Home » Building a house » Do it yourself
Alexander Korovaev 04/30/2020
11819 Views
In central Russia, it is simply impossible to get a good harvest of heat-loving crops without greenhouses. If they are also heated, then from the beginning of March you can plant seedlings of any plants in it, and also get early greens for the table. Moreover, installing most greenhouse heating systems with your own hands is quite simple and does not require special skills.
Infrared heaters
The latest developments in greenhouse heating include ceiling-mounted infrared heaters. They consume a minimal amount of electricity, plus the effect of their action far exceeds any other types of heating devices, including water radiators and even heated floors.
Infrared heaters
The heat from them does not rise upward, but spreads evenly throughout the room. Moreover, it is the soil that warms up most intensively, and not the air, which is very important for plants.
It should be noted that to heat greenhouses it is necessary to use only long-wave devices (preferably ceramic) with heating of the working fluid to 270-300°C. Unlike medium-wave emitters, which heat up to 1700-1900°C, they are not capable of burning plants.
Significant advantages of infrared heating also include:
- environmental friendliness and harmlessness: such heaters do not emit carbon dioxide and other combustion products into the air that are harmful to plant health
- infrared devices do not dry the air at all, since they do not heat it, but any objects and surfaces; no humidification of the room is required during their installation
- no heat loss - the efficiency of such heaters is 95%
- efficiency: since they heat the soil rather than the air, the required volume of thermal resources is reduced by 35%; Plus, such devices consume a minimum of electricity
- installation of systems is simple
- the risk of fire when using infrared devices is minimized
How to heat a polycarbonate greenhouse in early spring
Heating the greenhouse can be done in any available way:
- Gas boiler or burner.
- Solar panels.
- Infrared heaters.
- Convectors.
- Biological fuel – foliage, bark, branches, manure.
- Heating the greenhouse floor.
The choice of a specific method depends on the climatic characteristics of the region. For example, in early spring in Siberia, severe frosts down to 20-25 °C cannot be ruled out. Therefore, here the greenhouse must not only be heated, but also the floor must be insulated with polystyrene foam or other materials. Also, in areas with an unfavorable climate, it is necessary to install a floor heating system. To do this, use an electric cable or water heating.
Installing a gas burner, infrared tape or adding biological fuel are heating methods available to everyone. But if you install water, gas heating, or a solar battery, professional skills are required. In this case, it is not advisable to install the system yourself.
Underfloor heating system
Installation of heated floors
An ideal option for heating the soil in a greenhouse is also a heated floor system. After all, for successful plant growth, it is the roots that need to be warmed up.
Since heating a greenhouse with electric heating elements will cost a lot of money, it is better to install a stove or boiler in it. The heating system can be combined by installing radiators around the perimeter.
- It is better to use polyethylene pipes to heat the greenhouse. They are buried to a depth of about 40-50 cm in the drainage - a layer of crushed stone and sand
- It is not advisable to use metal-plastic for laying in the ground. After all, its fittings (connecting elements) require regular tightening. If you still decide to use such hard plastic, use compensation loops when laying the pipeline
- The first to be laid is a polyethylene film , which serves as waterproofing.
- Next, a layer of thermal insulation made of polystyrene foam or expanded polystyrene
- You can also reduce the thermal conductivity of the soil using compacted sand , which is poured over the heat-insulating layer to a height of 10-15 cm
- The distance between the pipelines should be 0.36 m. To ensure uniform heating, 2 collectors are placed along the edges of the greenhouse. Pipes are connected to them alternately
- To protect the pipeline from damage when digging the soil with a shovel or pitchfork, slate or metal mesh is laid on top of it
- The next 35-40 cm layer is fertile soil
Insulation with polystyrene foam
A lot of heat goes directly into the floor of the greenhouse - into the concrete base (if the structure is placed on a foundation) or into the ground. Therefore, even if you use the most powerful heating systems, the greenhouse floor must be carefully insulated.
This can be done using a thermal insulator, such as polystyrene foam. The material is sold in the form of sheets of different thicknesses. For laying on the foundation itself, you can use the material in a layer of 50 mm. Expanded polystyrene is placed on the surface and fixed with a special adhesive for thermal insulation (Penoplex). After this, apply sand (2-3 cm), level it and lay a productive layer of soil 25-30 cm in height.
Expanded polystyrene boards have excellent thermal insulation properties, so a layer 50 mm high will be sufficient
Important! The insulation can even be laid on the ground, i.e. This method is suitable for both mobile and stationary greenhouses.
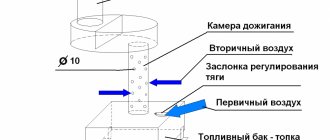
Heating with gas
Infrared burner
The disadvantages of such heating include the need for mandatory coordination with special services. Moreover, you will not be able to provide gas heating for the greenhouse - the design and installation of such systems is carried out only by specialists. Due to the high risk of ignition during operation, the operation of gas boilers will need to be constantly monitored. Due to the excess carbon monoxide generated during fuel combustion, ventilation .
But still, such devices have much more advantages. The cost of gas is not that high. You will only have to spend money on purchasing a boiler and equipment for it. Such designs ensure uniformity and rapid heating of the greenhouse, plus they are as easy as possible to maintain. But in order for it to heat up evenly, it is better to install heaters or connect several burners at once.
We list the main types of gas equipment used for heating greenhouses:
- convectors: industry produces special devices of this type specifically for heating greenhouses; built-in heat exchanger distributes heat evenly throughout the room; ventilation in it is provided using a coaxial (pipe in pipe) chimney
- heater with two open burners (the second of them serves as a spare) and a vertical chimney; the ventilation system is installed separately
- burners with infrared radiation: they are located in separate zones for local heating of certain types of crops or accelerating seed germination; equipped with a smoke exhauster that throws combustion products into the chimney; their operation does not require the installation of forced ventilation systems - natural is sufficient
In most cases, gas heating in greenhouses is combined with water heating . The principle of its arrangement is similar to that described above.
Heat gas gun
Heat gas gunsused for spot heating can be easily connected to both a gas main and a cylinder. Such structures are light in weight and quite mobile; they can easily be moved to any other place. The fuel in them burns completely, so the risk of carbon monoxide poisoning during their operation is minimal. Modern gas-fired heat guns are equipped with a temperature and even humidity control system.
Tips for choosing building materials
Most often, cellular polycarbonate is used to make greenhouses.
Cellular polycarbonate sheets
Such sheets are durable and transmit about 90% of light. The material practically does not transmit ultraviolet radiation. Sheets can have the following structure:
Structure of cellular polycarbonate
Instructions on how to choose the right polycarbonate for a greenhouse:
- First of all, you need to select the thickness of the sheets. The parameter should be selected based on wind load, bending and number of posts. For outdoor use, the minimum material thickness is 8 mm.
- Sheets of thinner thickness are cheaper, but you won’t be able to save money. If you use thin polycarbonate, you will need to make more frequent lathing steps, which entails additional costs.
For different purposes, material of different thicknesses should be used:
- 4 mm sheets are used for the construction of canopies and small greenhouses;
- 6 mm thick polycarbonate can be used to make small greenhouses;
- thickness 8 mm is suitable for medium-sized greenhouses;
- using 10 mm sheets you can perform continuous processing of large vertical bases;
- material with a thickness of 16 mm makes it possible to process roofs over large spans and is used in large complexes.
During the selection process, it is worth considering that the optimal density for installing a greenhouse is 800 g/m2. Density is the weight of the material per 1 m2 of sheet. The value affects strength. It can also be analyzed by visual inspection: if the material is packaged, then it should be placed evenly, and there should be no waves or bends on the sheets. If the foot is deformed, then it is better not to use the material.
Before purchasing, you need to study the inscriptions on the film. Sellers often offer lightweight and budget-friendly polycarbonate under the brands of global manufacturers. The labeling must be appropriate.
Recommendations to help you purchase quality material:
You can find a lot of low-quality polycarbonate on sale. It is recommended to give preference to well-known brands. Lightweight polycarbonate can be used in countries with warm climates
The material can hardly withstand temperature changes and has a short service life. It is worth paying attention to production standards. If the packaging says that the material has a thickness of 4 mm, but in fact the thickness is 3.5 mm, then you should not buy such a product. The weight of ordinary sheets is 10 kg. High-quality sheets have markings on the base that indicate the application of a special film to protect against sunlight.
When bent, high-quality material should not crack.
Experts advise checking documents for polycarbonate. The packaging must be of high quality. The sheets are placed in plastic film. There should be no unevenness on the polyethylene.
Solar batteries
The principle of operation of a solar battery
Collecting and accumulating the heat given off by the sun's rays will help to get an early harvest in the spring. Heating a greenhouse using solar batteries can also be used as an additional option. For the winter period, the heat received only from them will not be enough.
To accumulate solar energy, the greenhouse must be installed in the most open place and located from east to west. It has been proven that arched polycarbonate structures are capable of “collecting” the maximum number of rays. Plus, the air in the cells of this material will serve as a natural heat insulator.
Solar batteries are divided into:
- water : the heat storage in this case is water containers (barrels or pools); Moreover, several small containers have a higher efficiency than one large one, because water always warms up better closer to the surface; they are distributed evenly throughout the room
- stone : this material is capable of retaining heat for a long time, so it makes sense to line the walls of the greenhouse with stone or cover it with a sufficiently large layer around the perimeter of the structure
- air : are among the most efficient battery devices (see photo); for efficient heating, heat exchangers are positioned perpendicular to the direction of the sun's rays; heated air enters the greenhouse through pipes; cold air is taken in through the second duct
When installing an air heating system in a polycarbonate greenhouse, it is advisable to use fans to ensure rapid air exchange. The inlet pipe of the air duct is located as close to the ground as possible. The pipe through which heated air enters the greenhouse is placed in the upper part of the room.
DIY installation
Owners of dachas, private farms, vegetable gardens, and small farmlands use interesting heating systems.
We will talk about an unusual way of growing early vegetables using alternative methods of heating the soil, that is, with the help of the sun:
- In early spring, cover the prepared beds with film;
- the sun through the shelter will heat the soil to the desired temperature;
- then, without removing the covering material, holes are pierced, the seed is placed in the soil and covered with earth on top;
- in a warm environment the seeds will germinate early. As soon as the first shoots appear, the arcs that were previously laid out on the bed rise;
- the plants continue to grow in the sun-heated greenhouse;
- when a period of spring weather without frost arrives, the material is removed and stored until next spring.
With this method, a good early harvest is obtained.
Turnkey heating system installation
Some construction campaigns offer farmers to build turnkey small industrial greenhouses according to standard designs, priced with heating at the customer’s choice.
Advantages and disadvantages of the service
Among farms, such services are in great demand due to the undeniable advantages over homemade products:
- reliability;
- full or partial automation of the process;
- the ability to program the necessary agrotechnical parameters for different vegetables;
- modern low-cost heating systems that allow you to grow many useful plants all year round;
The only drawback is the cost: from 100,000 rubles. up to 500,000 rubles.
Price
Consists of the following components:
- design;
- frame manufacturing;
- system configuration;
- delivery to the installation site;
- installation of structure and heating;
- commissioning operations;
- commissioning.
Biological heating
Biofuel (self-heating substrate) has been used to heat plants since ancient times. Any summer resident knows that cucumbers get sick less and grow better not in open ground, but in warm manure.
Biofuel can also benefit a greenhouse. It can be used not only manure, but also plant residues, household organic waste (paper, rags, plant food residues), sawdust, leaves, straw. Later, when it completely rots and turns into humus, it is used as fertilizer. The best biofuel is obtained by mixing cow manure (1 part) with peat (3 parts). The mixture of conifer bark, sawdust and droppings heats up more slowly, so its heat lasts for a long time.
Biological heating
To heat a greenhouse using this method, it is necessary to remove the top layer of soil, lay a 15-centimeter layer of biofuel, and pour warm water over it. After a few days, when the organic mass begins to generate heat, it is again covered with removed soil and the beds are arranged.
When using straw, bales are placed in shallow ditches so that it rises slightly above the ground. To start the rotting process, the substrate is spilled with water, infusion of manure or chicken droppings. The seedlings can be planted after 2-3 days, when the temperature begins to rise.
Foundation
The greenhouse building has a heavy structure and requires laying a foundation for strength. There are 4 ways to base it:
- tape;
- brick;
- squared;
- stone foundation.
Practice shows that the most common is a strip foundation.
Work order:
- Construction site marking;
- digging a ditch about a meter deep;
- covering the bottom of the pit with waterproofing;
- production of reinforcement to strengthen the foundation;
- filling the ditch with cement mortar;
- coating of thermal insulation material on a completely hardened foundation.
Next, bolts are attached to the prepared foundation to construct the frame. When deciding how to build a winter greenhouse, some craftsmen lay one layer of brick on the foundation. With this method, the bolts must pass through the brickwork and penetrate the fabricated foundation.
How to heat a greenhouse with candles and bottles
This method can be useful in the event of return frosts. It allows you to increase the room temperature by several degrees in a short period of time.
When the temperature drops slightly below 0 °C, 4 candles are enough to heat a 6x3 m room . To prevent heat from immediately escaping upward, they must be covered with metal buckets, leaving a small gap between it and the ground for oxygen to enter. Buckets heated with a flame will begin to quickly heat the air.
You can replace metal buckets with ceramic pots, inserted one into the other and strung on a metal bolt. It will serve as a heat conductor.
Heating with a candle
You can also use regular water bottles to heat the greenhouse. Experienced gardeners stock up on large plastic containers and use them throughout the season. During the day, the bottles heat up in the sun, and at night, when the temperature in the greenhouse drops, they begin to release the accumulated heat into the air. Plus, in hot weather, containers with cold water save plants from excessive overheating and burns.
The best designs for greenhouse heating systems can be easily found online. For example, the author of the following video shares his own experience of heating such premises:
Air curtain
The air curtain is installed not in the greenhouse itself, but at the entrance. Therefore, this heating option is suitable for permanent rather than temporary structures. A classic curtain can be purchased and hung above the entrance. The vestibule can be heated independently using stove, gas or electric equipment. You can also place the main source of heating in it, which will reduce costs: the boiler is not in a cold room, but in a warm room. The use of curtains is especially important for regions with cold climates and for winter growing of plants. In autumn and summer there is no special need for such equipment.
Thermal curtain can be purchased at an affordable price