Updated: 02/19/2021 18:42:51
Expert: Andrey Nikolaevich Kuznetsov
*Review of the best according to the editors of expertology.ru. About the selection criteria. This material is subjective in nature, does not constitute advertising and does not serve as a purchase guide. Before purchasing, consultation with a specialist is required.
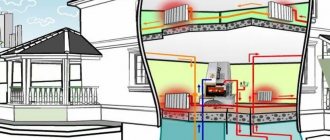
In autonomous heating systems, water circulates through pipes, transferring heat from the boiler to the radiators. It is cheap and effective, but requires regular supervision. If the house is visited periodically in winter or there are long trips on vacation, the system may become unfrozen. In the case of boilers that require an electrical connection, long-term power outages can provoke freezing of pipes and rupture of batteries. To prevent this, coolants with alcohol or oil are used, designed for heating systems in private homes and industrial facilities. They work the same way as antifreeze in cars and do not freeze in subzero temperatures. From the ratings and reviews below you will find out the best products in this category, which will help you make your choice.
What is propylene glycol
This substance is directly related to the class of dihydric alcohols. The reagent is a liquid substance with a barely pronounced odor and taste. In industry, it is obtained through the hydration of propylene oxide at a pressure of 16 megapascals and a temperature range of 160-200 degrees.
The chemical formula of propylene glycol is C3H6(OH)2. It is completely safe to use and does not contain toxic elements. For heating systems, aqueous solutions are used, which are based on this reagent.
Propylene glycol has a related composition to ethylene glycol - C2H4(OH)2. But the latter element is not used for heating residential buildings, as it has a fairly high level of toxicity. Moreover, the chemical formula of both substances has some similarity.
Experts do not recommend antifreeze for home heating
Molecule of ethylene glycol - a toxic substance
Let's figure out what is the reason for such a categorical position that it is impossible to pour antifreeze into the heating system of a house. To do this, let's start with the composition of antifreeze. It consists of:
- alcohol base;
- ethylene;
- inhibitors;
- compositions that prevent foaming.
This composition is typical for all foreign-made antifreeze liquids. Only as an active substance in addition to ethylene can there be:
Ethylene glycol is very poisonous, in any form. You can’t let it get on your skin, much less inside, you can’t inhale its vapors.
This is the cheapest composition, it has the lowest temperature at which the structure of the additives decomposes. After this, the antifreeze simply destroys the heating circuit, corroding it from the inside. These are all the reasons why it is not recommended to pour antifreeze into the heating system of a house. In principle, the same can be said about ethylene glycol antifreeze, there is no difference. That is, experts are against the use of compounds with ethylene, and antifreeze is one of these.
It is designed for cars, so it is produced only with poisonous ethylene, because where it is used, this does not matter. Non-toxic propylene glycol and glycerin antifreezes are produced abroad.
Ethylene glycol, which is part of antifreeze, can cause chemical burns
Forewarned is forearmed. Knowing that antifreeze is poisonous, you can take measures to prevent it from causing harm. The use of antifreeze in the heating system must be carried out in such a way that the composition does not have access to the room where people are located. Therefore, it is better if antifreeze is poured into a sealed heating circuit. If you need it to circulate along an open circuit, then you need to modify the design of the expansion tank. The expanzomat must be hermetically sealed with a lid, and there must be a hole in the lid. A tube is inserted into it and leads outside. That's all, ethylene glycol vapors are no longer scary.
Main characteristics
Propylene glycol is a hygroscopic substance that can dissolve in water, acetone, ethanol, chloroform and diethyl alcohol. This colorless liquid containing a carbon atom has a low degree of volatility. It is not capable of causing corrosion and is completely safe to use.
Among the characteristics of propylene glycol are:
- density – 1037 kg/m³, which is almost 4 percent more than that of water;
- a fairly high boiling point - 188 degrees above zero;
- thermal conductivity – 0.218 W/(m*K);
- the beginning of crystallization is at -60 degrees;
- specific capacity value – 2483 J/(kg*K).
What does propylene glycol look like
? The coolant propylene glycol is an aqueous solution that remains in liquid form at temperatures from -40 to 100 degrees. The finished substance, in addition to the main component dissolved in distilled water, includes dyes, as well as no more than 5 percent of anti-corrosion, stabilizing, softening additives.
The density of propylene glycol coolant depends on the concentration of the main component. The higher its percentage, the higher its maximum boiling level. The density indicator also increases accordingly. Based on this, percentage markings are indicated on the coolants produced.
Comparative characteristics of water and antifreeze
The advantages of using water as a coolant are obvious: availability, high specific heat capacity and low cost (not free, because the system should be filled with distilled water, or after appropriate water treatment, not from the tap). The main disadvantage is that water freezes at zero degrees, while it expands and breaks the elements of the heating system. Antifreeze freezes at very low temperatures (down to -70 C). However, they have some unpleasant features.
- Their specific heat capacity is 10-15% lower than that of water: they heat up more slowly and transfer heat less well, so a more powerful boiler will be required.
- They are denser (10-20%) and more viscous (30-50%) than water. Consequently, you will need a powerful pump to circulate the coolant, large-diameter pipes and more powerful heating radiators for antifreeze.
- When heated, they expand 30-40% more than water. This means that you will need a closed expansion tank twice as large in volume.
- Anti-freeze agents have no surface tension and are 50% more fluid than water. With the smallest flaws in the sealing of joints, antifreeze begins to leak, especially when the system cools, when the diameters of the pipeline elements decrease. Therefore, the heating system must have the minimum possible number of joints, and they must be accessible for inspection and repair at any time.
Therefore, a heating system designed for water is not suitable for the use of antifreeze liquids. If you plan to use antifreeze to heat your home, the system must be designed in advance, and it will cost significantly more.
Advantages and disadvantages
Propylene glycol is one of the most popular ready-made coolants for heating systems. Its main function is to protect heating equipment from ruptures, which occurs due to the ability to practically not change its volume at low temperatures. Therefore, in severe frosts when using it, there is no need to drain the system.
The advantages of using propylene glycol-based coolant include:
- Safety and environmental friendliness. The substance does not contain highly toxic components. The reagent does not have a negative effect when it comes into contact with the skin or mucous membranes of the eyes. Its vapors are quite harmless. When the floor finishing material gets on the surface, any chemical reactions are excluded.
- No corrosive activity. This property allows this coolant to be used for heating systems with various structural materials.
- High level of thermophysical characteristics. The use of an aqueous solution of propylene glycol for heating circuits promotes rapid and uniform heating of the room. At the same time, the heat is retained for a long time.
- No scale. When heated to high temperatures, this antifreeze does not form any solid deposits. At the same time, propylene glycol has bactericidal and cleaning properties. With its help, various deposits are removed from the internal areas of heating equipment.
The prepared propylene glycol solution is completely fireproof and its use eliminates the possibility of explosion.
This coolant also has some negative operational aspects:
- High turnover rate. Propylene glycol is able to penetrate through the smallest cracks. Its fluidity is somewhat higher from water, so sometimes leaks occur in places where they should not exist. But at the same time, this property can be considered a positive aspect, since it allows improving the assembly quality of a heat-conducting structure.
- The possibility of using propylene glycol as a coolant is excluded if there are parts containing zinc. If this precaution is not followed, the viscous antifreeze will eventually peel off the galvanizing, which will lead to clogging of the pipeline.
Also sometimes the negative aspects include the high cost of antifreeze based on propylene glycol. In this case, it must be replaced in the heating system at least every five seasons.
When is anti-freeze used?
Safe antifreeze heating fluid
Coolant circulates in the heating system. This could be water or non-freezing heating fluid. The main purpose of the coolant is to absorb heat from the heating elements of the boiler and distribute it to all heat exchangers. Through them, the coolant releases its heat into the room and returns again to the boiler. It turns out that the coolant also works as a coolant for the heating system, which simultaneously cools the boiler heat exchanger and heats the radiators. This cycle only occurs when the heating is active.
If the boiler does not work, as well as the pumps in the sealed circuit, then the circulation of the heating fluid stops. Along with it, accordingly, the coolant stops receiving energy from the heating elements of the boiler. The process of temperature reduction begins in accordance with weather conditions. The cooling rate depends on the degree of insulation of the room, that is, the level of heat loss. In winter, when the boiler is turned off, the coolant gradually reaches the crystallization temperature and turns into ice.
Ice has a larger volume than liquid, so it literally bursts pipes. To prevent this from happening in circuits where the heating is turned on irregularly, you need to fill in a non-freezing liquid for the heating system. In what situations can the heating circuit operate irregularly:
- in a temporary residence;
- in the country;
- in the garage;
- if there are power outages for a long period.
Spontaneous power outages are not scary if you have an uninterruptible heating system that will supply all volatile elements with current. But this is only effective if it is installed in a house where someone constantly lives. But at the dacha this method is not applicable. Typically, in country cottages, the heating is turned on only on weekends, and the rest of the time the circuit is idle. Accordingly, only non-freezing liquid for the heating system can be used as a coolant. You don’t plan to fill and drain water every time you want to heat the house. Moreover, there will be at least 200 liters in the heating system.
All about how to make greenhouse heating with your own hands from scratch.
Read about how to calculate greenhouse heating without the help of a specialist here.
Scope of application
Propylene glycol is quite in demand in modern industry. Coolants made on its basis are widely used not only for heating systems, but also as antifreeze for ventilation and air conditioning equipment.
The scope of application of propylene glycol in the industry is quite extensive:
- pharmaceuticals;
- tobacco production;
- production of food products;
- automotive and aviation industry;
- Oil and gas industry;
- cosmetology, perfumery;
- medicine.
Uses of propylene glycol include livestock and agriculture. It is practiced to improve the quality of feed, as well as to extend the shelf life of vegetable crops. In chemical production, a viscous substance is used in the production of polyurethanes, paint solvents, plastics or polymers.
Differences between propylene glycol and ethylene glycol
When ethylene glycol is heated, the liquid expands by 1.5%.
Ethylene glycol is an organic acid-containing solution, a representative of polyhydric alcohols. It is a colorless, transparent, odorless, oily liquid. Entering the body causes toxic poisoning.
Differences from propylene glycol:
- when freezing, the volume of water with propylene glycol increases by only 0.1%, and the coolant with ethylene glycol increases by 1.5%;
- the energy carrier with propylene glycol withstands the evaporation of water from solution and does not freeze down to -60°C, ethylene glycol crystallizes at -13°C, glycerin – +17°C;
- the toxicity of propylene glycol LD50 is from 20 to 30 thousand mg/kg, the same indicator for ethylene glycol is LD52 – 4700 mg/kg.
The toxic substance is quickly absorbed into the body, causing pulmonary edema and heart failure. The substance is not used in open systems, because it penetrates through the skin and through inhalation. The spent energy carrier based on ethylene glycol is not poured into the ground or sewer, but is sent for recycling.
Criterias of choice
The main point that should be taken into account when choosing a coolant for space heating systems is the manufacturer’s recommendation for heating equipment. The instructions for the boiler often indicate the requirements for the liquid that fills the water circuit, and sometimes the brand of antifreeze.
The main factors to consider when choosing a propylene glycol solution for heating systems are:
- Climatic conditions of use. Different brands of products indicate the maximum freezing temperature level. This indicator depends on the concentration of the solution, the percentage of which is also indicated in the name of the coolant.
- Manufacturer. The efficiency of the heating system depends on the quality of antifreeze. You can purchase good products from trusted manufacturers. High-quality products do not contain toxic substances and are completely safe for use.
- Characteristics of additives. Propylene glycol-based products included in ready-made coolants can have anti-corrosion characteristics, while providing protection against metal destruction. Softening components are often added to the composition, which protect rubber elements from deformation. Therefore, when choosing antifreeze, the technical and design features of heating equipment are taken into account.
When choosing a coolant based on propylene glycol, take into account the characteristics of the additives
Antifreeze with carboxylate-type additives is especially popular. Such a coolant can be used for almost any material included in the design of a thermal device.
Propylene glycol intended for heating systems must meet all technical requirements and comply with the characteristics of the heating equipment used.
Compound
“Anti-freeze” for heating is the same antifreeze or antifreeze. The main property of this coolant is not to turn into ice when the temperature drops. In this case, thickening of the cooled composition occurs. Any non-freezing liquid for heating systems is manufactured according to the same principle. It contains the following:
- substances (additives) responsible for the characteristics of the composition;
- substances (inhibitors) that prevent corrosion;
- main active ingredient;
- alcohol (glycol) base.
Features of use for heating
The coolant propylene glycol is poured into the system in accordance with the technical specifications. Before using antifreeze, a number of preparatory steps should be carried out:
- drain the liquid from the system, flush all circuits with caustic soda, remove all deposits and rust;
- perform sealing of all connections, including tappings and bends;
- remove and replace all zinc-containing parts.
After this, you can fill the system with propylene glycol solution. In this case, it is recommended to keep the drain valve open at the lowest point. This action will allow you to immediately see when the thermal contours are completely filled. After filling, the system is checked for leaks and a test run of the heating equipment is carried out.
Technical certificate
It is also important to take into account that the technical description for such equipment usually indicates only those parts and elements that are not affected by such a liquid. Naturally, it is also important to remember that often the technical documentation for a heating boiler and similar equipment contains a list of coolants used. Also, in most cases, the passport for heating equipment indicates “water can be used as a coolant.” But still, the majority of buyers either do not look at the technical documentation data at all (which they later regret very much), or look there only after the purchase.
Thermal carrier for the heating system.
Quite often we hear the question from our clients: “What should I put into the heating system?” There is no correct answer to this seemingly simple question. In our publication, we will tell you why the choice of antifreeze or water in the heating system must be made only after weighing all the pros and cons, and also taking into account the specifics of your heating system itself.
An indisputable advantage of using antifreeze is the protection of the system from freezing and rupture. This is very important for those who do not live in a cottage regularly, but only occasionally and do not have the opportunity to quickly respond to a boiler malfunction or power outage.
Let's take a closer look at the main arguments against adding antifreeze to the heating system of a personal home. This will help you make the right decision.
- Cost of antifreeze. Ordinary water, of course, is more accessible.
- An increase in the power of the circulation pump is required.
- An increase in the volume of the expansion tank is required to provide the necessary space for antifreeze, which becomes wider as the temperature decreases.
- It is necessary to flush the system before adding antifreeze.
- Flushing antifreeze from the system requires more effort and time.
- Glycol antifreeze has greater fluidity than ordinary water and is able to penetrate where water will not flow.
- Most manufacturers of heating equipment do not recommend using a heat carrier or insist on using a heat carrier of their own production. Otherwise, you risk having your warranty voided.
- Systems filled with antifreeze require annual maintenance or at least a check of the condition of the antifreeze. If necessary, the coolant is added additionally.
- In most cases, for example, when the permissible temperature of the coolant is exceeded, glycol-based antifreezes oxidize and can damage pipes, valves and other elements of the heating system.
If, after reading the above material, you decide to pour antifreeze into the heating system, let's go into detail about choosing a suitable coolant. Now there are several types of antifreeze; thermal media based on glycols - propylene glycol and ethylene glycol - are considered very popular.
Ethylene glycol or propylene glycol. What's better?
Both ethylene glycol and propylene glycol have the necessary parameters for use in heating systems that require frost protection. Specifically: high boiling point, low freezing point, stability under temperature changes, high thermal conductivity coefficient. In addition, when used with appropriate inhibitors, glycol antifreezes acquire good anti-corrosion properties, which helps to increase the service life of the entire system.
Please note that antifreezes used in the automotive industry are absolutely not suitable for heating systems in homes! Just don't use them!
Ethylene glycol-based solutions work very well as antifreeze for heating due to their excellent heat transfer properties. But they have one serious drawback - ethylene glycol is considered poisonous when taken orally, in other words, when swallowed. Because of this, we recommend considering propylene glycol-based thermal media for use in residential buildings.
A solution of propylene glycol with anti-corrosion additives (inhibitors) is best used as antifreeze in systems where accidental contact with clean water is possible. But still, although propylene glycol is considered a non-toxic substance, of course, it should not be taken as food.
Concentration of glycols in antifreeze.
The concentration of glycols in antifreeze solutions should be determined taking into account the low anticipated winter temperatures for the area. It is necessary to take into account all factors in order to provide the required protection against freezing, but at the same time avoid oversaturation of the solution, as this leads to an unjustified increase in price and a decrease in the operating efficiency of the system.
In most cases, solutions are prepared with a glycol concentration by volume of 20 to 50%. On average, if there is sufficient free space to increase the coolant and the concentration of the solution to 50%, sufficient protection against rupture of pipes in the system is provided. Solutions with a glycol concentration of more than 50% are already less energy efficient and less cost-effective.
The table below shows the freezing temperature of a glycol solution depending on its concentration:
Table 1. Freezing point
Concentration Ethylene glycol Propylene glycol
55% -45С -40С 50% -38С -33С 40% -26С -25С 30% -17С -15С
Antifreeze
The well-known low-quality antifreeze - engine antifreeze, which is sometimes also poured into the heating system - is made on an ethylene basis. However, if there is the slightest possibility of human contact with ethylene glycol, then its use should be abandoned for a number of reasons:
- In double-circuit boilers, there is an admixture into the hot water supply circuit.
- Possible leakage.
- Evaporation from an open type expansion tank is possible.
The use of ethylene glycol antifreeze liquids is not allowed for systems where a double-circuit boiler is used as a heater.
Heating fluid (liquid): which one is better? Types, choice
Have you ever thought about what kind of heating fluid moves in the pipes of your house? Maybe yes. The quality of the heating system first depends on what kind of coolant you decide to use.
Moreover, heating fluid affects not only the direct characteristics of heating systems, but also more ambiguous details that may be revealed in the future.
Antifreeze for pipes
Which option is better to use in your case? We'll try to figure it out right now.
What is a thermal fluid for a heating system?
Before you can answer which media is best to use for heating systems, you need to understand what it is.
Purpose
It is no secret that one of the most important components of a private home is the heating system. After all, only with the help of it can one endure severe frosts, from which no one in our country is immune, and in general, in winter this is far from a rare occurrence. But, despite the consumer’s readiness for frost, it is necessary to provide for some surprises in advance. And, perhaps, the most dangerous of them can be a frozen heating system - it’s not for nothing that this condition is considered an emergency.
An emergency situation does not bode well for the heating system. It is important to note that this can occur not only in a central boiler room, but also in an individual boiler. For this reason, when designing any system, it is necessary to consider the conditions for providing additional security.
According to experts, the most common problem in a private home is the failure of boilers, and, as a rule, this always happens unexpectedly. To prevent such unexpected surprises, as well as to prevent failure of the heating system and its subsequent cooling, experts advise using non-freezing liquid.
Choosing a coolant based on propylene glycol
Antifreezes for heating systems can be produced based on one of three substances. One such substance is propylene glycol.
What is this substance?
Propylene glycol is a dihydric alcohol, which under normal conditions is a colorless viscous liquid that has a faint odor and a sweetish taste. There is a similar substance called ethylene glycol, however, propylene glycol, unlike it, is considered a non-toxic substance, so propylene glycol is widely used in the perfume and food industries as an additive with the symbol E-1520. Its chemical formula is C3H6(OH)2. In addition, propylene glycol is very fluid, capable of leaking through very small holes and cracks, hygroscopic, and has a high ignition temperature - +421°C.
Ethylene glycol is a very toxic substance, which is also used as antifreeze, but not in residential areas, but in the automotive industry. Ethylene glycol has a similar chemical formula – C2H4(OH)2.
You should also not use ethylene glycol alcohol in domestic heating systems for the following reasons:
- When overheated, this alcohol decomposes into substances that cause scale and increased corrosion of metal parts;
- Overheating leads to foaming of ethylene glycol and airing of the system;
- This alcohol negatively affects rubber gaskets, reducing their service life.
Aqueous solutions based on propylene glycol are often used as a coolant for heating, air conditioning, ventilation and food cooling systems.
Other solutions of alcohols, such as ethylene glycol, are used as liquids for washing car windows in winter and in some heating systems as a coolant in compliance with all standards for the use of this toxic substance.
Advantages and disadvantages of propylene glycol as a coolant
To clearly evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of propylene glycol, it can be compared with another popular coolant fluid - water:
- Alcohol has a density of 1037 kg/m³, 3.7% more than that of water (1000 kg/m³);
- Boiling point – +187 °C, higher than that of water (+100 °C) by 87%;
- The freezing point is -60 °C, much lower than that of water (0 °C);
- The liquid has a specific heat capacity of 2483 J/(kg K), almost 2 times lower than that of water (4.187 J/(kg K));
- Thermal conductivity – 0.218 W/(m K), almost three times lower than that of water 0.6 W/(m K);
- Dynamic viscosity is 56 mPa s, eight hundred times greater than that of water (0.894 mPa s).
Having understood the given figures, we can come to the following conclusions:
- The liquid has a density slightly higher than water, which means that the static load and pressure in the heating system will be almost the same as with a standard coolant;
- The high boiling point – +187 °C – should not be misleading. After all, the specific heat capacity of propylene glycol is almost two times lower than the heat capacity of water. This means that bringing both liquids to a boil requires approximately the same amount of heat and they will reach the extreme temperature almost simultaneously, only one will bubble at +100 °C, and the other at +187 °C;
- In terms of freezing temperature, this coolant is clearly superior to water. In addition, when it freezes, it hardly expands like water and does not “break” the heating system;
- Low specific heat capacity gives an advantage, on the one hand, rapid heating of the heating system, and on the other hand, a disadvantage - propylene glycol is able to accumulate little heat.
- Thermal conductivity is three times worse than that of water, which means that the heating system will not warm up as quickly as it might seem from the previous paragraph;
- Dynamic viscosity is very high. This is an additional load on the circulation pump, which must drive coolant through pipes and radiators.
This alcohol has no obvious advantages over water. But there are situations when propylene glycol is simply necessary for heating systems:
- A dacha, a country house, and other premises that are rarely used require the coolant to be drained in the winter. But this accelerates the process of corrosion of parts made of ferrous metals and does not guarantee complete emptying of the heating system from water, which can lead to damage to the heating system. The propylene glycol solution does not need to be drained year-round;
- Antifreeze based on propylene glycol does not cause corrosion of the heating system and does not form scale.
It is also necessary to pay attention to what disadvantages this liquid has:
- Propylene glycol is much more expensive than water and requires replacement at least every five years;
- Parts containing zinc should not be used for the heating system. Propylene glycol will dissolve them or “wash away” the galvanization, clogging the narrowings of the pipes;
- Propylene glycol is very fluid and can penetrate connections in the heating system that water does not flow through.
To neutralize some of the negative characteristics of propylene glycol, such as high viscosity and low thermal conductivity, antifreeze based on it is diluted with water. This solution allows you to:
- Reduce the cost of antifreeze;
- Significantly reduce viscosity;
- Increase heat capacity;
- Increase heat transfer.
And as a consequence:
- The boiling point decreases, but this is not something to be afraid of. The boiler automation is still not designed for 160 °C;
- The freezing temperature increases, instead of -60 °C it becomes -30 - -40 °C degrees. Even when freezing, propylene glycol-based antifreeze expands very slightly and will not lead to destruction of the heating system.
Rating of the best coolants for heating systems
| Nomination | place | Name of product | rating |
| Rating of the best coolants | 1 | DIXIS-65 | 4.9 |
| 2 | Warm House Eco | 4.8 | |
| 3 | THERMAGENT-65 | 4.8 | |
| 4 | RODA | 4.7 | |
| 5 | AMT-300 | 4.7 | |
| 6 | Hot Stream | 4.7 | |
| 7 | Teplokom | 4.6 | |
| 8 | WARME BASIC-65 | 4.5 | |
| 9 | Thermagent Eco 30 | 4.5 | |
| 10 | FTX-30 | 4.5 | |
| 11 | PRIMOCLIMA ANTIFROST | 4.4 |
Heat capacity is an important property
But we forgot about the most important property of the coolant - its heat capacity. The more thermal energy a liter of liquid can transfer, the better. And here the undisputed leader is water, which has the maximum heat capacity. Let's create a table of the specific heat capacity of coolants:
- Water – 4.218 kJ/kg*K;
- Ethylene glycol – 2.2 kJ/kg*K;
- Propylene glycol – 2.483 kJ/kg*K;
- Glycerol – 2.43 kJ/kg*K.
Based on this table, we see that the maximum specific heat capacity is observed precisely at water. If we pour the same propylene glycol into the water system, then when we start the heating we will find that the radiators have become noticeably colder. There are three ways out of this situation:
- Increase the coolant temperature;
- Increase the coolant flow rate using a circulation pump;
- Increase the number of sections in heating radiators.
In some cases, special additives help increase the resistance of the coolant to thermal destruction, but in this case we get a whole chemical cocktail in the system.
It would seem that we have a lot of options. But it's not that simple. If you increase the temperature of the coolant, you will have to look for a liquid that will not collapse when overheated. In the second option, we will be faced with serious costs for the purchase of a particularly powerful pump and the low efficiency of this method. The third option is bad because it is labor intensive - in fact, you will have to rework almost the entire heating system of a country house.
How to pump coolant
Problems usually arise only with closed systems, since open ones are filled through an expansion tank. The coolant for the heating system is simply poured into it. It spreads throughout the system under the influence of gravity. It is important that all air vents are open when filling the system.
An open heating system is filled through an expansion tank
There are several ways to charge a closed heating system with coolant. There is a method of filling without the use of equipment - by gravity, there is a submersible pump of the “Kid” type or a special one, with the help of which pressure testing of the system is done.
Fill by gravity
Although this method of pumping coolant for a heating system does not require equipment, it takes a lot of time. You have to squeeze out the air for a long time and also gain the required pressure for a long time. By the way, we pump it up with a car pump. So you will still need equipment.
Finding the highest point. Usually this is one of the gas vents (we remove it). When filling, open the valve to drain the coolant (lowest point). When water runs through it, the system is full.
With this method, you can connect a hose from the water supply, you can pour prepared water into a barrel, raise it above the entry point and then pour it into the system. Antifreeze is also added, but when working with ethylene glycol you will need a respirator, protective rubber gloves and clothing. If the substance gets on fabric or other material, it also becomes toxic and must be destroyed.
You need to monitor the pressure using a pressure gauge
When the system is full (water runs out of the drain tap), take a rubber hose about 1.5 meters long and attach it to the entrance to the system. We select the entrance so that the pressure gauge is visible. At this point we install a check valve and a ball valve. To the free end of the hose we attach an easily removable adapter for connecting a car pump. Having removed the adapter, pour coolant into the hose (keep it raised up). After filling the hose, use an adapter to connect the pump, open the ball valve and pump liquid into the system. You need to make sure that air is not pumped in. When almost all the water contained in the hose has been pumped in, the tap is closed and the operation is repeated. On small systems, to get 1.5 Bar, you will have to repeat it 5-7 times, with larger ones you will have to tinker longer.
Fill using a submersible pump
To create working pressure, the coolant for the heating system can be pumped with a low-power submersible pump like Malysh. We connect it to the lowest point (not the system drain point). We connect the pump through a ball valve and a check valve, and install a ball valve at the drain point of the system.
We pour the coolant into the container, lower the pump, and turn it on. During operation, we constantly add coolant - the pump should not drive air.
We monitor the pressure gauge during this process. As soon as its needle moves from the zero mark, the system is full. Until this point, manual air vents on radiators can be opened and air will escape through them. As soon as the system is full, they must be closed.
Next, we begin to increase the pressure - we continue to pump the coolant for the heating system with the pump. When it reaches the required level, we stop the pump and close the ball valve. We open all the air vents (on the radiators too). The air comes out, the pressure drops. We turn on the pump again, pump up a little coolant until the pressure reaches the design value. We release the air again. We repeat this until air stops coming out of their air vents.
Next, you can start the circulation pump and bleed the air again. If the pressure remains within normal limits, the coolant for the heating system is pumped. You can put it to work.
We use a pump for crimping
The system is filled in the same way as in the case described above. In this case, a special pump is used. It is usually manual, with a container into which the coolant for the heating system is poured. From this container, liquid is pumped through a hose into the system. You can rent it from companies that sell water pipes. In principle, it makes sense to buy it - if you use antifreeze, you will have to change it periodically, that is, you will need to fill the system again.
This is a manual pump for pressure testing, with which you can pump coolant for the heating system
When the system is filled, the lever moves more or less easily, but when the pressure rises, it becomes more difficult to work. There is a pressure gauge both on the pump and in the system. You can follow where it is more convenient. Next, the sequence is the same as described above: pump up to the required pressure, deflate the air, repeat again. Do this until there is no air left in the system. After that, we also start the circulation system for about five minutes (or the entire system, if the pump is in the boiler), and bleed the air. We also repeat several times.
Finally, about coolants for electrode boilers
Electric water heaters of this type operate on the principle of a “soldier’s boiler” consisting of two blades connected to a 220 volt network. Water simultaneously serves as a coolant and electrolyte; heating occurs due to its conductivity, which depends on the content of magnesium and calcium salts.
This is why electrode boilers do not work with distillate and significantly lose power with under-salted water. According to the passport of the Galan heater, the resistance of the working fluid should be no more than 3200 Ohms per 1 cm.
If you pour regular ethylene glycol into an electrolysis heat generator, the substance will enter into a chemical reaction, foam and lose additives against corrosion and scale formation. The problem can be solved in 2 ways:
- A special antifreeze designed for electrode-type units is purchased. Special additives that resist foaming are dissolved in the working environment.
- A saline solution of the required concentration is prepared, as shown in the video below. Such water will begin to crystallize at a lower temperature, although it cannot be compared with antifreeze in terms of frost resistance.
You should pay attention to the preparation of tap water - pass it through a filter and let it sit for 1-3 days. A good solution is to buy a corrosion inhibitor separately and add it to the coolant for the heating system in advance.
Water
Water is the simplest and at the same time the most inexpensive way to transfer heat from the source to the radiators. If we compare water with other substances in percentage terms, then it accounts for about 70 percent. Actually, this is not surprising, since water is not toxic, although it still has disadvantages. First of all, this is high corrosion activity during contact with metals, as well as the fact that scale forms on the surface of the heat exchanger over time.
But the advantages that such a coolant has for heating systems are also significant: low cost and relative ease of use. Moreover, today a lot of inhibitors are sold, which several times reduce the harmful effects of water on the elements of the heating system. With the use of inhibitors, it becomes inert, which has a positive effect on the service life of the equipment.
Now about the cost. Using water costs practically nothing, unless you buy an additional inhibitor, but this, we repeat, is additional. But if heating will not be used regularly in winter, then it is advisable to abandon water altogether and resort to antifreeze.
Which antifreeze to choose
If the user wants to use an antifreeze liquid, then when choosing it, you should not focus only on cost. Antifreeze for the home is a product presented on market shelves in a large assortment.
The “Warm Home” product, produced by a Russian manufacturer, is popular. Some homeowners use this type of anti-freeze. Its cost is reasonable. The main advantage is that it has improved operating properties. It can not be changed in the heating system for 5-10 seasons.
Antifreeze “Warm Floor” is the most popular on the Russian market
Prices for antifreeze liquids vary, so each homeowner can choose the right one. The assortment expands every year. They are made from high-quality raw materials and are safe for the body. The non-freezing liquid Warme Hydro has proven itself well, as well as Galan, Thermagent ECO -30, BOILER -65 oC. A specialist from a specialized store will always help you with your choice.
It is forbidden to fill the heating network of the house with car antifreeze. It contains components that are not suitable for residential use.