chaser. If this tool is not available, then they are first marked with a grinder and then hollowed out with a hammer drill.
Pipe insulation
This must be done if hidden wiring is performed. The main purpose of insulation is to prevent heat loss and increase the efficiency of the system as a whole.
Insulation is carried out with a special heat insulator, which is made according to the diameter of the pipes. It is put on the pipes manually at the installation site. Rubber-based heat insulator is considered the most effective and durable. But its price is also higher compared to analogues.
Laying and securing pipes on building structures
Pipes must be secured not only with open, but also with hidden wiring of the heating system of a private cottage.
With open wiring, the pipes are attached to the walls with special clips. Self-tapping screws or nails are used as fasteners (depending on the wall material).
If hidden wiring is performed, then the pipes are secured to the wall in grooves or to the floor with special clamps or punched tape. If the main consists of several pipes, for example, coming from the collector, then they must be fastened into loops. The fasteners that are used are the same.
Connection to heating devices
Depending on the design of the radiator, pipes can be connected to it either directly or via multiflex. In any case, connection fittings are used for connection, which are supplied in the kit.
When manifold wiring the heating system of a private house, the connection is made not only to heating devices, but also to floor collectors. As in the previous case, connection is made using complete connecting fittings.
Hydraulic and pneumatic tests
This is a necessary component of installation work. During the process, the system is filled with water or air. Then, using a special pump or compressor, excess pressure is created in it (~1.5 workers when testing with water). After an hour, the results are taken - there should be no drop in pressure.
If during testing there is a drop in pressure in the system, then leak points are identified. Then work is carried out to eliminate the causes of the leak. After this, hydraulic tests of the system are carried out again.
Sealing holes
Filling the floor screed and sealing the grooves when laying hidden pipes must be done only after successful hydraulic tests. This is general construction work. The sealing of grooves is usually done manually, most often with plaster.
Registration of permits for the installation of autonomous heating
To install an autonomous heating system in a country house, you will have to contact the rural or city administration at your place of residence, since the installation of such a system is a reconstruction or redevelopment of the premises, you will need the following documents:
- Application in the approved form, which is specified in Government Decree No. 266 dated April 25, 2005.
- Certificate of ownership with accompanying documents: state registration, agreements of donation or transfer of ownership of housing, notarized right of inheritance.
- With shared participation, confirmation of real estate ownership will be required from all owners and their consent to install the system (signature of all residents on the application).
- A photocopy of the technical passport of the premises.
- Confirmation by architectural authorities and organizations involved in the protection of monuments, the status of housing - whether it represents architectural, historical or cultural value.
- A project for installation or redevelopment, consisting of a plan for the placement of a gas pipeline and the installation of a boiler.
- When installing a powerful electric boiler (if the value exceeds 30 kW), you will need a copy of its passport with confirmation of the maximum power, and a power supply agreement.
- A home renovation project (moving or dismantling internal partitions, walls, door and window openings), if it occurs during the installation of equipment. It is compiled by the design organization; the documents contain basic information on the installed system and technical calculations. Design solutions are also coordinated with fire services, sanitary and epidemiological stations, and gas workers.
- Technical conditions for connecting the gas main (issued by gas distribution government organizations or private owners of fuel and communications), ventilation devices in the room with the boiler.
This package of documents is submitted to the interdepartmental commission responsible for the operation of the housing stock and located in the administration; you should expect a response in about 45 days.
After the connection and installation of networks by the relevant services, an acceptance certificate is drawn up, a copy of which is submitted to the real estate registration service.
Rice. 19 Installed liquid fuel boiler
Collector (radial, fan) heating scheme
With manifold wiring, each heating device is connected to the distribution manifold by two lines - supply and return.
The main advantage of collector heating is that the circuit allows you to regulate the temperature of the coolant on each specific heating device or in each of the circuits in the water heated floor system.
When using heating pipelines made of modern materials (for example, cross-linked polyethylene or metal plastic), there are no pipe joints between the collectors and heating devices. This increases system reliability. In this case, there is no need to worry about the formation of leaks in hidden cavities. The collector heating circuit for a private house is carried out only in a hidden way. In cottages, this type of wiring is in demand more than others.
Recommendations for the selection and installation of pipes
To install the heating of a private house with your own hands, you first need to decide which pipes to choose for this. The modern market offers several types of metal and polymer pipes suitable for heating private homes:
- steel;
- copper;
- stainless steel;
- polypropylene (PPR);
- polyethylene (PEX, PE-RT);
- metal-plastic.
Heating lines made of ordinary “ferrous” metal are considered a relic of the past, since they are most susceptible to corrosion and “overgrowth” of the flow area. In addition, it is not easy to independently install such pipes: you need good welding skills to make a hermetically sealed joint. However, some homeowners still use steel pipes to this day when they install autonomous heating at home.
Copper or stainless steel pipes are an excellent choice, but they are too expensive. These are reliable and durable materials that are not afraid of high pressure and temperature, so if you have the means, these products are definitely recommended for use. Copper is joined by soldering, which also requires some skills, and stainless steel is joined using dismountable or press fittings. Preference should be given to the latter, especially when the installation is hidden.
Advice. For piping boilers and laying pipelines within the boiler room, it is best to use any type of metal pipes.
Heating made from polypropylene will cost you the cheapest. Of all types of PPR pipes, you need to choose those that are reinforced with aluminum foil or fiberglass. The low price of the material is their only advantage, since installing heating from polypropylene pipes is quite a complex and responsible task. And in appearance, polypropylene is inferior to other plastic products.
The joints of PPR pipelines with fittings are made by soldering, and it is not possible to check their quality. When the heating was insufficient during soldering, the connection will certainly leak later, but if it is overheated, the melted polymer will half block the flow area. Moreover, you won’t be able to see this during assembly; flaws will make themselves known later, during operation. The second significant drawback is the large elongation of the material during heating. To avoid “saber” bends, the pipe must be mounted on movable supports, and a gap must be left between the ends of the line and the wall.
Recommendation. Do not embed polypropylene products into floor screeds or wall strobes. This is especially true for pipe joints.
It is much easier to make your own heating from polyethylene or metal-plastic pipes. Although the price of these materials is higher than polypropylene. For a beginner, they are the most convenient, since the joints here are made quite simply. Pipelines can be laid in a screed or wall, but with one condition: connections must be made using press fittings, not collapsible ones.
Metal-plastic and polyethylene are used both for open laying of highways and hidden behind any screens, as well as for the installation of water-heated floors. The disadvantage of PEX pipes is that it tends to return to its original state, which can cause the installed heating manifold to appear slightly wavy. PE-RT polyethylene and metal-plastic do not have such a “memory” and easily bend as you need. More information about choosing pipes is described in the video:
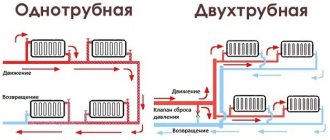
Two-pipe scheme
Heating a house with a two-pipe circuit involves connecting radiators in series. The lines are common to all heating devices.
There are two options for implementing a two-pipe system:
Two-pipe associated (Tichelman loop)
The movement of the coolant in the forward and return circuits occurs in one direction. The return circuit starts from the first radiator, and the supply circuit ends last. The correct movement of the coolant is organized by selecting the diameter of the pipelines. Using a Tichelman loop, you can achieve uniform heating of rooms.
Double-pipe dead-end
It differs from the previous type in the multidirectional movement of the coolant in the forward and return circuits and consists of several branches (arms). The last radiator in each branch is a dead end. The return circuit begins from this radiator.
A two-pipe dead-end heating system scheme is more difficult to implement than a passing one. Careful calculation of the hydraulic component of the system is necessary. In addition, it is necessary to maintain equality of load on each shoulder. It is recommended to equip each arm with no more than five heating devices.
The advantages of two-pipe systems are low sales price and reliable operation (compared to single-pipe systems).
One of the disadvantages is the need for a large number of heating pipe connections. This significantly reduces the reliability of the system, and is especially critical when the installation is hidden.
In addition, there is no possibility of individually configuring each heating device separately, which often does not allow setting the required temperature in a particular room.
With a two-pipe distribution, the lines can be laid both openly and hidden. In the first case, pipes made of copper or polypropylene are usually used, in the second - from cross-linked polyethylene. Cross-linked polyethylene is used due to the increased reliability of the connection between the pipe and the fitting.
Single-pipe scheme (“Leningrad”)
Single-pipe heating distribution is an outdated scheme, but sometimes still used. It uses one pipe, forming a ring circuit. Radiators are connected in series to this pipe. Through this pipe the coolant is supplied to the radiators and through it it goes back to the boiler.
The only advantage of the Leningradka is its low price. A significant drawback is the different temperatures of the coolant in the radiators. The radiators furthest from the boiler do not heat up enough. For heating in private houses in today's realities, the Leningrad scheme is practically not used precisely because of this.
Recommendations for choosing and connecting radiators
An ordinary homeowner, going to a heating equipment store and seeing a wide selection of different radiators there, can conclude that choosing batteries for his home is not so easy. But this is the first impression; in fact, there are not so many varieties of them:
- aluminum;
- bimetallic;
- steel panel and tubular;
- cast iron
Note. There are also designer water heating devices of a wide variety of types, but they are expensive and deserve a separate detailed description.
Sectional batteries made of aluminum alloy have the best heat transfer rates; bimetallic heaters are not far behind them. The difference between the two is that the former are made entirely of alloy, while the latter have a tubular steel frame inside. This was done for the purpose of using the devices in centralized heat supply systems of high-rise buildings, where the pressure can be quite high. Therefore, installing bimetallic radiators in a private cottage makes no sense at all.
It should be noted that heating installation in a private home will be cheaper if you purchase steel panel radiators. Yes, their heat transfer rates are lower than those of aluminum ones, but in practice you are unlikely to feel the difference. As for reliability and durability, the devices will successfully serve you for at least 20 years, or even more. In turn, tubular batteries are much more expensive, in this respect they are closer to designer ones.
Steel and aluminum heating devices have one useful quality in common: they lend themselves well to automatic control using thermostatic valves. The same cannot be said about massive cast iron batteries, on which it is pointless to install such valves. This is due to the ability of cast iron to heat up for a long time and then retain heat for some time. Also because of this, the rate of heating of the premises is reduced.
If we touch on the issue of appearance aesthetics, then the cast-iron retro radiators currently offered are much more beautiful than any other batteries. But they also cost incredible amounts of money, and inexpensive Soviet-style accordions MS-140 are only suitable for a one-story country house. From the above, the conclusion suggests itself:
For a private home, buy those heating devices that you like best and are comfortable with in terms of cost. Just take into account their features and choose the right size and thermal power.
Heating pipe materials
When developing a system, depending on the method of laying pipes, their material is selected. This is due to its thermal expansion and flexibility.
For example, steel pipes can be laid both inside and outside. It is recommended to lay cross-linked polyethylene and metal plastic in a hidden way. The open method of laying them is undesirable, since due to significant sagging the aesthetics of the interior are disrupted. It is advisable to lay polypropylene lines openly. Otherwise, possible leaks at the joints may not be detected in time.
Next, we will take a closer look at the main types of heating pipelines and list their main advantages and disadvantages.
Cross-linked polyethylene
Modern technologies for manufacturing pipes from this material make it possible to achieve high consumer properties. Pipes made using cross-linking methods are labeled PEX.
Leading manufacturers of cross-linked polyethylene pipes produce press fittings for them. They are crimped using a special tool. The resulting compounds are highly durable.
Advantages:
- Flexibility, tensile strength, ability to return to its original state even with severe deformation
- Ability to withstand high pressure - up to 10-12 atmospheres
- Simple heating installation when using these pipes
- Resistance to high temperatures and aggressive environments
Flaws:
- UV Vulnerability
- Softness of the coating (this can lead to the pipe walls being eaten by mice and rats). This is also why such pipes are used mainly in internal communications. It is recommended to lay them in the ground in metal shells
- XLPE pipes and fittings for them are relatively expensive
- High cost of tools for joining a pipe with a fitting
Polypropylene
This is a lightweight material obtained from petroleum products. Both the pipes themselves and fittings are made from it. The pipes are connected to each other using fittings using the soldering method.
Advantages:
- Low price
- Resistance to aggressive chemicals
- Easy to assemble
- Low price tools for soldering joints
Flaws:
- Deterioration of properties under the influence of sunlight
- Flammability
- Criticality to high (above 70 degrees C) coolant temperature
- Low durability
Installation of heating in a private house using polypropylene pipes is used when the internal heating system is laid open.
Modern polypropylene pipes, in order to improve their consumer qualities and reliability, are reinforced. Reinforcement materials are fiberglass or aluminum. The best option for heating is glass fiber reinforced polypropylene.
Metal-plastic
The name of the material reflects its structure. It consists of layers of polyethylene, aluminum and an adhesive layer. Pipes made from this material are used with brass fittings.
Advantages:
- High strength
- Durability
- Resistance to high temperatures, sunlight and aggressive environments
- Flexibility
- Ease of installation of metal-plastic pipes
Flaws:
- Weak resistance to system pressure
- Relatively high cost
- Tendency to thermal deformation
- Delamination when the maximum permissible pressure is exceeded
- High cost and lack of versatility of the tool for working with the material
Heating in a private house with metal-plastic pipes is used mainly for internal installation.
Steel
This material is traditionally used for the manufacture of heating pipelines. Until recently, almost all pipes for heating premises were made only from this material. Connections between lines are carried out by welding or using threaded fittings.
Advantages:
- High strength, resistance to mechanical loads
- Ability to withstand any temperature and coolant pressure
- Low price
- Low coefficient of thermal expansion
Flaws:
- Labor-intensive and complex installation of heating in a private house using these pipes
- Lack of flexibility
- Susceptibility to corrosion
- Internal overgrowth
- The service life (compared to modern materials) is relatively short - up to 15-20 years, depending on operating conditions.
Copper
Heating systems built on copper pipes are rare. The reason is the high price of such pipelines.
Advantages:
- High strength, resistance to mechanical stress, high temperature and pressure
- Long service life
- No corrosion
- Aesthetics (with open gasket)
Flaws:
- High price of material
- Criticality to the presence of impurities in the coolant and its composition
- Labor-intensive installation of heating in the house
- Negative galvanic processes when joining with certain materials
It should be remembered that installing copper pipes in front of steel pipes and radiators is unacceptable. This leads to negative galvanic processes. To avoid this, it is necessary to lay copper pipes after the steel sections along the flow of the coolant or make a galvanic gasket from a neutral material (for example, bronze, brass).
Stainless steel
Heating a house from stainless steel pipes is significantly more expensive, but they do not have one of the main disadvantages - susceptibility to corrosion. As a result, stainless steel pipelines last much longer and can be used in almost any heating systems. But their cost is very high and they are used in very rare cases.
Bellows pipes
They are corrugated flexible stainless steel hoses. They are not often used in heating systems. Sometimes they act as inlets to radiators or convectors, if the use of ordinary pipes for this purpose is difficult for some reason.
Construction of houses
0 votes
+
Vote for!
—
Vote against!
It makes no sense to prove that for comfortable year-round living in a cottage, it is necessary to install heating. Everyone already understands this. Many are interested in specific applied questions, which heating system to choose, what are the features of its arrangement and installation, and whether they can do everything themselves. All this can really be confusing, not so much because of the complexity, but because of the variety. The good old stove heating has sunk into oblivion; today the market can offer a lot of innovative and economical solutions that are easy to use and maintain. Therefore, within the framework of this article, we will talk about how you can arrange the heating of a cottage, what heating wiring diagrams exist, how to choose a boiler, radiators and heating pipes. We will also touch on applied issues: how to make a heating project and calculate everything, how to install the system yourself and what are the nuances.
- Cottage heating systems - which one to choose
- Coolant in heating systems
- Energy carrier/fuel for heating boiler
- Method for implementing a heating system with liquid coolant
- Cottage heating system diagram
- Which heating radiators to choose
- Heating radiators made of various materials
- Heating radiator power
- How to choose a heating boiler
- Which heating pipes to choose
- DIY cottage heating
- Cottage heating design
- Construction of a boiler room and installation of a heating boiler
- Installation of heating radiators
- Installation of heating system piping
- Starting the heating system
Cottage heating systems - which one to choose
There are several gradations by which heating systems differ. Let's start with the main one - the type of coolant that, by giving off heat, heats the room.
Coolant in heating systems
Based on the type of coolant, cottage heating systems are divided into water, electric, air and open fire. The latter are a stove, stove or fireplace; they can successfully heat a small one-story house, but the heat will spread unevenly: it will be hot right next to the fireplace, but cold at a distance, the floor will also be cold.
The water system is the most common; more than 90% of heating cases are implemented using it. It is a closed circuit that contains a boiler that heats water, pipes and radiators through which the water heated in the boiler moves, a circulation pump, an expansion tank or other related elements. Hot water moves from the boiler through pipes and radiators, and then, after cooling in them, it returns to the boiler, where it is heated, and the cycle is repeated again and again.
Water heating can be realized using various heating devices. This can be a gas, electric, solid fuel boiler, diesel, as well as alternative energy sources (wind turbines, etc.). And instead of water, there may be antifreeze in the system. Installation of such a heating system with all equipment and design work will cost approximately 9,000 - 10,000 USD.
The electrical system can be represented by electric convectors, infrared long-wave heaters (ceiling) and a “warm floor” system. Its installation is very simple, you just need to buy heaters and install them in the right places. Thanks to this, the price for installing electric heating for a cottage is the lowest; for a cottage of 100 m2 you will have to spend approximately 1200 - 1500 USD. for the purchase and installation of equipment. But at the same time, monthly energy bills will be astronomical. In other words, it is difficult to call such heating economical.
The air heating system of the cottage is based on the circulation of hot air. The system has a heat generator that heats the air, air ducts through which heated air moves and cold air returns to the heat generator. The heated air rises through the air ducts into the heated room and exits under the ceiling in such a place as to displace the cold air that has accumulated near the door or window. Cold air is forced into other ducts leading back to the heat generator. Air circulation can be realized in two ways: gravitational circulation due to temperature differences and forced ventilation using a special fan. The first method has one significant drawback: if the doors or windows are open, the circulation is disrupted.
A heat generator for an air heating system can burn natural gas, diesel or kerosene, the combustion products go into the chimney. It is possible to equip such a heating system for a cottage only at the stage of its construction, since the design itself must include structural elements and increase the height of the room for convenient placement of air ducts. It will cost approximately 11,000 USD.
Conclusion! The most thorough, cost-effective, familiar and convenient is the water heating system. Almost everyone chooses it. Electric heating devices can only be considered as additional elements of the cottage heating system, so to speak, a backup option. Air heating has not yet gained mass popularity, although if you include it in a project, it can turn out much better than water heating.
Energy carrier/fuel for heating boiler
The second gradation, which is important when choosing a heating system, is the type of fuel/energy carrier burned (or consumed). The cost of heating a cottage per month will directly depend on the chosen energy source.
There are boilers running on natural gas, electricity , solid fuel and diesel . The last option is used extremely rarely. Heating with an electric boiler is used as a complement and backup option to a gas or solid fuel boiler, especially in regions where electricity is cheaper at night. Solid fuel boilers are used in areas where there is no main natural gas. In addition to boilers loaded with coal or wood, there are modern solid fuel boilers, such as Ferolli, that operate on pallets.
Important! The most economical and convenient is gas heating (until gas becomes more expensive) and its combinations: gas + electric or gas + solid fuel. In areas where there is no gas main, it is more advisable to install a combined solid fuel boiler + electric system.
Method for implementing a heating system with liquid coolant
Since the most common and widely available water heating system is a water heating system, let’s look at how to make heating in a cottage using its example.
Radiators under windows are a familiar way of heating. It has good heat transfer, but the radiators themselves are sensitive to the coolant. Although for a cottage with autonomous heating this is not significant. In a radiator system, heat rises from the radiator up to the ceiling, reducing the penetration of cold air into the room through the windows, then passes under the ceiling and falls along the walls to the floor, gradually cooling. The air returns along the floor to the wall with the radiator, where it is heated again.
Water heated floor is a system that allows you to make the temperature near the floor as comfortable as possible. Particularly relevant for families with small children. The water floor pipes are laid out over the entire area of the room and embedded in the screed or raised floor. The water circulating through the pipes heats the floor screed, the air near it is warmest, then it rises. Heated floors cannot be used as the only heating system in a cottage with year-round use, since our winters do not allow such a luxury. It can only be installed in addition to the radiator.
The baseboard heating system incorporates the best from the radiator and underfloor heating systems. The pipes are located along all the walls along the entire perimeter of the room - below, where the baseboard is. The heat spreads evenly: both to the floor and to the walls. The room warms up at all points approximately equally. Another advantage of such a system is that the space is not occupied by radiators and furniture can be arranged more organically.
As a result, it should be noted that radiator and baseboard heating can be installed both in a new cottage and in an already built one. But the “warm floor” system is installed only at the construction stage, otherwise the floor will have to be completely redone.
Cottage heating system diagram
After choosing the type of heating system, you need to decide on its layout. We chose a water heating system implemented using radiators under the windows - the most common case.
There are 3 different schemes according to which the heating system pipes can be laid out: single-pipe, two-pipe and collector.
A single-pipe heating circuit is a closed circuit in which water passes through pipes and radiators one after another as if in a chain, and only after leaving the last radiator in the system does it return back to the boiler. It turns out that the temperature in the radiator farthest from the boiler is the lowest. The result is uneven heating of the cottage. Such a system is installed only in small houses and cottages, where the water in the heating system does not have time to cool down much.
The two-pipe heating scheme for a cottage is a more advanced option. All radiators are connected to the hot water pipeline in parallel. Each radiator is connected to two pipes: through one, hot water from the boiler enters it, through the second, cooled water leaves. In such a system there are losses, but not as large as in a single-pipe system. The last radiator in the system will be cooler, but not much.
The collector system is an ideal option for large cottages and houses. In it, hot water from the boiler first enters the collector, which then distributes it to each radiator separately. In the same way, one return pipe departs from each radiator. The collector heating circuit allows you to regulate the temperature in each individual room and even on each individual radiator. Heating occurs evenly. The only drawback is the large number of pipes that somehow need to be routed around the house. Most often, the collector system is installed in houses under construction: it is convenient to hide the pipes in the floor screed.
Which heating radiators to choose
The correct choice of heating radiators is no less important than the choice of boiler. Moreover, the material used to make the radiator will affect its characteristics, durability and may impose certain restrictions on the composition of the water in the system and the material of the pipes. Size and shape are also important, but this is more a matter of convenience and aesthetics, since the main parameters are: material, size, power.
Heating radiators made of various materials
Cast iron radiators are the oldest type of heating appliances. They are not afraid of corrosion, high pressure (withstand 9 – 15 atmospheres), and high acidity of water. The room is heated evenly. But at the same time they have a lot of weight and some difficulties in installing the pipeline. After several years of oblivion and complete rejection, cast iron radiators are gaining popularity again. This is due to the fact that modern radiators are much smaller in size and beautifully designed so that they do not interfere with the overall interior design.
Aluminum radiators are currently the most popular choice. They have low weight, low price, beautiful design and high heat transfer, and can withstand high pressure of 10 - 16 atmospheres. But at the same time, aluminum is very sensitive to the composition and acid-base balance of water; it must have at least 7–8 pH. Also, in aluminum radiators it is necessary to remove air from the upper collector; their weakest point is the threaded connections. However, they are considered quite reliable.
Steel radiators heat up very quickly and give off heat, i.e. have high heat transfer. The room is heated comfortably with maximum efficiency. The price of each kW of heat generated has the lowest price compared to other types of radiators. For example, in the West, steel radiators are a mass solution.
Bimetallic radiators combine the advantages of aluminum and steel radiators, since they are an aluminum radiator in which a system of steel pipes is mounted through which water circulates. As a result, the radiators turned out to be strong, durable, can withstand very high pressures of 20 - 40 atmospheres, and are not afraid of aggressive liquids. But it is not advisable to use them in the heating system of a cottage.
The choice of heating radiators depends on the personal preferences of the owners; the main thing is to pay attention to their power.
Heating radiator power
An important parameter for choosing a heating radiator is power; it is indicated on the product itself and in the passport. It is marked something like this: 1700 W DN 70/50. Let's decipher it. This means that if water enters the radiator at a temperature of 70 °C, then passing through the radiator and cooling to 50 °C, 1.7 kW of energy is released.
But more often, manufacturers indicate power for another temperature range 90/70, which are used extremely rarely. Therefore, it is necessary to reduce the specified power by 30%. Then you will get an approximate return at coolant temperatures of 70/50. It is better to choose a radiator with a larger power - with a margin - than a smaller one.
size matters , since they are installed under the window sill on the basis that at least 10 cm should remain free above it (to the window sill) and 15 cm from the floor. Otherwise, normal air circulation will not occur. The size is usually indicated as follows: 500x1500. This means that the product is 1.5 m long and 50 cm high.
Connection points in radiators can also be located either at the bottom or at the top. Which one is needed in a particular case depends on the project and pipe layout.
When choosing a radiator, you must also take into account the specifics of the room, the thickness and location of the walls, the number of windows and doors. The power and size of the radiator, which are calculated in the heating project, directly depend on these indicators.
How to choose a heating boiler
There are gas , electric , solid fuel and diesel boilers . You need to choose the one whose energy source is the most accessible in your region and the cheapest.
In addition, it should be taken into account that for residents it is more convenient to use boilers that run on gas, diesel fuel and electricity, operating in automatic mode, i.e. they do not require constant outside intervention. Servicing of such boilers is carried out once a year, after the end of the heating season. And a solid fuel boiler must be constantly loaded with fuel (pallets). Despite the fact that there are combined boilers that use two types of fuel, it is better to choose the type of boiler that runs on only one coolant; it is more reliable.
Heating boilers are single-circuit and double-circuit. Single-circuit ones provide only heating or only heating of hot water for domestic needs. Dual circuits can perform both functions simultaneously. In cottages, either a double-circuit boiler or two single-circuit boilers are most often installed.
The boiler power is selected based on calculations carried out during the design. In fact, the boiler power is the total power of all installed radiators, plus 20-30% reserve.
Which heating pipes to choose
The most common and proven option for heating pipes over the years is steel pipes made of alloy steel . They are strong, durable, not afraid of water hammer and high pressure, high temperatures, and they are quite affordable. But at the same time, they rust over time, and suspensions settle inside and deposits build up; steel pipes also conduct stray currents, which leads to their rapid destruction. The biggest drawback is the complexity and labor-intensive installation (threading and welding).
Copper pipes are the most expensive and most ideal option for heating pipes. They are not afraid of rust, do not react to the composition of water, are flexible, and can withstand high pressure and temperature. But there are some restrictions on their use: they cannot be joined to products made of unalloyed steel, and when installed in plaster, they must be wrapped in a polyethylene coating to protect them from temperature deformation.
Corrugated stainless steel pipes are not yet universally popular, but in vain - because they are ideal for heating. In addition to the fact that they do not rust, are not afraid of high pressure and temperatures, fungus and mold, they are so flexible that they can be installed with a minimum number of joints, they have high heat transfer, so you can do without radiators altogether, laying only pipes.
Metal-plastic pipes are not subject to corrosion, do not accumulate deposits inside, are durable, flexible, so they are convenient to use in rooms with complex geometry. But at the same time, such pipes are afraid of ultraviolet radiation, mechanical stress and open fire (they burn). Detachable connections of metal-plastic pipes are not very reliable.
Polypropylene pipes are the most popular choice today. They have a lot of advantages: they do not rust, are not afraid of chemicals, do not make noise, durable, strong, relatively cheap (economically beneficial), connected monolithically and reliably. Mounted using a special welding machine.
The main disadvantage of plastic pipes is very dangerous - they burn. If there is suddenly a serious fire, all polypropylene pipes will burn out. You can guess for yourself what this will lead to. Therefore, when choosing, pay attention to this and think carefully.
DIY cottage heating
Arrangement of heating in a cottage is an extremely important task. Therefore, if you have even the slightest doubt that you can handle the design and installation yourself, it is better to turn to professionals. Or at least order a heating project from a design office, and then purchase all the necessary materials and carry out the installation, having studied the rules and instructions. This way you will at least be sure that you are making the right system.
Cottage heating design
Heating begins with a project. You should not rely on chance and on the average temperature in the room. You can start design calculations with a piece of paper. It is necessary to depict the cottage floor by floor with all the rooms and their sizes, and the locations of windows and doorways with dimensions should also be indicated. Then the material and thickness of the walls, floor and ceiling, and roof are indicated. This is necessary in order to calculate the heat loss of the cottage.
Heat loss can be calculated using the Valtec program or any other. It is in order to enter the parameters of the cottage into the calculation calculator that you will need a drawing on paper with dimensions and materials. In addition, you must specify the climate zone. The obtained value of the heat loss of the cottage is necessary in order to calculate the boiler power.
If, for example, the heat loss is 8 kW, then the boiler must be 20–25% more powerful, i.e. 10 – 12 kW.
The cottage heating project should include: the location of the boiler and chimney, the location of radiators in each room, their size and power, the diameter and material of the pipes, the layout of the heating pipes and the hydraulic calculation of the system. The power of each radiator should be indicated here; it is also calculated in heat loss and depends on the size of the room and the number of windows, external walls and doorways.
Once the project is ready, you can purchase a boiler, radiators, pipes and related materials and begin installation.
Construction of a boiler room and installation of a heating boiler
Installation of heating for a cottage begins with the installation of a boiler, for which it is necessary to allocate a special room, which in the project will be called a “boiler room”.
The boiler room can be located both inside and outside the cottage, but in any case, special requirements are imposed on it:
- Ceiling height not less than 2.5 m;
- Volume not less than 15 m3;
- Fire-resistant walls and floors made of non-combustible material;
- Window opening of at least 0.03 m2 per 1 m3 of room;
- Supply and exhaust ventilation with a chimney with a diameter of at least 130 mm, ensuring a threefold exchange of air in the room. Those. for 15 m3 it is necessary to provide 45 m3 of air in 1 hour;
- The door should open outwards;
- The boiler must be grounded;
- Free area in front of the boiler of at least 1 m2;
- Technological supply openings of at least 0.01 m2 in size for every 10 kW of the boiler. They can be performed in the boiler room door;
- The diameter of the chimney pipe must be no less than the diameter of the boiler pipe.
By the way, heating boilers can be floor-mounted or wall-mounted. Their installation is different, and there are fewer requirements for wall-mounted ones. Chimneys can also be implemented in various ways: a straight up pipe, a chimney in an adjacent wall, and a chimney that faces the street horizontally. A wall-mounted boiler can be connected to a chimney using a corrugated pipe, since the temperature of the exhaust gases is not too high, but floor-standing boilers can only be connected to a chimney using sheet iron.
Important! Before installing the boiler, be sure to read the instructions. The sequence of work and the necessary requirements will be indicated there.
To install a wall-mounted boiler, you need to select a location, then mark the mounting locations. The boiler comes with a mounting plate or bracket. We drill holes in the wall, fasten the strip and hang the boiler, connecting it to the chimney. There are pipe outlets at the bottom of the gas boiler. A single-circuit boiler has 3 pipes: hot water, return and gas. The double-circuit one has 5 pipes. We connect the gas pipeline to the boiler.
Installation of heating radiators
The radiator kit should also include brackets and dowels, a plug, 4 plugs and a Mayevsky tap. Additionally, it is necessary to purchase radiator taps and pipes: if the main pipeline pipe is 25 mm, then the inlet and outlet pipes to the radiator should be 20 mm, and if the main one is 32 mm, then the inlet and outlet pipes should be 25 mm, tees of the corresponding diameters, 2 for each radiator.
First, we outline places for installing radiators. We drill holes for the brackets and secure them.
Important! The brackets must be secured so that they are located between the radiator sections. We set them according to level - strictly horizontally. In order not to make a mistake with the dimensions (there should be 10 cm above the radiator, 15 cm below it), we attach the radiator to the wall and make notes.
We assemble the radiator: unscrew the threaded part from the radiator faucet, wrap tow or flax on the thread, lubricate it with plumbing paste designed for high temperatures, put on the union nut from the faucet and then screw it into the radiator cap. Using the same scheme, we screw the Mayevsky tap and plug into the remaining plugs.
Next, screw the plugs into the radiator. To do this, you can use standard gaskets, or you can also use flax or tow. Now we screw on the radiator taps.
At this stage, it is necessary to install sections of inlet and outlet pipes, as well as a bypass pipe, if designed. When cutting pipes for these sections, it should be taken into account that the pipe must go inside the part being connected.
Important! We make sure that the direction of the tee coincides with the direction of the radiator valve.
We fix the radiator to the brackets. We repeat the procedure for all radiators in the cottage.
Installation of heating system piping
Now you need to connect the boiler and all heating radiators with a pipeline. Various materials are used for this, but we will only consider stainless steel pipes, as they are among the best. And you will find instructions for installing polypropylene pipes. But remember, they burn.
Corrugated stainless steel pipes are sold in coils. Their flexibility makes installation very easy. You can lay a route with virtually no connections. For convenience, it is advisable to install a hydraulic pump after the boiler so that the water in the system circulates forcibly, then there is no need to ensure a mandatory slope of the pipeline.
We unwind the pipe and measure the required length from the boiler to the radiator. We cut with reserve. We connect it to the fitting, pressing the nut a little, insert the pipe into the fitting, then crimp it and everything is ready.
Then we connect it to the boiler in the hole from which hot water should come. We stretch the pipe to the radiator. This can be done openly along the wall, through the wall, or inside the wall in plaster, and difficult areas and doorways can be done in the floor. We attach the pipe to the radiator, or rather to the radiator valve. Then we fix it to the wall using fastening clips.
We install all other sections of the pipeline, both coming from the boiler and returning to it.
Starting the heating system
Before turning on the heating boiler, it is necessary to check the strength of all connections that we have made. To do this, the system must be pressure tested. This can be done with both air and water. In any case, it will be necessary to use a compressor and a pressure gauge. You can connect anywhere in the pipeline by simply unscrewing the Mayevsky tap.
Apply pressure 2 - 3 times more than working pressure. For example, if in autonomous heating systems there is usually 1.5 - 2 atmospheres, then we check at 5 atmospheres. We leave the system pressurized for at least a day. Then we check again, maybe it’s missing somewhere.
Important! If you pressurized simply with air, then leaks can be seen by smearing the connection with a soap solution.
If the test results are good, then we start the boiler and set it to 40 °C. We check whether all the radiators are filled, whether they are heated evenly, and whether all the return flow has returned to the boiler. Here we bleed air from the system using the Mayevsky valve. After satisfactory test results, we start the boiler at 60 - 80 °C. We also check the uniformity of heating and return temperature.
The heating system can now be used. As you can see, the installation of heating a cottage itself, although complex, is quite feasible for a person with intelligence and straight hands. But whether to do the design yourself is worth thinking about again. Nobody wants to freeze in winter when the boiler is at maximum load.
Heating devices
For water heating in a house, various types of heating devices can be used - radiators, convectors, registers, heated floors. We will tell you more about each of these devices below.
Radiators
The most common heating devices are radiators. They may differ in the number of sections (in addition, there are non-sectional radiators) and material. The larger the front surface area, the more heat the device generates.
Radiators are divided into the following types:
- Steel
- Panel
- Tubular
- Bimetallic sectional
- Aluminum sectional
- Cast iron
May have the following connection type:
- Lower
- Lateral
- Diagonal
Convectors
In addition to radiators, home heating can be done with water convectors. The principle of their operation is based on the fact that heated air rises, displacing cold air. This phenomenon is called convection, hence the name of this device. As a rule, convectors are installed under windows. The warm air coming up from them creates a “curtain” that blocks the flow of cold air from outside.
According to their location, convectors can be:
- Wall mounted
- Floor-standing
- Built-in
Wall-mounted units are attached to the wall using special brackets. They are lightweight, so, unlike radiators, they can be installed even on plasterboard partitions.
Floor convectors are mounted on the floor using the supplied legs. They are small in size but have high heat transfer.
Built-in convectors are installed in a niche under the floor. The grille located at the top of the device is flush with the floor. In some cases, this grille is decorated to match the style of the interior.
Based on the type of convection, convectors can be divided into devices:
- With natural convection
- With forced convection
In the first case, warm air flows flow upward, cold air flows downwards due to the difference in density, where, in turn, they are heated by the converter. This process then occurs cyclically, naturally.
In models with forced convection, electric fans are built into the devices. Due to the operation of fans, the convection process accelerates and heat transfer increases.
Convectors, as a rule, look more aesthetically pleasing than radiators, and built-in ones are not visible at all (except for the grille). Therefore, they are often installed when design is of great importance. They are also used where traditional radiators cannot be used, for example:
- In front of the glass doors of the balconies
- With “low windows”
Convectors are often used not only for heating residential premises, but also in swimming pools and winter gardens.
Gas heaters
Gas interior heaters differ from the “competitors” discussed above in their power source. In this case, the devices operate on liquefied gas.
The main advantages of the designs are ease of execution, safety in use, and complete independence from anything. With such a heater you don’t have to worry about the battery draining.
In addition, gas combustion products do not poison passengers, but are discharged into the street, which guarantees safety even for long-term use.
The principle of operation of the device is to circulate air flows in the car. Heat transfer occurs due to natural convection of air in the car.
For more active mixing, an additional low-power fan can be mounted in the cabin.
Gas autonomous heaters do not cause problems during operation; they have no rotating elements, which ensures maximum reliability and safety.
Structurally, the device is a system of coaxial pipes, when each of the subsequent pipes is located inside the other. One pipe carries clean air from the street, and the second pipe removes exhaust gases.
As a result, the air in the cabin is not used or burned out. All that remains is warmth.
The device does not depend on the performance of the car, so even if the engine breaks down or the battery is discharged in winter (even in an open field), you can turn on the device to enjoy the warmth.
The average lifespan of such devices is about 14 years.
Advantages of gas autonomous heaters:
- affordable price due to the lack of electronics in the device;
- the presence of a climate control system, which is found in most modern devices. At the same time, you can always set and maintain the optimal temperature;
- independence from vehicle resources, which guarantees performance in any conditions;
- the ability to power the device from cylinders of various capacities - 12 and 24 liters.
Basic operating rules:
- the heater can be turned on both when parked and while moving;
- to activate the device, just open the tap through which gas is supplied, turn on the device and start it;
- deactivation is carried out by triggering the corresponding toggle switch.
For example, a good option is SELENA PILOT-2 -E1. The heater requires only gas to operate.
Power - about 2 kW, heated area - up to 20 sq. meters. Thanks to this power, it can be used not only to heat the cabin, but also to warm up the space inside the body.
Gas autonomous heaters are used wherever autonomous heat is needed - in cars (trucks and cars), in the garage, when working on special equipment, and so on.
Registers
Another type of heating devices are registers. They are welded or assembled structures made of metal (usually steel) pipes. The pipes are connected to each other by jumpers through which the coolant circulates. Cottages are extremely rarely heated by registers, due to their unattractive appearance. Registers are most often used at industrial facilities.
Heating a house with water heated floors
In recent years, water-based heated floors have been gaining popularity. If the room is large, radiators do not always effectively heat the entire space, especially in the center of the room. In this case, in addition to radiators, it is advisable to install heated floors. The heated air rising from them evenly fills the entire space.
Water heated floor
A warm floor is a heating system consisting of plastic pipes poured into a concrete floor screed through which a coolant (usually water) flows, heated by a boiler. It is used in low temperature systems.
One of the important advantages of heated floors is uniform heating of the air. In a room heated with underfloor heating, there will be no overheated places or “cold corners”.
If thermal insulation is performed correctly, then a warm floor turns out to be the most comfortable and economical heating system. It is used both independently and in combination with panel steel heating radiators.
The disadvantage is the relatively high price. Installing a heated floor will cost 15-20% more than installing a heating system using only radiators.
Other components of the heating system
Heating a home, in addition to pipelines and heating devices, may include the following elements.
Circulation pump
The circulation pump is used in circuits with forced movement of coolant. A circulation pump is installed on the return pipe between the boiler and the nearest radiator located along this pipe.
The principle of its operation is as follows. The pump motor is driven by a rotating rotor. The pump begins to take coolant from the circuit on one side and push it through the pipes on the other.
Expansion tank
This is a steel tank with two chambers inside. These chambers are separated by a membrane. One of them is designed to be filled with water, the second is an air compensator.
Expansion tanks are installed in closed heating systems to compensate for possible water hammer.
Buffer capacity
Its purpose is to store a supply of heated coolant and ensure operation of the heating system for a certain time with the heat source turned off.
Heating in a house using solid fuel functions optimally when using this container. During the day, when a solid fuel boiler is operating, the coolant is heated in a buffer tank. And at night the cottage can be heated from this container with the boiler not working until the coolant has cooled down.
Solid fuel boilers
Solid fuel boilers are divided into 3 types: direct combustion, pyrolysis and pellet. The units are popular due to their low operating costs, because compared to other energy sources, firewood and coal are inexpensive. The exception is natural gas in the Russian Federation, but connecting to it is often more expensive than all the heating equipment including installation. Therefore, wood and coal boilers, which have an acceptable cost, are being purchased by people more and more often.
On the other hand, operating a solid fuel heat source is very similar to simple stove heating. You need to spend time and effort to prepare, carry firewood and load it into the firebox. The unit also requires serious piping to ensure its long-lasting and safe operation. After all, a conventional solid fuel boiler is characterized by inertia, that is, after closing the air damper, the heating of water does not stop immediately. And efficient use of generated energy is possible only if there is a heat accumulator.
Important. Boilers that burn solid fuels generally cannot boast of high efficiency. Traditional direct combustion units have an efficiency of about 75%, pyrolysis units - 80%, and pellet units - no more than 83%.
The best choice in terms of comfort is a pellet heat generator, characterized by a high level of automation and virtually no inertia. It does not require a heat accumulator and frequent trips to the boiler room. But the price of equipment and pellets often makes it inaccessible to a wide range of users.
Coolant
The main types of coolants in heating systems are water, various antifreezes and their mixtures in certain proportions.
Antifreeze is a liquid that is an aqueous solution of ethylene glycol, propylene glycol or potassium acetate with the addition of modifying additives. They lower its freezing point.
Heating a house using a coolant to which special inhibitors are added helps prevent oxidation, corrosion, and scale formation. Their content can range by weight from fractions of a percent to 3-4%.
Which coolant to choose is decided individually, depending on the situation. If the probability of boiler failure is low, there are no problems with fuel, it is better to use water. Many boiler manufacturers prohibit the use of antifreeze, and there are frequent cases of warranty denial on this basis.
Step-by-step instructions for beginners
Having no experience in matters of autonomous heating, it is better to give preference to electricity. Although the energy bill can boggle the mind, significant savings arise due to the ease of installation and operation of the device.
In any case, the development of the project and its implementation is carried out according to the following scheme:
- Calculate or order a heating system calculation from specialists.
- Add at least 20% margin to the calculated number of radiator sections. This will allow them to be used effectively throughout their entire service life, when the internal surfaces become coated.
- Radiators are being installed.
- The boiler is being installed.
- Pipes are run from the boiler to the radiators.
- Upon completion of installation, the system is tested for leaks.
If installation skills are not enough, it is better to invite an experienced locksmith, since you cannot allow the house to be flooded with hot water in winter.
Preparatory work
Before starting work on heating installation in a private house, it is necessary to carry out preparatory work. Their goal is to reduce the possibility of downtime for the installation team to a minimum during the work process. Preparatory work includes:
- Ensuring construction readiness - the thermal circuit must be closed, the premises must be cleared of construction debris, there must be interfloor ceilings or joists
- Construction of niches for the installation of radiators and manifold cabinets - if necessary
- Preparing the wall surface for installing radiators - preferably a fine finish
- Complete finishing of the boiler room
- Making all the necessary holes in the interfloor ceilings, making grooves and niches
Read other articles on this topic
| Heating options for a frame house | Heating system for a private house using a warm baseboard |
| Collector heating system for a private house | Features of heating a country house with electricity |
| About heating schemes for a private house with a gas boiler | Autonomous heating of a private house |
| Heating a private house with underfloor heating | Do-it-yourself heating of a private house made of polypropylene |
| Heating a private house with convectors | Basic rules for the location of radiators when heating a private house |
| Thermal trace - purpose, classification, use cases | Heating a private house from metal-plastic pipes |
| Infrared heating of houses | Heating the house with liquefied gas |
| Heating wiring diagrams from a boiler in a private house | Heating system for a private house with natural circulation |
| How to heat your home without gas | Combined heating system for a private house |
| Heating your home is the most economical way | Heating a private house with forced circulation |
| Heating diagram for a two-story house | The best heating for a private home |
| Installation of a heating system: rules and description | Gas consumption for heating a private house - consumption calculation |
| Installation of a heating system in a private house | How to save on heating a country house |
| Country house heating system | Heating a private house with a heat pump - pros and cons |
| Heating distribution for a two-story house | Heating a private house with electricity |
| How is pressure testing of a heating system performed? | Heating and water supply of a country house: description of installation technology |
| Heating project for a private house | Water heating in a private house |
Services on this topic
| Heating design | Turnkey solid fuel heating |
| Turnkey gas heating | Turnkey heating |
| Heating in a turnkey wooden house | Turnkey water heated floor |
| Installation of water heated floor | Heating a two-story house |
| Heating installation in a cottage | Heating a country house: options and prices |
| Heating installation | Heating installation in a private house |
| Installation of plumbing and heating engineering systems | Diesel heating of a country house |
| Autonomous heating on a turnkey basis | Air heating of a country house |
| Prices for heating installation in a private house | Design and installation of heating systems |
| Water heating in a private house | Electric heating of a country house: options and prices |
| Heating in a townhouse | Gas heating design |
| Heating design cost | Heating calculator for a private house |
| Installation of water heated floors in a private house | Price for installing a water heated floor |
| Installation of water heated floors on a wooden floor |
Recommendations for choosing a boiler
At the moment, there are various types of heating, characterized by the energy carrier or type of fuel used. Which one to choose is up to you, and we will present all types of boilers with a brief description of their pros and cons. To heat residential buildings, you can purchase the following types of household heat generators:
- solid fuel;
- gas;
- electrical;
- on liquid fuel.
The following video will help you choose an energy carrier, and then a heat source: