When designing large-scale heating systems (in particular, calculating the adjustment of the heating system of an apartment building and its full functioning), especially close attention is paid to the external and internal factors of equipment operation. Several heating schemes for central heating have been developed and are successfully used in practice, differing from each other in structure, working fluid parameters and pipe routing patterns in apartment buildings.
How does a centralized heating system work?
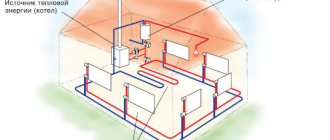
A heating unit that distributes coolant coming from a thermal power plant along a pipeline made of pipes.
Centralized heating is a method of supplying heat from a single source to residential and industrial premises located over a large area.
The general scheme looks like this:
- The coolant is heated at separately located objects to the required temperature.
- Heat is supplied to houses through pipes laid in the ground or in an open way.
- Thermal units organize accounting of spent energy and distribution of heat throughout the entrances of the house.
- The hot coolant is supplied to each apartment and to the staircases through the risers of the in-house wiring.
- To heat apartments, heat exchangers are used, which are commonly called radiators or radiators.
A boiler room located in the house itself is a special case of central heating.
Each of the systems can be arranged in different ways and perform additional functions.
Heat sources
A boiler house serving one apartment building is a variant of central heating.
The coolant is heated in specially built combined heat and power plants (CHPs), state district power plants (SDPPs) or boiler houses serving several residential areas.
The names of thermal power plants and state district power plants remain from Soviet times, although their owners are now private energy companies.
Thermal power plants, state district power plants and boiler houses differ:
- main purpose and mode of operation;
- power;
- radius of the service area.
Based on economic feasibility, thermal power plants are built in settlements with a population of over 100 thousand people and developed industry. State district power plants are designed for small and medium-sized cities with low electricity consumption. Boiler houses heat residential and public buildings and industrial facilities within a radius of no more than 3 km.
Combined heat and power plants are designed in such a way that during the cold season their main purpose is to heat water for heating purposes. During the non-furnace period, the station switches to electricity production mode.
State-owned power plants are needed to generate electricity. Heat is released during the operation of turbines and is directed to heating purposes.
Boiler houses exclusively heat water for heating systems; they do not generate electricity.
The final stage of work
At the last stage, the radiators are connected, and their internal diameter and volume of sections are calculated taking into account the type of supply and cooling rate of the coolant.
Since central heating is a complex system of interconnected components, it is quite difficult to replace radiators or repair jumpers in a particular apartment, because dismantling any element can cause interruptions in the heating supply of the entire house. Therefore, apartment owners who use central heating for heating are not recommended to independently carry out any manipulations with radiators and the piping system, since the slightest intervention can turn into a serious problem.
In general, a well-designed, efficient heating scheme for a residential apartment building allows one to achieve good performance in matters of heat supply and heating.
Heat generation scheme
The functional schemes of the operation of thermal power plants and state district power plants are very similar, the difference lies in the power and construction of the equipment.
Electrical and thermal energy is generated at thermal power plants and state district power plants by burning fuel. To operate, you need coal, fuel oil or natural gas.
CHP device
The main components of the thermal power plant are:
- fuel facilities - a set of places for storing and preparing fuel;
- boiler room consisting of a boiler and auxiliary equipment;
- turbine and electrical equipment;
- condensate installation;
- heat exchangers that remove heat for central heating;
- technical water supply system.
Additional systems include smoke removal and smoke purification systems, ash and slag removal systems, and pipelines.
Boiler houses are much simpler - they do not contain turbines, condensate units, or other auxiliary equipment.
Algorithm for operation of heat sources
The principle of operation of thermal power plants,
thermal power plants and state district power plants are extremely complex structures, but the principle of operation of heating the coolant is not difficult to understand:
- The prepared fuel is supplied to the boiler room. The coal must be ground, preferably to a dust state. For combustion, air is supplied to the combustion chamber by pumps.
- In the boiler room, process water in boilers is brought to the state of steam, which is under high pressure.
- Through pipelines, steam is supplied to the turbine blades, which, as they rotate, generate electrical energy.
- After the turbine, the cooled steam enters the heat exchanger, where it transfers thermal energy to water for a centralized heating system.
- The cooled steam passes into the liquid phase, which the condensate unit cleans of vapors and impurities.
- Purified water is supplied to the boiler room, where a new heating cycle begins.
In summer use, when much less hot water is required, CHP plants are switched to electricity generation mode. In this case, the steam is cooled in cooling towers to the state of water, pumped to a height of up to 12 meters and sprayed with special installations. Excess steam is released into the atmosphere.
The water enters the pool, where it is cooled. Then it is supplied to the boiler room by condensing units. The process is repeated. To compensate for losses, water is added from external sources - rivers or lakes.
Coal-fired thermal power plants and state district power plants must be equipped with smoke removal systems.
Heat exchanger design
Plate heat exchangers of various capacities
The task of heat exchangers is to take heat from the steam passing through the turbine.
Devices are classified by design:
- shell-and-tube;
- sectional (element);
- lamellar.
Each type has many designs.
The most common and effective is the shell-and-tube version of the device. Steam under pressure enters a bundle of pipes, which is located in a sealed housing. Chilled water is supplied inside the housing. A heat exchange process occurs - tubes heated by steam heat the water inside the container. Pumps create pressure to move fluid in the pipelines of a central heating system.
Features of district boiler houses
Depending on the intermediate coolant, boiler houses are divided into steam and water.
In the first case, water is brought to the state of steam, in the second, water below 100 degrees participates in heat exchange. The option depends on the project, distance to objects, and other technical features of the construction.
Steam is used less frequently as a coolant for supplying apartments; it can only be found in older housing stock.
In-house heating equipment
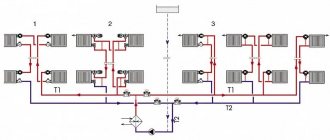
Pipe distribution diagrams for central heating
Heat distribution throughout the premises of an apartment building is carried out according to one of the following schemes:
- single-pipe with top filling;
- single-pipe with bottom filling;
- two-pipe with bottom filling;
- two-pipe with top filling.
In the first case, the coolant under pressure rises along the central riser to the upper floor. Then, by gravity, the water, having given up some of the heat to the batteries, returns to the heating unit and is then transported towards the thermal power plant (boiler house).
The risers run inside the apartments and disconnecting your home from the general system is technically difficult and sometimes impossible. The temperature of the radiators can be regulated by special thermostats, the installation of which requires welding. In high-rise buildings, additional pumps are installed in heat supply units to supply coolant to the top floor, which increases costs and the cost of services provided.
Interfering with the operation of the second scheme is also technically impossible - the pipes here also run inside the apartments.
It is possible to replace central heating radiators from cast iron to bimetallic
Recently, in new houses and during the reconstruction of old buildings, two-pipe schemes have been used with the location of common communications in the entrances or technological shafts. In such cases, it becomes possible to disconnect an individual apartment from the heat supply.
Russian legislation categorically prohibits turning off the heating without authorization for any reason.
There are restrictions on the installation of radiators in apartment buildings. The pressure in a 5-story building is from 2 to 4 Atm, and in a 9-story building up to 7 Atm.
In the summer, after repair work on communications, pressure testing is carried out - the pressure is raised to 10-12 atm to detect leaks. When the system is filled with coolant, water hammer may occur.
Based on possible loads, when replacing radiators, they abandon all-aluminum products, choosing bimetallic radiators. Pay attention to the guaranteed pressure indicators that the battery can withstand.
What to do if the batteries are cold
What could be worse than cold radiators in winter? This is not only discomfort and violation of temperature norms, but also the threat of getting sick.
It is important to know what limits the timing of a possible emergency heat shutdown. They should not collectively exceed 24 hours per month, and last no more than 16, 8 and 4 hours in a row, if the temperature is not lower than 12, 10, and 8˚C, respectively.
If the radiators remain cold during the heating season, you need to contact:
- To the heating network dispatch service. If they do not know the reasons, they are required to check for the lack of heat.
- To the management organization (or others). Perhaps they are the ones carrying out the repair work.
- To the city housing inspectorate with a complaint about violation of housing standards.
- To law enforcement agencies (Rospotrebnadzor, prosecutor's office), if the heat is not restored on time and the problem is not solved.
If the heating network does not see a problem, an independent heating expert may be required.
We recommend that you find out in more detail what to do if there are cold radiators in the apartment.
Advantages and disadvantages of centralized heating
Heat loss is always present, since the length of the main line can be several tens of kilometers.
Any equipment, technical systems and communications have advantages and disadvantages. The pros and cons are considered in conjunction with the economic component and ease of use.
The positive qualities of centralized heating include:
- Operating costs with a central system are comparable or lower than fees for energy purchased individually.
- Most thermal power plants, state district power plants, and district boiler houses operate on any type of fuel, which makes it possible to create emergency reserves for work.
- The only heating equipment in residential premises is radiators. Boiler installations are located away from residential areas, and sanitary zones are installed around them, which improves the environment.
- The owner does not purchase expensive equipment (boilers).
- Heating of the apartment does not depend on the supply of energy and electricity to the house.
- The likelihood of accidents and disasters associated with gas leaks is reduced.
- There is no need to enter into contracts and pay for servicing gas equipment.
- Accidents are eliminated by the supplying organization as soon as possible at its own expense.
Heat tariffs are set by regional commissions
. Disadvantages include:
- losses in networks delivering heat to the house - the length of the pipeline can be 10 km;
- the supplying organization includes possible costs in the tariffs, so the payment is significantly higher than it could be;
- limited temperature control in the apartment caused by the schemes for constructing intra-house networks;
- the impossibility of disconnecting an individual apartment from the general building network without a court decision;
- dependence on tariffs (set by regional commissions), which the homeowner is not able to influence.
The most important drawback in ease of use is considered to be the inability to heat the house during the non-furnace period. In spring and autumn, sudden temperature changes are common, to which the thermal power plant cannot quickly respond. Changing operating modes entails large financial losses.
The final stage of work
At the last stage, the radiators are connected, and their internal diameter and volume of sections are calculated taking into account the type of supply and cooling rate of the coolant. Since central heating is a complex system of interconnected components, it is quite difficult to replace radiators or repair jumpers in a particular apartment, because dismantling any element can cause interruptions in the heating supply of the entire house.
Therefore, apartment owners who use central heating for heating are not recommended to independently carry out any manipulations with radiators and the piping system, since the slightest intervention can turn into a serious problem.
In general, a well-designed, efficient heating scheme for a residential apartment building allows one to achieve good performance in matters of heat supply and heating.
How do they heat houses in other countries?
One of the ways to save is energy-efficient houses.
Our country inherited central heating as a legacy of the socialist economy. In a planned economy and with large energy resources, centralized heating was built and, for the most part, paid for by the state.
Pipes with coolant cooled in houses on the way to the thermal power plant were a source of heat for greenhouses, industrial enterprises, and cattle breeding complexes.
Mass production of equipment for individual heating began systematically in the mid-90s; before that there was a shortage even for private households.
There are very few countries on the planet with similar climatic conditions and comparable population density. To save resources, heating in most parts of the world is decentralized.
Heat in the ground can be used for heating, but installations are expensive
In Germany, France, Canada, systems similar to ours were built until the 50s of the last century. The ensuing global energy crisis prompted the development of heating systems that serve one or more multi-storey buildings. A separate boiler room is being built for this purpose. There are no long communications for transporting hot water - losses are minimized.
The installations are easy to put into operation during a sudden cold snap, and on warm days it is possible to reduce energy consumption by reducing the temperature of the circulating water.
There is no centralized heating in France and the UK - there, each apartment has a separate boiler with a closed combustion chamber, the operation of which is controlled by the owner of the apartment.
The availability and accessibility of energy resources in the region plays an important role.
In Poland and China, many homes are heated with coal, in Iceland - with water from thermal springs. Norway actively uses cheap electricity.
Indoor heating devices and temperature conditions
The type of batteries installed in apartments depends on the year the building was built. If it was built in the Soviet era, then one of the following types of radiators will be installed in the apartments:
- Steel convectors having a metal body in which there are coils of DU-20 pipe and connected by a cross section.
- Cast iron sectional batteries, which not only have a significant weight, but also significant heat transfer. Each radiator provides up to 150 W. Their disadvantages include the risk of leaks and unattractive appearance.
The size of radiators or sections in them depends on what floor the apartment is on and what type of coolant circulation in the house. For example, if it is upper, then the coolant reaching the first floor will lose its temperature. This means that in order for the heating of an apartment building to be effective, in the apartment, if it is located on the lower floors, the number of sections should be increased or larger radiators should be installed.
In modern multi-storey buildings, bimetallic radiators are usually installed. Of course, if the water
Attention: Such radiators are made of aluminum and have excellent heat dissipation, which is approximately 200 W per battery. But the cost of such radiators is quite high
But their efficiency is also excellent. The apartment owner must answer a fairly common question - whether to install bimetallic batteries or not - by deciding for himself whether he is ready to “fork out” so that he can have heat.
The temperature regime in apartments is indicated in the current provisions of SNiP. If there is central heating, it is:
- bathroom – 25 degrees;
- living rooms and bedroom – 20 degrees;
- kitchen - 22 degrees;
- corner rooms - 22 degrees.
The maximum water temperature in the heating system pipes has also been established. It should not exceed 95 degrees.
Centralized heating of an apartment building allows you to effectively warm the room, but at the same time, the temperature in the apartment completely depends on the operation of the boiler room and other external factors. In this, this system is significantly inferior to individual heating, which does not have this drawback.
Ways to reduce costs
Insulating the heating main is one of the ways to save energy.
There are few opportunities to reduce operating costs for the supplier and heating costs for apartment owners:
- high-quality thermal insulation of main pipelines, especially those located on the surface;
- installation of general house meters for energy consumption, which compare the temperature of the coolant at the inlet and outlet - knowing the volume of flowing liquid, the equipment automatically calculates the calories consumed;
- installation of individual metering devices in each apartment, which is applicable only for schemes 3 and 4 discussed above.
There are no other options to influence payment.